What is risk management in project management?
Utilizing Quality Risk Management practices during the design and engineering phase of a project is a regulatory expectation to manage risk associated with product quality and patient safety. Risk management activities throughout a system’s life cycle should be planned and documented for each system.
What is quality risk management?
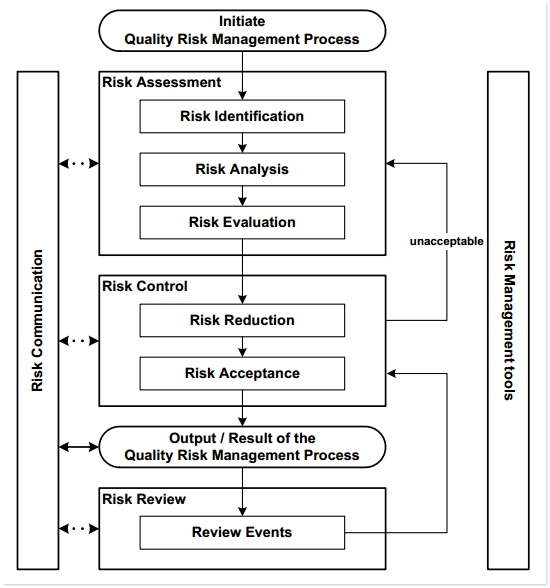
Quality Risk Management : A systematic process for the assessment, control, communication and review of risks to product quality and the safety of the patient. What is “Quality Risk Management”…?
What does quality mean in project management?
While the definition of quality can be challenging to pin down, in project management, "quality" can be considered something that measures up to — or exceeds — the generally accepted standard for deliverables in its category. When you’ve achieved quality, your stakeholders or customers will be happy with the product or service they receive.
Why is risk management included in PMP certification?
It is just one reason Project Management Institute’s (PMI) standards and certifications for the Project Management Professional (PMP)® certification include risk management. The universal fact of risk is every project will have a unique blend of risk types and categories that need managing.
What is quality risk example?
Examples of such events could be customer complaints, product recalls, audit reports, product or product changes, information obtained from the corrective or preventative action process, etc., .. Risk Communication.
What causes quality risk?
Quality risks can occur when the incentives of the supplier and those of the buyer are not aligned, so that the supplier of outsourced services tries to take advantage of the outsourcing relationship, to the detriment of the buyer.
What are the 4 types of risk in project management?
There are four main types of project risks: technical, external, organizational, and project management. Within those four types are several more specific examples of risk.
What are the 3 types of project risk?
Types of Project RisksFinancial Risks: Financial risks involve a project's monetary factors. ... Strategic Risks: Strategic risks involve the strategies chosen to complete a project. ... Performance Risks: Performance risks involve the overall project performance.More items...•
How do you manage quality risk?
Quality Risk Management ProcessStep 1: Before Starting. Form a cross-functional team and choose a leader. ... Step 2: Risk Assessment. Define the problem: Ask “What might go wrong?” ... Step 3: Risk Control Selection. ... Step 4: Risk Control Implementation. ... Step 5: Risk Review & Risk Communication.
What are the principles of quality risk management?
This principle embodies the four stages of an effective quality risk-management process as defined by ICH Q9: risk assessment (i.e., risk identification, analysis, and evaluation); risk control (i.e., risk reduction and acceptance); risk communication; and risk review.
What are the 4 risk categories?
There are many ways to categorize a company's financial risks. One approach for this is provided by separating financial risk into four broad categories: market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk.
What are the five main categories of risk?
They are: governance risks, critical enterprise risks, Board-approval risks, business management risks and emerging risks. These categories are sufficiently broad to apply to every company, regardless of its industry, organizational strategy and unique risks.
How do you identify risk categories?
Some of the categories could be:External: Government related, Regulatory, environmental, market-related.Internal: Service related, Customer Satisfaction related, Cost-related, Quality related.Technical: Any change in technology related.Unforeseeable: Some risks about 9-10% can be unforeseeable risks.
What are the 8 categories of risk?
These risks are: Credit, Interest Rate, Liquidity, Price, Foreign Exchange, Transaction, Compliance, Strategic and Reputation. These categories are not mutually exclusive; any product or service may expose the bank to multiple risks.
What are the two types of project risk?
Let's start by defining the 2 broadest categories of project risk: internal vs. external. Internal risks exist within your organization and are easier for you and your team to mitigate and manage. External risks happen outside of your organization and are typically beyond your control as a team or project manager.
How do you measure project risk?
Steps to perform a project risk assessmentStep 1: Identify risks. Analyse potential risks and opportunities. ... Step 2: Determine probability. ... Step 3: Determine the impact. ... Step 4: Treat the risk. ... Step 5: Monitor and review the risk.
What are threats to quality?
In the context of emergent quality, threats would be any practices, processes, technologies, and yes people, that prevent you from achieving the business goals, nested bets and outcomes set out by your team, CTO and/or company.
What is quality risk analysis?
Risk Analysis It is the qualitative or quantitative process of linking the likelihood of occurrence and severity of harms. This is essential for understanding the impact of risk on business goals and objectives, as well as how likely it is the risks could happen, and when.
What is quality risk management in industrial pharmacy?
Quality Risk Management (QRM) is the process of identifying, evaluating, and mitigating recognized risks connected with medicines and healthcare goods. An excellent Quality Risk Management programme can be created to reduce risk to a manageable level and deliver high-quality products to protect citizens' health.
What is risk and quality management in healthcare?
Risk management in healthcare is a complex set of clinical and administrative systems, processes, procedures, and reporting structures designed to detect, monitor, assess, mitigate, and prevent risks to patients.
What is quality risk management?
What is “Quality Risk Management”…? Current global GMP regulations require that manufacturing processes be designed and controlled to assure that in-process materials and the finished product meet predetermined quality requirements and do so consistently and reliably as demonstrated through Process Validation.
What is risk assessment?
Risk Assessment: A systematic process for organizing information to support a risk decision that is made within a risk management process. The process consists of the identification of hazards and the analysis and evaluation of risks associated with exposure to those hazards. Risk Management: The systematic application of quality management ...
What is QRM in manufacturing?
Conclusion. QRM will help manufacturers meet regulatory expectations for validation of critical processes and systems. The FDA and industry thought-leaders believe that modern quality systems, when coupled with manufacturing process and product knowledge and the use of effective risk management practices, should allow a firm to make changes ...
Why is QRM important?
QRM should be a vital component of an organization’s Quality System and best practices to achieve higher levels of process control and to manage and control risks to product quality and patient safety. QRM helps today’s manufacturers demonstrate that their system or process is suitable for its intended use.
What are critical aspects?
Critical Aspects: Functions, features, abilities, and performance or characteristics necessary for the manufacturing process and systems to ensure consistent product quality. Critical Quality Attribute: A property of a product or output of the process that is reflective of the process performing as expected.
What is quality risk management?
Quality risk management is a systematic, risk-based approach to quality management. The process is composed of the assessment, control, communication, and review of quality risks. It is especially critical in the pharmaceutical industry, where product quality can greatly affect consumer health and safety.
Why Quality Risk Management is Important?
Quality risk management is important because it can facilitate better and more informed decisions. With QRM, decision-making has the following qualities:
What is risk acceptance?
Risk acceptance is a decision to accept risk since it cannot be eliminated. This form of risk control is typically only chosen when mitigating the risk is out of the QRM team’s control. Another case where it may be the best option is when risk reduction has already been applied and the remaining risk is at an acceptable level.
What is Hazard Operability Analysis?
Hazard Operability Analysis ( HAZOP) is a risk management technique used to determine functional flaws in manufacturing systems. Similar to FMEA, it involves exploring different scenarios where a process, design, or procedure could deviate from its intended function.
What is the output of a risk assessment?
The output of the risk assessment will either be a numeric value or qualitative description expressing the overall level of risk posed by the problem.
What is risk reduction?
Risk reduction is the set of actions taken to minimize the likelihood of occurrence and the severity of consequences. It may also include improving the detectability of hazards (i.e. making hazard identification easier) and risks (i.e. catching risks before they cause further damage).
What is risk analysis?
Risk analysis: Estimate risk associated with identified hazards. For each estimated risk, define the likelihood of occurrence and the severity of consequences.
What is a quality management system that incorporates risk?
A quality management system that incorporates risk will be successful when continual improvement is performed and maintained . Therefore, continual improvement tools will result in outcomes that are compliant with pre-defined quality goals, and will help to develop preventative measures that can reduce the reoccurrence of failures further down the line.
How to improve quality management?
Accordingly, incorporating risk into a quality management system and applying continual improvement tools will help to: 1 establish a proactive culture of prevention and continual improvement; 2 minimise impacts and enhance benefits; 3 ensure high quality of the final product; 4 anticipate issues and opportunities; 5 increase customer satisfaction; 6 improve process performance and efficiency.
What is the PQI in oil and gas?
Quality performance can be measured by different indices, one of which is the project quality index (PQI), which is a performance indicator that measures the effectiveness of QMS implementation, and project compliance to mandatory standards and codes. Oil and gas projects, for example, are executed in three major phases: design, procurement and construction. For each of these project phases, quality-related KPIs are developed to measure progress towards predefined quality goals and objectives, and the sum of the weighted average scores of quality KPIs is used to calculate the PQI.
Why are key performance indicators (KPIs) important?
Towards this goal, key performance indicators (KPIs) are developed to determine the effectiveness of certain processes to implement a sustainable QMS in organisations (as per ISO 9001:2015). KPIs are imperative because they keep business objectives at the forefront of decision-making, allowing project managers to gauge the effectiveness of the process at hand.
What are the risks of a QMS?
Risks are potential threats that may cause failure and loss which can lead to negative effects to a particular project. Therefore, risk is integrated when determining quality objectives, and is monitored through KPIs. These include: the work acceptance rate, number of deficient equipment items, preservation failure rate, and welding repair rate (WRR). For each of those, a quality objective is set based on the risk mitigation factors.
What is ISO 9001:2015?
ISO 9001:2015 provides a framework which organisations can apply to their quality management system (QMS) to deliver sustainable development solutions and to improve the overall performance of their businesses. Performance enhancement outcomes are created by conducting a sequential set of activities on each individual process of a project. Those activities are based on evidence-based decision-making, which utilise continual improvement opportunities to achieve quality objectives.
What is continuous monitoring of KPIs?
Through the continuous monitoring of KPIs, project teams can take immediate action to address any reported product or process deficiencies. It is important to not only focus on corrective action, but to also ensure that sustainable results are achieved, which can occur by utilising continual improvement tools, such as Six Sigma, Lean, Kaizen and Deming’s Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) cycle. The ISO 9001:2015 Standard uses the PDCA cycle to enhance and improve processes using a four-phase iterative approach. The PDCA cycle ensures that the processes are sufficiently resourced and maintained, and that the improvement opportunities are effectively captured by the organisation.
What Is Project Quality Management?
Project quality management is defined by Adobe as “the process of continually measuring the quality of all activities and taking corrective action until the desired quality is achieved.” Commonly used in the world of business, the term project quality management refers to a specific plan or process that helps achieve the desired end goal of a project or action. In simpler terms: whatever a project is meant to accomplish, project quality management helps ensure that all steps are taken properly to meet that goal or goal (s). It also typically describes the processes of quality planning, quality assurance, and quality control.
Should quality be planned for?
Quality should be planned for at the start. It doesn’t happen just by accident. While it looks easy enough to do, it requires an in-depth understanding of the needs of the stakeholder, the limitation of the system, and how much can be accomplished given time and money constraints.
Risk Types PMP
Just as organizing project tasks can be approached systematically to break down what is needed and when, so can risk. Begin with the four types of project risk.
How to Manage Risk
Managing risk is a big component in project management and is certainly addressed within the PMP® exam. Access other articles to continue to grow your knowledge and skills within risk management. At a high level, keep in mind these techniques for managing risk categories:
What do Risk Types and Categories drive in Risk Management?
Although referenced by multiple names including “risk types PMP,” “PMP risk types,” “Risk Categorization PMP®,” or “Risk Categories PMP®,” the core concept is the same: consistent organization of project risks results in better overall risk management.
Conclusion
Do not be overwhelmed by the fact there is uncertainty in your project. In fact, risk can bring great success if managed properly. Use risk types and categories to better organize and track risks, and to more effectively mitigate risk when it occurs.
What is quality system risk management?
The Quality System Risk management is a systematic process for identification, assessment, control, communication and review of risks to the quality system processes.
Why do we need Quality Risk Management in QMS?
By adding quality risk management into your processes, especially at the design and planning phase, you can take actions to ensure that anticipated problems don’t occur or have steps in place to deal with them when they do. The saying goes that an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure, and equally, an hour identifying potential risks can be worth several days scurrying around trying to deal with an unexpected problem. The initial investment in the risk management process will prevent the loss of time, money, brand image due to unanticipated product failures.
What is Risk Control Measures 4.1?
Risk control measures identified in Section 4.1 will be evaluated against risk acceptability matrix. Justification of acceptability as well as residual risk will be completed in the following table. Additional hazards identified (if any) shall be transferred to Section 3.0 for risk evaluation.
What is the justification for tolerable risk levels?
1.4 Justification for Tolerable Risk Levels: There may be instances where, after the implementation of action plans, the risk levels cannot be brought to Acceptable values, the risk levels may be accepted as tolerable. In such instances, justification or rationale shall be documented for tolerable risk levels.
What is risk reduction?
Risk reduction focuses on processes for mitigation or avoidance of quality risk when it exceeds a specified (acceptable) level .Risk reduction might include actions taken to mitigate the severity and/or probability of harm.Processes that improve the detect-ability of hazards might also be used as part of a risk control strategy.The implementation of risk reduction measures can introduce new risks into the system or increase the significance of other existing risks.
What is risk analysis?
Risk analysis is the estimation of the risk associated with the identified hazards. It is the qualitative or quantitative process of linking the likelihood of occurrence and severity of harms.
How to calculate overall risk level?
1.3 Risk Analysis Matrix: Using the following formula, calculate the overall risk level of the hazards. The Overall Risk Level of Hazard = Severity of the harm x Occurrence of the harm. Then compare the Overall Risk Level with the values from Risk Analysis matrix. If the results of overall risk are in the Intolerable region, then define action plan to bring down the overall Risk Level to Acceptable region.

Monitoring Continuous Improvement
Oil and Gas Case Study
- In an oil and gas ‘mega project’, the PDCA cycle was implemented during the project execution in collaboration with the contractor. The goal was to reduce the welding rejection rates (WRR) from 11 per cent to five per cent, which was the quality objective. The ‘plan’ phase was initiated by clearly identifying the core problem in the project. The goals were set according to the objective …
Benefits and Outcomes
- The project not only complied with the quality objective, which had a target of five percent for the WRR, but it also saved $535,040 US dollars in costs and prevented a six-month schedule delay in the project. Accordingly, incorporating risk into a quality management system and applying continual improvement tools will help to: 1. establish a proac...