Radioactive elements are made up of atoms whose nuclei are unstable and give off atomic radiation as part of a process of attaining stability. The emission of radiation transforms radioactive atoms into another chemical element, which may be stable or may be radioactive such that it undergoes further decay.
What does it mean if an element is radioactive?
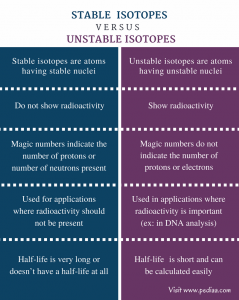
radioactive elements are elements that are considered unstable due to the unbalanced number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus. The nucleus may have more neutrons than protons or vice versa. This elements therefore disintegrate to a more stable isotope by releasing either energetic particles or radiation.
What do elements tend to be radioactive?
Radioactivity is the physical phenomenon of certain elements - such as uranium - of emitting energy in the form of radiation.This energy comes from the decay of an unstable nucleus. Any nuclear species (particular configuration of protons, neutrons and energy) that exhibit radioactivity are known as radioactive nuclei.Additionally, radioactivity or simply activity can be used as a measurement ...
What radioactive element is used to generate energy?
Nearly all Nuclear power stations use uranium as the fuel. Thorium -232 element can be used in breeder reactors to generate uranium-233 which in turn can be used as fissile material for generating power by nuclear fission reaction. Types of radioactive elements used in nuclear power stations
Which elements have the highest initial radioactivity?
- Strontium-90
- Thallium-204
- Carbon-14
- Tritium

What is radioactive element with example?
For example, uranium and thorium are two radioactive elements found naturally in the Earth's crust. Over billions of years, these two elements slowly change form and produce decay products such as radium and radon. During this process, energy is released. One form of this energy is alpha radiation.
Why are elements called radioactive?
What are Radioactive elements? Some elements of atomic nuclei are unstable because of the presence of excess nuclear charge inside it so these nuclei undergo radioactive decay to form stable nuclei. These elements are called radioactive elements.
What is radioactive element Class 11?
Solution : (i) The phenomenon of nuclear decay of certain elements with the emission of radiations like alpha, beta and gamma rays is called as "radioactivity".
(ii) The elements which undergo this phenomenon are called as "radioactive elements ". Loading Books. Answer.
What does radioactive mean?
1 : the giving off of rays of energy or particles by the breaking apart of atoms of certain elements (as uranium) 2 : the rays or particles that are given off when atoms break apart. radioactivity. noun. ra·dio·ac·tiv·i·ty | \ -ak-ˈtiv-ət-ē \
Which element is most radioactive?
Polonium. Because it is a naturally-occurring element that releases a huge amount of energy, many sources cite polonium as the most radioactive element. Polonium is so radioactive it glows blue, which is caused by excitation of the gas particles by radiation.
What are two radioactive elements?
Keep in mind, all elements can have radioactive isotopes. If enough neutrons are added to an atom, it becomes unstable and decays....Radioactive Elements.ElementMost Stable IsotopeHalf-life of Most Stable IsotopeAstatineAt-2108.1 hoursRadonRn-2223.82 daysFranciumFr-22322 minutesRadiumRa-2261600 years33 more rows•Jul 30, 2019
What are radioactive elements called?
Elements that emit ionizing radiation are called radionuclides. When it decays, a radionuclide transforms into a different atom - a decay product.
What is the SI unit of radioactivity?
becquerel (Bq)The System International of units (SI system) uses the unit of becquerel (Bq) as its unit of radioactivity.
Who discovered radioactive elements?
March 1, 1896: Henri Becquerel Discovers Radioactivity. In one of the most well-known accidental discoveries in the history of physics, on an overcast day in March 1896, French physicist Henri Becquerel opened a drawer and discovered spontaneous radioactivity.
What is another word for radioactive?
What is another word for radioactive?activecontaminateddangerousemitting radiationharmfulhotenergeticirradiated
How is radioactivity made?
Humans make radioactive material by causing nuclear reactions in nuclear reactors and particle accelerators. Some radioactive materials pour their energy out quickly, and others pour it out slowly.
What are radioactive elements called?
Elements that emit ionizing radiation are called radionuclides. When it decays, a radionuclide transforms into a different atom - a decay product.
How do atoms become radioactive?
After an atom expels energy from the nucleus, the composition of the nucleus changes, and we are left with a different element that is more stable. This process is known as radioactive decay.
Why some elements are radioactive but some are not?
If the ratio of neutrons to protons becomes too large or the atomic number is above 83 an isotope will be radioactive. According to the theory, If the ratio of neutrons to protons more than one, or becomes too large, the isotope is radioactive or the atomic number is above 83, the isotope will be radioactive.
Why is uranium so radioactive?
Uranium is naturally radioactive: Its nucleus is unstable, so the element is in a constant state of decay, seeking a more stable arrangement. In fact, uranium was the element that made the discovery of radioactivity possible.
What is a radioactive element?
Some elements of atomic nuclei are unstable because of the presence of excess nuclear charge inside it so these nuclei undergo radioactive decay to...
What are the 4 radioactive elements?
The common 4 radioactive elements are Uranium, Radium, Polonium, Thorium etc.
Are smokers lungs radioactive?
Cigarettes made from tobacco contain radioactive materials: polonium-210 and lead-210. These radioactive particles settle in smokers’ lungs, where...
What is uranium used for?
U-235 and U-238 occur naturally in nearly all rock, soil, and water. Uranium is now used to power commercial nuclear reactors that produce electric...
What are the examples of radioactive waste?
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Any activity related to the nuclear fuel cycle that produces or...
What are radioactive elements made of?
Radioactive Elements. Everything around us is made of elements, or different types of atoms. While these atoms are way too small to see, if you break an object or organism down enough, ultimately everything is made of these tiny particles. And although your coffee table or text book might seem pretty stable, some elements break down over time, ...
How to tell if an element is an isotope or an element?
Elements can be distinguished from isotopes by their mass number, or the total number of neutrons and protons in an atom. If there are more or less, the isotope will have a different mass number than the original element. For example, normally carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, giving it a mass number of 12.
What happens to the alpha particles during radioactive decay?
However, since alpha particles are very big, they don't get too far and are easily blocked by our clothing. When an element undergoes alpha decay, it releases protons, which turn it into a different element entirely .
What happens when a neutron ejects an electron and becomes a proton?
Beta decay occurs when one neutron ejects an electron and becomes a proton. Alpha decay often creates unstable isotopes that undergo beta decay. Beta particles are a bit lighter than alpha particles, so they can go farther and penetrate materials deeper. However, clothing will still stop beta particles.
How many neutrons does carbon-14 have?
The isotope carbon-14 has two extra neutrons, making the isotope carbon-14. Some isotopes are unstable and release neutrons, protons, or energy as time goes on during radioactive decay. There are three main types: alpha, beta, and gamma decay, which we'll discuss next.
How do electrons determine the identity of an element?
Electrons float around the nucleus in a cloud-like structure. The number of protons in an atom determines the identity of the element. Each atom has a set number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, but sometimes there are more or less neutrons than usual, which makes the element an isotope.
Is radioactive matter everywhere?
Radioactive elements are everywhere. Here, we'll go over a few key examples related to energy production, archaeology, and medicine.
Where are radioactive elements produced?
These radioactive elements are produced in nuclear reactors and accelerators . There are different strategies used to form new elements. Sometimes elements are placed within a nuclear reactor, where the neutrons from the reaction react with the specimen to form desired products.
Which isotopes can decay to form secondary radionuclides?
For example, primordial isotopes thorium-232, uranium-238, and uranium-235 can decay to form secondary radionuclides of radium and polonium. Carbon-14 is an example of a cosmogenic isotope. This radioactive element is continually formed in the atmosphere due to cosmic radiation.
Where Do Radionuclides Come From?
Radioactive elements form naturally, as a result of nuclear fission, and via intentional synthesis in nuclear reactors or particle accelerators.
How do radionuclides affect organisms?
Radioactivity exists in nature, but radionuclides can cause radioactive contamination and radiation poisoning if they find their way into the environment or an organism is over-exposed. 1 The type of potential damage depends on the type and energy of the emitted radiation.
What is the name of the product produced by nuclear fission?
Nuclear fission from nuclear power plants and thermonuclear weapons produces radioactive isotopes called fission products. In addition, irradiation of surrounding structures and the nuclear fuel produces isotopes called activation products. A wide range of radioactive elements may result, which is part of why nuclear fallout and nuclear waste are so difficult to deal with.
What are some examples of radionuclides?
In other cases, particle accelerators bombard a target with energetic particles. An example of a radionuclide produced in an accelerator is fluorine-18. Sometimes a specific isotope is prepared in order to gather its decay product. For example, molybdenum-99 is used to produce technetium-99m.
Which element has no stable isotopes?
A good example of this is tritium, a radioactive isotope of hydrogen naturally present at extremely low levels. This table contains the elements that have no stable isotopes. Each element is followed by the most stable known isotope and its half-life . Note increasing atomic number doesn't necessarily make an atom more unstable.
Why is radioactivity a nuclear phenomenon?
Likewise, radioactivity is a nuclear phenomenon that happens (naturally) because of the nuclear instability of atoms. In 1896 Henri Becquerel first observed the phenomena of radioactivity, but the term ‘radioactivity’ was coined by Marie Curie.
When did Marie Curie discover radioactive elements?
Marie Curie discovered the radioactive elements namely Polonium and Radium in 1898.
What are beta particles?
Beta particles are the fast moving electrons emitted by some radio nuclides during the radioactive decay (also known as beta decay).
What is the process of emission of particles from nuclei because of the nuclear instability?
The process of emission of particles from nuclei because of the nuclear instability; is known as radioactivity. The substance that releases such energy/rays is known as radioactive substance. The invisible rays released from such radioactive substance are known as radioactive rays.
Why are alpha particles so weak?
Because of slow speed, Alpha particles have very weak penetrating powers; these particles are even stopped by a thin paper sheet (see image given above). Because of having the double positive charge, alpha particles are highly ionizing.
How many protons are in an alpha particle?
Alpha particles are usually composed of two protons and two neutrons, which are tightly bound together.
Which particles have the most energy?
Among all three particles (alpha, beta, and gamma), gamma particles are the most energetic photons.
What is radioactive material?
So, what is a radioactive chemical material? One of the nine chemicals material classification is chemical material that has an ability to emits radioactive rays with more than 0,002 microcurie/gram is called the radio active chemical material. A substance is marked radioactive using the trefoil symbol.
What is the name of the element that is involved in a nuclear reaction?
Nuclear reaction by a non-stable element emits radiation and the involved element is called radioactive .
What is the use of radioactive chemicals?
The use of radioactive chemicals, in general, divided into two, as a tracer and as a radiation source. 1. Tracer. Medical field: The general usage as a tracer in the medical field is to diagnose or detect disease. Maybe, some of you ever happened to be falling or injured then got an X-ray photo.
What are some examples of radioactive radiation?
Maybe, some of you ever happened to be falling or injured then got an X-ray photo. This thing is an example of radioactive usage. Because radiation of a radioactive can blacken a film. Other examples are: Technetium 99 (Tc-99): absorbs damaged tissue in the heart, liver, and lungs.
How long does radiation last?
Shorten lifespan: High dosage of radiation can be deadly. Dosage of 400 rem can cause death to half population that receives the radiation for 60 days. Causing genetic mutation: Radioactive rays can cause dissolution of important chemical bonds (DNA and chromosomes).
What is the atomic number of an element with a radioactive trait?
Elements with atomic number more than 83 naturally have a radioactive trait and known as radioactive isotope or radioisotope. Along with the advancement of science and technology, radioisotope can be made from stable isotope. Also read: Radioactive Isotopes Used in Medicine.
How does radioactive waste affect plants?
Environment impact. Radioactive waste that enters the environment and touch plants can cause genetic mutation or even death to plants. If this plant is consumed by human constantly, it can cause serious health problems. Moreover, plants that are contaminated remains along the food chain.
Where are radioactive isotopes found?
Radioactive isotopes of radium, thorium, and uranium, for example, are found naturally in rocks and soil. Uranium and thorium also occur in trace amounts in water. Radon, generated by the radioactive decay of radium, is present in air. Organic materials typically contain small amounts of radioactive carbon and potassium.
How many radioactive isotopes are there?
More than 1,000 radioactive isotopes of the various elements are known. Approximately 50 of these are found in nature; the rest are produced artificially as the direct products of nuclear reactions or indirectly as the radioactive descendants of these products. Radioactive isotopes have many useful applications.
How do radioactive isotopes dissipate energy?
A radioactive isotope, also known as a radioisotope, radionuclide, or radioactive nuclide, is any of several species of the same chemical elementwith different masses whose nuclei are unstable and dissipate excess energy by spontaneously emitting radiationin the form of alpha, beta, and gammarays. Every chemical element has one or more radioactive isotopes. For example, hydrogen, the lightest element, has three isotopes, which have mass numbers 1, 2, and 3. Only hydrogen-3 (tritium), however, is a radioactive isotope; the other two are stable. More than 1,800 radioactive isotopes of the various elements are known. Some of these are found in nature; the rest are produced artificially as the direct products of nuclear reactions or indirectly as the radioactive descendants of these products. Each “parent” radioactive isotope eventually decays into one or at most a few stable isotope “daughters” specific to that parent.
What is the radioactive isotope used in breath tests?
Another medically important radioactive isotope is carbon -14, which is used in a breath test to detect the ulcer -causing bacteria Heliobacter pylori. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now.
How many isotopes are there in the elements?
Only hydrogen-3 ( tritium ), however, is a radioactive isotope; the other two are stable. More than 1,800 radioactive isotopes of the various elements are known.
What are the elements that make up organic materials?
Organic materials typically contain small amounts of radioactive carbon and potassium. Cosmic radiation from the Sun and other stars is a source of background radiation on Earth. Other radioactive isotopes are produced by humans via nuclear reactions, which result in unstable combinations of neutrons and protons.
What is the name of the element that dissipates energy?
A radioactive isotope, also known as a radioisotope, radionuclide, or radioactive nuclide, is any of several species of the same chemical element with different masses whose nuclei are unstable and dissipate excess energy by spontaneously emitting radiation in the form of alpha, beta, and gamma rays. Every chemical element has one ...
Which element is the most radioactive?
Polonium . Because it is a naturally-occurring element that releases a huge amount of energy, many sources cite polonium as the most radioactive element. Polonium is so radioactive it glows blue, which is caused by excitation of the gas particles by radiation.
Why is relative radioactivity difficult?
It's somewhat complicated, trying to determine relative radioactivity because there can be many unstable steps in the decay process before an element finally breaks into stable pieces. All of the elements from element 84 on up are extremely radioactive. These elements have no stable isotopes .
Which element has the heaviest nucleus?
Element Number 118 . According to the Periodic Table of Radioactivity, at this time the most radioactive element known to man is element number 118, Oganesson. The decay rates for the latest man-made elements are so fast that it's hard to quantify how quickly they break apart, but element 118 has the heaviest known nucleus to date.
What is the half life of polonium?
The half-life for these elements is measured in mere minutes! Contrast this with the half-life of polonium, which is 138.39 days.

Introduction
- The process of emission of particles from nuclei because of the nuclear instability; is known as radioactivity.
- The substance that releases such energy/rays is known as radioactive substance.
- The invisible rays released from such radioactive substance are known as radioactive rays.
- Likewise, radioactivity is a nuclear phenomenon that happens (naturally) because of the nucl…
- The process of emission of particles from nuclei because of the nuclear instability; is known as radioactivity.
- The substance that releases such energy/rays is known as radioactive substance.
- The invisible rays released from such radioactive substance are known as radioactive rays.
- Likewise, radioactivity is a nuclear phenomenon that happens (naturally) because of the nuclear instability of atoms.
Radioactive Rays
- After long years of experiment, Ernest Rutherford along with his colleague (Hans Geiger and his student Ernest Marsden), discovered alpha rays, beta rays, and gamma rays.
Alpha (α) Particles
- Alpha particles are usually composed of two protons and two neutrons, which are tightly bound together.
- Alpha particles are being released during radioactive decay (or alpha decay) from the nucleus radio nuclides.
- The alpha particles are identical to the nucleus of either normal helium atom or doubly ionize…
- Alpha particles are usually composed of two protons and two neutrons, which are tightly bound together.
- Alpha particles are being released during radioactive decay (or alpha decay) from the nucleus radio nuclides.
- The alpha particles are identical to the nucleus of either normal helium atom or doubly ionized helium atom.
- In comparison to other particles (i.e. Gamma and Beta), alpha particles are heavy and slow. Therefore, alpha particles have very small range in the air.
Beta (β) Particles
- Beta particles are the fast moving electrons emitted by some radio nuclides during the radioactive decay (also known as beta decay).
- Beta particles are of much lighter weight and carry a single negative charge.
- Beta particles are rarely ionizing than the alpha particles.
- Because of having lighter weight, beta particles can travel much farther than alpha particles; …
- Beta particles are the fast moving electrons emitted by some radio nuclides during the radioactive decay (also known as beta decay).
- Beta particles are of much lighter weight and carry a single negative charge.
- Beta particles are rarely ionizing than the alpha particles.
- Because of having lighter weight, beta particles can travel much farther than alpha particles; however, beta particles can be stopped by several sheet of papers or one sheet of aluminum.
Gamma (Ү) Particles
- Gamma particles are the bundle of high energy namely electromagnetic energy (photon) emitted by the radioactive elements during the radioactive decay.
- Among all three particles (alpha, beta, and gamma), gamma particles are the most energetic photons.
- Gamma particles, which are the form of electromagnetic radiation(EMR), originate from the n…
- Gamma particles are the bundle of high energy namely electromagnetic energy (photon) emitted by the radioactive elements during the radioactive decay.
- Among all three particles (alpha, beta, and gamma), gamma particles are the most energetic photons.
- Gamma particles, which are the form of electromagnetic radiation(EMR), originate from the nucleus.
- The wavelengths of gamma are the shortest among all three.