Decreased Cardiac Output. Decreased Cardiac Output: Inadequate blood pumped by the heart to meet the metabolic demands of the body. Cardiac output is the amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute. It is the product of the heart rate, which is the number of beats per minute, and the stroke volume, which is amount pumped per beat.
What are the signs of decreased cardiac output?
The psychological alterations, signs and symptoms associated with decreased cardiac output include:
- Restlessness
- Anxiety
- Changes in terms of mental status and level of consciousness
- Confusion
What causes decreased cardiac output?
What causes decreased cardiac output? Conditions like myocardial infarction, hypertension, valvular heart disease, congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, pulmonary disease , arrhythmias, drug effects, fluid overload, decreased fluid volume, and electrolyte imbalance is common causes of decreased cardiac output.
What can decrease the cardiac output?
There is no single cause for decreased cardiac output. This condition can occur due to several reasons which may include: Valvular heart disease; Hypertension or hypotension; Anaphylaxis; Congenital heart defects; Malnutrition; Kidney diseases; High cholesterol level; Smoking; Diabetes; Electrolyte imbalances; Drug use; Nursing Care Plans for Decreased Cardiac Output
What are the factors that increase cardiac output?
Cardiac output (heart rate x stroke volume), blood pressure, and resistance to peripheral blood flow all increase. Cardiac output is influenced by four factors: (1) heart rate, (2) myocardial contractility (force of contraction), (3) blood volume, and (4) venous return of blood to the heart.

What causes reduced cardiac output?
Decreased cardiac output is an often-serious medical condition that occurs when the heart does not pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body. It can be caused by multiple factors, some of which include heart disease, congenital heart defects, and low blood pressure.
What are symptoms of decreased cardiac output?
The physical alterations, signs and symptoms associated with decreased cardiac output include:Hypotension.Hypercapnea.Cardiac arrhythmias.Chest pain.Diminished peripheral pulses and poor perfusion tissue and organ perfusion.Clammy and cool skin.Deteriorating arterial blood gases.Fainting.More items...
What is risk for decreased cardiac output?
Results: The label 'risk for decreased cardiac output' was considered representative of a nursing diagnosis defined as 'at risk of developing a health status characterized by an insufficient quantity of blood pumped by the heart to meet physical metabolic demands'.
What diagnosis may cause decreased cardiac output?
Conditions like myocardial infarction, hypertension, valvular heart disease, congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, pulmonary disease, arrhythmias, drug effects, fluid overload, decreased fluid volume, and electrolyte imbalance is common causes of decreased cardiac output.
What happens to blood pressure when cardiac output decreases?
Blood pressure decreases with decreased cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance, volume of blood, viscosity of blood and elasticity of vessel walls.
What are the signs and symptoms of poor cardiac perfusion?
Table II.Symptoms and signs of low perfusionSymptoms and signs of congestionFatigueFatigueConfusionTachycardiaAgitationRaised jugular venous pressureDecreased level of consciousnessBreathlessness and hypoxemia11 more rows
What are the factors affecting cardiac output?
Factors affect cardiac output by changing heart rate and stroke volume. Primary factors include blood volume reflexes, autonomic innervation, and hormones. Secondary factors include extracellular fluid ion concentration, body temperature, emotions, sex, and age.
How is cardiac output measured?
How It’s Measured. Your cardiac output is your heartbeats per minute multiplied by the amount of blood pumped with each beat. Your doctor can measure it in lots of ways. Pulmonary artery catheter. Your doctor inserts this device into the arterythat sends blood to the lungsto pick up oxygen. Echocardiogram.
Why is my cardiac output high?
High Output. Sometimes, sepsis, your body’s response to blood infections that can lead to a dangerous drop in blood pressureand organ failure, can cause high cardiac output. High output also can happen when your body lacks enough oxygen-carrying red blood cells, a condition called anemia.
What happens if your heart doesn't pump enough blood to supply your body and tissues?
Low Output. If your heart doesn’t pump enough blood to supply your body and tissues, it could signal heart failure. Low output also could happen after you’ve lost too much blood, had a severe infection called sepsis, or had severe heart damage.
What happens if your heart doesn't pump enough blood?
If your heart doesn’t pump enough blood to supply your body and tissues, it could signal heart failure. Low output also could happen after you’ve lost too much blood, had a severe infection called sepsis, or had severe heart damage.
What does it mean when your heart pumps too much blood?
If your heart pumps too little or too much blood through your body, it could be a sign of heart failure or other medical problems. Normal Output. It’s different for different people, depending on their size. Usually, an adult heartpumps about 5 liters of bloodper minute at rest.
How much blood does the heart pump when you run?
It’s different for different people, depending on their size. Usually, an adult heart pumps about 5 liters of blood per minute at rest. But when you run or exercise, your heart may pump 3-4 times that much to make sure your body gets enough oxygen and fuel.
How to reduce cardiac output in nursing?
Provide decreased cardiac output nursing care plan adjusted for home care. Promote healthy lifestyle and diet. Promote healthy lifestyle and diet. Provide plan to decrease stress and prevent anxiety.
What is cardiac output?
Cardiac output (CO) , expressed in L/min, is the volume of blood in the heart pump in one minute, depending on the heart’s rate, contractility, preload and afterload. Cardiac output is directly influenced by the heart rate and stroke volume. Regulation of cardiac output includes autonomic nervous system, endocrine and paracrine signaling.
What are the risks of blood pooling in the ventricles?
In addition, blood pooling in the ventricles can increase the risk for stroke and pulmonary embolism. Decreased cardiac output nursing care plan and nursing interventions for decreased cardiac output are crucial steps to prevent possible life-threatening complications.
What is HF in nursing?
Heart failure (HF) is defined as failure of either the left and/or right chambers of the heart resulting in insufficient output to meet tissue needs resulting in pulmonary and systemic vascular congestion. In addition, blood pooling in the ventricles can increase the risk for stroke and pulmonary embolism. Decreased cardiac output nursing care plan ...
What happens when your heart pumping blood?
Cells, tissues and organs rely on the heart pumping the blood to deliver nutrients. Decreased cardiac output may result in insufficient blood supply and compromise vital reactions. This can result in transition towards anaerobic metabolic pathways which lead to production of lactic acid, reduced cellular pH, enzyme denaturation, ...
output
the yield or total of anything produced by any functional system of the body. When measuring output for a patient record, the volume of urine, drainage from tubes, vomitus, and any other measurable liquid should be recorded.
decreased cardiac output
A state in which the blood pumped by the heart is inadequate to meet the metabolic demands of the body. Cardiac output and tissue perfusion are interrelated. When cardiac output is decreased, tissue perfusion problems will develop. Tissue perfusion also can be impaired when there is normal or high cardiac output, for example, in septic shock.)
CAUTION!
In a hypermetabolic state, although cardiac output may be within normal range, it may still be inadequate to meet the needs of the body's tissues.
What happens to the ventricles during diastole?
During diastole, the ventricles relax. But in relaxing, the ventricles open to regain their pre-contractile size, effectively dropping the chamber pressure below that of the vena cava. As a result, blood is drawn into the ventricle during ventricular (and atrial) diastole. Then the cardiac cycle begins again.
Why are the atria and ventricles synchronized?
The synchronized actions of the atria and the ventricles are coordinated to maximize pumping efficiency. Rhythm disturbances can greatly impair this synchrony, resulting in a less effective cardiac cycle. During ventricular systole, the tricuspid valve closes – otherwise, it remains open.
What is the purpose of the cardiac cycle?
The purpose of the cardiac cycle is to effectively pump blood. During a heartbeat, both atria simultaneously contract followed by the contraction of the ventricles. Systole refers to the contractile phase of each chamber while diastole is the relaxation phase. The right heart delivers deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
What is cardiac output?
Cardiac output (‘Q’ or ‘CO’) is the amount of blood ejected by the heart in a minute. It is pumped out of the left ventricle and is the product of stroke volume and heart rate. Sufficient cardiac output is necessary to sustain energy and life.
How much does cardiac output increase with strenuous activity?
With strenuous activity, the cardiac output of an adult can increase to 25 litres per minute to satisfy the body’s demands for oxygen and nutrients. Cardiac output is a product of heart rate (beats per minute) and stroke volume. Stroke volume is the amount of blood ejected by the left ventricle with each contraction.
What happens if your cardiac output is low?
Low cardiac output will reduce energy levels. For example, if your cardiac output fell to 3.5 L/m (about 2/3 of normal) your oxygen -and hence your energy supply – would be decreased as well. Your brain with 1/3 less energy may be less sharp, confused or even unconscious.
How does heart rate affect cardiac output?
Heart rate and cardiac output have a direct relationship. As heart rate increases, so does cardiac output. As mentioned earlier, as energy demands rise (oxygen demands), cardiac output increases. A heart rate of 100/minute will almost always result in more blood ejected per minute than a heart rate of 80/minute.
Why is the prevalence of low cardiac output state increasing?
What we do know is that the overall prevalence of heart failure is increasing; this is in part due to the aging population and increased survival after acute myocardial infarction and improved primary and secondary prevention. The number of people living with heart failure in the community is increasing and this is associated with an increase in admissions of people with acute exacerbations of chronic heart failure. The ESC state that ‘heart failure’ is the cause of 5% of hospital admissions across their member states and 2% of national health expenditure.
Why is a flow chart used for low cardiac output?
Flowchart for Treating Low Cardiac Output. The main reason for hospitalization of patients with worsening or acute heart failure is related to symptoms of congestion. However, in some patients the dominant manifestations are of reduced cardiac output and tissue hypoperfusion with or without congestion.
What is cardiac dysfunction?
Broadly, cardiac dysfunction can result from any cardiac structural disorder or functional disorder that disrupts cardiac filling or emptying. Cardiac dysfunction results in a reduced cardiac output; the consequences of this are an imbalance between oxygen supply and demand in the tissues.
What is the continuum of cardiogenic shock?
There is a continuum from a low-cardiac-output state to cardiogenic shock. The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) defines cardiogenic shock as “evidence of tissue hypoperfusion induced by cardiac dysfunction after correction of preload.”. It is usually characterized by:
What is the recommended blood pressure for a vasodilator?
This can be achieved by using a vasodilator in patients who have a systolic blood pressure of greater than or equal to 110 mmHg. Vasodilators are not recommended in those with a systolic BP less than 90 mmHg and a MAP less than 65 mmHg to avoid hypotension and further compromising organ perfusion.
Does hypoglycemia impair renal function?
Renal function is frequently impaired in chronic heart failure. Low cardiac output leads to poor peripheral perfusion; this will result in reduced renal perfusion and deterioration in renal function unless forward flow and perfusion is improved. Glucose. Hypoglycemia will impair cardiac function.
Is blood pressure an indicator of perfusion?
Blood pressure is an “indicator” of organ perfusion but is an insensitive hemodynamic parameter. Mean arterial pressure (MAP) best approximates organ perfusion in non-cardiac tissues. A reduction in blood pressure due to reduced cardiac output will only be seen once compensatory mechanisms have been exhausted.
What is afterload in cardiac output?
Afterload is proportionate to systemic blood pressures and is inversely related to stroke volume, unlike preload and contractility. Cardiac output can be increased by a variety of signaling methods including enhancement of sympathetic tone, catecholamine secretion, and circulation of thyroid hormone.
How many people died from cardiac dysfunction in 2006?
However, it is important to understand that all diseases due to cardiac dysfunction share a compromised ability of the heart’s ability to supply oxygen to the body effectively. Clinical Significance. Cardiovascular diseases cause 1 in 6 deaths in the US in 2006, and each year about 795,000 people will have strokes.
What is CO in medical terms?
Last Update: September 15, 2020. Introduction. Cardiac output (CO) is the amount of blood pumped by the heart minute and is the mechanism whereby blood flows around the body, especially providing blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. The body’s demand for oxygen changes, such as during exercise, and the cardiac output is altered by ...
Why does cardiac output increase during physiologic stress?
During times of physiologic stress, cardiac output will increase to ensure adequate tissue perfusion. Fick’s principle illustrates this notion and can be used to calculate cardiac output based on oxygen exchange through a capillary bed.
What is the regulation of cardiac output?
As a result, the regulation of cardiac output is subject to a complex mechanism involving the autonomic nervous system, endocrine, and paracrine signaling pathways .[1] Cardiac output (CO) is the amount of blood pumped by the heart minute and is the mechanism whereby blood flows around the body, especially providing blood flow to ...
What is the final determinant of stroke volume?
The final determinant of stroke volume is afterload. Afterload represents all the factors that contribute to total tension during isotonic contraction.
What is the term for a heart failure with reduced CO?
Acute failure of the heart, with reduced CO, and the ability to perfuse tissue is called shock. Four primary categories exist based on origin: cardiogenic, distributive, hypovolemic, and obstructive. [12] Therapy for each class of acute heart failure is guided by etiology, symptomology, and patient characteristics.
What does reduced cardiac output mean?
Reduced cardiac output results in reduced perfusion of the kidneys, with a resulting decrease in urine output. For patients with increased preload, limit fluids and sodium as ordered. Fluid restriction decreases extracellular fluid volume and reduces demands on the heart.
What is cardiac output?
Cardiac output is the amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute. It is the product of the heart rate, which is the number of beats per minute, and the stroke volume, which is the amount pumped per beat. CO = HR X SV.
What is ECG in cardiac?
Monitor electrocardiogram (ECG) for rate, rhythm, and ectopy. Cardiac dysrhythmias may occur from low perfusion, acidosis, or hypoxia. Tachycardia, bradycardia, and ectopic beats can further compromise cardiac output. Older patients are especially sensitive to the loss of atrial kick in atrial fibrillation.
What are the symptoms of decreased cerebral perfusion?
Decreased cerebral perfusion and hypoxia are reflected in irritability, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating. Aged patients are particularly susceptible to reduced perfusion. Assess heart rate and blood pressure.
Can poorly functioning ventricles tolerate increased fluid volumes?
In patients with decreased cardiac output, poorly functioning ventricles may not tolerate increased fluid volumes. Auscultate heart sounds; note rate, rhythm, presence of S3, S4, and lung sounds. The new onset of a gallop rhythm, tachycardia, and fine crackles in lung bases can indicate onset of heart failure.
Can low cardiac output cause chest pain?
Hypoxemia is common, especially with activity. Check symptoms for chest pain. Low cardiac output can further decrease myocardial perfusion, resulting in chest pain. Assess for reports of fatigue and reduced activity tolerance. Fatigue and exertional dyspnea are common problems with low cardiac output states.
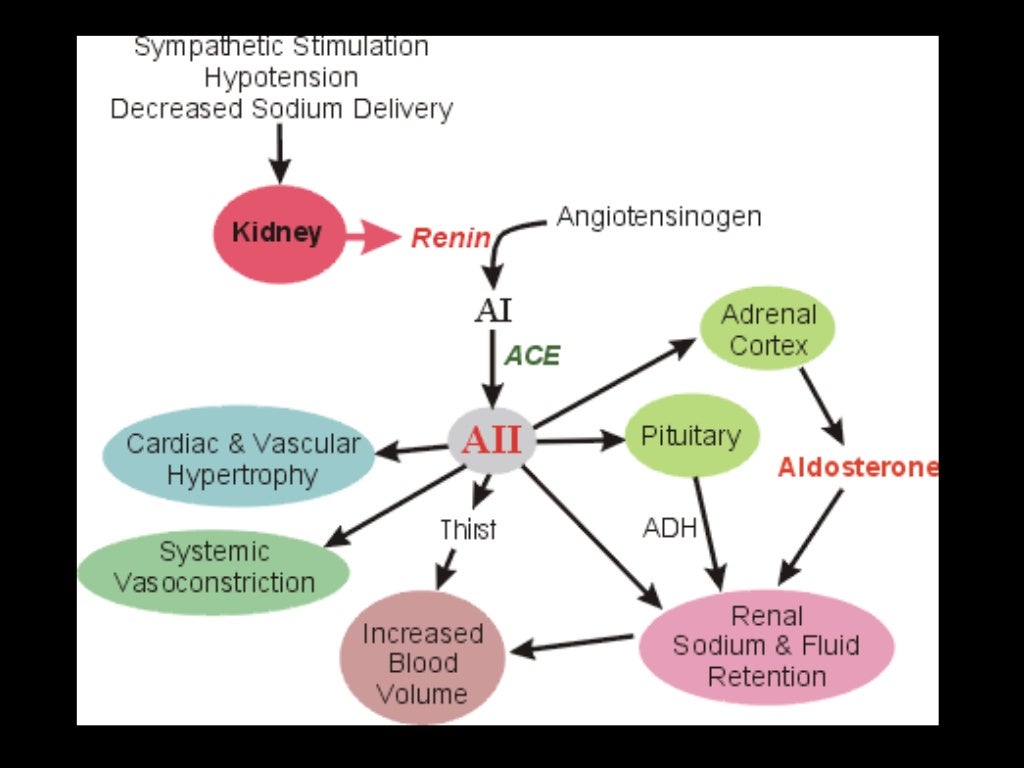
Introduction/Pathophysiology
Nursing Interventions For Decreased Cardiac Output
- Cardiac function
1. Increased HR 2. Altered myocardial contractility 3. Diagnosis for Atrial Fibrillation 4. Structural changes 5. Jugular vein distention 6. Extra heart sounds 7. Diminished peripheral pulses - Neurologic/Sensory function
1. Mental status change 2. Restlessness 3. Anxiety 4. Lethargy
Supplemental Material
- Client case
Client presents to the ER with the chief complaint of fatigue and shortness of breath when engaging in mild physical activity. Client has also noticed a recent weight gain and swelling in ankles. Client’s current blood pressure is 146/80 and heartbeat is 70 bpm. Client has a history o… - Based on the client case, what are the symptoms predictive of heart failure?
Answer: shortness of breath, fatigue, edema
References
- Vincent JL. Understanding cardiac output. Crit Care. 2008;12(4):174. doi:10.1186/cc6975
- King J, Lowery DR. Physiology, Cardiac Output. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; September 15, 2020.