What does RCBD mean in research?
Definition. Randomized complete Block design, commonly referred to as RCBD, is an experimental design in which the subjects are divided into blocks or homogeneous unit. Eeach block/unit contains a complete set of treatments which are assigned randomly to the units.
What is randomized complete block design (RCBD)?
A Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) is defined by an experiment whose treatment combinations are assigned randomly to the experimental units within a block. Generally, blocks cannot be randomized as the blocks represent factors with restrictions in randomizations such as location, place, time, gender, ethnicity, breeds, etc.
What are the main assumptions of RCBD?
The main assumption of the RCBD is that there is no interaction between the treatments and the block effects hence controlling variation. RCBD is often preferred over all other designs because it governs the effects of the treatments on the response variables.
Is RCBD with replication available on real statistics website?
I haven’t included RCBD with replication on the Real Statistics website yet. I plan to add this capability in one of the next releases. First try to collect data from more number of plants. then, yes average it out so you get 15 data points. if i have disc plough, disc harrow, mouldboard plough, use for five treatment, what will the block design be
What is RCBD in a randomized design?
What is RCBD design?
What is the effect model for RCBD?
What is CRD and Rcbd?
CRD - each experimental unit is randomly assigned. RCBD - each replicate is grouped into a block and treatments are randomized within eachreplicate.
What is Rcbd ANOVA?
21.4 RCBD. The Randomized Complete Block Design is also known as the two-way ANOVA without interaction. A key assumption in the analysis is that the effect of each level of the treatment factor is the same for each level of the blocking factor.
What is Rcbd model?
RCBD is a mixed model in which a factor is fixed and other is random. The main assumption of the design is that there is no contact between the treatment and block effect. Randomized Complete Block design is said to be complete design because in this design the experimental units and number of treatments are equal.
What is randomized design in statistics?
A completely randomized design (CRD) is one where the treatments are assigned completely at random so that each experimental unit has the same chance of receiving any one treatment. For the CRD, any difference among experimental units receiving the same treatment is considered as experimental error.
Why is Rcbd used?
The RCBD is the standard design for agricultural experiments where similar experimental units are grouped into blocks or replicates. It is used to control variation in an experiment by accounting for spatial effects in field or greenhouse.
Why do we use randomized block design?
This kind of design is used to minimize the effects of systematic error. If the experimenter focuses exclusively on the differences between treatments, the effects due to variations between the different blocks should be eliminated.
Is Rcbd one way ANOVA?
RCBD is a kind of two-way ANOVA, surely.
How is RBD calculated?
Generally each treatment is used exactly once within each block, in conclusion: if we have k treatments and b block, then the total sample size is n = b · k.
Is RBD and Rcbd same?
A RBD can occur in a number of situations: A randomized block design with each treatment replicated once in each block (balanced and complete). This is a randomized complete block design (RCBD). A randomized block design with each treatment replicated once in a block but with one block/treatment combination missing.
What is the difference between random sampling and randomization?
Random selection, or random sampling, is a way of selecting members of a population for your study's sample. In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample into control and experimental groups.
What are the types of randomization?
It is very important to select a method that will produce interpretable, valid results for your study.Simple Randomization. Randomization based on a single sequence of random assignments is known as simple randomization. ... Block Randomization. ... Stratified Randomization. ... Covariate Adaptive Randomization.
What are the 3 principles of experimental design?
There are three basic principles behind any experimental design:Randomisation: the random allocation of treatments to the experimental units. ... Replication: the repetition of a treatment within an experiment allows: ... Reduce noise: by controlling as much as possible the conditions in the experiment.
Is Rcbd one way Anova?
RCBD is a kind of two-way ANOVA, surely.
How is RBD calculated?
Generally each treatment is used exactly once within each block, in conclusion: if we have k treatments and b block, then the total sample size is n = b · k.
What is nested ANOVA?
A nested ANOVA (also called a hierarchical ANOVA) is an extension of a simple ANOVA for experiments where each group is divided into two or more random subgroups. It tests to see if there is variation between groups, or within nested subgroups of the attribute variable.
What is RBD in agriculture?
Randomized Block Design. Ø It is also called RBD. Ø RBD is the most commonly used experimental design in agriculture. Ø Here the 'local-control' is adopted and the experimental material is grouped into homogenous subgroups. Ø Each such sub-group is called blocks.
The Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) - PBGworks
• The objective of this tutorial is to give a brief introduction to the design of a randomized complete block design (RCBD) and the basics of how to analyze the RCBD using SAS.
Chapter 6 Randomized Block Design Two Factor ANOVA Interaction in ANOVA
Example Fire extinguishers tested to see how quickly they put out fires. Factor A: 3 different chemicals in the extinguishers A1, A2, A3 Factor B: 2 types of fires, B1= wood, B2= gas Ykj=time to put out the fire of type Bjwith chemical Ak Questions of interest:
5.3.3.2. Randomized block designs - NIST
with L 1 = number of levels (settings) of factor 1 L 2 = number of levels (settings) of factor 2 L 3 = number of levels (settings) of factor 3 L 4 = number of levels (settings) of factor 4 L k = number of levels (settings) of factor k. Example of a Randomized Block Design: Example of a randomized block design: Suppose engineers at a semiconductor manufacturing facility want to test whether ...
5.3.3.1. Completely randomized designs - NIST
These designs are for studying the effects of one primary factor without the need to take other nuisance factors into account: Here we consider completely randomized designs that have one primary factor.
Lecture.15 Completely randomized design – description – layout ...
1 Lecture.15 Completely randomized design – description – layout – analysis – advantages and disadvantages Completely Randomized Design (CRD)
What is blocking in CRD?
Blocking is a technique for dealing with nuisance factors, i.e. a variable which is not of interest, except that it has some influence on the variables that are of interest. For the design described in CRD & RCDB, the Farm is such a nuisance factor since each farm potentially has different levels of moisture, fertility, etc.
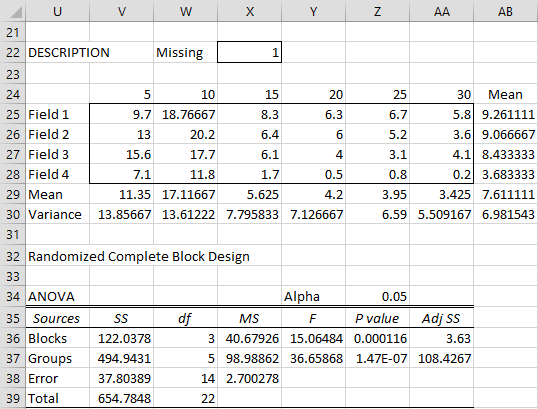
Can a randomized complete block design be implemented using two factor ANOVA without replication?
We use a randomized complete block design, which can be implemented using Two Factor ANOVA without Replication. A key assumption for this test is that there is no interaction effect. We test this assumption by creating the chart of the yields by field as shown in Figure 2.
Introduction
The randomized complete block design (RCBD) is a standard design for agricultural experiments in which similar experimental units are grouped into blocks or replicates. It is used to control variation in an experiment by, for example, accounting for spatial effects in field or greenhouse.
Additional Resources
Clewer, A. G., and D. H. Scarisbrick. 2001. Practical statistics and experimental design for plant and crop science. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., New York.
Funding Statement
Development of this lesson was supported in part by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) Solanaceae Coordinated Agricultural Project, agreement 2009-85606-05673, administered by Michigan State University.
What is RCBD in soil science?
An RCBD is used to make sure treatments are compared under similar circumstances. For example, imagine the natural fertility of a field varies from one end to the other. If you are conducting a field experiment to compare different types of fertilizer, then clearly the natural fertility could affect your conclusions. For example, if you used a completely randomize design, then there is some chance that one fertilizer treatment may end up with more replicates on the more fertile part of the field. As a result, you might conclude that this fertilizer treatment was better than the others. In such a situation, it is said that the effects of the fertilizer was “confounded” with the natural fertility of the land (i.e., the natural soil fertility is interfering with the conclusions about the fertilizer effects).
Why is fertilizer rate a continuous variable?
The rate of fertilizer is referred to as a continuous variable because there are many possible rates in addition to the ones the researcher selected to use in the experiment. If you use an ANOVA, you will be able to determine if one or more treatments is different than the others, but you will not be able to look at the full spectrum of possible fertilizer rates. What if 130 kg N ha-1 actually produces the highest yields?
What is RCBD in biology?
Randomized complete Block design , commonly referred to as RCBD, is an experimental design in which the subjects are divided into blocks or homogeneous unit. Eeach block/unit contains a complete set of treatments which are assigned randomly to the units. The design is said to complete mainly because experimental units and the number of treatments are equal. The main assumption of the RCBD is that there is no interaction between the treatments and the block effects hence controlling variation. RCBD is often preferred over all other designs because it governs the effects of the treatments on the response variables.
Why is RCBD design considered complete?
The design is said to complete mainly because experimental units and the number of treatments are equal. The main assumption of the RCBD is that there is no interaction between the treatments and the block effects hence controlling variation. RCBD is often preferred over all other designs because it governs the effects of the treatments on ...
Is Statisticsguruonline available 24/7?
For any with your statistics homework help contact us. Statisticsguruonline has a team of professional statisticians who are ready to help you with your homework. Our support team is available 24/7 to answer to your queries.
What is RCBD in a randomized design?
In the completely randomized design (CRD), the experiments can only control the random unknown and uncontrolled factors (also known as lucking nuisance factors). However, the RCBD is used to control/handle some systematic and known sources ( nuisance factors) of variations if they exist.
What is RCBD design?
Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) is arguably the most common design of experiments in many disciplines, including agriculture, engineering, medical, etc. In addition to the experimental error reducing ability, the design widens the generalization of the study findings. For example, if the study contains the place as a blocking factor, the results could be generalized for the places. A fertilizer producer can only claim that it is effective regardless of the climate conditions when it is tested in various climate conditions.
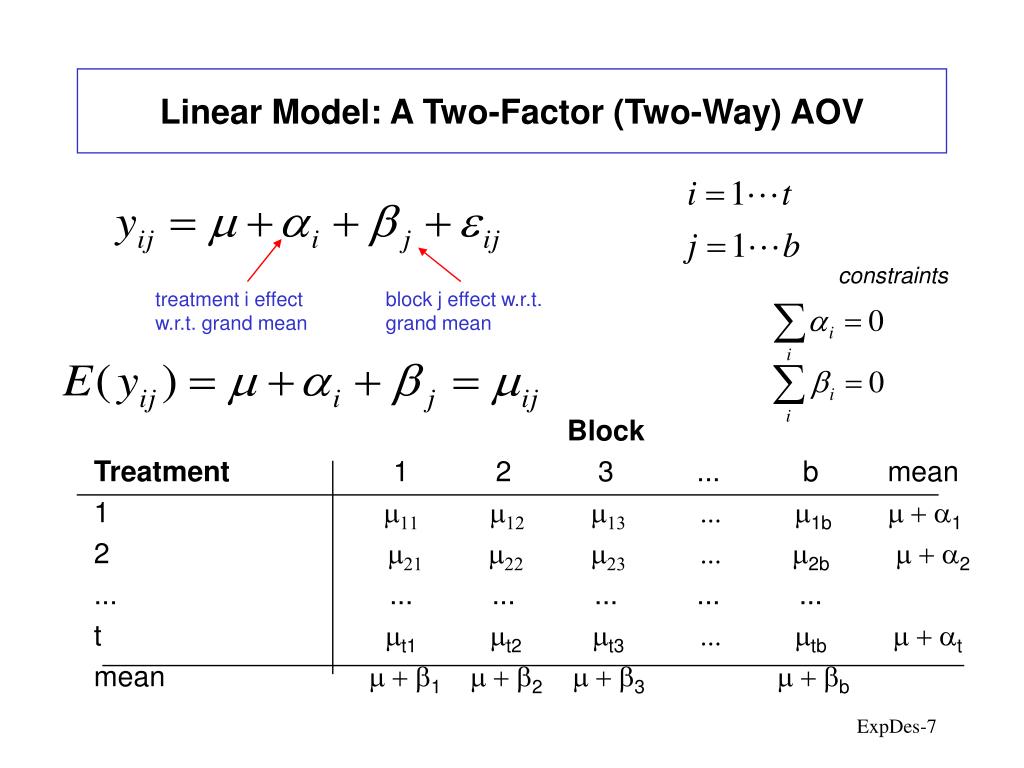
What is the effect model for RCBD?
The effects model for the RCBD is provided in Equation 1. Equation 1. The primary interest is the treatment effect in any RCBD, therefore the hypothesis for the design is statistically written as.