What are the advantages of raster data?
Rasters as basemaps. A common use of raster data in a GIS is as a background display for other feature layers. For example, orthophotographs displayed underneath other layers provide the map user with confidence that map layers are spatially aligned and represent real objects, as well as additional information.
How to get started using GIS mapping software?
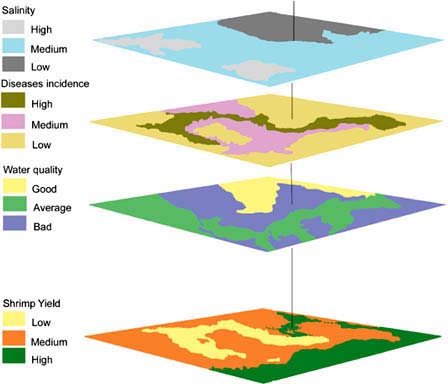
Raster data in detail¶ Raster data is used in a GIS application when we want to display information that is continuous across an area and cannot easily be divided into vector features. When we introduced you to vector data we showed you the image in figure_landscape. Point, polyline and polygon features work well for representing some features on this landscape, such …
What are the sources of GIS data?
Mar 21, 2020 · What is raster data model in GIS? raster data model : [ data models ] A representation of the world as a surface divided into a regular grid of cells. Raster models are useful for storing data that varies continuously, as in an aerial photograph, a satellite image, a surface of chemical concentrations, or an elevation surface.
What are some uses for GIS?
Continuous and thematic rasters may be displayed as data layers along with other geographic data on your map but are often used as the source data for spatial analysis with the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst or ArcGIS Image Analyst extension. Picture rasters are often used as attributes in tables—they can be displayed with your geographic data and are used to convey additional …
What is raster data in GIS?
Raster data is any pixelated (or gridded) data where each pixel is associated with a specific geographical location. The value of a pixel can be continuous (e.g. elevation) or categorical (e.g. land use). If this sounds familiar, it is because this data structure is very common: it's how we represent any digital image.
What is raster and vector data model?
DEFINITIONS: • RASTER DATA MODEL. A spatial data model that uses a grid and cells to represent the spatial variation of a feature. • VECTOR DATA MODEL. A data model that uses points and their x-, y- coordinates to construct spatial features.
What is GIS explain raster and vector data model in GIS?
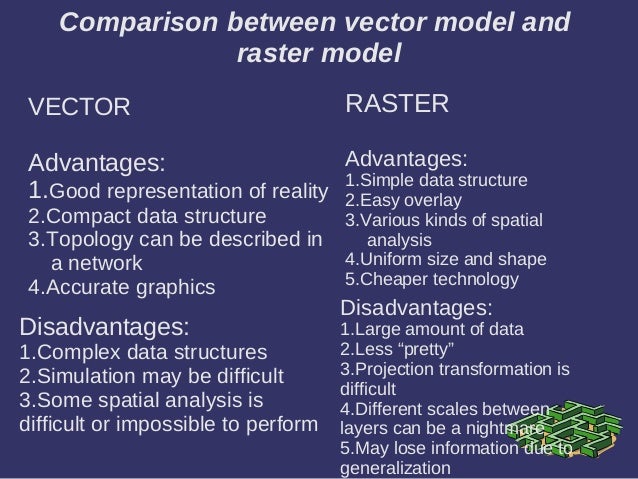
When we come to depict any spatial data in GIS, from physical assets and locations to real-world events and trends, there are two differing systems to display data; Raster and Vector representations. Both of these methods present data in their own format, with their own advantages and disadvantages.
What are the types of raster GIS model?
There are three types of raster data that can be stored in a geodatabase: raster datasets, raster catalogs, and raster as attributes. Raster datasets are single images that are stored in the database.
What is a raster model?
Raster data models present information through a grid of cells. Raster grids are usually made up of square or rectangular cells. Unlike vector data models, which show geographic data through points, lines, or polygons, raster data is displays one value in each cell.Aug 22, 2017
What is spatial data model?
Spatial Data Model: An abstraction of the real world which incorporates only those properties thought to be relevant to the application at hand, define specific groups of entities, and their attributes and the relationships between these entities. • A data model is independent of a computer system.Sep 24, 2019
What is spatial data example?
A common example of spatial data can be seen in a road map. A road map is a two-dimensional object that contains points, lines, and polygons that can represent cities, roads, and political boundaries such as states or provinces. A road map is a visualization of geographic information.
What are the examples of raster data in GIS?
There are two types of raster data: continuous and discrete. An example of discrete raster data is population density. Continuous data examples are temperature and elevation measurements. There are also three types of raster datasets: thematic data, spectral data, and pictures (imagery).May 1, 2021
What are the elements of raster data model?
There are three elements in a raster data model. Point, Line and Area.Sep 28, 2012
Why is raster data useful in GIS?
For example, measuring infra-red light can be useful in identifying water bodies. Because having images containing multiple bands of light is so useful in GIS, raster data are often provided as multi-band images.
How to get raster data?
Raster data can be obtained in a number of ways. Two of the most common ways are aerial photography and satellite imagery. In aerial photography , an aeroplane flies over an area with a camera mounted underneath it. The photographs are then imported into a computer and georeferenced.
How many numbers are needed to store a raster?
To store all the information contained in the raster, you will need to store 9 numbers in the computer’s memory. Now imagine you want to have a raster layer for the whole of South Africa with pixels of 1 km x 1 km. South Africa is around 1,219,090 km 2 .
What is georeferencing in GIS?
Georeferencing is the process of defining exactly where on the earth’s surface an image or raster dataset was created . This positional information is stored with the digital version of the aerial photo. When the GIS application opens the photo, it uses the positional information to ensure that the photo appears in the correct place on the map. Normally this positional information consists of a coordinate for the top left pixel in the image, the size of each pixel in the X direction, the size of each pixel in the Y direction, and the amount (if any) by which the image is rotated. With these few pieces of information, the GIS application can ensure that raster data are displayed in the correct place. The georeferencing information for a raster is often provided in a small text file accompanying the raster.
Why are rasters important?
satellite images and aerial photographs), they are also good for representing more abstract ideas. For example, rasters can be used to show rainfall trends over an area, or to depict the fire risk on a landscape.
What is a raster made of?
Rasters are made up of a matrix of pixels (also called cells), each containing a value that represents the conditions for the area covered by that cell (see figure_raster ). In this topic we are going to take a closer look at raster data, when it is useful and when it makes more sense to use vector data.
Why do people use raster data?
Many people use raster data as a backdrop to be used behind vector layers in order to provide more meaning to the vector information. The human eye is very good at interpreting images and so using an image behind vector layers, results in maps with a lot more meaning.
What is a raster model?
The model most commonly takes the form of a grid-like structure that holds values at regularly spaced intervals over the extent of the raster. Rasters are especially well suited for storing continuous data such as temperature and elevation values, but can hold discrete and categorical data such as land use as well.
How do rasters work?
Rasters record one or more values at each grid point. Grid values may be very simply recorded row-by-row staring at the upper left corner in the same manner that text is written in English. Alternative ordering systems may be used to improve efficiency, including row prime, Morton, or Peano-Hilbert methods. Memory demands for rasters are influenced by the type of data recorded (e.g., Boolean, integer, float, or string), the resolution and spatial extent of the raster, and any compression applied to the image. Compression can be used to exploit repetition or redundancy in the data to reduce overall storage demands, and many schemes are available accomplish this, including chain codes, block codes, run length codes and quadtrees.
How does doubling the resolution of a raster affect the linear distance of a cell?
The number of cells in a raster increases quadratically as resolution increases; a doubling of the resolution of a raster reduces the linear distance of a cell by one-half (e.g., moving from a 2 m cell to a 1 m cell), but increases the number of cells by a factor of four (doubling the number of cells in two directions).
What is raster grid?
Raster grids are usually made up of square or rectangular cells. Unlike vector data models, which show geographic data through points, lines, or polygons, raster data is displays one value in each cell. This value can be interpreted to mean several different things. Changing the cell size of Raster data can make the projected image more ...
Why can't cartographers use raster data?
Limitations of Raster Data. Most of the output maps for raster data could not be used by cartographers because of it's inaccuracy. The image of a non-contiguous maps will not be as accurate as vector data map would be due to the distortion created by the different cell sizes.
How to store raster data?
In most raster data structures, the array is stored as an ordered list of values, either going across the cells in a row then going to the beginning of the next row ( row-major) or going down the cells in a column then going to the beginning of the next column ( column-major ). A header is included at the beginning of the file, providing at least the basic metadata necessary to arrange the list as a two-dimensional grid in the proper spatial location: 1 the x,y coordinate of the sample in the first row and column (usually either the Northwest or Southwest corner) 2 the dimensions or spacing of each cell, known as the cell size or resolution. Traditionally, the cell size has been required to be the same in the x and y directions (i.e., the cells are square), but some modern structures allow this to vary. 3 the number of rows and columns. Technically, only one of these is required to know how to arrange the list as an array (depending on whether it is row-major or column-major), but both are usually included. 4 the data type of each value (e.g., short integer, long integer, double-precision floating point, ASCII character), specifically the number of bytes needed for each value.