
A physical system tends to possess static equilibrium if and only if it satisfies the following conditions:
- The Sum of all the forces acting in every direction must be equal to zero. i.e., ΣFX =ΣFY = 0
- The Sum of total torque acting in clockwise and counterclockwise directions must be zero. i.e., ΣτX=ΣτY=0
- The linear momentum of each particle in the physical system must be zero.
What are the conditions for static equilibrium?
Identify the physical conditions of static equilibrium. Draw a free-body diagram for a rigid body acted on by forces. Explain how the conditions for equilibrium allow us to solve statics problems. We say that a rigid body is in equilibrium when both its linear and angular acceleration are zero relative to an inertial frame of reference.
How do you analyze a static equilibrium?
Analyzing a Static Equilibrium Situation. "Static" means stationary or at rest. A common physics lab is to hang an object by two or more strings and to measure the forces that are exerted at angles upon the object to support its weight. The state of the object is analyzed in terms of the forces acting upon the object.
What are the laws of equilibrium in physics?
Equilibrium and Statics. If an object is at equilibrium, then the forces are balanced. Balanced is the key word that is used to describe equilibrium situations. Thus, the net force is zero and the acceleration is 0 m/s/s. Objects at equilibrium must have an acceleration of 0 m/s/s. This extends from Newton's first law of motion.
How many people can achieve complete static equilibrium?
Only 3% of people can do this. Click to play for free! To achieve complete static equilibrium, a system must have both rotational equilibrium (have a net torque of zero) and translational equilibrium (have a net force of zero). Why is static equilibrium important?

What creates static equilibrium?
When all the forces that act upon an object are balanced, then the object is said to be in a state of equilibrium. The forces are considered to be balanced if the rightward forces are balanced by the leftward forces and the upward forces are balanced by the downward forces.
What are the requirements for equilibrium?
The sum or resultant of all external forces acting on the body must be equal to zero. The sum or resultant of all external torques from external forces acting on the object must be zero.
What is the first condition for static equilibrium?
Statics is the study of forces in equilibrium. Two conditions must be met to achieve equilibrium, which is defined to be motion without linear or rotational acceleration. The first condition necessary to achieve equilibrium is that the net external force on the system must be zero, so thatnet F=0.
What are the 3 condition of equilibrium?
A solid body submitted to three forces whose lines of action are not parallel is in equilibrium if the three following conditions apply : The lines of action are coplanar (in the same plane) The lines of action are convergent (they cross at the same point) The vector sum of these forces is equal to the zero vector.
What are the conditions for static and dynamic equilibrium?
For example a book lying on a table is in static equilibrium. ii When a body remains in the same state of motion translational or rotational under the influence of the applied forces the body is said to be in dynamic equilibrium.
What is static equilibrium in physics?
Static equilibrium is a state where bodies are at rest; dynamic equilibrium is a state where bodies are moving at a constant velocity (rectilinear motion). In both cases the sum of the forces acting on them is zero.
What are the 3 equations of static equilibrium?
In order for a system to be in equilibrium, it must satisfy all three equations of equilibrium, Sum Fx = 0, Sum Fy = 0 and Sum M = 0.
What is an example of static equilibrium?
For an object to be considered in static equilibrium, it should satisfy two conditions: (1) the net force acting on the object is zero; and (2) the net torque acting on the object is also zero. A book at rest on top of a table and a balanced seesaw are examples of systems under static equilibrium.
What are the 4 types of equilibrium?
5.6: Types of EquilibriumStable Equilibrium.Unstable Equilibrium.Metastable Equilibrium.
Which of these objects is in static equilibrium?
Objects in static equilibrium are objects that are not accelerating (either linear acceleration or angular acceleration). These objects may be stationary, such as a building or a bridge, or they may have a constant velocity, such as a car or truck moving at a constant speed on a straight patch of road.
How do you know if a reaction is at equilibrium?
If K > Q, a reaction will proceed forward, converting reactants into products. If K < Q, the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction, converting products into reactants. If Q = K then the system is already at equilibrium.
What is the equation for the equilibrium?
The equilibrium equations (balance of linear momentum) are given in index form as(1.4)σji,j+bi=ρu¨i,i,j=1,2,3where σij are components of (Cauchy) stress, ρ is mass density, and bi are body force components.
How do you know if a mixture is in equilibrium?
If Qc < Kc, the reaction will go to the right. If Qc = Kc, the reaction mixture is at equilibrium. The equilibrium constant allows us to calculate final equilibrium composition of reactants and products for given initial concentrations.
What is the composition of the equilibrium mixture?
Equilibrium composition is defined as the composition of reaction products occurring after the reaction rates and reaction temperature have stabilized adiabatically.
What is static equilibrium?
A special case of static equilibrium occurs when all external forces on an object act at or along the axis of rotation or when the spatial extension of the object can be disregarded. In such a case, the object can be effectively treated like a point mass. In this special case, we need not worry about the second equilibrium condition, Figure, because all torques are identically zero and the first equilibrium condition (for forces) is the only condition to be satisfied. The free-body diagram and problem-solving strategy for this special case were outlined in Newton’s Laws of Motion and Applications of Newton’s Laws. You will see a typical equilibrium situation involving only the first equilibrium condition in the next example.
How to tell if a rigid body is in static equilibrium?
We say that a rigid body is in static equilibrium when it is at rest in our selected frame of reference. Notice that the distinction between the state of rest and a state of uniform motion is artificial —that is, an object may be at rest in our selected frame of reference, yet to an observer moving at constant velocity relative to our frame, the same object appears to be in uniform motion with constant velocity. Because the motion is relative, what is in static equilibrium to us is in dynamic equilibrium to the moving observer, and vice versa. Since the laws of physics are identical for all inertial reference frames, in an inertial frame of reference, there is no distinction between static equilibrium and equilibrium.
What is the first equilibrium condition?
The first equilibrium condition, Figure, is the equilibrium condition for forces, which we encountered when studying applications of Newton’s laws.
When solving static equilibrium problems, are we free to choose the pivot location?
This example shows that when solving static equilibrium problems, we are free to choose the pivot location. For different choices of the pivot point we have different sets of equilibrium conditions to solve. However, all choices lead to the same solution to the problem.
What is the equilibrium equation for the x direction?
The equilibrium equation for the x -direction tells us that the tension T 1 T 1 in the 5.0-cm string is twice the tension T 2 T 2 in the 10.0-cm string. Therefore, the shorter string will snap. When we use the first equation to eliminate T 2 T 2 from the second equation, we obtain the relation between the mass m m on the pan and the tension T 1 T 1 in the shorter string:
How many terms are in each equilibrium condition?
Each equilibrium condition contains only three terms because there are N = 3 N = 3 forces acting on the car. The first equilibrium condition, Figure, reads
What happens when there is only one external force acting on an object?
If there is only one external force (or torque) acting on an object, it cannot be in equilibrium.
How to solve static equilibrium?
By the end of this section, you will be able to: 1 Identify the physical conditions of static equilibrium. 2 Draw a free-body diagram for a rigid body acted on by forces. 3 Explain how the conditions for equilibrium allow us to solve statics problems.
How to tell if a rigid body is in static equilibrium?
We say that a rigid body is in static equilibrium when it is at rest in our selected frame of reference. Notice that the distinction between the state of rest and a state of uniform motion is artificial —that is, an object may be at rest in our selected frame of reference, yet to an observer moving at constant velocity relative to our frame, the same object appears to be in uniform motion with constant velocity. Because the motion is relative, what is in static equilibrium to us is in dynamic equilibrium to the moving observer, and vice versa. Since the laws of physics are identical for all inertial reference frames, in an inertial frame of reference, there is no distinction between static equilibrium and equilibrium.
What is the first equilibrium condition?
The first equilibrium condition, (Figure), is the equilibrium condition for forces, which we encountered when studying applications of Newton’s laws.
When solving static equilibrium problems, are we free to choose the pivot location?
This example shows that when solving static equilibrium problems, we are free to choose the pivot location. For different choices of the pivot point we have different sets of equilibrium conditions to solve. However, all choices lead to the same solution to the problem.
How many terms are in each equilibrium condition?
Each equilibrium condition contains only three terms because there are N =3 N = 3 forces acting on the car. The first equilibrium condition, (Figure), reads
Why is critical mass smaller in an elevator?
If the elevator moves up with acceleration, the critical mass is smaller because the weight of M +m M + m becomes larger by an apparent weight due to the acceleration of the elevator. Still, in all cases the shorter string breaks first.
Which equilibrium condition expresses rotational equilibrium?
The second equilibrium condition for the static equilibrium of a rigid body expresses rotational equilibrium:
Which is the correct option for static equilibrium?
A1 The correct option is A., which is “it is the equilibrium of a system whose parts are in motion.” This is because static equilibrium is the equilibrium of a system whose parts are at rest.
What is the basic condition of static equilibrium?
The fundamental and basic condition for static equilibrium is that an object must not be experiencing any type of motion, irrespective of translational or rotational. Furthermore, an object which is in translational equilibrium does not travel from one place to another.
What is the requirement of translational equilibrium?
The requirement with translational equilibrium is that the vector sum of all external forces is zero. Moreover, the directions and magnitude of external forces cancel each other out. The requirement with rotational equilibrium is that all the external torques cancel each other out.
Why is static equilibrium important?
An object which is in static equilibrium is unable to move. This is because all the forces which act on it compensate for one another. This concept is quite important in the design of rigid structures.
Which equilibrium condition expresses rotational equilibrium?
The second equilibrium condition for the static equilibrium of a particular rigid body expresses rotational equilibrium:
Which equation shows the first equilibrium condition?
Equation (2) shows the first equilibrium condition. Moreover, this is the equilibrium condition for forces which one encounters when studying the applications of Newton’s laws.
Is equilibrium valid for rotational dynamics?
Moreover, this equation for equilibrium is certainly valid for rotational dynamics about any axis of rotation.
What is static equilibrium?
Static Equilibrium is when the net force of an object is 0, and the object is at rest. For example, if you put your phone on the table, there are two forces acting on it. The force of gravity and the normal force.
What is the first condition for equilibrium?
The first condition for equilibrium is that the net external force is equal to zero. Expressed in vector form, the first condition is stated,
How to find torque as a result of gravity?
In summary, to find the torque as a result of gravity acting on an object, find the vector between the axis and the center of mass of the object, and calculate the cross product of that vector and the force of gravity on the object.
When considering what makes a new high-tech product or service successful, what is the first inclination?
When considering what makes a new high-tech product or service successful, our first inclination directs us to the underlying technologies that differentiate the product. Are these components suitable to achieve the target goal for performance? Let’s assume they do, your journey has only
Is an airplane in static equilibrium?
However, because it is maintaining a constant velocity, it is not in static equilibrium.
Does the condition of chemical equilibrium specify cessation of chemical change?
As always, the condition of chemical equilibrium does NOT specify cessation of chemical change, it DOES specify equality of forward and reverse rates … and so the forward and reverse rates STILL operate DYNAMICALLY….
Is a phone static?
Therefore, your phone is at static equilibrium. The force of gravity is cancelled out by the normal force (the force the table exerts on it to support it). Pretty much anything in the real world that has no acceleration whatsoever, is at static equilibrium. However, it must not be moving. If it is moving, the equilibrium is no longer considered static.
What is static equilibrium?
If all the forces acting on a motionless object are balanced, it is said to be in static equilibrium. To understand the concept of static equilibrium is it important to determine the forces acting on the object and, their directions. On determining the forces, we must find the vector sum of these forces.
When is a body in equilibrium?
A body is said to be in equilibrium when its neither in a state of motion nor its state of energy changes over a period of time. An undisturbed object continues to remain in its state of equilibrium. ScienceStruck explains with examples how to compute static equilibrium.
How to tell if a system is stable or unstable?
Equilibrium can be stable or unstable depending upon how long the system can remain in its state of equilibrium . A body in equilibrium that is disturbed, but comes back to equilibrium is said to be stable. Consider stirring tea in a mug. It becomes still after sometime. A body in equilibrium that is disturbed, and loses it state of equilibrium permanently is said to unstable. Consider a tennis ball balanced on a racket. It can fall if moved a little. When an object is disturbed by external forces which impart acceleration to it, it loses its stable state of equilibrium. This article will help you with static equilibrium calculations.
What happens to an object in equilibrium when it is disturbed?
Consider a tennis ball balanced on a racket. It can fall if moved a little. When an object is disturbed by external forces which impart acceleration to it, it loses its stable state of equilibrium.
What does it mean when the vector sum of all the forces acting on an object is zero?
If the vector sum of all the forces acting on the object is zero, implies that object is in translational equilibrium. In other words net external force should be zero. If the sum of torques acting externally on the object is zero, implies that the object is in rotational equilibrium.
What forces are in opposite directions when a book is placed on a table?
Book placed on a table. A book placed on the table experiences two forces, the upward force of the table and downward force of gravity. These forces are in opposite directions and have the same magnitude thus, balancing each other. Hence, the book is considered to be in a state of equilibrium.
Is a body under the influence of equal and opposite forces always in equilibrium?
A body under the influence of equal and opposite forces is not always in equilibrium. Consider the following two cases.
What is the net force of equilibrium?
In conclusion, equilibrium is the state of an object in which all the forces acting upon it are balanced. In such cases, the net force is 0 Newton. Knowing the forces acting upon an object, trigonometric functions can be utilized to determine the horizontal and vertical components of each force. If at equilibrium, then all the vertical components must balance and all the horizontal components must balance.
Why are two objects at equilibrium?
Note that the two objects are at equilibrium because the forces that act upon them are balanced; however, the individual forces are not equal to each other. The 50 N force is not equal to the 30 N force. If an object is at equilibrium, then the forces are balanced.
Is 0 m/s/s an object at equilibrium?
But having an acceleration of 0 m/s/s does not mean the object is at rest. An object at equilibrium is either ... at rest and staying at rest, or. in motion and continuing in motion with the same speed and direction. This too extends from Newton's first law of motion.
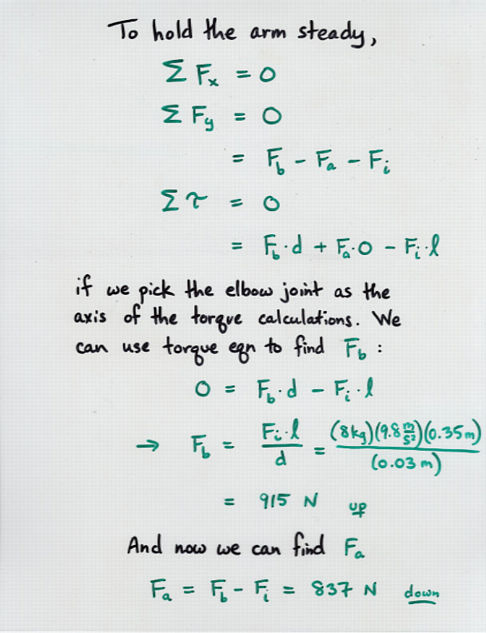
Definition and Meaning of Static Equilibrium
A Balance of Forces
- The fundamental and basic condition for static equilibrium is that an object must not be experiencing any type of motion, irrespective of translational or rotational. Furthermore, an object which is in translational equilibrium does not travel from one place to another. In contrast, an object in rotational equilibrium is certainly not rotating arou...
Conditions and Equations For Static Equilibrium
- According to Newton’s second law of motion, the linear acceleration of a rigid body takes place due to net force acting on it. Its representation is as follows: ∑kF⃗ k=ma⃗ CM. (1) Here, the sum of all the external forces acting on the object or body, “m” is its mass and a⃗ CM refers to the linear acceleration of its centre of mass. Furthermore, in equilibrium, the acceleration certainly happen…
Solved Question For You
- Q1Which of the following is not true with regards to static equilibrium? A. It is the equilibrium of a system whose parts are in motion B. It refers to any system in which the sum of the forces, and torque, on each particle of the system happens to be zero C. It takes place when all the forces acting on an object are balanced and the object is not in motion in relation to the relative plane D…