What are different methods of resolution of racemic mixture?
The resolution processes can be classified in general into chiral and kinetic resolution. In a chiral resolution, the interaction of the racemic mixture with a pure enantiomer forms diastereomers. These are then separated owing to the difference in their physical properties.
What is racemic modification and resolution of racemic mixture?
A mixture of equal parts of enantiomers is called a racemic modification. The process of separating a racemate into pure enantiomers is known as resolution. Recently, various optically active drugs are used for the treatment for various diseases.
Which is the best method for resolution of racemic mixture?
A chiral base such as brucine, strychnine, l-phenyl ethanamine can be used to dissolve racemic acids. Racemic bases can also be treated by using chiral acids such as (+) tartaric acid, (–) malic acid, (–) mandelic acid, and (+) camphoric acid.
What is racemic mixture with example?
It is always optically inactive since rotation caused by the molecules of one enantiomer is exactly cancelled by equal and opposite rotation caused by the molecules of the other enantiomers. for example, an equimolar mixture of (+)-2-bromobutane and (-)-2-bromobutane is called a racemix mixture.
Why is resolution of enantiomers important?
Chiral resolution, or enantiomeric resolution, is a process in stereochemistry for the separation of racemic compounds into their enantiomers. It is an important tool in the production of optically active compounds, including drugs. Another term with the same meaning is optical resolution.
Why is the resolution of racemic mixture difficult?
Separation of racemates into their component enantiomers is a process called resolution. Since enantiomers have identical physical properties, such as solubility and melting point, resolution is extremely difficult.
What is method of resolution?
Separation of different components in a racemic mixtwre is known as resolution. Different methods used for resolutpon are 1) By using enzymes 2) Conversion to diastereomers 3) Chromatographic method using special adsorbents.
What is meant by resolution in chemistry?
resolution, also called optical resolution or chiral resolution, in chemistry, any process by which a racemic mixture is separated into its two constituent enantiomers.
Why racemic mixture is formed?
Racemic mixtures are often formed when achiral substances are converted into chiral ones. This is due to the fact that chirality can only be distinguished in a chiral environment. An achiral substance in an achiral environment has no preference to form one enantiomer over another.
Is a racemic mixture optically active?
One interesting aspect about a racemic mixture is that it is optically inactive, meaning it does not rotate plane polarized light. Actually to be more technical, it does rotate light but it rotates it in both directions by equal degrees and so the net rotation is zero.
What is the difference between racemic mixture and enantiomers?
Enantiomers are stereoisomers which are nonsuperimposable, mirror images. A mixture of equal amounts of two stereoisomers of an optically active substance is called a racemic mixture or racemate.
Are enantiomers optically active?
Enantiomers have identical chemical and physical properties and are indistinguishable from each other except for the direction of rotation of the plane of polarized light. They are described as optically active.
What are the different methods of resolution?
Different methods used for resolutpon are 1) By using enzymes 2) Conversion to diastereomers 3) Chromatographic method using special adsorbents. 4) Mechanical Separation 5) Deracemization.
What is racemic mixture Class 12?
racemic mixture, also called racemate, a mixture of equal quantities of two enantiomers, or substances that have dissymmetric molecular structures that are mirror images of one another.
What is biochemical method of resolution?
Resolution by the biochemical method which makes use of the ability of the microorganisms, their enzymatic systems, to destroy one enantiomer more rapidly than the other.
What is enzymatic resolution?
The enzymatic kinetic resolution involves the use of a biocatalyst to discriminate between the enantiomers and improve the rate of hydrolysis or esterification of one instead of the other.
1. How can you identify the compounds of a racemate mixture?
A racemic mixture, or racemate, is a solution in which both enantiomers of a substance are present in equal proportions. A (d/l)- or ()- prefix in...
2. What are the other difference in the physical properties of enantiomers?
It is hard to find differences between two enantiomers as their physical properties are almost similar. Apart from the polarization effect, enantio...
3. Where do enantiomers get their name ‘racemate’ from?
The term ‘racemate’ comes from the Latin word ‘racemes’ which means a bunch of grapes. As the first enantiomers, tartaric acid and racemic acid wer...
4. How is racemate synthesized?
A chemical process that produces a chiral product will always give a racemate if there is no chiral influence (for example, a chiral catalyst, solv...
5. What are the properties of the racemic mixture?
There is no net rotation of plane-polarized light in a racemate, making it optically inert. The two enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light in dif...
What is a 1:1 equimolar mixture?
Thus, an equimolar ( 1:1) mixture of the enantiomers ( dextro and laevo forms) is called a racemic mixture. It is represented as dl forms and will be optically inactive. The process of converting d or l form of an optically active compound in a racemic form ( dl) is called as racemisation and the process of separation of a racemic mixture ...
What is a mixture that when dissolved in water does not rotate the path of plane polarized light?
Such a mixture is referred to as a racemic mixture . Thus, an equimolar ( 1:1) mixture of the enantiomers ( dextro and laevo forms) is called a racemic mixture .
Why is racemic mixture formed simultaneously?
Racemic Mixture: Whenever we synthesize an enantiomer in the laboratory, the other enantiomer of the same compound is also formed simultaneously because the two forms differ only in the tetrahedral arrangement of the atoms or group of atom about asymmetric carbon.
Why is it so difficult to separate enantiomers?
It is quite difficult to separate enantiomers because they possess similar physical properties and cannot be separated by ordinary methods such as fractional distillation or fractional crystallisation. Resolution of the racemic mixture is carried out by special techniques.
What reagents can be used to resolve aldehydes?
Aldehydes and Ketones- These can be resolved with the help of optically active reagents such as methyl hydrazine, menthyl semicarbazide etc.
Which acid can be resolved with the help of optically active bases?
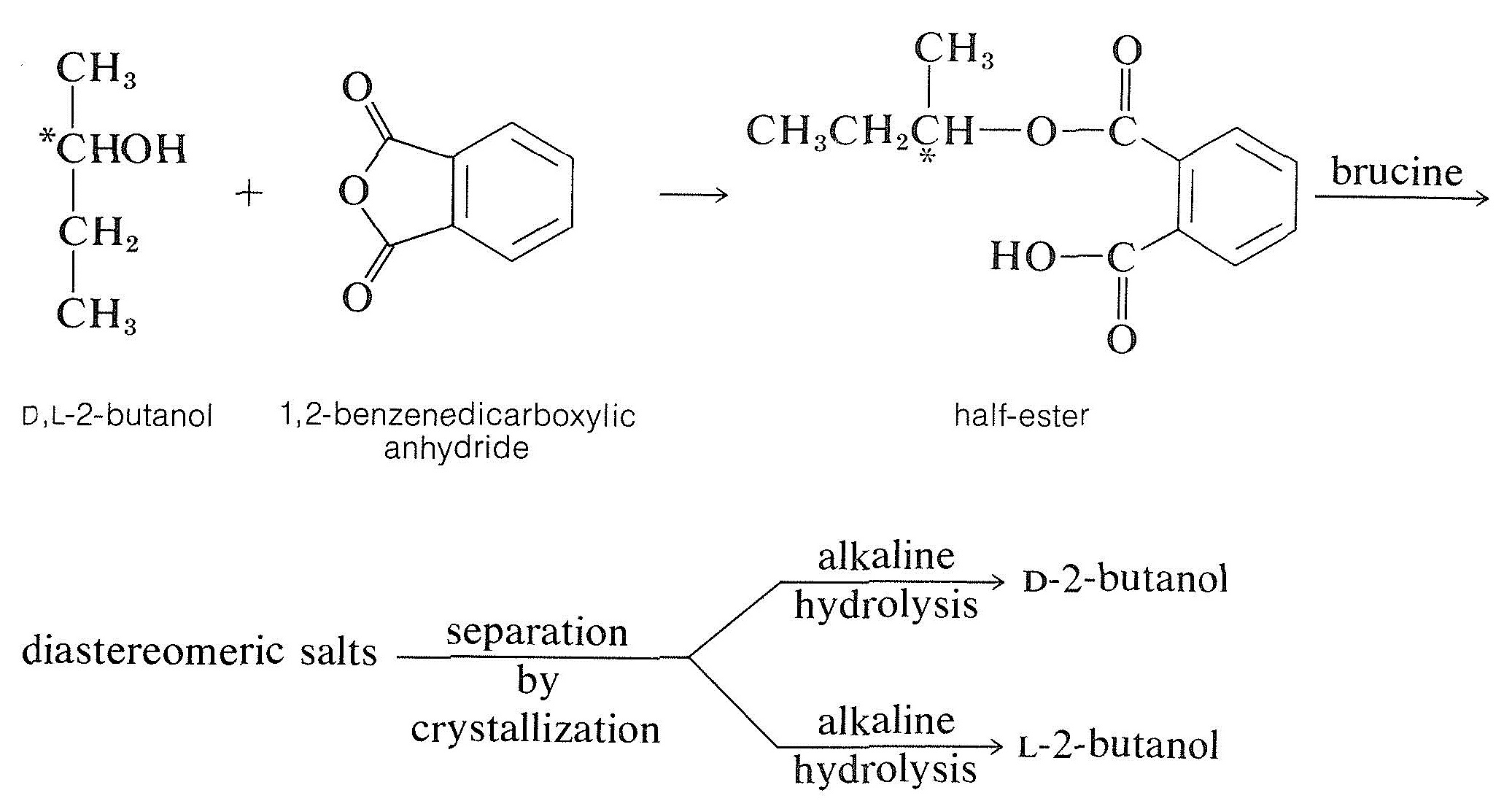
Acids- Racemic modification s of acids can be resolved with the help of optically active bases such as brucine, strychnine, quinine, morphine etc.
What is the tendency of a process to occur naturally called?
They are also called feasible processes. Thus, the tendency of a process to occur naturally is called the spontaneity. The spontaneous processes occur with or without the initiation. Spontaneous processes need not to be instantaneous. Spontaneous processes include both physical and chemical reactions.
What is a 1:1 equimolar mixture?from gkscientist.com
Thus, an equimolar ( 1:1) mixture of the enantiomers ( dextro and laevo forms) is called a racemic mixture. It is represented as dl forms and will be optically inactive. The process of converting d or l form of an optically active compound in a racemic form ( dl) is called as racemisation and the process of separation of a racemic mixture ...
What is a mixture that when dissolved in water does not rotate the path of plane polarized light?from gkscientist.com
Such a mixture is referred to as a racemic mixture . Thus, an equimolar ( 1:1) mixture of the enantiomers ( dextro and laevo forms) is called a racemic mixture .
Why is racemic mixture formed simultaneously?from gkscientist.com
Racemic Mixture: Whenever we synthesize an enantiomer in the laboratory, the other enantiomer of the same compound is also formed simultaneously because the two forms differ only in the tetrahedral arrangement of the atoms or group of atom about asymmetric carbon.
Why is it so difficult to separate enantiomers?from gkscientist.com
It is quite difficult to separate enantiomers because they possess similar physical properties and cannot be separated by ordinary methods such as fractional distillation or fractional crystallisation. Resolution of the racemic mixture is carried out by special techniques.
What reagents can be used to resolve aldehydes?from gkscientist.com
Aldehydes and Ketones- These can be resolved with the help of optically active reagents such as methyl hydrazine, menthyl semicarbazide etc.
Which acid can be resolved with the help of optically active bases?from gkscientist.com
Acids- Racemic modification s of acids can be resolved with the help of optically active bases such as brucine, strychnine, quinine, morphine etc.
What is the tendency of a process to occur naturally called?from gkscientist.com
They are also called feasible processes. Thus, the tendency of a process to occur naturally is called the spontaneity. The spontaneous processes occur with or without the initiation. Spontaneous processes need not to be instantaneous. Spontaneous processes include both physical and chemical reactions.
What is a racemic isomer?
Racemic mixture, also called racemate, a mixture of equal quantities of two enantiomers, or substances that have dissymmetric molecular structures that are mirror images of one another.
Why is the racemic mixture optically inactive?
Each enantiomer rotates the plane of polarization of plane-polarized light through a characteristic angle, but, because the rotatory effect of each component exactly cancels that of the other , the racemic mixture is optically inactive.
What is the name of the acid that is made of dextrorotatory and levorot answer?
The name is derived from racemic acid, the first example of such a substance to be carefully studied. Racemic acid, or, more properly, racemic tartaric acid, is a mixture of equal amounts of dextrorotatory and levorotatory tartaric acids; it is customarily designated D - or L -, or (+)- or (–)-, respectively, tartaric acid.
What is resolution in chemistry?
Resolution, in chemistry, any process by which a racemic mixture is separated into its two constituent enantiomers. (Enantiomers are pairs of substances that have dissymmetric arrangements of atoms and structures that are nonsuperposable mirror images of one another.) Two important methods of resolution…. History at your fingertips.
What is tartaric acid?
tartaric acid. Tartaric acid, a dicarboxylic acid, one of the most widely distributed of plant acids, with a number of food and industrial uses. Along with several of its salts, cream of tartar (potassium hydrogen tartrate) and Rochelle salt (potassium sodium tartrate), it is obtained from by-products of…. resolution.
What is an enantiomer?
Enantiomer, either of a pair of objects related to each other as the right hand is to the left—that is, as mirror images that cannot be reoriented so as to appear identical. An object that has a plane of symmetry cannot be an enantiomer because the object…
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
Racemic Modification
Racemic modifications or racemates are enantiomer mixtures of (+) and (-). When the enantiomers of a substance are mixed in equal amounts, a molecule of the isomer is canceled exactly by a molecule of the enantiomer. Therefore, the racemate has no overall optical rotation. There is no optical action in a racemic modification.
Resolution of Racemic Mixture
Known as resolution, this is the process of splitting a racemate into its enantiomers. Because enantiomers share the same physical properties (bp, mp, solubility), conventional methods cannot separate them. If enantiomers are converted into diastereomers, their differences in physical properties can be used to separate diastereomers.
Slideshows for you (19)
Surface and Interfacial tension [Part-4]u000b (Adsorption at liquid interface, Sur...
Featured (20)
Bridging the Gap Between Data Science & Engineer: Building High-Performance T...
Resolution of racemic mixture
5. METHODS: 1.Mechanical separation: some enantiomeric compounds form left-handed and right- handed (chiral) crystals which allow their separation by hand using magnifying glass and small forceps.
Major Properties
They are optically inactive mixtures because they cannot rotate the plane of plane-polarized light.
Separation of a racemate
It is very difficult to separate the two enantiomers in a racemic mixture because both the enantiomers have similar physical properties like melting point and boiling points, etc. But, we can separate the two enantiomers by using the method of crystallization, by using an enzyme, or by the conversion of enantiomers into diastereomers.
Examples of Racemic mixtures
S N 1reaction usually yields a pure racemic mixture because of 50% inversion and 50% retention in the reaction mechanism of an optically active organic compound. The reason behind this racemate formation is the intermediate sp 2 hybridized carbonation. This reaction mechanism (S N 1) is favored by polar aprotic solvents.
Enantiomers
The isomers that are non superimposable mirror images to each other are called enantiomers.
Racemic Mixture
A racemic mixture or a racemate is a 50/50 or equivalent ratio mixture of ‘+’ or ‘_’ enantiomers. So the overall optical rotation is zero. A racemate is denoted by d/l or +_.
Resolution of Racemic Mixture
A racemic mixture resolves to separate it into original or pure enantiomers. This is called resolution of racemic mixture. As enantiomers have similar physical properties like boiling point, solubility factor, chromatographic retention time, that’s why these cannot be resolved by common physical methods.
Methods Of Resolution Of Racemic Mixture
There are following some methods to resolve racemic mixture into enantiomers.
1. Mechanical Separation method
Based on different shapes crystals of enantiomers are separated from the racemic mixture. Crystals of two forms have different shapes these are separated by magnifying lenses or forceps. This method was first used by Pasteur who used the method to resolute sodium ammonium tartrate that crystallized in the form of a racemic mixture below 27 degree.
2. Biochemical separation method
This method was introduced by Pasteur. In this method, small membrane-bounded organisms like bacteria, fungi, molds, and yeast are grown into dilute racemic solution as a result of which these organisms eat one of the enantiomers immediately rather than the other.
3. Crystallization Method
In this method seedling of a saturated solution of a racemic mixture occur with a pure crystal of one of two enantiomers. After adding an enantiomer the solution becomes supersaturated and crystallization starts.
