A positive result means you have one or more RBC Red blood cells, also known as RBCs, red cells, red blood corpuscles, haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or gills of fish, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries.Red blood cell
How do antibodies destroy red blood cells?
antibodies. Antibodies attach to red blood cells and travel throughout the body, fighting germs and other foreign substances that should not be there. In AIHA, the body makes antibodies that attack the red blood cells because they think they are foreign or unwanted substances. They destroy the red blood cells, and this results in anemia.
What does it mean to have a positive antibody screen?
Q: What does a positive antibody test mean? A: If you have a positive test result on a SARS-CoV-2 antibody test, it is possible that you have recently or previously had COVID-19.
What antigens are found in red blood cells?
Aside from the sugar (glycan or carbohydrate) antigens, the red blood cell membrane contains three types of protein that carry blood group antigens: single-pass proteins, multi-pass proteins, and glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked proteins.
What antibodies does a person with AB- blood have?
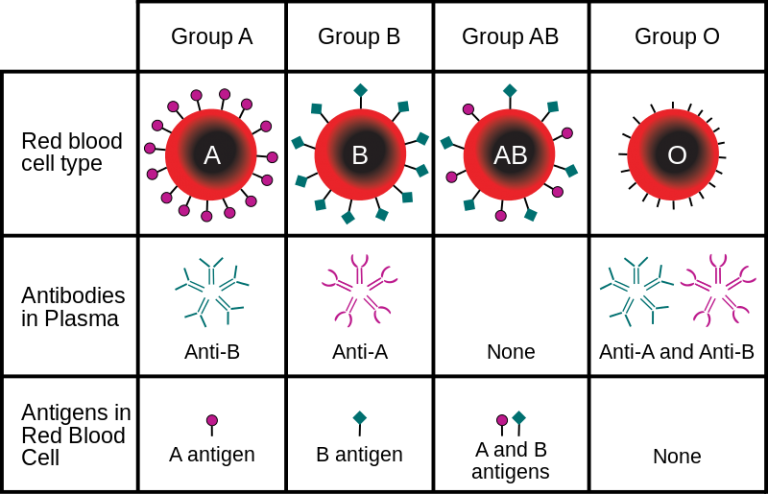
→ Blood type B has Anti-A antibodies circulating in their blood. → Blood type AB has neither Anti-A antibodies, nor Anti-B antibodies circulating in their blood. Similarly, an individual with type B blood has pre-formed anti-A antibodies. Individuals with type AB blood, which has both antigens, do not have preformed antibodies to either of these.

What Do My Test Results Mean?
Test results may vary depending on your age, gender, health history, the method used for the test, and other things. Your test results may not mean...
Does This Test Pose Any Risks?
Having a blood test with a needle carries some risks. These include bleeding, infection, bruising, and feeling lightheaded. When the needle pricks...
How Do I Get Ready For This Test?
You don't need to prepare for this test. Be sure your healthcare provider knows about all medicines, herbs, vitamins, and supplements you are takin...
How do antibodies form?
These antibodies may have formed from a blood transfusion, from an earlier pregnancy, or even from exposure to some viruses or bacteria. If your fetus has a different blood group than yours, your immune system may also make antibodies against that "foreign" blood group.
What are the different types of blood cells?
Red blood cells fall into 1 of 4 main groups: O, A, B, or AB. Blood types can be further divided into other, minor groups. Each blood type is also identified as being positive or negative, depending on the presence or absence of the Rh factor.
What is this test?
This test looks for antibodies to red blood cells (RBCs) in your blood. These antibodies can cause problems during blood transfusions or, if you're pregnant, with your unborn baby.
Why do I need this test?
You may need this test before a blood transfusion to check your specific blood traits.
What do my test results mean?
Test results may vary depending on your age, gender, health history, the method used for the test, and other things. Your test results may not mean you have a problem. Ask your healthcare provider what your test results mean for you.
Can you test for antibodies while pregnant?
If not, the blood bank will select another blood type. Test results if you're pregnant will show whether you have RBC antibodies of the immunoglobulin G, IgG, subtype. Only this type can cross the placenta from your bloodstream and cause problems with your baby.
What does it mean when your blood test results vary?
Test results may vary depending on your age, gender, health history, the method used for the test, and other things. Your test results may not mean you have a problem. Ask your healthcare provider what your test results mean for you.
What does a blood test for pregnancy show?
This test finds out blood compatibility in advance of a blood transfusion. When you are pregnant, this test can find out whether you have RBC antibodies that might affect your fetus. These antibodies may have formed from a blood transfusion, from an earlier pregnancy, or even from exposure to some viruses or bacteria.
What is this test?
This test looks for antibodies to red blood cells (RBCs) in your blood. These antibodies can cause problems during blood transfusions or, if you're pregnant, with your unborn baby.
Why do I need this test?
You may need this test before a blood transfusion to check your specific blood traits.
How is this test done?
The test is done with a blood sample. A needle is used to draw blood from a vein in your arm or hand.
What happens if a fetus has a different blood group than yours?
If your fetus has a different blood group than yours, your immune system may also make antibodies against that "foreign" blood group.
Is blood positive or negative?
Blood types can be further divided into other, minor groups. Each blood type is also identified as being positive or negative, de pending on the presence or absence of the Rh factor. If you get blood from a person whose blood group is different from yours, your body may make antibodies against this other blood.
What is a clinically significant antibody?
Depending on the antigen and antibody involved and the quantity of RBCs affected, this can cause a reaction ranging from mild to severe and potentially life-threatening. Antibody/antigen combinations capable of destroying RBCs are called clinically significant.
What is being tested for RBC?
What is being tested? Red blood cell antibodies are proteins produced by the body's immune system directed against "foreign" red blood cells (RBCs). This test identifies the specific red blood cell antibodies present in the blood of an individual who has a positive screening test for RBC antibodies ...
What type of antigens do people inherit?
Each individual inherits a specific combination of RBC antigens, structures found on the surface of the cells, including those associated with the major blood types A, B, AB, and O. Normally, people will only produce antibodies directed against "foreign" antigens not found on their own cells. All individuals naturally produce antibodies against ...
How are antibodies made?
Antibodies to these antigens are not made naturally and are only produced by the body when exposed to them through blood transfusion or when a mother is exposed to a baby's blood cells during pregnancy, labor and delivery. These antibodies may or may not be associated with adverse reactions, and identification of the specific type ...
What antigens are not on RBCs?
All individuals naturally produce antibodies against the A and/or B antigens that are not on their own RBCs. For example, a person who is blood type A will have antibodies in their blood to the B antigen. Another important RBC antigen is an Rh antigen called the D antigen.
When to take RBC into account?
If the antibody identified is considered clinically significant, then it will need to be taken into account with each transfusion and/or pregnancy. If clinically significant RBC antibodies have been identified during pregnancy, the baby's condition will be monitored.
When is an antibody test ordered?
The antibody identification test may be ordered when an RBC antibody screen or a direct antiglobulin test is positive. The test may also be performed when a person has a transfusion reaction or when a mother has a baby with hemolytic disease of the newborn.
Why do people make antibodies to RBCs?
People who have many transfusions make antibodies to RBCs because they are exposed to foreign RBC antigens with each transfusion.
What are the major antigens on a person's blood?
The major antigens or surface identifiers on human RBCs are the O, A, and B antigens , and a person's blood is grouped into an A, B, AB, or O blood type according to the presence or absence of these antigens.
Why do people with transfusions make antibodies?
People who have many transfusions make antibodies to RBCs because they are exposed to foreign RBC antigens with each transfusion. During pregnancy, with blood type incompatibility between mother and baby: A baby may inherit antigens from the father that are not on the mother's RBCs.
How to determine if a person is rh positive?
A person is considered to be Rh-positive if the D antigen is present on the person's RBCs and Rh-negative if the D antigen is not present . An Rh-negative mother may develop an antibody when she is exposed to blood cells from an Rh-positive fetus. To prevent this, an Rh-negative mother should have an RBC antibody screen performed early in her pregnancy, at 28 weeks, and again at the time of delivery. If there are no Rh antibodies present at 28 weeks, then the woman is given an injection of Rh immune globulin (RhIg) to clear any Rh-positive fetal RBCs that may be present in her bloodstream to prevent the production of Rh antibodies by the mother.
Why do people have RBCs?
The primary reason that a person may have RBC antibodies circulating in the blood is because the person has been exposed, through blood transfusion or through pregnancy, to RBCs other than his or her own (foreign RBCs).
What blood groups are RBC?
In addition, there are many other types of RBC antigens that make up lesser-known blood groups, such as Kell, Lewis, and Kidd blood groups . There are a few reasons why someone may produce antibodies against RBC antigens.
How long does it take for a Rh negative mother to get an antibody?
Pregnancy: If an Rh-negative mother has a negative RBC antibody screen, then an Rh immune globulin injection is given within 72 hours to prevent antibody production. If she has a positive test, then the antibody or antibodies present must be identified.
What to do if antibody screen is positive?
American Association of Blood Banking states that if an antibody screen is positive, an attempt should be made to identify the antibody and cross match for the same along with ABO and RH. If the antibody screen is negative, they recommend only ABO/RH compatibility testing to be done before transfusion. However, there is great paucity of literature regarding the scenario where the antibody screen is positive but the antibody identification (ABID) is inconclusive, to see if this has any clinical implications. This study was undertaken to review the clinical implications of a positive antibody screen with inconclusive ABID.
What is an inconclusive antibody screen?
An inconclusive antibody screen is defined as test reactive for gel screen (which is a two cell screen) and no defined pattern on antibody identification panel.
What is routine blood type and screen?
The routine blood type and screen involves screening for unexpected antibodies, in addition to checking the ABO group and RH type. Most of these antibodies are IgM type, also known as nuisance antibodies. They are thought not to have much clinical significance. A positive antibody screen can sometimes be associated with inconclusive antibody ...
Can you have an antibody screen if you have an inconclusive antibody?
Patients who have an inconclusive ABID on antibody screen are usually ignored as having not much clinical significance. Our study indicates that although transfusion appears relatively safe in such patients, they can rarely have transfusion reactions, likely due to yet unidentified antibodies. Although 48% of patients retested will have a negative antibody screen, about a quarter of patients will have an antibody identified on subsequent testing. Hence, all patients with inconclusive ABID screen should be tested again, to identify if an antibody is present, in order to avoid any untoward reactions.
