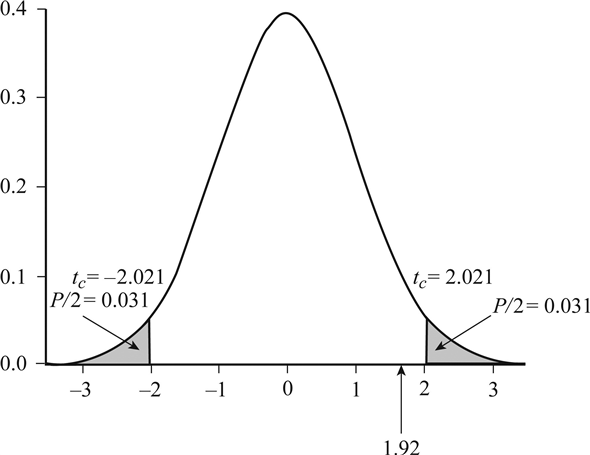
What is the rank condition in physics?
The rank condition investigates whether two or more equations are linearly dependent on each other, which would be the case if the sum of two equations would equal a third equation in the model. If that is the case it is impossible to identify all structural parameters. The basic steps in this decision rule is best described by an example.
What is the rank condition in structural analysis?
The rank condition investigates whether two or more equations are linearly dependent on each other, which would be the case if the sum of two equations would equal a third equation in the model. If that is the case it is impossible to identify all structural parameters.
Is the rank condition a sufficient or necessary condition?
The rank condition is a necessary and sufficient condition, which means that if we can identify the equations using the rank condition we can be sure that the equation really is identified.
How do you check the rank condition of an equation?
The first step in checking the rank condition is to put up a matrix that for each equation mark which of the six variables that are included (marked with 1) and which that are excluded (marked with 0) from the equation. For our system we receive the following matrix:
What is rank condition?
How many variables are in a rank condition?
When using larger systems, it is quite possible that the order condition says that a particular equation is identified even though the?
What is the order condition of identification?
What does K mean in math?
See 2 more
What is rank condition of identification?
THE RANK CONDITION FOR IDENTIFICATION In a system of G equations any particular equation is identified iff it is possible to construct at least one non-zero determinant of the order.
What is the order condition in econometrics?
More specifically, the order condition, a necessary condition for identification, is that for each equation ki + ni ≤ k, which can be phrased as “the number of excluded exogenous variables is greater or equal to the number of included endogenous variables”.
How do you know if an equation is identified?
0:294:48Identification Problem in Econometrics - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipProblem we show whether the structural coefficients can be obtained from the reduced formMoreProblem we show whether the structural coefficients can be obtained from the reduced form coefficients. If they are obtainable. We say that the particular equation is identified if not we say it is
What is simultaneous equation bias in econometrics?
Simultaneity bias is a term for the unexpected results that happen when the explanatory variable is correlated with the regression error term, ε (sometimes called the residual disturbance term), because of simultaneity.
What is the meaning of order condition?
Order of Conditions means an order directing a defendant to comply with this prescribed treatment plan, or any other condition which the court determines to be reasonably necessary or appropriate, and, in addition, where a defendant is in custody of the commissioner, not to leave the facility without authorization.
What is spurious regression in econometrics?
Spurious regression refers to the regression that tends to accept a false relation or reject a true relation by flawed regression schemes. It is well known that there are two types of errors that may occur in statistical inference.
What are dummy variables in econometrics?
Dummy variables (also known as binary, indicator, dichotomous, discrete, or categorical variables) are a way of incorporating qualitative information into regression analysis. Qualitative data, unlike continuous data, tell us simply whether the individual observation belongs to a particular category.
What is identification in regression?
The problem of identification exists any time one or more endogenous variables appear on the RHS of a regression equation. This situation implies an existence of a (specified or unspecified) simultaneous equation model.
What is a parameter in economic model?
The constants B0 and B1 are called coefficients or parameters of the model. They measure the position and slope of the line representing the expenditure function. The linear functional form has the property that a change in Y of a given amount always causes the same change in E.
What is endogeneity problem in econometrics?
In econometrics the problem of endogeneity occurs when the independent variable is correlated with the error term in a regression model. Endogeneity can arise as a result of measurement error, autoregression with autocorrelated errors, simultaneity and omitted variables.
What is endogeneity in regression?
Endogeneity refers to situations in which a predictor (e.g., treatment variable) in a linear regression model is correlated to the error term. You call such predictor an endogenous variable.
What are the sources of endogeneity?
In summary, each of the three sources of endogeneity bias (i.e., measurement error, omitted variables, and simultaneity) leads to questionable causal inferences.
What are instrumental variables in econometrics?
An instrumental variable (sometimes called an “instrument” variable) is a third variable, Z, used in regression analysis when you have endogenous variables—variables that are influenced by other variables in the model. In other words, you use it to account for unexpected behavior between variables.
What is meant by indirect least square method?
The indirect least squares (ILS) approach is broadly regarded as a procedure of deriving the structural parameters of a simultaneous equation system indirectly from the estimates of reduced-form parameters.
Order & Rank Conditions of Identification - Blogger
M = number of endogenous variables in the model K = number of exogenous variables in the model m = number of endogenous variable in an equation k = number of exogenous variables in a given equation Rank condition is defined by the rank of the matrix, which should have a dimension (M-1), where m is the number of endogenous variables.This matrix is formed from the coefficients of the variables ...
CHAPTER 6. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS - University of California, Berkeley
2 0 20 40 60 80 100 Wage 0 20 40 60 80 100 Quantity Fig. 1. Demand & Supply of Economists D' D" S' S" will not in general lie along either the demand curve or the supply curve.
simultaneous models FINAL
Munich Personal RePEc Archive Programming identification criteria in simultaneous equation models Halkos, George and Tsilika, Kyriaki University of Thessaly, Department of Economics
What does "identification" mean in econometrics, and it is relevant ...
A parameter is identifiable when it can be determined uniquely with the available data. The problem is very well known in the context of simultaneous equations but it is not exclusive to that case.
Chapter 17 Simultaneous Equations Models - IIT Kanpur
Econometrics | Chapter 17 | Simultaneous Equations Models | Shalabh, IIT Kanpur 6 Note that ˆˆ 11 21and are the numerical values of the estimates.So now there are two equations and four unknown parameters 121 2,, and .So it is not possible to derive the unique estimates of parameters of
What is rank condition?
The rank condition is a necessary and sufficient condition, which means that if we can identify the equations using the rank condition we can be sure that the equation really is identified. The rank condition investigates whether two or more equations are linearly dependent on each other, which would be the case if the sum of two equations would equal a third equation in the model. If that is the case it is impossible to identify all structural parameters. The basic steps in this decision rule is best described by an example.
How many variables are in a rank condition?
This system contains three endogenous variables (Y1, Y2, Y3) and three exogenous variables (X1, X2, X3), which means that we in total has six variables. The first step in checking the rank condition is to put up a matrix that for each equation mark which of the six variables that are included (marked with 1) and which that are excluded (marked with 0) from the equation. For our system we receive the following matrix:
When using larger systems, it is quite possible that the order condition says that a particular equation is identified even though the?
When using larger systems it is quite possible that the order condition says that a particular equation is identified even though the rank condition says it is not. When that happens it might still be possible to generate estimates, but those estimates will not have any economic meaning since they will represent averages of those equations that are linear combinations of each other. Hence, you should not be content that you have received identified results just because the order condition says so and the econometric software generates results for you. When using systems of more than two equations you should also confirm the identification using the rank condition.
What is the order condition of identification?
The order condition of identification. The first decision rule for identification is the so called order condition . This rule specifies the necessary conditions for identification and is the more popular one of the two rules that will be discussed. Unfortunately it is not a sufficient rule, which means that it is possible ...
What does K mean in math?
K = The number of variables (endogenous and exogenous) in the model excluded from the equation under consideration.
What is rank condition?from ebrary.net
The rank condition is a necessary and sufficient condition, which means that if we can identify the equations using the rank condition we can be sure that the equation really is identified. The rank condition investigates whether two or more equations are linearly dependent on each other, which would be the case if the sum of two equations would equal a third equation in the model. If that is the case it is impossible to identify all structural parameters. The basic steps in this decision rule is best described by an example.
When using larger systems, it is quite possible that the order condition says that a particular equation is identified even though the?from ebrary.net
When using larger systems it is quite possible that the order condition says that a particular equation is identified even though the rank condition says it is not. When that happens it might still be possible to generate estimates, but those estimates will not have any economic meaning since they will represent averages of those equations that are linear combinations of each other. Hence, you should not be content that you have received identified results just because the order condition says so and the econometric software generates results for you. When using systems of more than two equations you should also confirm the identification using the rank condition.
What is the order condition of identification?from ebrary.net
The order condition of identification. The first decision rule for identification is the so called order condition . This rule specifies the necessary conditions for identification and is the more popular one of the two rules that will be discussed. Unfortunately it is not a sufficient rule, which means that it is possible ...
What does K mean in math?from ebrary.net
K = The number of variables (endogenous and exogenous) in the model excluded from the equation under consideration.
Description
is.positive.definite tests whether all eigenvalues of a symmetric matrix are positive.
Arguments
tolerance for singular values and for absolute eigenvalues - only those with values larger than tol are considered non-zero (default: tol = max (dim (m))*max (D)*.Machine$double.eps)
What should the expected value of the mean of the error terms of OLS regression be?
The expected value of the mean of the error terms of OLS regression should be zero given the values of independent variables.
Why is regression likely to suffer from autocorrelation?
yearly data of unemployment), then the regression is likely to suffer from autocorrelation because unemployment next year will certainly be dependent on unemployment this year. Hence, error terms in different observations will surely be correlated with each other.
Why is it important to know the underlying assumptions of OLS regression?
This is because a lack of knowledge of OLS assumptions would result in its misuse and give incorrect results for the econometrics test completed.
What happens if the variance is not constant?
If this variance is not constant (i.e. dependent on X’s), then the linear regression model has heteroscedastic errors and likely to give incorrect estimates.
How to check for multicollinearity?
Assumption of No Multicollinearity (OLS assumption 4) – You can check for multicollinearity by making a correlation matrix (though there are other complex ways of checking them like Variance Inflation Factor, etc.). Almost a sure indication of the presence of multi-collinearity is when you get opposite (unexpected) signs for your regression coefficients (e. if you expect that the independent variable positively impacts your dependent variable but you get a negative sign of the coefficient from the regression model). It is highly likely that the regression suffers from multi-collinearity. If the variable is not that important intuitively, then dropping that variable or any of the correlated variables can fix the problem.
Is OLS required for linear regression?
If a number of parameters to be estimated (unknowns) are more than the number of observations, then estimation is not possible. If a number of parameters to be estimated (unknowns) equal the number of observations, then OLS is not required. You can simply use algebra.
Is OLS required for an estimate?
This makes sense mathematically too. If a number of parameters to be estimated (unknowns) are more than the number of observations, then estimation is not possible. If a number of parameters to be estimated (unknowns) equal the number of observations, then OLS is not required. You can simply use algebra.
What is rank condition?
The rank condition is a necessary and sufficient condition, which means that if we can identify the equations using the rank condition we can be sure that the equation really is identified. The rank condition investigates whether two or more equations are linearly dependent on each other, which would be the case if the sum of two equations would equal a third equation in the model. If that is the case it is impossible to identify all structural parameters. The basic steps in this decision rule is best described by an example.
How many variables are in a rank condition?
This system contains three endogenous variables (Y1, Y2, Y3) and three exogenous variables (X1, X2, X3), which means that we in total has six variables. The first step in checking the rank condition is to put up a matrix that for each equation mark which of the six variables that are included (marked with 1) and which that are excluded (marked with 0) from the equation. For our system we receive the following matrix:
When using larger systems, it is quite possible that the order condition says that a particular equation is identified even though the?
When using larger systems it is quite possible that the order condition says that a particular equation is identified even though the rank condition says it is not. When that happens it might still be possible to generate estimates, but those estimates will not have any economic meaning since they will represent averages of those equations that are linear combinations of each other. Hence, you should not be content that you have received identified results just because the order condition says so and the econometric software generates results for you. When using systems of more than two equations you should also confirm the identification using the rank condition.
What is the order condition of identification?
The order condition of identification. The first decision rule for identification is the so called order condition . This rule specifies the necessary conditions for identification and is the more popular one of the two rules that will be discussed. Unfortunately it is not a sufficient rule, which means that it is possible ...
What does K mean in math?
K = The number of variables (endogenous and exogenous) in the model excluded from the equation under consideration.
