Why is sodium reabsorption so important in the kidney?
Feb 16, 2020 · In renal physiology, reabsorption or tubular reabsorption is the process by which the nephron removes water and solutes from the tubular fluid (pre-urine) and returns them to the circulating blood. Substances are reabsorbed from the tubule into the peritubular capillaries.
What does reabsorption mean in kidney?
Mar 08, 2020 · In renal physiology, reabsorption or tubular reabsorption is the process by which the nephron removes water and solutes from the tubular fluid (pre-urine) and returns them to the circulating blood. The kidneys sense low blood pressure. Release renin into the blood.
What happens in the nephron During secretion or reabsorption?
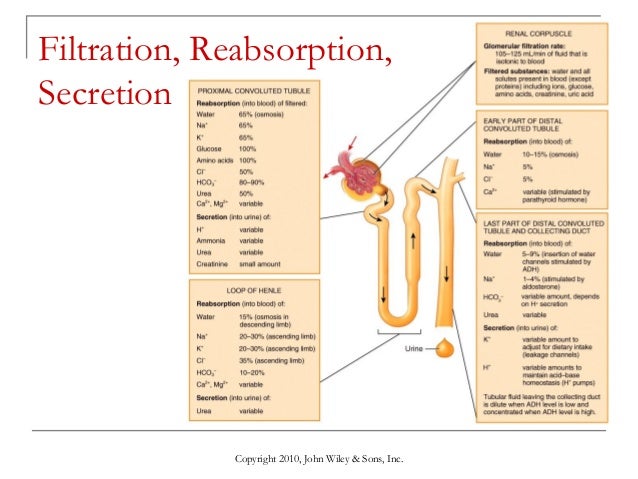
Kidney Reabsorption. Once inside the lumen of the nephron, small molecules, such as ions, glucose and amino acids, get reabsorbed from the filtrate: Specialized proteins called transporters are located on the membranes of the various cells of the nephron. These transporters grab the small molecules from the filtrate as it flows by them.
What happens in tubular reabsorption?
Apr 17, 2022 · At least seven different aquaporin isoforms are expressed in the kidney. What is reabsorption in urine formation class 11? Tubular reabsorption: the necessary substances such as water, glucose, amino acids, vitamins, mineral ions in the filtrate are reabsorbed by the tubules of the nephrons. The loop of Henle regulates the water reabsorption.

What is and what is not reabsorbed in the kidney?
Sodium is actively pumped out, while potassium and chloride diffuse down their electrochemical gradients through channels in the tubule wall and into the bloodstream. The walls of the thick ascending limb are impermeable to water, so in this section of the nephron water is not reabsorbed along with sodium.
What are the two substances that is reabsorbed by the kidney?
Answer: Two substances which are selectively reabsorbed from the tubules of a nephron are Amino acids and Glucose.May 11, 2018
What are 3 different ions reabsorbed by the kidney?
At least three ions, K+, Ca++, and Mg++, diffuse laterally between adjacent cell membranes (transcellular). About 67 percent of the water, Na+, and K+ entering the nephron is reabsorbed in the PCT and returned to the circulation.
What happens in the PCT?
The PCT is responsible for reabsorbing 50–60% of the glomerular ultrafiltrate. Thus, it is a site for high volume reabsorption, but not for regulation of the final composition of the urine. The latter task is the responsibility of the collecting duct. The PCT reabsorbs solute isosmotically.
Where does reabsorption occurs in the kidney name the substances reabsorbed?
The proximal convoluted tubule is where a majority of reabsorption occurs. About 67 percent of the water, Na+, and K+ entering the nephron is reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule and returned to the circulation.
Which one is reabsorbed actively in the nephron?
sodiumHence, the Proximal convoluted tubule actively reabsorbs sodium.
What is renal tubular reabsorption?
In renal physiology, reabsorption or tubular reabsorption is the process by which the nephron removes water and solutes from the tubular fluid (pre-urine) and returns them to the circulating blood.
Why is reabsorption in the kidneys important?
This is essential for the kidneys to rapidly remove waste and toxins from the plasma efficiently. Reabsorption is the movement of water and solutes from the tubule back into the plasma. Reabsorption of water and specific solutes occurs to varying degrees over the entire length of the renal tubule.
What are the factors that affect reabsorption?
Two major factors affect the reabsorption process: 1 Concentration of small molecules in the filtrate - the higher the concentration, the more molecules can be reabsorbed. Like our children in the fish pond game, if you increase the number of fish in the stream, the children will have an easier time catching them. In the kidney, this is true only to a certain extent because: There is only a fixed number of transporters for a given molecule present in the nephron. There is a limit to how many molecules the transporters can grab in a given period of time. 2 Rate of flow of the filtrate - flow rate affects the time available for the transporters to reabsorb molecules. As with our fish pond, if the stream moves by slowly, the children will have more time to catch fish than if the stream were moving faster.
Where are the transporters located?
Specialized proteins called transporters are located on the membranes of the various cells of the nephron. These transporters grab the small molecules from the filtrate as it flows by them. Each transporter grabs only one or two types of molecules.
