Why is secondary analysis of data important in quantitative research?
Because of the ways in which it can be more readily standardised, anonymised, and curated, secondary analysis of quantitative data is more common than for qualitative studies. Secondary analysis promotes transparency, reproducibility, and replication in research and facilitates the cumulative growth of knowledge.
What is second secondary data?
Secondary data is the data that has already been collected through primary sources and made readily available for researchers to use for their own research. It is a type of data that has already been collected in the past.
What is primary data in qualitative research?
Primary data is collected first hand by the researcher for a specific research purpose. The researcher might collect information via observation, psychometric test, interview etc and this data may be qualitative or quantitative.
Is secondary data reliable for research?
Secondary data is used for a multitude of research purposes. However, the data acquired from previously sourced and analysed sources are not always reliable for the research process. Secondary data has advantages and disadvantages, which every analyst and researcher should know before proceeding to use.

Why is secondary data quantitative?
The quantitative method of secondary data analysis is used on numerical data and is analyzed mathematically. The qualitative method uses words to provide in-depth information about data. There are different stages of secondary data analysis, which involve events before, during, and after data collection.
What are 2 examples of quantitative data?
Quantitative data examples in researchWeight in pounds.Length in inches.Distance in miles.Number of days in a year.A heatmap of a web page.
What is quantitative secondary analysis?
Secondary data analysis, by contrast, is the process of analysing data that have been collected and compiled by another researcher or research organisation or that have originally been collected for a different purpose.
Is secondary data quantitative or qualitative?
Secondary data can be both quantitative and qualitative in form. Secondary quantitative data is often available from official government sources and trusted research organizations.
What are 5 examples of quantitative data?
Some examples of quantitative data include:Revenue in dollars.Weight in kilograms.Age in months or years.Length in centimeters.Distance in kilometers.Height in feet or inches.Number of weeks in a year.
What are 5 examples of quantitative research?
There are five main types of quantitative research designs and they are:Descriptive Research Design.Survey Research.Correlational Research Design.Quasi-experimental Research Design.Experimental Research Design.
How do you collect secondary quantitative data?
The secondary data can be both qualitative and quantitative. The qualitative data can be obtained through newspapers, diaries, interviews, transcripts, etc., while the quantitative data can be obtained through a survey, financial statements and statistics.
How do you analyze secondary quantitative data?
2. How to carry out secondary data analysisStep 1: Define a research topic.Step 2: Establish your statement of purpose.Step 3: Design your research process.Step 4: Locate and collect your secondary data.Step 5: Evaluate your secondary data.Evaluating the secondary dataset's relevance.More items...•
Is quantitative research secondary?
Types of secondary data The two most common types of secondary research are, as with all types of data, quantitative and qualitative.
What are the types of secondary data?
There are two common types of secondary data: Internal data and External data. Internal data is the information that has been stored or organized by the organization itself. External data is the data organized or collected by someone else.
What method is secondary data?
Secondary Data Collection Methods Secondary data is data collected by someone other than the actual user. It means that the information is already available, and someone analyses it. The secondary data includes magazines, newspapers, books, journals, etc.
What are the 4 types of quantitative research?
There are four main types of Quantitative research: Descriptive, Correlational, Causal-Comparative/Quasi-Experimental, and Experimental Research. attempts to establish cause- effect relationships among the variables. These types of design are very similar to true experiments, but with some key differences.
What are 2 examples of qualitative data?
Examples of qualitative dataDiary accounts. Diary accounts are collected as part of diary studies. ... Documents. ... Case studies. ... Photographs. ... Audio recordings. ... Video recordings. ... Transcriptions. ... Descriptions.More items...•
What is an example of quantitative and qualitative data?
Start with yourself as an example. To acquire qualitative data, consider identifiers like the color of your clothes, type of hair, and nose shape. For quantitative data, consider measurable values like your height, weight, age, and shoe size.
What are the four types of quantitative data?
There are four main types of Quantitative research: Descriptive, Correlational, Causal-Comparative/Quasi-Experimental, and Experimental Research. attempts to establish cause- effect relationships among the variables.
What are examples of qualitative?
Qualitative Information – Involves a descriptive judgment using concept words instead of numbers. Gender, country name, animal species, and emotional state are examples of qualitative information.
Why is secondary data important?
Secondary data sources are extremely useful. They allow researchers and data analysts to build large, high-quality databases that help solve business problems. By expanding their datasets with secondary data, analysts can enhance the quality and accuracy of their insights. Most secondary data comes from external organizations. However, secondary data also refers to that collected within an organization and then repurposed.
How does secondary data help you?
Secondary data can build useful relationships: Acquiring secondary data usually involves making connections with organizations and analysts in fields that share some common ground with your own. This opens the door to a cross-pollination of disciplinary knowledge. You never know what nuggets of information or additional data resources you might find by building these relationships.
How long is the data analytics course?
To learn more about data analytics, check out this free, five-day introductory data analytics short course. You can also check out these articles to learn more about the data analytics process:
Where does secondary data come from?
As mentioned, secondary data is not limited to that from a different organization. It can also come from within an organization itself.
Is secondary data always suited to a problem?
The data isn’t always suited to the problem at hand : While secondary data may tick many boxes concerning its relevance to a business problem, this is not always true. For instance, secondary data collection might have been in a geographical location or time period ill-suited to your analysis. Because analysts were not present when the data were initially collected, this may also limit the insights they can extract.
Can you be sure how data was collected?
You can’t be sure how the data were collected: A structured, well-ordered secondary dataset may appear to be in good shape. However, it’s not always possible to know what issues might have occurred during data collection that will impact their quality. For instance, poor response rates will provide a limited view. While issues relating to data collection are sometimes made available alongside the datasets (e.g. for government data) this isn’t always the case. You should therefore treat secondary data with a reasonable degree of caution.
Do you have to pay for secondary data?
They aren’t always free: Sometimes, it’s unavoidable—you may have to pay for access to secondary data. However, while this can be a financial burden, in reality, the cost of purchasing a secondary dataset usually far outweighs the cost of having to plan for and collect the data firsthand.
What are some examples of quantitative data?
Examples of quantitative data include numerical values such as measurements, cost, and weight; examples of qualitative data include descriptions (or labels) of certain attributes, such as “brown eyes” or “vanilla flavored ice cream”. Now we know the difference between the two, let’s get back to quantitative data.
How to collect quantitative data?
Another way to collect quantitative data is through questionnaires and surveys. Nowadays, it’s easy to create a survey and distribute it online—with tools like Typeform, SurveyMonkey, and Qualtrics, practically anyone can collect quantitative data. Surveys are a useful tool for gathering customer or user feedback, and generally finding out how people feel about certain products or services. To make sure you gather quantitative data from your surveys, it’s important that you ask respondents to quantify their feelings—for example, asking them to rate their satisfaction on a scale of one to ten.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
But, to summarize, the differences between quantitative and qualitative data are as follows: Quantitative data is countable or measurable, relating to numbers; qualitative data is descriptive, relating to words. Quantitative data lends itself to statistical analysis; qualitative data is grouped and categorized according to themes.
What is discrete data?
Discrete data is quantitative data that can only take on certain numerical values. These values are fixed and cannot be broken down. When you count something, you get discrete data. For example, if a person has three children, this is an example of discrete data. The number of children is fixed—it’s not possible for them to have, say, 3.2 children. Another example of discrete quantitative data could be the number of visits to your website; you could have 150 visits in one day, but not 150.6 visits. Discrete data is usually visualized using tally charts, bar charts, and pie charts.
Why is quantitative data important?
The main advantages of working with quantitative data are as follows: Quantitative data is relatively quick and easy to collect, allowing you to gather a large sample size. And, the larger your sample size, the more accurate your conclusions are likely to be . Quantitative data is less susceptible to bias.
What are the two types of data?
Data professionals work with two types of data: Quantitative and qualitative. In simple terms, quantitative data is measurable while qualitative data is descriptive—think numbers versus words. If you plan on working as a data analyst or a data scientist (or in any field that involves conducting research, like psychology), ...
What is continuous data?
Continuous data, on the other hand, can be infinitely broken down into smaller parts. This type of quantitative data can be placed on a measurement scale; for example, the length of a piece of string in centimeters, or the temperature in degrees Celsius. Essentially, continuous data can take any value; it’s not limited to fixed values. What’s more, continuous data can also fluctuate over time—the room temperature will vary throughout the day, for example. Continuous data is usually represented using a line graph.
What is secondary data?from statswork.com
Secondary data is categorised into internal (from the organization which is under observation) data which is routinely supplied by management and external (from outside the organization) data which is obtained from various resources such as internet, journals, books, directories, Non-governmental statistical data and Census data.
Why is data with high validity and accuracy not useful?from statswork.com
The data with high validity and accuracy can’t be useful if the content of the data is not good. Sometimes, there may be no proper link between the relationships examined by the data and the measurement categories adopted by the researcher. For example, the data may consider the relationship between salary levels and motivation. However, motivation may have been defined and measured in a way that is inconsistent or inappropriate with how the researcher considering the secondary data wishes to measure motivation.
Why is secondary data important?from careerfoundry.com
Secondary data sources are extremely useful. They allow researchers and data analysts to build large, high-quality databases that help solve business problems. By expanding their datasets with secondary data, analysts can enhance the quality and accuracy of their insights. Most secondary data comes from external organizations. However, secondary data also refers to that collected within an organization and then repurposed.
What influences the choice of alternative research methodologies in the case of consultancy research projects?from statswork.com
Preferences and values of the client are found to extremely influence the choice of alternative research methodologies in the case of consultancy research projects. For example, the consultancy may feel that data for a particular project can be effectively collected through observation. But the client may tell that his department won’t allow observation method. In this case, it is necessary to discuss in terms of research methodology at the contracting stage of the consultancy process.
What is a statement of purpose in analytics?from careerfoundry.com
Before beginning any data analytics project, you should always have a clearly defined intent. This is called a ‘statement of purpose.’ A healthcare analyst’s statement of purpose, for example, might be: ‘Reduce admissions for mental health issues relating to Covid-19′. The more specific the statement of purpose, the easier it is to determine which data to collect, analyze, and draw insights from.
What is secondary data analysis?from careerfoundry.com
Secondary data analysis uses data collected by somebody else. This contrasts with primary data analysis, which involves a researcher collecting predefined data to answer a specific question. Secondary data analysis has numerous benefits, not least that it is a time and cost-effective way of obtaining data without doing the research yourself.
What is a final report for data analytics?from careerfoundry.com
A final report for past data analytics is great for summarizing key characteristics or findings. However, if you’re planning to use those data for a new project, you’ll need the original documentation. At the very least, this should include access to the raw data and an outline of the methodology used to gather them. This can be helpful for many reasons. For instance, you may find raw data that wasn’t relevant to the original analysis, but which might benefit your current task.
What is secondary data?
Secondary data is the data that has already been collected through primary sources and made readily available for researchers to use for their own research. It is a type of data that has already been collected in the past.
What is secondary data analysis?
Secondary data analysis is the process of analyzing data collected from another researcher who primarily collected this data for another purpose. Researchers leverage secondary data to save time and resources that would have been spent on primary data collection.
What are the Secondary Data Collection Tools?
Popular tools used to collect secondary data include; bots, devices, libraries, etc. In order to ease the data collection process from the sources of secondary data highlighted above, researchers use these important tools which are explained below.
Why is secondary data not authentic?
This is a very common disadvantage with online sources due to a lack of regulatory bodies to monitor the kind of content that is being shared.
What do you need to know before collecting secondary data?
Before collecting secondary data for analysis, you need to know your statement of purpose. That is, a clear understanding of why you are collecting the data—the ultimate aim of the research work and how this data will help achieve it.
Why is secondary data important?
Secondary data makes it easy to carry out longitudinal studies without having to wait for a couple of years to draw conclusions. For example, you may want to compare the country's population according to census 5 years ago, and now.
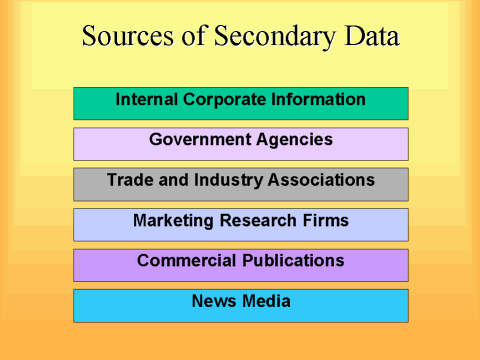
What are secondary sources?
Sources of Secondary Data. Sources of secondary data includes books, personal sources, journal, newspaper, website, government record etc. Secondary data are known to be readily available compared to that of primary data. It requires very little research and need for manpower to use these sources.
What is Secondary Data?
In brief, secondary data is the previously sourced, arranged and analysed data which is readily available for researchers to research their research.
Types of Secondary Data
Secondary data is typically gathered from various sources, though occasionally, it is also gathered from within the same organisation. There are two sorts, according to the source.
Internal Secondary Data
Secondary data is not always sought from other sources. Sometimes it is sourced from the previously recorded data within the organisation as well. Such type of data is known as internal secondary data.
Uses of Secondary Data
Even though all data is intended to provide information for analysis, secondary data can be used in a variety of ways depending on the context and the nature of a research endeavour. As a result, they can be useful for:
How to Analyse Secondary Data?
Now that we know what secondary data is and its many uses, the next step is to understand how to analyse the data.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Secondary Data
Secondary data is used for a multitude of research purposes. However, the data acquired from previously sourced and analysed sources are not always reliable for the research process. Secondary data has advantages and disadvantages, which every analyst and researcher should know before proceeding to use.
Conclusion
Secondary data has a wide range of applications in research, industry, and statistics. Researchers choose secondary data for a variety of factors, including cost, availability, and even research goals.
What does it mean when someone uses secondary data?
When a researchers uses secondary data, this means that someone else has already collected the information, for a different purpose and the information has been stored on record for use by other researchers. The researcher will re-analyse this second hand data for a new purpose. Results of psychological studies are classed as secondary data ...
What is secondary data in psychology?
In clinical psychology, secondary data might include medical records made by doctors including diagnoses of disorders or how a patient has responded to treatments options. It could also include school reports which provide insight into an individual’s life before the onset of a disorder.
What is primary data?
Primary data is collected first hand by the researcher for a specific research purpose. The researcher might collect information via observation, psychometric test, interview etc and this data may be qualitative or quantitative. With quantitative primary data, the researcher might analyse the data using descriptive and inferential statistics or with qualitative primary data they might conduct a grounded theory or discourse analysis.
What are some examples of secondary data in clinical psychology?
A specific example of the use of secondary data in clinical psychology was Gottesman and Shields as an example of a twin study where pre-existing diagnoses of schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders had already been made in their twin pairs whose information was gathered from records held by Bethlem and Maudsley hospital.
What are some examples of qualitative primary data collection?
An example of a qualitative primary data collection from clinical psychology would be when Brown et al (1986) interviewed participants and information was collected about self esteem, life events and perceived social support over the course of the longitudinal study.
What is the difference between primary and secondary data?
Difference 1: The collection of primary data may be more expensive then secondary data because…. Difference 2: Primary data could be considered more valid then secondary data because…. Difference 3: Secondary data may be less reliable then primary data because…. Difference 4: Secondary data may be more practical and lead to more credible findings ...
Do clinical psychologists collect data?
Researchers in clinical psychology often use hospital records as part of their data collection. They may also collect data directly from their participants. Explain why different types of data are used and evaluate the use of these different types of data. (6)
What is secondary data analysis?
Secondary data analysis uses data collected by somebody else. This contrasts with primary data analysis, which involves a researcher collecting predefined data to answer a specific question. Secondary data analysis has numerous benefits, not least that it is a time and cost-effective way of obtaining data without doing the research yourself.
Why is it important to understand why data were collected?
Understanding why the data were originally collected will tell you a lot about their suitability for your current project. For instance, was the project carried out by a government agency or a private company for marketing purposes? The answer may provide useful information about the population sample, the data demographics, and even the wording of specific survey questions. All this can help you determine if the data are right for you, or if they are biased in any way.
What is a statement of purpose in analytics?
Before beginning any data analytics project, you should always have a clearly defined intent. This is called a ‘statement of purpose.’ A healthcare analyst’s statement of purpose, for example, might be: ‘Reduce admissions for mental health issues relating to Covid-19′. The more specific the statement of purpose, the easier it is to determine which data to collect, analyze, and draw insights from.
What is the first step in data analytics?
The first step in any data analytics project is defining your goal. This is true regardless of the data you’re working with, or the type of analysis you want to carry out. In data analytics lingo, this typically involves defining:
What is a scientific journal?
Scientific journals that outline research methodologies and data analysis by experts in fields like the sciences, medicine, etc.
What is government statistics?
Government statistics, e.g. demographic data, censuses, or surveys, collected by government agencies/departments (like the US Bureau of Labor Statistics).
Why do you need to carry out a careful review of data?
First, you must carry out a careful review of the data. Why? To ensure that they’re appropriate for your needs . This involves two main tasks:
What is quantitative research?
Revised on February 15, 2021. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting ...
Why is quantitative research important?
Quantitative research is often used to standardize data collection and generalize findings. Strengths of this approach include: Replication. Repeating the study is possible because of standardized data collection protocols and tangible definitions of abstract concepts. Direct comparisons of results.
What is mixed methods research?
In mixed methods research, you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research?
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analyzing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
What is experimental research?
In experimental research, you systematically examine whether there is a cause-and-effect relationship between variables. Correlational and experimental research can both be used to formally test hypotheses, or predictions, using statistics.
Why do you assess the reliability and validity of your data collection methods?
You can also assess the reliability and validity of your data collection methods to indicate how consistently and accurately your methods actually measured what you wanted them to.
What is the meaning of validity?
Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure). If you are doing experimental research, you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
