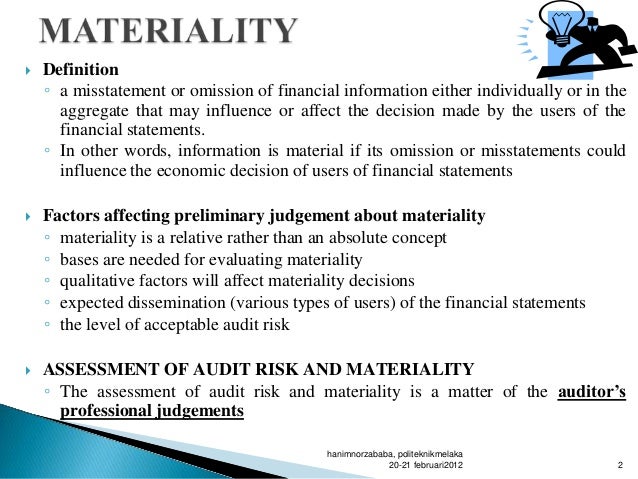
Quantitative Materiality In an audit, materiality is a matter of professional judgment that auditors need to decide for any audit engagement. There is no professional standard that states how much amount or percentage auditors should use for calculation of materiality.
What is materiality in qualitative research?
Materiality: qualitative considerations. Item cannot be considered as immaterial only because it is below a predetermined quantitative threshold. When a misstatement is made intentionally to achieve a particular presentation or result, then the misstatement is considered to be material irrespective of the amount.
What is materiality in accounting?
Materiality concerns the significance of an item to users of a registrant's financial statements. A matter is "material" if there is a substantial likelihood that a reasonable person would consider it important. In its Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 2, the FASB stated the essence of the concept of materiality as follows:
What are the different types of materiality?
Types of Materiality in Audit In the audit work, auditors must calculate materiality for financial statements as a whole, which is known as overall materiality, and performance materiality in order to use as guidance in performing the audit. Qualitative and Quantitative Factors of Materiality in Audit
What are assessing materiality facts?
Assessing Materiality Facts: During the course of preparing or auditing year-end financial statements, financial management or the registrant's independent auditor becomes aware of misstatements in a registrant's financial statements.

What are the 2 types of materiality?
Overall Materiality (for the Financial Report as a whole)Overall Performance Materiality.Specific Materiality (for particular classes of transactions,
What are the 3 types of materiality?
Table of contents#1 – Overall Materiality.#2 – Overall Performance Materiality.#3 – Specific Materiality.
What is qualitative aspect of materiality?
Qualitative materiality refers to the nature of a transaction or amount and includes many financial and non-financial items that, independent of the amount, may influence the decisions of a user of the financial statements.
What is a quantitative audit?
The audit inquiry most typically utilized by insurance carriers is the quantitative audit, which examines the amount and breakdown of time that attorneys have invoiced. The goal of this type of audit is to determine whether the law firm has substantially complied with the billing guidelines imposed by the carrier.
What is materiality and its types?
Materiality relates to both the content of the financial statements and the level and type of testing to be done. The decision is based on judgements about the size, nature and particular circumstances of misstatements (or omissions) that could influence users of the financial reports.
How do you measure materiality?
Auditors determine overall materiality at the planning stage of the audit, typically by applying a percentage to a chosen benchmark. Common benchmarks include profit before tax or normalised (ie. adjusted) profit before tax, total income or total expenses, gross profit, total assets or net assets.
What is qualitative and quantitative materiality?
Given the variety of users, determining materiality is a matter of professional judgement. An item or group of items may be material due to their amount (quantitative materiality), nature or the context in which the deviation occurs (qualitative materiality).
What are the example of quantitative?
Quantitative Information – Involves a measurable quantity—numbers are used. Some examples are length, mass, temperature, and time. Quantitative information is often called data, but can also be things other than numbers.
Is data qualitative or quantitative?
Quantitative data are measures of values or counts and are expressed as numbers. Quantitative data are data about numeric variables (e.g. how many; how much; or how often). Qualitative data are measures of 'types' and may be represented by a name, symbol, or a number code.
Are audits qualitative or quantitative?
3. Research Methodology. An audit plan is assessed more with qualitative criteria rather than quantitative ones. Its impact on audit quality and risk management is also out of focus and practically not measured anywhere without any methods.
What is a qualitative audit?
A qualitative audit analyzes the quality and effectiveness of the content. Your findings from this analysis provide insight to whether or not the content is useful, usable, enjoyable, and persuasive to your audience.
What is the importance of quality audit?
Quality audits are an important function for driving growth within organisations. They provide mechanisms to evaluate the efficiency of the business and help managers to identify whether applied strategies are delivering results.
What are the 3 types of audit risk?
There are three primary types of audit risks, namely inherent risks, detection risks, and control risks.
What is materiality with example?
A classic example of the materiality concept is a company expensing a $20 wastebasket in the year it is acquired instead of depreciating it over its useful life of 10 years. The matching principle directs you to record the wastebasket as an asset and then report depreciation expense of $2 a year for 10 years.
What are the three types of misstatements?
Three types of misstatement include factual misstatement, judgmental misstatements, and projected misstatements.
What are the factors of materiality?
Materiality depends on the size and nature of the omission or misstatement judged in the surrounding circumstances. The size or nature of the item, or a combination of both, could be the determining factor.
What is materiality in auditing?
Materiality concept in auditing referred to the concept that the information is important or significant enough to affect the decisions making of users of financial statements if such information is removed or change how it is presented. It helps auditors to focus their attention on the areas where the material errors or omission may occur.
Why is materiality important in auditing?
In auditing, the materiality concept usually applies when auditors evaluate whether the client’s financial statements contain material misstatement or not.
Why do financial analysts need to apply the materiality concept?
Hence, they need to apply the materiality concept so that they can make sure that there are no errors or omissions that would materially affect the decision making of the users of financial statements.
What is the materiality concept of different users?
Materiality Concept of Different Users. Different users of information may have different preferences when applying the materiality concept in auditing. Hence, it is very important for accountants or auditors to define who is the primary user of financial information.
Why do accountants use materiality?
In accounting, accountants usually use the materiality concept as a basis for preparing financial statements. For example, accountants usually come across a lot of circumstances where they need to make the best estimate. Hence, they need to apply the materiality concept so that they can make sure that there are no errors or omissions ...
When assessing the materiality of an audit, what type of information do auditors need to consider?
When assessing the materiality, auditors usually need to consider what type of information, they are dealing with; and how much the amount is involved. For the materiality concept in auditing, these are usually referred to as qualitative and quantitative factors of the materiality concept.
What is qualitative consideration?
Quantitative consideration is simply about the relative size of the items in the financial statements. On the other hand, qualitative factors usually include the nature of information, the circumstance and possible cumulative effects of error or omission of such information.
How to determine if multiple misstatements cause the financial statements to be materially misstated?
In determining whether multiple misstatements cause the financial statements to be materially misstated, registrants and the auditors of their financial statements should consider each misstatement separately and the aggregate effect of all misstatements. 23 A registrant and its auditor should evaluate misstatements in light of quantitative and qualitative factors and "consider whether, in relation to individual line item amounts, subtotals, or totals in the financial statements, they materially misstate the financial statements taken as a whole." 24 This requires consideration of -
What is the purpose of the staff accounting bulletin?
SUMMARY: This staff accounting bulletin expresses the views of the staff that exclusive reliance on certain quantitative benchmarks to assess materiality in preparing financial statements and performing audits of those financial statements is inappropriate; misstatements are not immaterial simply because they fall beneath a numerical threshold.
What is the result of a misstatement in a registrant's financial statements?
When combined, the misstatements result in a 4% overstatement of net income and a $.02 (4%) overstatement of earnings per share. Because no item in the registrant's consolidated financial statements is misstated by more than 5%, management and the independent auditor conclude that the deviation from generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP") is immaterial and that the accounting is permissible. 1
What is material omission?
The omission or misstatement of an item in a financial report is material if, in the light of surrounding circumstances, the magnitude of the item is such that it is probable that the judgment of a reasonable person relying upon the report would have been changed or influenced by the inclusion or correction of the item. 3
What is the assessment of materiality?
Under the governing principles, an assessment of materiality requires that one views the facts in the context of the "surrounding circumstances," as the accounting literature puts it, or the "total mix" of information, in the words of the Supreme Court.
When was the Big Five Audit Materiality Task Force convened?
The staff understands that the Big Five Audit Materiality Task Force ("Task Force") was convened in March of 1998 and has made recommendations to the Auditing Standards Board including suggestions regarding communications with audit committees about unadjusted misstatements.
Can misstatements affect financial statements?
Even though a misstatement of an individual amount may not cause the financial statements taken as a whole to be materially misstated, it may nonetheless, when aggregated with other misstatements, render the financial statements taken as a whole to be materially misleading. Registrants and the auditors of their financial statements accordingly should consider the effect of the misstatement on subtotals or totals. The auditor should aggregate all misstatements that affect each subtotal or total and consider whether the misstatements in the aggregate affect the subtotal or total in a way that causes the registrant's financial statements taken as a whole to be materially misleading. 26
What is materiality in accounting?
Materiality is one of the essential accounting concepts and is designed to ensure all of the crucial information related to the business are presented in the financial statement. The purpose of materiality is to ensure that the financial statement user is provided with financial information that does not have any significant omissions/misstatements.
What is the most common application of materiality in accounting?
The most common application of materiality in accounting is observed in capitalization, adoption of accounting standards, and deciding if corrections should be made in the books for some specific error.
What is materiality by impact?
Materiality by impact refers to the concept that even a trivial amount can be material if its impact is higher on the financial statement. For instance, if a trivial amount changes loss into profit, the amount is considered to be material due to its impact.
How to calculate materiality?
For instance, materiality is taken to be 0.5% to 1% of the total sales, 1% to 2% of the total assets, 1% to 2% of gross profit, and 5% to 10% of the net profit.
Why is materiality important in accounting?
Further, the concept of materiality helps to decide if certain omissions/misstatements should be corrected in the books of accounts. As a bottom line, there must not be any omission/misstatement in the financial statement.
Why do companies charge immaterial items of purchase in the income statement?
As capitalization of the assets increases administrative tasks for the business. So, companies charge immaterial items of purchase (capital assets) in the income statement rather than capitalizing and increasing administrative efforts.
Why do companies set capitalization thresholds?
The companies set capitalization thresholds to ensure only material items are capitalized, depreciated, and tracked. This helps the companies to utilize their resources on monitoring capital items with significant value.
Which level of evaluation should materiality be described in?
Judgment – Materiality should be described in both qualitative and quantitative terms, and it should be evaluated at the component level.
Who reviews materiality concepts?
The materiality concepts statement is under due process review by the Secretary of the Treasury, the Director of the Office of Management and Budget, and the Comptroller General.
Why was materiality removed from the draft?
The Board also agreed to delete the wording regarding relevance because materiality is entity specific and relevance is a general notion about what type of information is useful to users.
What chapter is materiality guidance in SFFAC 1?
The Board agreed to insert a chapter titled Materiality between the current chapter 6: Qualitative Characteristics of Information in Financial Reports and chapter 7: How Accounting Supports Federal Financial Reporting.
When is the ED materiality deadline?
In light of the partial government shutdown, FASAB has extended the comment deadline for the ED Materiality to March 11, 2019.
Is there a need to align materiality?
The Board noted that the accounting and auditing materiality issues are different and, therefore, there is not a need to align the definitions. The Board proposed “could reasonably be expected” in its ED and received positive feedback on the proposed materiality concepts. The Board concluded that the term “could reasonably be expected” is appropriate in assessing materiality in the federal financial reporting environment.
What are the qualitative factors of finance?
Qualitative factors traditionally considered by the finance community relate to the nature of the enterprise (firm characteristics) and its operating environment (including peer and industry characteristics). Questions are asked about its type of products and services, its size and market position, reputation, labour or capital intensiveness, capital structure, type of institutional ownership, and regulatory risks / opportunities. These factors, in addition to the importance of circumstances under which materiality is decided, have been recognized in the 1970s in a 246-page memorandum by FASB in the USA on “Criteria for Determining Materiality”.
What is ISA 320?
More recent, the ISA 320 Audit Materiality (IFAC 2004) standard refers to consideration of the size of an item, its nature as well as the circumstances of the entity involved. Take the circumstances of the public sector as example. In the USA the Government Accounting Standards Board (GASB) has confirmed that qualitative factors considered in the case of reporting by governmental institutions would be matters such as the possibility of fraud, illegal acts, conflicts of interest and politically sensitive material that may cause quantitatively immaterial items to be determined as material.
What is quantitative information?
Quantitative information can involve generic empirical information (e.g. physical metrics) or monetary values (e.g. financial metrics) that signal a certain magnitude of financial effect on the reporting organization. Traditionally accountants and auditors have been most attentive to financial data that show actual or potential impact on cash (liquidity). This can be the effect in one year, but consideration also needs to be given to accumulative impact over a number of years. It considers the interest of the providers of financial capital in the profitability, liquidity and solvency of the reporting organization.
Is reputation a qualitative or quantitative factor?
The norm has been to prefer quantitative information, and complement this with qualitative descriptions. Still the qualitative deserves attention in its own right. An example is reputation, an intangible asset that senior executives often cite as the most important driver for their sustainability investments (despite the woolly nature of “reputation”). Qualitative factors considered range from enterprise specific cases of compliance and business ethics to operating environment factors such as market and regulations, to broader societal factors such as economic trends, political realities and social licence to operate.
What is materiality in accounting?
, the definition for materiality is “The omission or misstatement of an item in a financial report is material if, in light of surrounding circumstances, the magnitude of the item is such ...
What is the materiality threshold in audit?
The materiality threshold in audits refers to the benchmark used to obtain reasonable assurance that an audit does not detect any material misstatement that can significantly impact the usability of financial statements. It is not feasible to test and verify every transaction and financial record, so the materiality threshold is important ...
What is materiality in financial statements?
Stated otherwise, materiality refers to the potential impact of the information on the user’s decision-making relating to the entity’s financial statements or reports. Users of financial statements include: Shareholders. Creditors.
What is IFRS accounting?
IFRS Standards IFRS standards are International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) that consist of a set of accounting rules that determine how transactions and other accounting events are required to be reported in financial statements. They are designed to maintain credibility and transparency in the financial world.
Why are auditors important?
Auditors are highly important people because, ultimately, they are. Accounting Policies. Accounting Policies Accounting policies are rules and guidelines that are selected by a company for use in preparing and presenting its financial statements. Audit Legal Implications.
How much margin impact does a $1 million misstatement have?
So, for a company with $5 million in revenue, the $1 million misstatement can represent a 20% margin impact, which is very material.
What happens if you misstate $1.00?
Clearly, if the $1.00 transaction was misstated, it will not make much of an impact for users of financial statements, even if the company was small. However, an error on a transaction of $1,000,000 will almost certainly make a material impact on the user’s decisions regarding financial statements.
What is cumulative impact of immaterial misstatements?
E.g. a failure to recognise a liability and expense of $100/year for the last 10 years results in an understatement of liabilities by $1,000. While $100 may not be material in any given year, understatement of liabilities by $1,000 at the reporting date may be a material omission. If this is the case, entities cannot recognise $1,000 of liability and expenses in current period as this would materially misstate current results. In such a case, entities need to make a retrospective correction of error even though this error was not material in any previous year.
What is materiality in financial reporting?
Materiality concept. Materiality is a crucial concept in financial reporting. A requirement in IFRS (including disclosure) need not be applied if the effect of not applying it is immaterial (see paragraph 8 of IFRS Practice Statement 2 Making Materiality Judgements).
Why can't an item be considered immaterial?
Materiality: qualitative considerations. An item cannot be considered as immaterial only because it is below a predetermined quantitative threshold. When a misstatement is made intentionally in order to achieve a particular presentation or result, the misstatement is considered to be material irrespective of the amount.
Why is it so that such a misstatement would not have been made if the entity would not expect it?
It is so because such a misstatement would not have been made if the entity would not expect it to influence decisions made by users of financial statements. This is not to be confused with simplifications adopted by an entity, as these are not intended to achieve a particular presentation or result.
When do immaterial items become material?
Therefore, immaterial item may become material when taken together with other individually immaterial items. It is therefore important to keep track of any uncorrected misstatements identified during a period in order to be able to assess their collective materiality.
When did the IFRS become effective?
The amended IFRS which became effective in 2020 explain that information is obscured if it is disclosed using vague or unclear language or it is ‘lost’ in immaterial information so that a reader is unable to determine which information is material and which isn’t (IAS 1.7).
Is materiality a quantitative threshold?
Materiality is entity specific and IFRS do not give any quantitative thresholds. IASB issued a non-binding IFRS Practice Statement 2 Making Materiality Judgements which is worth reading when considering materiality concept.
