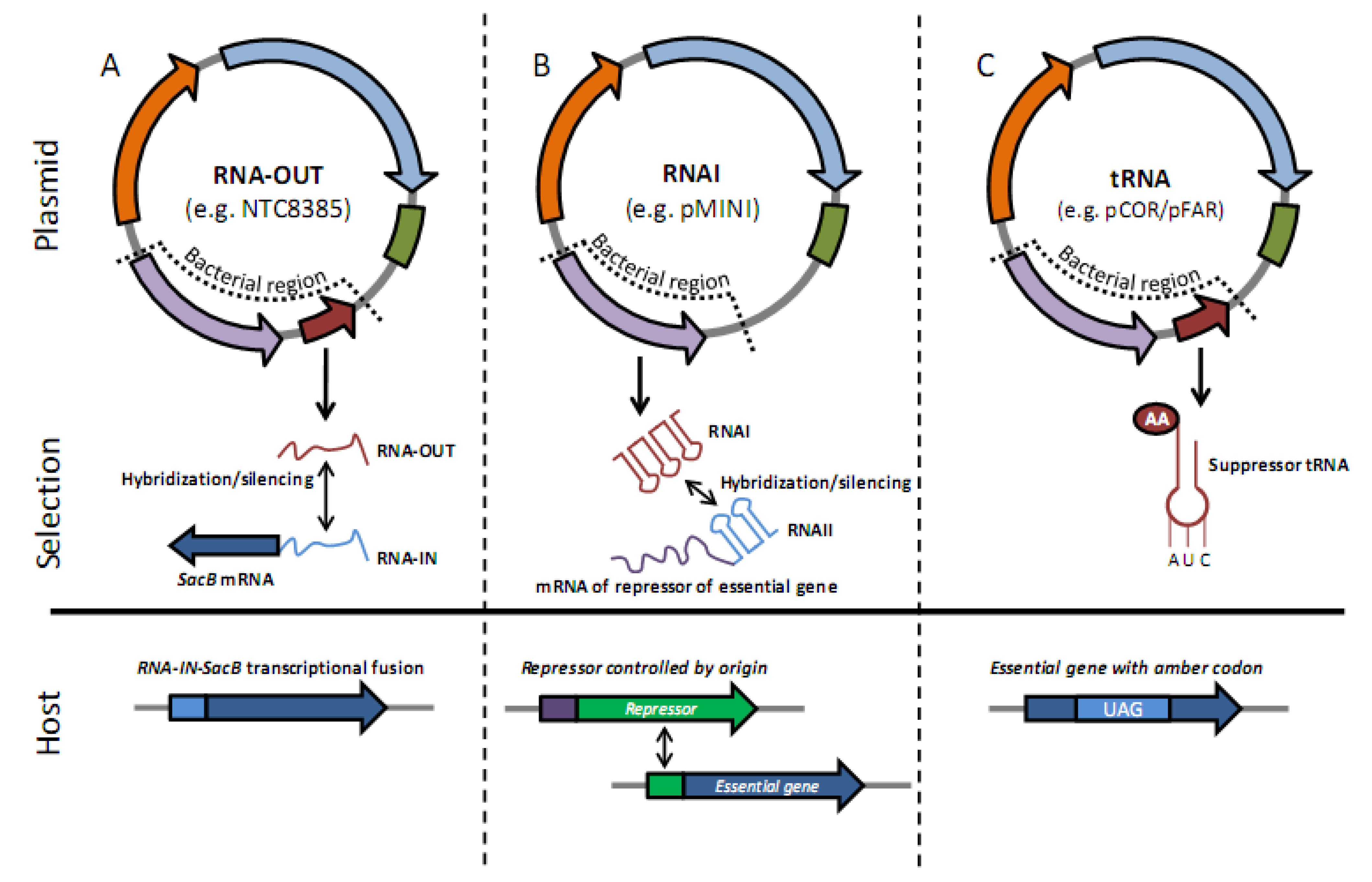
What are recombinant proteins used for?
Recombinant proteins can be used to develop enzymatic assays. When used in conjunction with a matched antibody pair, recombinant proteins can be used as standards such as ELISA standards. Moreover, recombinant proteins can be used as positive controls in Western blots.
What are the applications of recombinant proteins?
- What Is A Recombinant Protein?
- History of Recombinant Proteins
- Two Methods of Producing Recombinant Proteins 1. Through Molecular Cloning 2. Through Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- Applications of Recombinant Proteins 1. Control Glycosylation Process 2. Improve the Efficiency of Central Carbon Mechanism 3. Map and Sequence Genes 4. ...
- References
Why are some human proteins produced by transgenic cows?
These human genes are designed to produce, in the animal's milk, a specific therapeutic protein to combat a human disease. For instance, the animal might be bioengineered to produce a protein to treat hemophilia. The therapeutic protein would be extracted from the milk, purified and packaged as a drug.
What is UniProt's human proteome?
The human proteome, as we define it in UniProt, is the set of protein sequences that can be derived by translation of all protein-coding genes of the human reference genome, including alternative products such as splice variants.

How to express recombinant protein?
The strategy for expressing recombinant protein involves transfecting a particular cell with DNA vector containing the template of recombinant DNA. The cells containing the template are then cultured, so that they can transcribe and translate the protein of interest.
How did the idea of recombinant proteins emerge?
The recombinant DNA is created by fusing sequences that may not be normally present in an organism.
What is recombinant protein used for?
Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce pharmaceutical products, protein-based polymers for drug delivery, antibodies and enzymes for disease treatment, protein scaffolds for tissue engineering, as well as for a myriad of other uses . molekuul_be | Shutterstock.
What is the purpose of the eukaryotic protein system?
This system is used to perform structural analysis, functional assays, generation of antibodies, but also to study protein interactions. This system can be used to process eukaryotic proteins and is scalable up to fermentation. The media requirements are also simple in this case. However, for generating very high yields, fermentation is required and growth conditions often need to be optimised.
What is the function of a cell culture system?
This system is used to perform functional assays, structural analysis, expressing intracellular proteins and protein complexes, production of viruses, etc. The processing methods in this case are similar to the methods to process proteins in mammalian systems. However, in this system, the cell culture conditions are more demanding than culturing prokaryotic cells. Also, producing the recombinant vectors is time-consuming in insect systems.
What are the functions of mammals?
Mammalian systems are used to perform functional assays, structural analysis, antibody production, protein interaction, production of viruses, etc. A main advantage of this system is either transient or stable production of proteins.
What is cell free system?
Cell-free system. This system is used to study toxic proteins, incorporation of unnatural amino acids, screening of translational inhibitors etc. Since this is an open system, it is possible to add unnatural components. Also, the expression is fast and simple.
What is recombinant technology?
Recombinant technology is the process involved in the formation of recombinant protein. Recombinant Protein is a protein encoded by a gene — recombinant DNA — that has been cloned in a system that supports expression of the gene and translation of messenger RNA (see expression system ). Modification of the gene by recombinant DNA technology can ...
What is recombinant protein?
Recombinant protein is a manipulated form of protein, which is generated in various ways to produce large quantities of proteins, modify gene sequences and manufacture useful commercial products. The formation of recombinant protein is carried out in specialized vehicles known as vectors. Recombinant technology is the process involved in ...
Is BIC a reliable partner?
Choose BIC as your reliable partner for your protein research, and we can help you accelerate your discovery in a timely and cost-effective manner at every step of the way, and at a very affordable price. Contact us today to speak with our protein specialists.
Do we guarantee the stability and solubility of proteins?
We guarantee the stability and solubility of proteins , but not the biological and functional properties of proteins.
What are recombinant proteins?
The proteins that are formed into a host by transfecting foreign genes into them are recombinant proteins. Recombinant proteins are the new combination of genes that makes up the DNA. Whilst recombinant proteins are made of the cloned DNA sequences that have encoded enzymes or proteins.
How are recombinant proteins made?
Recombinant protein production initiates at the gene level, where the protein of interest is selected with the coding sequence that produces a recombinant protein of interest. After selection, it is isolated, cloned in an expression plasmid vector.
Applications of recombinant proteins
With the production of recombinant protein capturing a significant space in life sciences. There are various applications associated with it, right from drug delivery to production and transformation. Recombinant proteins have substantial applications in the following:
How are recombinant proteins made?
Recombinant protein production begins at the genetic level, where coding sequence for the protein of interest is first isolated and cloned into an expression plasmid vector . Most recombinant proteins for therapeutic use are from humans but are expressed in microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, or animal cells in culture. Human genes are very complex, often containing non-coding DNA sequences known as introns. Therefore, an intron-free version of the gene is often made by converting the mRNA into cDNA. Because the cDNA lacks regulatory regions, the expression vectors provide promoter, ribosome-binding site, and terminator sequences. Recombinant protein production for research purposes is mainly driven by the cost-effectiveness, simplicity, and speed of the process in conjunction with adequate yields of the product. Proteins co-expressed in bacteria would not possess post-translational modifications, e.g. phosphorylation or glycosylation; eukaryotic expression systems are needed for this.
How many RPs are produced?
However, more than 170 RPs are produced and used in medicine worldwide. Recombinant human insulin was a very early example of the use of biotechnology in drug development. Recombinant proteins are potent medicines that are safe from off-target side effects, and take a shorter time to develop than small molecules.
What is recombinant DNA?
Modification of the gene by recombinant DNA technology can lead to expression of a mutant protein. Recombinant protein is a manipulated form of native protein, which is generated in various ways in order to increase production of proteins, modify gene sequences, and manufacture useful commercial products.
Why is RP important?
The importance of RP has increased rapidly for basic life science research, diagnostic reagents and therapeutic drugs. Their role in biotechnology is irreplaceable. We also look forward to seeing more progress in the treatment of various diseases with recombinant proteins.
What is the function of proteins in a cell?
Proteins are the workhorse in biological systems facilitating most of biological processes in a cell, including gene expression, cell growth, proliferation, nutrient uptake, intercellular communication and apoptosis. The blue print for protein synthesis is stored in DNA, which serves as a template for highly regulated transcriptional processes ...
What are therapeutic proteins?
Common therapeutic proteins include antibodies, Fc fusion proteins, hormones, interleukins, enzymes, and anticoagulants. Human proteins obtained through genetic engineering play a key role in therapeutic medicines market. One of the many RP vaccines approved by the FDA is the Hepatitis B vaccine for prevention of infection caused by all known ...
How is mRNA translated into protein?
The message coded by mRNA is then translated into defined sequences of amino acids that form a protein. Proteins are synthesized in a similar two-step process in all organisms – DNA is first transcribed into RNA, then RNA is translated into protein.
What is the peptide obe?
Recently, Sun et al. (2012) expressed a short 23 amino acid peptide obestatin (Obe) in T. reesei. Obestatin is present in animal and human intestinal tract and suppresses food intake, inhibits small intestine contraction and decreases body-weight gain. The expression construct featured the cbh1 promoter and CBHI catalytic core, a linker containing a Kex2-like cleavage site, obestatin encoding DNA, a linker containing a Tobacco Etch Virus proteolytic site and an HFBI tag for purification in a liquid two phase system. It appeared that Obe-HFBI was successfully processed from the carrier protein and formed multimers in the production host as established by Western blotting ( Sun et al., 2012 ). Despite the rather low yield, 7 μg/l in shake flask cultivations, this seems to be the first published example of expression of a very short heterologous peptide in T. reesei.
What is a veg trap?
As with the Macugen and Lucentis protein moieties, VEGF Trap is a potent inhibitor of VEGF action. It is a recombinant fusion protein that contains the binding domains of VEGF receptors 1 and 2 and human IgG Fc. As such, it competes with and inhibits VEGF binding to authentic receptors in vivo. Treatment with VEGF Trap has completed Phase I of a clinical trial. The drug is given by IV administration instead of as an injection into the eye. Nguyen et al. (2006) have reported positive results from a Phase I clinical trial in CNV in which safety, pharmacokinetics and efficacy were assessed. In this study, the maximum tolerated dose was determined and some efficacy elements were established. A natural protein that acts as a VEGF antagonist is pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) ( Stellmach et al., 2001 ). As described above, PEDF is a relatively small protein naturally found in many tissues of the body but synthesized in abundant amounts by retinal pigment epithelial cells. Importantly, Mori et al. (2002) demonstrated the feasibility of gene therapy in supplying PEDF as a therapeutic agent in ocular neovascularization. Armed with all this information, the GenVec company has sponsored a clinical trial to investigate the use of AV-delivered PEDF (AdPEDF) in choroidal neovascularization. A Phase I dose-escalation study was performed on 28 patients given intravitreal injection of the AdPEDF ( Campochiaro et al., 2006 ). No serious side effects were observed and GenVec reports “positive changes in vision and retinal appearance at the higher dose cohorts in some patients”. To complete this study, GenVec has enrolled 21 patients with less severe disease. Given success in these patients, subsequent phases of the trial can commence. This is a landmark study in that it, may not only be the first successful gene therapy treatment in the eye, but in any tissue affected by a major disease.
What is belatacept used for?
It is approved for use in combination with basiliximab, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), and corticosteroids for prophylaxis of rejection in kidney transplantation. Serious infections, including PML, polyomavirus, and tuberculosis, 42 are a major concern in patients receiving belatacept. In particular, post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) of the central nervous system was found to be associated with belatacept use. 43 Thus, the agent’s use should be restricted to those patients known to be EBV seropositive, as PTLD is particularly associated with primary EBV infection. Before treatment, latent TB should be screened for and treated. During treatment, CMV and Pneumocystis prophylaxis is recommended. The greater association of infections with belatacept, in comparison with the similar compound abatacept, presumably relates in part to the difference in patient populations that are targeted.
What is the abatacept?
The costimulation modulator abatacept (Orencia), which was developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb, USA, represents a soluble recombinant fusion protein containing the extracellular domain of the human CTLA-4 and a fragment of the Fc domain of human IgG1, which was modified to prevent complement fixation [246 ]. It binds to the CD80 or CD86 molecule, thereby preventing the T-cell activation. It was approved in June 2007 for the treatment of patients with RA who are not responding well to common treatment options. While hypertension has been described as a common side effect of abatacept [247] blood pressure was not found to be increased in a recent trial that investigated the influence of abatacept on aortic stiffness as a marker of cardiovascular risk [248]. In this study, abatacept treatment led to an increase in all lipid parameters. Even though this increase was only significant for HDL it did not significantly decrease the atherogenic index. Abatacept did not have a positive influence on aortic stiffness possibly due to insufficient control of inflammation or the unfavorable change in lipid levels [248]. Abatacept is the basis for the second-generation belatacept, which is intended to be used for immune suppression after organ transplantation and which was shown to have a better cardiovascular and metabolic profile [249].
What are the two dominant PCNA epitopes?
Two dominant PCNA epitopes involve residues 111–125 and 181–195. Most residues of the first epitope {VSDYEMKLMDLVEQ} contribute to its antigenicity. The reactivity of SLE sera to PCNA is related to the 261 N-terminal residues, and most are conformation-dependent as shown by immunoprecipitation. Some SLE sera, however, show additional reactivity with denatured protein as shown by immunoblotting. In a wheat germ cell-free translation system, 8/10 SLE sera required full length PCNA, 2/10 recognized the COOH terminal sequences, Lupus sera reacted with 15 and 17 kDa fragments, thus classifying their binding into Type A – 17 kDa, Type B – both 17 and 15 kDa, and Type C – only 15 kDa binding. Many proteins interact with PCNA through a small conserved consensus motif QxxLxxFF. A recent functional analysis of PCNA-binding peptides from protein sequence, interaction screening (mostly EGFP-pep102 fusion proteins, or rational design (con1)) using yeast and human cells showed that peptide aptamers can be identified that are functional in mammalian cells which might be exploited for anti-proliferative therapies directed at these small molecules.
What is PCNA used for?
Purified PCNA, recombinant fusion proteins and synthetic peptides based on the cloned sequence were used to examine epitopes bound by SLE sera or monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). As in other autoantigen–autoantibody systems, the epitopes recognized by natural autoantibodies are highly conserved and conformationally dependent domains; whereas, most induced antibodies react with non-conserved domains.
What is affinity tag chromatography?
Affinity tag chromatography permits purification of recombinant proteins from growth media or from cell lysates. New chromatography techniques take advantage of DNA cloning that produces recombinant fusion proteins and allows such proteins to be easily purified. Recombinant proteins can be engineered to contain affinity tag sequences to create a fusion protein. The tag possesses unique affinity characteristics that serve as the basis for subsequent purification. Affinity chromatography is carried out using the immobilized ligand of the tag, which yields a highly purified fusion protein. A variety of affinity tag sequences are used such as hexa-histidine for metal chelate separation, enzyme tags that allow isolation using immobilized substrate, or epitope sequences for separation by an immobilized monoclonal antibody. An enzyme cleavage site is usually included between the tag and protein for removal of the tag from the fusion protein after purification. Once an effective purification strategy has been established for one fusion protein, it can be used for any protein that is engineered to include the same tag.
Why are lysosomal proteins difficult to produce?
Lysosomal proteins: Lysosomal proteins are difficult to produce recombinantly due to the number and type of post-translational modifications that they have (e.g. glycosylation ). As a result, recombinant lysosomal proteins are usually produced in mammalian cells. Plant cell culture was used to produce FDA-approved glycosylated lysosmal ...
What is the prefix for recombinant human?
In many cases, recombinant human proteins have replaced the original animal-derived version used in medicine. The prefix "rh" for "recombinant human" appears less and less in the literature. A much larger number of recombinant proteins is used in the research laboratory. These include both commercially available proteins (for example most ...
Can lysosomal proteins be recombinant?
Recent studies have shown that it may be possible to produce recombinant lysosomal proteins with microorganisms such as Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Recombinant lysosomal proteins are used for both research and medical applications, such as enzyme replacement therapy.
Is isolation required for ribosome studies?
However, isolation is still required for the studies of the whole ribosome.
Is human insulin a BHI?
human insulin (BHI): Humulin from Lilly and Novolin from Novo Nordisk among others largely replaced bovine and porcine insulin for human therapy. Some prefer to continue using the animal-sourced preparations, as there is some evidence that synthetic insulin varieties are more likely to induce hypoglycemia unawareness. Remaining manufacturers of highly purified animal-sourced insulin include the U.K.'s Wockhardt Ltd. (headquartered in India), Argentina's Laboratorios Beta S.A., and China's Wanbang Biopharma Co.