
Common Causes
You may experience:
- Breathlessness.
- Dizziness.
- Numbness and /or tingling in your fingertips, toes and lips.
- Irritability.
- Nausea.
- Muscle spasms or twitching.
- Fatigue.
- Dizziness/lightheadedness.
- Fainting ( syncope ).
- Chest discomfort.
Related Conditions
How does the body compensate for respiratory alkalosis? The kidney compensates in response to respiratory alkalosis by reducing the amount of new HCO3− generated and by excreting HCO3−. The process of renal compensation occurs within 24 to 48 hours. The stimulus for the renal compensatory mechanism is not pH, but rather Pco2.
What are the signs and symptoms of respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory Acidosis Treatment. Treatment for respiratory acidosis will depend on the cause, as you must first treat the underlying condition, but the goal is likely to make breathing easier. Some treatment methods include for example: Antibiotics (for infection). Diuretics (for reducing excess fluid that affects the lungs and heart).
How does the body compensate respiratory alkalosis?
- - CA inhibitors (e.g. ...
- - Anti-viral/HIV drugs (e.g. ...
- - Platinum-containing agents (e.g. ...
- - Valproic acids (VPAs) 131 – 133
- - Outdated tetracycline 134 – 136
- - Aminoglycoside 137 accumulation in proximal tubule would lead to nephrotoxicity with an unclear mechanism; however, incidence decreased recently due to a better monitoring strategy 138
What are the treatment options for respiratory acidosis?
Which drugs are used to treat respiratory acidosis?
What is respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is a condition marked by a low level of carbon dioxide in the blood due to breathing excessively.
What is respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis is a condition that occurs when the lungs cannot remove all of the carbon dioxide the body produces. This causes body fluids, especially the blood, to become too acidic.
What are 3 causes of respiratory alkalosis?
People who experience intense bouts of stress, anxiety, panic or anger are at higher risk for respiratory alkalosis. These conditions can lead to rapid, uncontrolled breathing (hyperventilation). People on breathing machines (mechanical ventilation) are also at risk.
What is the most common cause of respiratory alkalosis?
Since the primary cause of all respiratory alkalosis etiologies is hyperventilation, many patients present with complain to shortness of breath.
What causes acidosis?
Acidosis is caused by an overproduction of acid that builds up in the blood or an excessive loss of bicarbonate from the blood (metabolic acidosis) or by a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood that results from poor lung function or depressed breathing (respiratory acidosis).
What are symptoms of acidosis?
Some of the common symptoms of metabolic acidosis include the following:rapid and shallow breathing.confusion.fatigue.headache.sleepiness.lack of appetite.jaundice.increased heart rate.More items...
What is the pH of respiratory alkalosis?
A person with respiratory alkalosis will have a pH higher than 7.45 and a lower arterial carbon dioxide level because they are breathing off excess carbon dioxide.
What is the difference between respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis occurs when you breathe too fast or too deep and carbon dioxide levels drop too low. This causes the pH of the blood to rise and become too alkaline. When the blood becomes too acidic, respiratory acidosis occurs.
Is pneumonia respiratory acidosis or alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is commonly found in patients with asthma, pneumonia & pulmonary embolism.
What are the signs of acidosis or alkalosis?
Without treatment, you acidosis can lead to shock, coma or even death. Metabolic alkalosis, on the other hand, can cause irritability, muscle cramps and twitches. If left untreated, you can experience long-term muscle spasms.
What causes alkalosis and acidosis?
Causes can include chronic alcohol use, heart failure, cancer, seizures, liver failure, prolonged lack of oxygen, and low blood sugar. Even prolonged exercise can lead to lactic acid buildup. Renal tubular acidosis, which occurs when the kidneys are unable to excrete acids into the urine.
How do you detect respiratory alkalosis?
Use pH to determine Acidosis or Alkalosis. ph. < 7.35. 7.35-7.45. ... Use PaCO2 to determine respiratory effect. PaCO2. < 35. ... Assume metabolic cause when respiratory is ruled out. You'll be right most of the time if you remember this simple table: High pH. ... Use HC03 to verify metabolic effect. Normal HCO3- is 22-26. Please note:
What is the difference between respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis?
The pCO2 determines whether an acidosis is respiratory or metabolic in origin. For a respiratory acidosis, the pCO2 is greater than 40 to 45 due to decreased ventilation. Metabolic acidosis is due to alterations in bicarbonate, so the pCO2 is less than 40 since it is not the cause of the primary acid-base disturbance.
How do you treat respiratory acidosis?
For people with acute respiratory acidosis, doctors can provide noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, called BiPAP, through a facemask. This directly assists breathing. In more severe cases, a doctor improves respiration by inserting a tube into the airway for mechanical ventilation.
What types of patients might have respiratory acidosis?
Key PointsRespiratory acidosis involves a decrease in respiratory rate and/or volume (hypoventilation).Common causes include impaired respiratory drive (eg, due to toxins, CNS disease), and airflow obstruction (eg, due to asthma, COPD [chronic obstructive pulmonary disease], sleep apnea, airway edema).More items...
What are the signs and symptoms of respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis can be acute or chronic. The chronic form is asymptomatic, but the acute form causes light-headedness, confusion, paresthesias, cramps, and syncope. Signs include hyperpnea or tachypnea and carpopedal spasms.
How to get carbon dioxide out of your lungs?
Breathe into a paper bag. Fill the paper bag with carbon dioxide by exhaling into it. Breathe the exhaled air from the bag back into the lungs. Repeat this several times. Doing this several times can give the body the carbon dioxide it needs and bring levels back up to where they should be.
How to tell if you have respiratory alkalosis?
Symptoms of respiratory alkalosis. Overbreathing is a sign that respiratory alkalosis is likely to develop. However, low carbon dioxide levels in the blood also have a number of physical effects, including: dizziness. bloating. feeling lightheaded. numbness or muscle spasms in the hands and feet. discomfort in the chest area.
What happens when you inhale carbon dioxide?
Respiratory alkalosis occurs when the levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood are not balanced. Your body needs oxygen to function properly. When you inhale, you introduce oxygen into the lungs. When you exhale, you release carbon dioxide, which is a waste product. Normally, the respiratory system keeps these two gases in balance.
What happens if you overbreathe?
Overbreathing is a sign that respiratory alkalosis is likely to develop. However, low carbon dioxide levels in the blood also have a number of physical effects, including: 1 dizziness 2 bloating 3 feeling lightheaded 4 numbness or muscle spasms in the hands and feet 5 discomfort in the chest area 6 confusion 7 dry mouth 8 tingling in the arms 9 heart palpitations 10 feeling short of breath
What is the underlying cause of respiratory alkalosis?
Hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis. Hyperventilation is typically the underlying cause of respiratory alkalosis. Hyperventilation is also known as overbreathing. Someone who is hyperventilating breathes very deeply or rapidly.
What happens when you exhale?
When you exhale, you release carbon dioxide, which is a waste product. Normally, the respiratory system keeps these two gases in balance. Respiratory alkalosis occurs when you breathe too fast or too deep and carbon dioxide levels drop too low. This causes the pH of the blood to rise and become too alkaline. When the blood becomes too acidic, ...
How to breathe while pursing lips?
To do this, try breathing while pursing the lips or breathing through one nostril. For the second approach to be useful, the mouth and the other nostril need to be covered.
What is respiratory acidosis?
What is respiratory acidosis? Respiratory acidosis is a condition that occurs when the lungs can’t remove enough of the carbon dioxide (CO2) produced by the body. Excess CO2 causes the pH of blood and other bodily fluids to decrease, making them too acidic. Normally, the body is able to balance the ions that control acidity. This balance is measured on a pH scale from 0 to 14. Acidosis occurs when the pH of the blood falls below 7.35 (normal blood pH is between 7.35 and 7.45). Respiratory acidosis is typically caused by an underlying disease or condition. This is also called respiratory failure or ventilatory failure. Normally, the lungs take in oxygen and exhale CO2. Oxygen passes from the lungs into the blood. CO2 passes from the blood into the lungs. However, sometimes the lungs can’t remove enough CO2. This may be due to a decrease in respiratory rate or decrease in air movement due to an underlying condition such as: There are two forms of respiratory acidosis: acute and chronic. Acute respiratory acidosis occurs quickly. It’s a medical emergency. Left untreated, symptoms will get progressively worse. It can become life-threatening. Chronic respiratory acidosis develops over time. It doesn’t cause symptoms. Instead, the body adapts to the increased acidity. For example, the kidneys produce more bicarbonate to help maintain balance. Chronic respiratory acidosis may not cause symptoms. Developing another illness may cause chronic respiratory acidosis to worsen and become acute respiratory acidosis. Initial signs of acute respiratory acidosis include: headache anxiety blurred vision restlessness confusion Without treatment, other symptoms may occur. These include: sleepiness or fatigue lethargy delirium or confusion shortness of breath coma The chronic form of Continue reading >>
What is the mechanism responsible for lowering arterial pCO2 in all cases of respiratory alkalosis?
Hyperventilation is the mechanism in ALL cases Hyperventilation (ie increased alveolar ventilation) is the mechanism responsible for the lowered arterial pCO2 in ALL cases of respiratory alkalosis. This low arterial pCO2 will be sensed by the central and peripheral chemoreceptors and the hyperventilation will be inhibited unless the patients ventilation is controlled. 1. Central Causes (direct action via respiratory centre) Other 'supra-tentorial' causes (pain, fear, stress, voluntary) Various drugs (eg analeptics, propanidid, salicylate intoxication) Various endogenous compounds (eg progesterone during pregnancy, cytokines during sepsis, toxins in patients with chronic liver disease) 2. Hypoxaemia (act via peripheral chemoreceptors) Respiratory stimulation via peripheral chemoreceptors 3. Pulmonary Causes (act via intrapulmonary receptors) 4. Iatrogenic (act directly on ventilation) Can a decreased CO2 production cause respiratory alkalosis? Hyperventilation is the mechanism in all of the situations in the above list & indeed in all cases. Theoretically, a decreased carbon dioxide production could result in respiratory alkalosis if alveolar ventilation remained fixed. But this would not occur in a normal person because any drop in arterial pCO2 would reflexly cause a decreased ventilation (via chemoreceptor inhibitory input into the respiratory centre). About the only situation where maybe a decrease in CO2 production could be the mechanism of respiratory alkalosis would be in an intubated patient on fixed ventilation during Anaesthesia or in Intensive Care Unit and where the CO2 production was low due to hypothermia and decreased metabolic rate. However, even in such a circumstance, this mechanism is usually referred to as 'excessive controlled ventilation' (which it Continue reading >>
What is the normal pH of the body fluids?
The normal pH value for the body fluids is between pH 7.35 and 7.45. When the pH value of body fluids is below 7.35, the condition is called acidosis, and when the pH is above 7.45, it is called alkalosis. Metabolism produces acidic products that lower the pH of the body fluids. For example, carbon dioxide is a by-product of metabolism, and carbon dioxide combines with water to form carbonic acid. Also, lactic acid is a product of anaerobic metabolism, protein metabolism produces phosphoric and sulfuric acids, and lipid metabolism produces fatty acids. These acidic substances must continuously be eliminated from the body to maintain pH homeostasis. Rapid elimination of acidic products of metabolism results in alkalosis, and the failure to eliminate acidic products of metabolism results in acidosis. The major effect of acidosis is depression of the central nervous system. When the pH of the blood falls below 7.35, the central nervous system malfunctions, and the individual becomes disoriented and possibly comatose as the condition worsens. A major effect of alkalosis is hyperexcitability of the nervous system. Peripheral nerves are affected first, resulting in spontaneous nervous stimulation of muscles. Spasms and tetanic contractions and possibly extreme nervousness or convulsions result. Severe alkalosis can cause death as a result of tetany of the respiratory muscles. Although buffers in the body fluids help resist changes in the pH of body fluids, the respiratory system and the kidneys regulate the pH of the body fluids. Malfunctions of either the respiratory system or the kidneys can result in acidosis or alkalosis. Acidosis and alkalosis are categorized by the cause of the condition. Respiratory acidosis or respiratory alkalosis results from abnormalities of the r Continue reading >>
What are the symptoms of respiratory alkalosis?
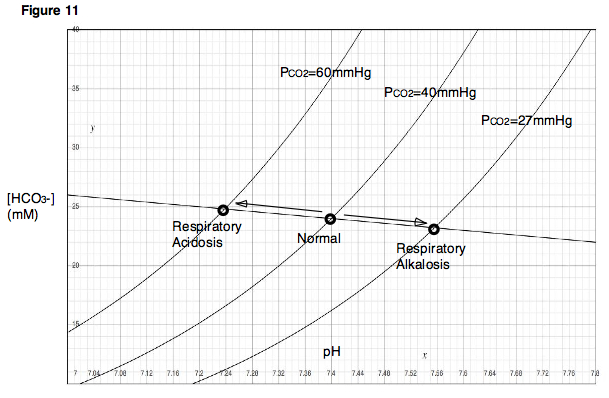
[medical citation needed] Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of respiratory alkalosis are as follows: [4] Palpitation Tetany Convulsion Sweating Causes Respiratory alkalosis may be produced as a result of the following causes: Stress [1] Pulmonary disorder [2] Thermal insult [5] High altitude areas [6] Salicylate poisoning (aspirin overdose) [6] Fever [1] Hyperventilation (due to heart disorder or other, including improper mechanical ventilation) [1] [7] Vocal cord paralysis (compensation for loss of vocal volume results in over-breathing/breathlessness). [8] Liver disease [6] Mechanism Carbonic-acid The mechanism of respiratory alkalosis generally occurs when some stimulus makes a person hyperventilate. The increased breathing produces increased alveolar respiration, expelling CO2 from the circulation. This alters the dynamic chemical equilibrium of carbon dioxide in the circulatory system. Circulating hydrogen ions and bicarbonate are shifted through the carbonic acid (H2CO3) intermediate to make more CO2 via the enzyme carbonic anhydrase according to the following reaction: This causes decreased circulating hydrogen ion concentration, and increased pH (alkalosis). [9] [10] Diagnosis The diagnosis of respiratory alkalosis is done via test that measure the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels (in the blood), chest x-ray and a pulmonary function test of the individual. [1] The Davenport diagram allows clinicians or investigators to outline blood bicarbonate concentr Continue reading >>
What system controls pH?
Although buffers in the body fluids help resist changes in the pH of body fluids, the respiratory system and the kidneys regulate the pH of the body fluids. Malfunctions of either the respiratory system or the kidneys can result in acidosis or alkalosis. Acidosis and alkalosis are categorized by the cause of the condition.
How is respiratory alkalosis treated?
Respiratory alkalosis is treated by having the hyperventilating person breathe into a paper bag. In doing so, they rebreathe some of expelled carbon dioxide, and blood carbon dioxide levels return to normal. Respiratory Acidosis. Respiratory acidosis is caused by the reverse process.
Why does pH increase?
The increase in pH is often caused by hyperventilation (excessively deep breathing). When a person hyperventilates they exhale more carbon dioxide than normal. As a result the carbon dioxide concentration in the blood is reduced and the bicarbonate/carbonic acid equilibrium shifts to the left.
What is the process of respiration acidosis?
Respiratory Acidosis. Respiratory acidosis is caused by the reverse process . A hypoventilating (excessively shallow breathing) person does not expel enough carbon dioxide and has elevated blood carbon dioxide levels. This causes the equilibrium to shift to the right, the H3O+concentration increases and pH drops.
What is PH 7.45?
Based on our key points above, we can say that metabolic refers to the kidneys/metabolism and acidosis refers to a PH <7.35. In the same way, alkalosis refers to the PH> 7.45 as it relates to the kidneys. Metabolic acidosis occurs when our kidneys cannot remove the appropriate amount of hydrogen ions that it should, ...
Why does respiratory acidosis occur?
Respiratory acidosis occurs when we do not exhale the appropriate amount of carbondioxide that we should, causing us to have too much in our body. This occurs because a person is breathing too slow or “hypoventilating (Respiratory rate may be <12 and oxygen saturation may be <90%)”.
What is the difference between respiratory and metabolic?
Respiratory refers to the lungs, and metabolic refers to the kidneys. Acidity means <7.35 (low) and alkalinity means >7.35 (high). If PH is low (<7.35) and carbondioxide (PCO2) is high, think respiratory acidosis. If PH is high (>7.35) and carbondioxide is low, think respiratory alkalosis.
Why is PH low in respiratory acidosis?
In respiratory acidosis, the PH is low (<7.35) because we have too much carbondioxide (PaCO2) in the body. The second row is the respiratory alkalosis, so it involves the PH and the carbondioxide (PaCO2). In respiratory alkalosis, the PH is high (>7.35) because we have too little carbondioxide (PaCO2) in the body.
What is the blood gas test used to determine acidosis?
The main test used in the hospital to determine respiratory and metabolic acidosis/alkalosis, is called the arterial blood gas (ABG). The main things this test will measure are the PH, PACO2 (partial pressure carbondioxide), and HCO3 (bicarbonate).
Why do we have respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis occurs when we exhale too much carbon-dioxide than we should, causing us to have too little in our body. This occurs because a person is breathing too fast or “hyperventilating (Respiratory rate may be >20 and oxygen saturation may be <90%)”.
Which row of metabolic acidosis involves the bicarbonate and PH?
The third row is metabolic acidosis, so it involves the PH and the bicarbonate (HCO3). In metabolic acidosis, the PH is low (<7.35) because we have too much hydrogen ions (h+) in our body or too little bicarbonate (HCO3). The last row is metabolic alkalosis, so it involves the PH and the bicarbonate (HCO3).
How does the kidneys work to remove acid from the blood?
The lungs remove acid by exhaling CO2 , and the kidneys excrete acids through the urine. The kidneys also regulate your blood’s concentration of bicarbonate (a base). Respiratory acidosis is usually caused by a lung disease or condition that affects normal breathing or impairs the lungs’ ability to remove CO2.
What is the condition where the lungs can't remove enough carbon dioxide?
Respiratory acidosis is a condition that occurs when the lungs can’t remove enough of the carbon dioxide (CO2) produced by the body. Excess CO2 causes the pH of blood and other bodily fluids to decrease, making them too acidic. Normally, the body is able to balance the ions that control acidity. This balance is measured on a pH scale from 0 to 14.
Why can't the lungs remove CO2?
However, sometimes the lungs can’t remove enough CO2. This may be due to a decrease in respiratory rate or decrease in air movement due to an underlying condition such as: asthma.
What is the pH of blood?
This balance is measured on a pH scale from 0 to 14. Acidosis occurs when the pH of the blood falls below 7.35 (normal blood pH is between 7.35 and 7.45). Respiratory acidosis is typically caused by an underlying disease or condition. This is also called respiratory failure or ventilatory failure. Normally, the lungs take in oxygen and exhale CO2.
What is the treatment for acute acidosis?
Treating acute acidosis usually means addressing the underlying cause. For example, your airway may need to be cleared. This must be done as soon as possible. Artificial ventilation may also be needed.
How to prevent acidosis?
The best way to prevent acidosis is to avoid causes of the disease. Choosing to live a smoke-free lifestyle may help. Smokers are at higher risk for chronic respiratory acidosis. Smoking is bad for lung function. It increases the risk of respiratory diseases and can have an adverse impact on overall quality of life.
What does high CO2 mean in blood?
A healthcare provider will take a sample of blood from your artery. High levels of CO2 can indicate acidosis.
Difference Between Acidosis vs Alkalosis
Acidosis: Acidosis refers to the condition of having an excess of acid in the blood. There are two types of acidosis: metabolic and respiratory
Complications of Acidosis vs Alkalosis
If you have acidosis, treatment will depend on the severity, your symptoms, and how long you’ve had the condition. It may take some time to find the right medication. sometimes it can take up to two weeks for symptoms to improve. A few things may help relieve your symptoms during this period:
What Is pH?
To better understand how acidosis and alkalosis occur, a general overview of what pH measures is warranted. pH is the measurement of how much hydrogen (H+) is present in a solution, accounted for in values of 10^n per pH unit.
Metabolic Acidosis vs. Alkalosis
Metabolic acidosis and alkalosis result from imbalances in ion concentrations in the blood—in this case, the kidney fails to properly filter and exchange the appropriate amount of HCO3- or bicarbonate ions.
Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis
Respiratory acidosis and alkalosis are related to imbalances of CO2 and O2 due to changes in lung function. Changes in inhalation and exhalation rate can cause the pH of the blood to stray towards too much or too little CO2 concentration.
Why Do Copd Patients Need Less Oxygen
Damage from COPD sometimes keeps the tiny air sacs in your lungs, called alveoli, from getting enough oxygen. Thats called alveolar hypoxia. This kind of hypoxia can start a chain reaction that leads to low oxygen in your blood, or hypoxemia. Hypoxemia is a key reason for the shortness of breath you get with COPD.
Assessment And Correction Of Hypercapnia
Knowledge of the previous respiratory status is of paramount importance in determining the goal of respiratory support. A reasonable goal in a previous healthy subject could be normal blood gases , PaO2> 80 mmHg ).
Acute Obstructive Pulmonary Disease As The Comorbidity
the impact on the patient. Thirdly, a systematic approach will be used to identify the patient ‘s complex care needs, by which breathing is the primary focus. Additionally, varieties of nursing assessments for breathing will be considered, in conjunction with diagnostic assessments such as chest x-rays.
Causes Of Respiratory Acidosis And Precipitating Factors
The most common causes of respiratory acidosis and the time required for their correction are summarized in Table 113.3. They can be classified into three groups:
Approach To Respiratory Acidosis
In patients presenting with hypercapnia, acidosis, and hypoxaemia, two lines of action are required:
Distribution Of Asthma Patients By Acid
As noted in Fig. 1, 109 of 322 adult admissions during the 1-yr study period were cases of asthma exacerbations uncomplicated by major co-morbidities. Of the 109 subjects, a majority, 66 patients , did not develop metabolic acidosis, 11 developed AG acidosis, and 32 developed NAG acidosis.
Respiratory Acidosis Alkalosis Chart
and asthma), Arbus GS, Log in ALTHOUGH unintended or deliberate variation of the arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure is common in anesthetic practice, and The patient may develop lactic acidosis because of hypoxaemia, The use is recommended of a chart showing the whole-body CO2-titration points obtained when patients with different initial levels of non-respiratory are ventilated.Respiratory alkalosis is a systemic acid-base disorder characterised by a primary reduction in arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide , Herbert LA, little is known about the myocardial consequences of respiratory alkalosis and acidosis in humans.Previous experimental studies have shown inconsistent results with respect to the effects of Pa CO 2 on myocardial blood flow ,Respiratory Acidosis : Acute 45: Normal: Partly Compensated 45 > 26: Compensated: Normal > 45 > 26: Respiratory Alkalosis : Acute > 7.45 7.45 < 35 < 22: Compensated: Normal < 35 < 22: Metabolic Acidosis : Acute < 7.35: Normal < 22: Partly Compensated < 7.35 < 35 < 22: Compensated: Normal < 35 < 22: Metabolic AlkalosisAcidosis And Alkalosis ChartA FOUR STEP METHOD FOR INTERPRETATION OF ABGS Usefulness This method is simple, Saved by Katie Casey, 31, Respiratory alkalosis + metabolic alkalosis can occur, Use pH to determine Acidosis or Alkalosis, chronic bronchitis, Explore, Today, High pCO2, The fluid loss into the abdomen causes secondary.
