What are redox reactions?
In electrochemistry, redox reactions are oxidation-reduction chemical reactions. They can be broken down into two distinct processes, a reduction process, and an oxidation process. The oxidation and reduction reactions take place at the same time in a redox reaction.
What is electrochemistry and how does it work?
Broadly speaking, electrochemistry looks at the interactions between electricity and chemical reactions. The chemical reaction that takes place in an electrochemical reaction causes electrons to move from one side to another, known as redox reactions. In electrochemistry, redox reactions are oxidation-reduction chemical reactions.
What is an oxidation and reduction reaction?
Many chemical reactions involve transfer of electrons from one chemical substance to another. These electron transfer reactions are termed as oxidation-reduction or Redox reaction, or those reactions which involve oxidation and reduction both simultaneously are known as oxidation and reduction/ Redox reaction.
What is redox potential in chemistry?
) is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons from or lose electrons to an electrode and thereby be reduced or oxidised respectively. Redox potential is measured in volts (V), or millivolts (mV).

Is electrochemistry related to redox reaction?
Electrochemistry is the interchange of chemical and electrical energy. The key to electrochemistry is a redox reaction. This unique type of reaction produces a flow of electrons that can be used to do work like light a flashlight bulb or perhaps your favorite…
How are the redox reactions related with the electrochemical cells?
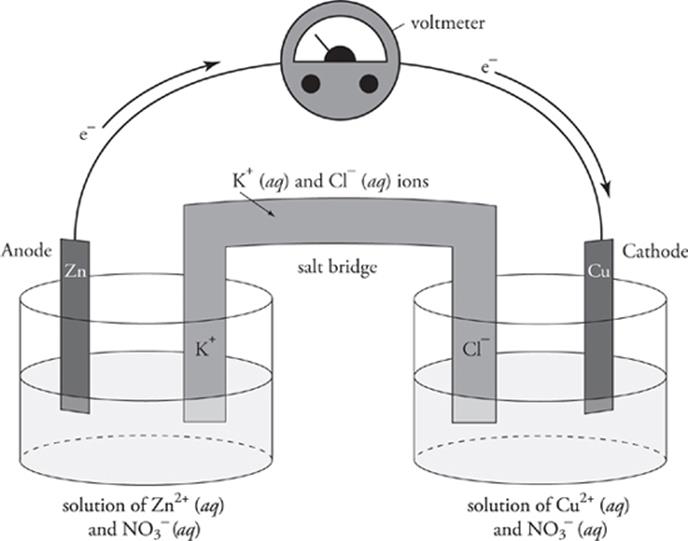
An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction involves the transfer of electrons from the reducing agent to the oxidising agent. A voltaic electrochemical cell involves two half cells one containing an oxidising agent and the other a reducing agent. salt bridge to complete the circuit and maintain electrical neutrality.
Why must an electrochemical process involve a redox reaction?
When the redox reaction is direct, those electrons cannot be made to do work. Instead, we must separate the oxidation process from the reduction process and force the electrons to move from one place to another in between. That is the key to the structure of the electrochemical cell.
How can a redox reaction be used as a source of electrical energy?
In oxidation–reduction (redox) reactions, electrons are transferred from one species (the reductant) to another (the oxidant). This transfer of electrons provides a means for converting chemical energy to electrical energy or vice versa.
What is reduction in electrochemistry?
Electrochemical reduction describes the transformation in the electrochemical circuit of metallic cation to metals by electron transfer.
Do all electrochemical cells involve redox reactions?
Not all electrodes undergo a chemical transformation during a redox reaction. The electrode can be made from an inert, highly conducting metal such as platinum to prevent it from reacting during a redox process, where it does not appear in the overall electrochemical reaction.
How do you do electrochemistry?
Method 2: Half-Reaction MethodStep 1: Determine oxidation numbers for each atom.Step 2: Use oxidation numbers to determine what is oxidized and what is reduced.Step 3: Write a half-reaction for reduction.Step 4: Write a half-reaction for oxidation.Step 5: Balance all elements except H and O.More items...•
What type of reactions are fundamental reactions of electrochemistry?
In electrochemistry, spontaneous reaction (redox reaction) results in the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy. The reverse process is also possible where a non-spontaneous chemical reaction occurs by supplying electricity. These interconversions are carried out in equipment called electrochemical cell.
What type of chemical reaction is involved in all electrochemical processes?
What type of chemical reaction is involved in all electrochemical processes? all electrochemical processes involve redox reactions.
How do electrons flow in redox reactions?
In a redox reaction, electrons transfer from a set of orbitals on the electron donor called the donor orbitals into a set of orbitals on the acceptor called the acceptor orbitals. The redox electrons are in the donor orbitals, so the donor must be in a reduced form of the substance, which is designated Red1.
Why can a redox reaction be used to create electricity quizlet?
2) Why can a redox reaction be used to create electricity? Oxidation-reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons. This also results in the transfer of energy, usually in the form of heat. Some of these reactions can be used to produce electricity.
How does electricity contribute to chemical reactions?
electrochemical reaction, any process either caused or accompanied by the passage of an electric current and involving in most cases the transfer of electrons between two substances—one a solid and the other a liquid.
1. What is a Redox Reaction?
Many chemical reactions involve transfer of electrons from one chemical substance to another. These electron transfer reactions are termed as oxida...
2. Explain a Few Features of Oxidising Agents and Oxidants?
1.Oxidising agents are lewis acid.2. Substance which can oxidise others and reduce themselves.3.Substance which shows decrease in oxidation number....
3. Explain a Few Features of Reducing Agents?
1.Reducing agents are Lewis base.2.Substances which can reduce others and oxidise themselves.3.Substance which shows decrease in oxidation number.4...
4. Explain different Types of Redox Reactions?
There are mainly three types of redox reactions, they are:1.Intermolecular Redox ReactionWhen oxidation and reduction take place separately in the...
What is a chemical reaction called?
The chemical reaction is spontaneous and produces electricity. This is called a voltaic cell or a galvanic cell. The chemical reaction is non-spontaneous and is forced by electricity from an external source. This kind of cell is called an electrolysis cell. We will look at the first situation first.
What determines the product of electrolysis?
There are three factors that determine product that we will find in any given electrolysis cell: the electrode material, the solvent and the electrolyte. Often, we use inert electrodes and/or pure liquids to help alleviate some of the complications from competing chemistry, other times, we must simply carefully adjust conditions (concentrations and voltages) to ensure that the desired product is achieved.
Can oxygen be reduced to water?
We’ve seen that the oxygen from the air can be reduced to water and that the reduction potential for this half-reaction is very positive . More positive, in fact than that for most metal reduction process. This means that any metal in contact with oxygen from the air and in the presence of an electrolyte solution will oxidize. Since mining and production of metal is a fairly energy-intensive process, it is very useful to be able to find ways to reduce or eliminate the oxidation of these metals if at all possible. There are several ways to reduce oxidation of metals
Does sodium metal oxidize in water?
In fact, sodium metal in water will spontaneously (explosively) oxidize to Na + ions and the water will reduce to hydrogen gas and leave a basic solution (equation 6).
What is a redox reaction?
What is Redox Reaction. Many chemical reactions involve transfer of electrons from one chemical substance to another. These electron transfer reactions are termed as oxidation-reduction or Redox reaction, or those reactions which involve oxidation and reduction both simultaneously are known as oxidation and reduction/ Redox reaction.
What are the different types of redox reactions?
There are mainly three types of redox reactions, they are: 1.Intermolecular Redox Reaction. When oxidation and reduction take place separately in the different compounds called intermolecular redox reactions. SnCl2+ 2FeCl3-------SnCl4+2FeCl2.
What does oxidation number mean?
Oxidation Number. It represents the number of electrons gained or lost by an atom when it changes in compound from free state. It is also defined as charge on an atom when the atom is in combining state. If electrons are gained by an atom in the formation of compounds the oxidation number is given a negative sign.
What are reducing agents?
Reducing Agents or Reductant. The substances which donate electrons in a chemical reaction are reducing agents i.e electron donors are reducing agents. Reducing agents are Lewis base. Substances which can reduce others and oxidise themselves. Substance which shows decrement in oxidation number.
What is the term for the transfer of electrons from one chemical substance to another?
Many chemical reactions involve transfer of electrons from one chemical substance to another. These electron transfer reactions are termed as oxidation-reduction or Redox reaction, or those reactions which involve oxidation and reduction both simultaneously are known as oxidation and reduction/ Redox reaction.
What is reduction in chemistry?
Reduction is a process which involves: Removal of oxygen. Addition of hydrogen. Removal of electronegative elements. Addition of electropositive elements. Decrement in oxidation state of electropositive elements.
Which substance accepts electrons in a chemical reaction?
The Substance which accept electrons in a chemical reaction i.e electron acceptors are oxidising agents: Oxidising agents are lewis acid. Substance which can oxidise others and reduce themselves. Substance which shows decrement in oxidation number.
What is oxidation reduction?
An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two species. An oxidation-reduction reaction is any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of a molecule, atom, or ion changes by gaining or losing an electron.
Can oxidative and reductive strengths be compared?
The oxidative and reductive strengths of a variety of substances can be compared using standard electrode potentials. Apparent anomalies can be explained by the fact that electrode potentials are measured in aqueous solution, which allows for strong intermolecular electrostatic interactions, and not in the gas phase.
Which chemical reaction takes place at the electrodes?
The chemical reaction that takes place at the electrodes are: ● Sodium-ion migrates to the cathode, where sodium ion gains one electron and reduce to sodium metal. ● Chloride ions migrate towards the anode where it loses one electron and gets oxidised to chlorine gas.
What are the two types of electrochemical reactions?
Electrochemistry is the subdiscipline of chemistry that deals with the study of the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes. Chemical reactions that involve the input or generation of electric currents are called electrochemical reactions. Such reactions are broadly classified into two categories: 1 Production of chemical change by electrical energy i.e. the phenomenon of electrolysis 2 Conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy. i.e., the generation of electricity by spontaneous redox reactions.
How does an electrolytic cell convert electrical energy to chemical energy?
The electrolytic cell converts electrical energy to chemical energy. Here the electrodes are dipped in an electrolytic solution containing cations and anions. On supplying current the ions move towards electrodes of opposite polarity and simultaneous reduction and oxidation take place.
How does a galvanic cell convert chemical energy into electrical energy?
A galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell, used to supply electrical current by making the transfer of electrons through a redox reaction. During redox reactions , the galvanic cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy by transferring energy between the electrons.
What is chemical reaction?
Chemical reactions that involve the input or generation of electric currents are called electrochemical reactions. Such reactions are broadly classified into two categories: Production of chemical change by electrical energy i.e. the phenomenon of electrolysis. Conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy.
How is electricity produced?
Electricity can be produced when electrons move from one element to another in certain types of reactions ( such as redox reactions). Typically, electrochemistry deals with the overall reactions when multiple redox reactions occur simultaneously, connected via some external electric current and a suitable electrolyte.
When the potential difference is applied between the two electrodes, what happens?
When the potential difference is applied between the two electrodes, Na + and H + ions move towards the cathode and Cl – and OH – ions move towards the anode. At cathode H + ions get reduce in preference to giving hydrogen gas because hydrogen has a higher reduction potential than sodium.
What determines the redox potential of an electrode couple?
Similar to how the concentration of hydrogen ion determines the acidity or pH of an aqueous solution, the tendency of electron transfer between a chemical species and an electrode determines the redox potential of an electrode couple.
What is the redox potential of a solution?
In aqueous solutions, redox potential is a measure of the tendency of the solution to either gain or lose electrons when it is subjected to change by introduction of a new species. A solution with a higher (more positive) reduction potential than the new species will have a tendency to gain electrons from the new species (i.e. to be reduced by oxidizing the new species) and a solution with a lower (more negative) reduction potential will have a tendency to lose electrons to the new species (i.e. to be oxidized by reducing the new species). Because the absolute potentials are next to impossible to accurately measure, reduction potentials are defined relative to a reference electrode. Reduction potentials of aqueous solutions are determined by measuring the potential difference between an inert sensing electrode in contact with the solution and a stable reference electrode connected to the solution by a salt bridge.
What is the measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons from or lose electrons to an electrode
Reduction potential. ) is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons from or lose electrons to an electrode and thereby be reduced or oxidised respectively. Redox potential is measured in volts (V), or millivolts (mV).
What is the standard reduction potential?
The standard reduction potential (#N#E 0 {displaystyle E_ {0}}#N#) is measured under standard conditions: 25 °C, a 1 activity for each ion participating in the reaction, a partial pressure of 1 bar for each gas that is part of the reaction, and metals in their pure state. The standard reduction potential is defined relative to a standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) reference electrode, which is arbitrarily given a potential of 0.00 V. However, because these can also be referred to as "redox potentials", the terms "reduction potentials" and "oxidation potentials" are preferred by the IUPAC. The two may be explicitly distinguished in symbols as#N#E 0 r {displaystyle E_ {0}^ {r}}#N#and#N#E 0 o {displaystyle E_ {0}^ {o}}#N#.
What is an enzymatic reaction?
Biochemistry. Many enzymatic reactions are oxidation–reduction reactions, in which one compound is oxidized and another compound is reduced. The ability of an organism to carry out oxidation–reduction reactions depends on the oxidation–reduction state of the environment, or its reduction potential (.
Is hydrogen an oxidizing agent?
Hydrogen (whose reduction potential is 0.0) acts as an oxidizing agent because it accepts an electron donation from the reducing agent lithium (whose reduction potential is -3.04), which causes Li to be oxidized and Hydrogen to be reduced.