10 Examples of Qualitative Data
- Observation Notes. Observation is an important method of qualitative data collection. ...
- Semi-structured interviews. ...
- Open-ended survey. ...
- Participant diaries or journals. ...
- Portfolios of evidence. ...
- Concept Maps. ...
- Case Studies. ...
- Focus Groups. ...
- Video and recordings. ...
- Qualitative Audits. ...
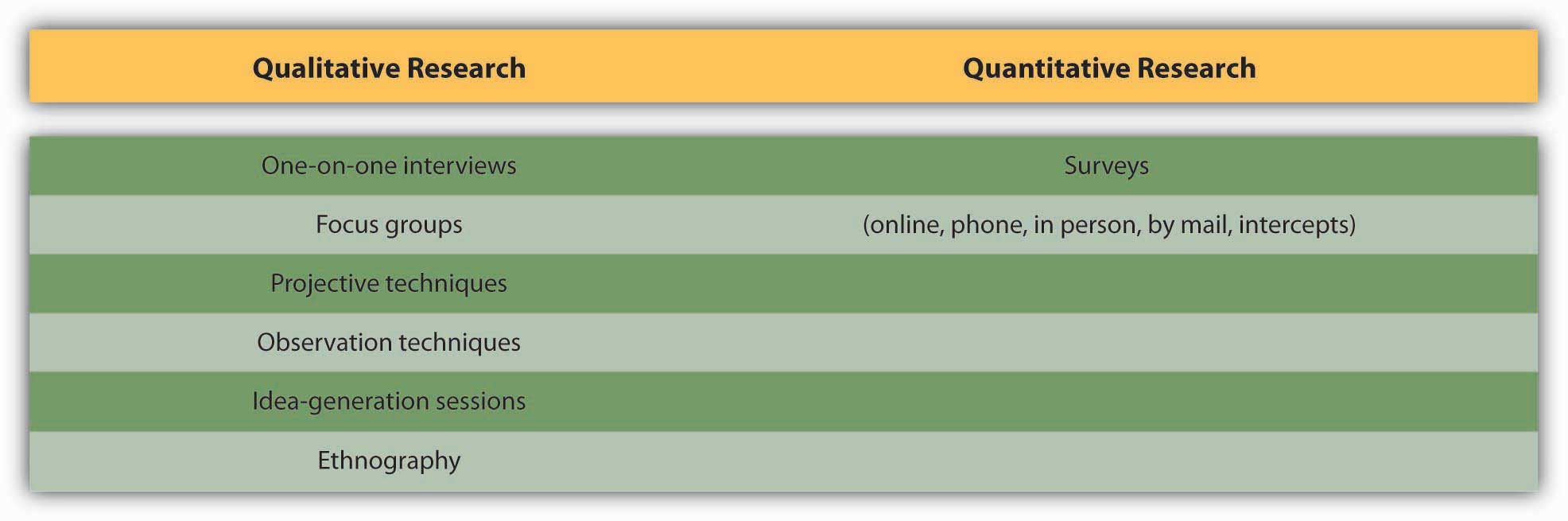
What are the 6 types of qualitative research?
These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys: distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
What is the difference between qualitative data and quantitative data?
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
- Qualitative data uses methods like interviews, participant observation, focus on a grouping to gain collective information. 1. ...
- Data format used in it is textual. Datasheets are contained of audio or video recordings and notes. ...
- Qualitative data talks about the experience or quality and explains the questions like ‘why’ and ‘how’. ...
What are some examples of qualitative research?
- "What were your initial thoughts when you saw the shoes for the first time?"
- "Where might you wear these shoes? About how often would you wear them during a normal week?"
- "What do you normally pay for sneakers?"
- "How much do you think these shoes cost?"
- "Would you buy these shoes? What color would you choose?"
What are the advantages of qualitative data?
- It's a time-consuming process.
- You can't verify the results of qualitative research.
- It's a labor-intensive approach.
- It's difficult to investigate causality.
- Qualitative research is not statistically representative.

What are some examples of qualitative data?
Examples of qualitative dataDiary accounts. Diary accounts are collected as part of diary studies. ... Documents. ... Case studies. ... Photographs. ... Audio recordings. ... Video recordings. ... Transcriptions. ... Descriptions.More items...•
What are 10 examples of qualitative data?
Here are ten examples of qualitative data:Observation Notes. Observation is an important method of qualitative data collection. ... Semi-structured interviews. ... Open-ended survey. ... Participant diaries or journals. ... Portfolios of evidence. ... Concept Maps. ... Case Studies. ... Focus Groups.More items...
What are 5 examples of qualitative research?
5 Types of Qualitative Research MethodsEthnography. Ethnography, one of the most popular methods of qualitative research, involves the researcher embedding himself or herself into the daily life and routine of the subject or subjects. ... Narrative. ... Phenomenology. ... Grounded Theory. ... Case study.
What is qualitative data?
Qualitative data is information that cannot be counted, measured or easily expressed using numbers. It is collected from text, audio and images and shared through data visualization tools, such as word clouds, concept maps, graph databases, timelines and infographics.
What are 5 examples of quantitative data?
Some examples of quantitative data include:Revenue in dollars.Weight in kilograms.Age in months or years.Length in centimeters.Distance in kilometers.Height in feet or inches.Number of weeks in a year.
What are 3 examples of qualitative research?
These are some of the most common qualitative methods:Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.More items...•
What is quantitative data example?
Quantitative data is data that can be counted or measured in numerical values. The two main types of quantitative data are discrete data and continuous data. Height in feet, age in years, and weight in pounds are examples of quantitative data.
What are examples of qualitative and quantitative data?
Start with yourself as an example. To acquire qualitative data, consider identifiers like the color of your clothes, type of hair, and nose shape. For quantitative data, consider measurable values like your height, weight, age, and shoe size.
What is qualitative data vs quantitative data?
Quantitative data are data about numeric variables (e.g. how many; how much; or how often). Qualitative data are measures of 'types' and may be represented by a name, symbol, or a number code. Qualitative data are data about categorical variables (e.g. what type).
What is meant by quantitative data?
Quantitative data is data expressing a certain quantity, amount or range. Usually, there are measurement units associated with the data, e.g. metres, in the case of the height of a person. It makes sense to set boundary limits to such data, and it is also meaningful to apply arithmetic operations to the data.
Why is qualitative data used?
Qualitative data provides the means by which analysts can quantify the world around them. You would use qualitative data to help answer questions like who your customers are, what issues or problems they're facing, and where they need to focus their attention, so you can better solve those issues.
What are the two types of qualitative data?
Qualitative Data can be divided into two types, namely; Nominal and Ordinal Data. In statistics, nominal data (also known as nominal scale) is a classification of categorical variables, that do not provide any quantitative value. It is sometimes referred to as labelled or named data.
What is qualitative data analysis?
Quantitative data analysis is the process of moving from the qualitative data collected into some form of explanation or interpretation of the subject under investigation. There are two main stages of qualitative data analysis.
What are some examples of ordinal data?
Other examples of ordinal data include the severity of a software bug ( critical, high, medium, low), fastness of a runner, hotness of food, etc. In some cases, ordinal data is classified as a quantitative data type or said to be in between qualitative and quantitative.
What is ordinal data?
Ordinal data is a data type that has a scale or order to it. This order is used to calculate the midpoint of a set of qualitative data. For example, qualitative data on the order of arrangement of goods in a supermarket will help us determine the goods at the centre of the supermarket.
Why are phone numbers considered qualitative data?
Numbers like national identification number, phone number, etc. are however regarded as qualitative data because they are categorical and unique to one individual. Examples of qualitative data include sex (male or female), name, state of origin, citizenship, etc.
What is qualitative inductive approach?
The inductive approach to qualitative data analysis is the process of developing a new theory or hypothesis for data analysis. Researchers find themes, patterns, and relationships in the data and work to develop a theory that can explain them. This is a more difficult and time-consuming approach compared to the former.
Why is it so hard to generalize a sample?
This is because making general assumptions on a large population-based on a small sample may lead to wrong conclusions.
What is qualitative data?
Qualitative data, also called “categorical data,” is used to categorize and describe something using adjectives and adverbs. Qualitative data includes physical traits such as:
How is qualitative data gathered?
Qualitative data is useful in many types of studies and you can gather qualitative data through the following methods:
How is qualitative data different from quantitative data?
Qualitative data is observational and descriptive, while quantitative data is numerical and measurable. Researchers often use qualitative and quantitative data together when doing studies or analyses. They might collect quantitative data that fits within certain qualitative data parameters.
Types of qualitative data
Researchers and statisticians often categorize qualitative data into three types:
Qualitative data examples
You can find several examples of qualitative data in your everyday work and particularly in the research and statistics industries.
The definition of qualitative data
Qualitative data, also called categorical data, is used to categorize something in a descriptive, expressive way, rather than through numerical values. Simply put, it’s information about an object or subject that you can see or feel.
The importance of qualitative data
At a high level, qualitative data analysis provides data analysts a way to identify trends in the world around them.
Qualitative (categorical) vs. quantitative data
Before we get into types and examples, here’s a quick breakdown of the differences between qualitative and quantitative data.
Types of qualitative data
As we narrow down the importance of qualitative data, you should understand that there are different types. Data analysts often categorize qualitative data into three types:
Qualitative data examples
Qualitative data is all around you. We’re going to cover how this type of data might appear in descriptions, research, work, and statistics.
Pros and cons of qualitative data
Qualitative data is a detailed, deep understanding of a topic through observing and interviewing a sample of people. There are both benefits and drawbacks to this type of data.
A qualitative data collection tool
By collecting qualitative data using a Digital Experience Intelligence (DXI) solution like FullStory, data analysts have access to customer intelligence and robust research capabilities. Data analysis is made easy with an efficient data collection tool that replays real-time sessions.
What is qualitative data?
In statistics, qualitative data—sometimes referred to as categorical data—is data that can be arranged into categories based on physical traits, gender, colors or anything that does not have a number associated with it.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
It's pretty easy to understand the difference between qualitative and quantitative data: the former doesn't include numbers in its definition of traits of an object or group of objects while the latter does. Still, it can get confusing when thinking in terms of statistical attributes, which include size and dimensions, which are quantitative and not qualitative data.
What is qualitative data?
Qualitative data is used to characterize objects or observations. It is observable data that might use your sense of sight, smell, taste, touch, and hearing. It does not refer to aspects that can be numbered or measured. Qualitative aspects are subjective and abstract qualities, not objective or concrete factors.
What is qualitative observation?
Qualitative Observation in Research. Qualitative observations and data can be extremely helpful to research and scientific studies. Explore qualitative data used in studies. During an experiment, it was observed that after adding the iodine, the potato turned purplish.
What can psychologists observe?
A psychologist may observe children at play and make assumptions about their relationships. Animals can be observed in their natural habitat, and certain conclusions may be made about behavioral traits. Surveys or focus groups ask questions to collect participants' opinions.
What is qualitative data?
Qualitative data is categorical. It can be used to analyze language, and through this, to develop an understanding of subjective perception. Qualitative data describes characteristics. It is usually gathered from interviews, observations, surveys, or focus groups.
Where can qualitative data be found?
Qualitative data, particularly that used for narrative or discourse analysis can be found in film records of events , recording of interview, or video diaries. Times when this form of data is most useful is either when the generation of it forms part of the programme activities by participants, or when it is easier to be present in the moment, than to be working with pen, paper, or screen. This allows researchers to revisit key themes, and in the case of video, to make other observations about surroundings, noise levels, environments, or body language.
How do surveys help?
Surveys are useful tools for measuring how preferences or perceptions change over time, or to gather information on key experiences of informants . Surveys may make use of ranked scales such as ‘always, sometimes, never’, or a ranked scale of from strongly agree to strongly disagree. These are useful tools for not only measuring perception, but behavioral change. Creating space for comments, or thoughts creates space for deeper reflection, and as in semi-structured interviews explored above, can allow for the research to uncover pathways for change which were not considered in the design of the programme logic, but which better explain what took place and why.
Why is observation important?
Observation is an important method of qualitative data collection. Observation may be guided by a semi-structured assessment tool, guiding what is being observed, by asking key questions around what is taking place. It is important however, not to lead the observer, by defining what to look for.
Is qualitative data ordinal?
Qualitative or categorical data can be ordinal (ordered on degrees of, or ranked scales), or Nominal (for example gender or demographic information). The important thing is that the categories should be mutually exclusive and should not overlap. Here are ten examples of qualitative data:
What are 2 examples of qualitative?
The hair colors of players on a football team, the color of cars in a parking lot, the letter grades of students in a classroom, the type of coins in a jar, and the shape of candies in a variety pack are all examples of qualitative data.
What do you mean by qualitative data?
Qualitative data consists of questionnaires, interviews, or observation. Analyzing data allows us to explore ideas.
What is quantitative data and qualitative data?
Quantitative data is measures of values or counts and are expressed as numbers. A name, symbol, or a number code can be used to represent qualitative data. Data about categorical variables are the types of qualitative data.