Full Answer
What is RFLP and why is it important?
It’s a highly efficient way to make many copies of a DNA sequence. RFLP is Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism, which is a method for characterizing DNA on the basis of the size of the fragments that occur when you digest the DNA with a restriction enzyme.
What is the difference between real time PCR and RFLP?
Both are two different techniques. RFLP allows to identify DNA fragments based on unique patterns of restriction enzyme cutting in specific regions of DNA and see them in gel.whereas, Real time PCR, is an amplification of your target gene using specific primers and you can monitor the reaction in real time.
How do you detect RFLPs?
The basic technique for the detection of RFLPs involves fragmenting a sample of DNA with the application of a restriction enzyme, which can selectively cleave a DNA molecule wherever a short, specific sequence is recognized in a process known as a restriction digest.
What is the difference between RFLP markers and RFLPs probes?
Most RFLP markers are co-dominant (both alleles in heterozygous sample will be detected) and highly locus-specific. An RFLP probe is a labeled DNA sequence that hybridizes with one or more fragments of the digested DNA sample after they were separated by gel electrophoresis,...

What is RFLP and PCR?
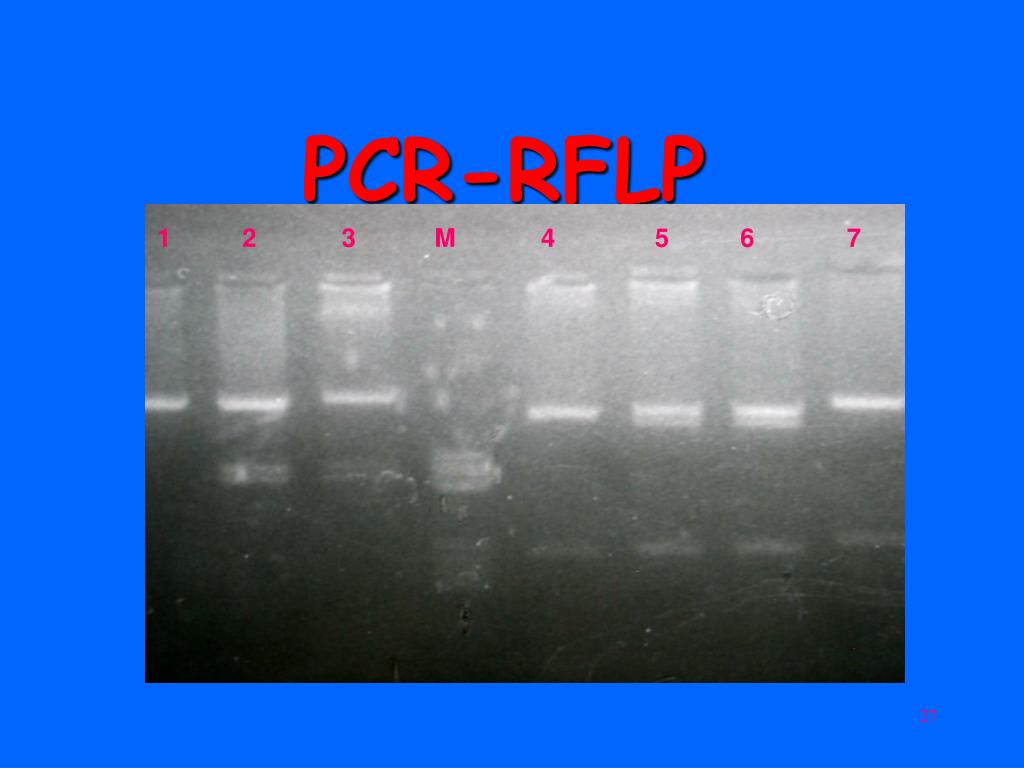
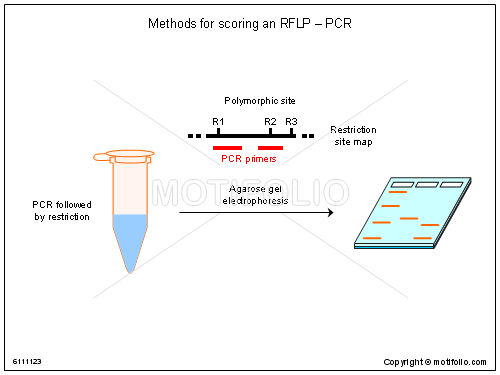
PCR-RFLP. Isolation of sufficient DNA for RFLP analysis is time consuming and labor intensive. However, PCR can be used to amplify very small amounts of DNA, usually in 2-3 hours, to the levels required for RFLP analysis. Therefore, more samples can be analyzed in a shorter time.
What is RFLP and how is it used?
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Such variation results in different sized (or length) DNA fragments produced by digesting the DNA with a restriction enzyme. RFLPs can be used as genetic markers, which are often used to follow the inheritance of DNA through families.
What is the principle of RFLP?
The principle of RFLP markers is that any genomic DNA can be differentiated according to the presence or absence of restriction enzyme sites. Restriction enzymes recognize and cut at the particular site.
What are the 4 steps of RFLP?
(1) Extract DNA from individuals A and B. (2) Use restriction enzymes to cut DNA. (3) Electrophoreses DNA fragments on agarose gel to separate them by size. (4) Transfer the DNA in the gel to a nylon membrane by Southern blot.
Why is RFLP important?
RFLP is a difference in the size of DNA restriction fragment (restriction map) between individuals. It can serve as a useful genetic marker for the analysis and mapping of a large genome. RFLP is based on the principle that small differences in the DNA sequence can alter restriction enzyme cutting patterns.
Is RFLP still used?
Although RFLP is less widely used now, it still has an important role in enabling mapping of the human genome as well as investigating genetic diseases. RFLP analysis is useful in finding where a specific gene for a disease lies on a chromosome and was one of the first methods used for genetic typing.
How does the RFLP method work quizlet?
The basic technique for detecting RFLPs involves fragmenting a sample of DNA by a restriction enzyme, which can recognize and cut DNA wherever a specific short sequence occurs, in a process known as restriction digest.
What are the advantages of RFLP?
The main advantages of RFLPs include: 1) high reliability, because it is generated from specific sites via known restriction enzymes and the results are constant over time and location. 2) Co-dominance, which means investigators are able to distinguish heterozygotes from homozygotes.
How is DNA isolated from a target?
Once the the DNA is isolated from the sample it is subjected to restriction digestion using restriction enzymes. The digested DNA sample is then subjected to gel electrophoresis, in which the DNA is separated based on its size.
What happens when two organisms differ in the distance between sites of cleavage of a particular restriction endon?
If two organisms differ in the distance between sites of cleavage of a particular restriction endonuclease, the length of the fragments produced will differ when the DNA is digested with a restriction enzyme. The similarity and differences of the patterns thus generated can be used to differentiate species (and even strains) from one another.
What is RFLP in biology?
Simply, the variations in the restriction DNA fragments length between individuals of a species is called RFLP. The basic technique of identifying such restriction fragment length polymorphisms involve fragmenting a sample of DNA by a restriction enzyme, which can recognize and cut DNA wherever a specific short sequence occurs, ...
What is RFLP analysis?
Although now largely obsolete due to the rise of inexpensive DNA sequencing technologies, RFLP analysis was the first DNA profiling technique inexpensive enough to seek widespread application.
How is DNA separated?
The resulting DNA fragments are then separated by length through a process known as agarose gel electrophoresis, and transferred to a membrane via the Southern blot procedure . Hybridization of the membrane to a labeled DNA probe then determines the length of the fragments which are complementary to the probe.
What is the advantage of RFLP analysis over PCR?
The main advantage of RFLP analysis over PCR-based protocols is that no prior sequence information, nor oligonucleotide synthesis, is required.
What is RFLP in genetics?
To measure recombination rates which can lead to a genetic map with the distance between RFLP loci. In the characterization of genetic diversity or breeding patterns in animal populations. RFLP has been developed for chromosomes mapping of humans, mice, maize, tomato, rice, etc.
How is RFLP used in genetics?
Analysis of RFLP variation in genomes was formerly a vital tool in genome mapping and genetic disease analysis. If researchers were trying to initially determine the chromosomal location of a particular disease gene, they would analyze the DNA of members of a family afflicted by the disease, and look for RFLP alleles that show a similar pattern of inheritance as that of the disease (see genetic linkage ). Once a disease gene was localized, RFLP analysis of other families could reveal who was at risk for the disease, or who was likely to be a carrier of the mutant genes. RFLP test is used in identification and differentiation of organisms by analyzing unique patterns in genome. It is also used in identification of recombination rate in the loci between restriction sites.
What is RFLP in PCR?
RFLP is still used in marker-assisted selection. Terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (TRFLP or sometimes T-RFLP) is a technique initially developed for characterizing bacterial communities in mixed-species samples. The technique has also been applied to other groups including soil fungi. TRFLP works by PCR amplification of DNA using primer pairs that have been labeled with fluorescent tags. The PCR products are then digested using RFLP enzymes and the resulting patterns visualized using a DNA sequencer. The results are analyzed either by simply counting and comparing bands or peaks in the TRFLP profile, or by matching bands from one or more TRFLP runs to a database of known species. The technique is similar in some aspects to temperature gradient or denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE and DGGE).
What is RFLP analysis?
In RFLP analysis, a DNA sample is digested into fragments by one or more restriction enzymes, and the resulting restriction fragments are then separated by gel electrophoresis according to their size. Although now largely obsolete due to the emergence of inexpensive DNA sequencing technologies, RFLP analysis was the first DNA profiling technique ...
What is RFLP in biology?
In molecular biology, restriction fragment length polymorphism ( RFLP) is a technique that exploits variations in homologous DNA sequences, known as polymorphisms, in order to distinguish individuals, populations, or species or to pinpoint the locations of genes within a sequence.The term may refer to a polymorphism itself, as detected through the differing locations of restriction enzyme sites, or to a related laboratory technique by which such differences can be illustrated. In RFLP analysis, a DNA sample is digested into fragments by one or more restriction enzymes, and the resulting restriction fragments are then separated by gel electrophoresis according to their size.
How long does it take to complete RFLP?
It requires a large amount of sample DNA, and the combined process of probe labeling, DNA fragmentation, electrophoresis, blotting, hybridization, washing, and autoradiography can take up to a month to complete. A limited version of the RFLP method that used oligonucleotide probes was reported in 1985. The results of the Human Genome Project have largely replaced the need for RFLP mapping, and the identification of many single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in that project (as well as the direct identification of many disease genes and mutations) has replaced the need for RFLP disease linkage analysis (see SNP genotyping ). The analysis of VNTR alleles continues, but is now usually performed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods. For example, the standard protocols for DNA fingerprinting involve PCR analysis of panels of more than a dozen VNTRs.
How to detect RFLPs?
The basic technique for the detection of RFLPs involves fragmenting a sample of DNA with the application of a restriction enzyme, which can selectively cleave a DNA molecule wherever a short, specific sequence is recognized in a process known as a restriction digest. The DNA fragments produced by the digest are then separated by length through a process known as agarose gel electrophoresis and transferred to a membrane via the Southern blot procedure. Hybridization of the membrane to a labeled DNA probe then determines the length of the fragments which are complementary to the probe. A restriction fragment length polymorphism is said to occur when the length of a detected fragment varies between individuals, indicating non-identical sequence homologies. Each fragment length is considered an allele, whether it actually contains a coding region or not, and can be used in subsequent genetic analysis.
Why is RFLP important?
RFLP analysis was an important early tool in genome mapping, localization of genes for genetic disorders, determination of risk for disease, and paternity testing .
How to type scrub typhus?
Scrub typhus isolates can be typed by PCR/RFLP or sequencing methods employing the conserved groEL operon and the more variable 56-kDa antigen genes [7,19,26,110,112] . The antigenic variation of O. tsutsugamushi is predominantly determined by the variablility of the 56-kDa TSA on the bacterial surface [113]. The encoding gene (approximately 1.6 kb) has been used for classification through full-length or partial nucleotide sequencing facilitating the discovery of new genotypes [22,110]. In 1993 a nested PCR with PCR/RFLP analysis based on the first hypervariable region (V1) of the 56-kDa type-specific antigen (TSA) gene enabled differentiation of prototype groups Karp, Kato, Gilliam, Kawasaki, Kuroki and Shimokoshi in patient samples and chigger mites [108]. A detailed study based on RFLP analysis of near-full length amplification of the 56-kDa TSA and antigenic determination of strains using type-specific monoclonal antibodies helped optimize this method further but required six restriction enzymes [114]. Horinouchi et al. designed a nested PCR assay specifically amplifying the first three hypervariable regions and optimized the RFLP procedure, reducing the number of restriction enzymes used from ten (HhaI, HinFI, AluI, PstI, HaeIII, NcoI, StyI, BamHI, Bsp1286I and BstEII) to two (HhaI, HinFI) without losing discriminatory power [110]. In Thailand, PCR/RFLP analyses of rodent and mite samples with restriction enzymes HhaI, HinfI and AluI [115], revealed the practical limitations of AluI digests, as the fragments are small and closely grouped rendering interpretation by gel electrophoresis difficult. The addition of other antigen genes to the 56-kDa TSA gene such as the 22-kDa, 47-kDa and scaC may provide a more robust approach for characterizing Orientia isolates [28,116,117]. For example, the recently characterized O. chuto found in the UAE was characterized using a multiple gene approach, including sequences of the 16 S rRNA gene (rrs), partial 56-kDa gene, and the full open reading frame of the 47-kDa gene.
What is kDNA analysis of T. cruzi?
kDNA RFLP analyses unraveled an unexpectedly high amount of genetic diversity in T. cruzi. Together with cloning experiments, kDNA restriction analysis demonstrated for the first time that single strains of T. cruzi could contain two or more distinct clonal genotypes ( Morel et al., 1980 ). The existence of these multiclonal T. cruzi strains was later confirmed by several groups using different techniques ( Deane et al., 1984; De Araujo and Chiari, 1988; Carneiro et al., 1991; Macedo et al., 1992a; Oliveira et al., 1998, 1999 ). Schizodemes presented some correlation with the isoenzyme classification, demonstrating that linkage disequilibrium can even occur between different (nuclear and mitochondrial) genome compartments ( Tibayrenc and Ayala, 1987 ).
What is RFLP pattern analysis?
RFLP pattern analysis usually involves comparison of RFLP fingerprints obtained for a given set of isolates. Pattern comparison should be objective, consistent, and scientifically based. Comparison or detection of differences between simple PCR-RFLP fingerprints may rely on direct visual inspection, but standardization becomes critical, when the aim is to compare a large set of diverse and complex RFLP fingerprints. Several software packages are available, allowing objective comparative analysis of fingerprints as well as long-term data storage. With such computer software, RFLP fingerprints can be normalized to a standard and then stored in a database so that a new fingerprint can be compared with those deposited previously. The computer software is also a prerequisite for a large-scale comparison as many software packages allow for cluster analysis or a comparison of a large data set. In general, a comparative analysis of RFLP fingerprints has two stages: first, a similarity matrix is created based on either the presence or absence of bands or variations in band intensities. After this, the fingerprints are grouped based on pattern similarities. The results of the comparisons usually are presented as a dendrogram, which is a tree illustrating the similarities of the RFLP patterns included in the analysis by grouping the fingerprints sharing common bands into a subset or cluster.
What is RFLP in DNA?
RFLP is an abbreviation of restriction fragment length polymorphism. It is a commonly employed tool to check the small but specific variations in a sequence of double-stranded DNA. It is based on the specificity of restriction endonucleases, which recognize a set of nucleotides called restriction site and cleave the DNA at those sites.
When was the first study of DNA polymorphism?
The first studies on DNA polymorphism of T. cruzi were published in 1980 by Morel et al., who reported on RFLPs of kinetoplast DNA (kDNA) minicircles (Morel et al., 1980 ). All members of the order Kinetoplastidae are characterized by the presence of a kDNA network within a single large mitochondrion.
How many species of Mangifera are there?
A study by Eiadthong et al. (1999), on 13 Mangifera species, classified the species into two groups based on eight informative mutation sites detected by four endonuclease enzymes. The monomorphic group of 11 Mangifera species formed a cluster with A. occidentale. This study used a combination of two types of molecular markers, RFLP and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP).
What is restriction fragment length polymorphism?
Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is one of the easiest ways to study the diversity of the microbes. The technique uses the simple restriction digestion of purified DNA from bacteria, and variation in the banding pattern in the digestion reveals the genetic diversity. RFLP has been successfully used for the study of diversity of V. cholerae strains ( Chowdhury et al., 2010 ). In a recent study, it has been stated that RFLP can be used to the study taxonomy of Y. pestis ( Qi et al., 2016 ). A recent study from Iran has suggested that RFLP can be used to study the S. aureus coagulase gene diversity from food products ( Dallal et al., 2016 ). Madec et al. recently used RFLP to study diversity in the plasmid from E. coli which was isolated from water source. RFLP is also useful for the study of Mtb diversity study ( Peres et al., 2018 ).
What is the difference between PCR and RFLP?
PCR is a technique to make many copies of a specific DNA region in vitro while RFLP is used to identify DNA fragments based on unique patterns of restriction enzyme cutting in specific regions of DNA and see them in gel.
What is PCR in biology?
PCR is the Polymerase Chain Reaction - a method for DNA amplification (making copies of a DNA segment). It’s a highly efficient way to make many copies of a DNA sequence.
What is RFLP grammarly?
It’s a highly efficient way to make many copies of a DNA sequence. RFLP is Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism, which is a method for characterizing DNA on the basis ...
Why are SNPs better than STRs?
The advantage of SNPs over STRs is that PCR fragments for SNPs are much shorter than for STR so that degraded DNA can also be used. SNPs are also more abundant in the genome than STR and have a lower mutation rate. Due to the single nucleotide variation, most SNPs have two different forms (alleles) in a population.
How are STRs analyzed?
DNA samples are analyzed by amplifying one or several of these STR regions. If there were differences in the size of the STRs between the samples it can be seen by size separation on gel.
Why is PCR important?
This is a big part of why PCR is an important tool: it produces enough copies of a DNA sequence that we can see or manipulate that region of DNA. Applications of PCR. Using PCR, a DNA sequence can be amplified millions or billions of times, producing enough DNA copies to be analyzed using other techniques.
Why is high temperature used in PCR?
As we'll see, high temperature is used repeatedly in PCR to denature the template DNA, or separate its strands. PCR primers. Like other DNA polymerases, Taq polymerase can only make DNA if it's given a primer, a short sequence of nucleotides that provides a starting point for DNA synthesis.
What is the difference between RFLP and real time PCR?
RFLP allows to identify DNA fragments based on unique patterns of restriction enzyme cutting in specific regions of DNA and see them in gel.whereas, Real time PCR, is an amplification of your target gene using specific primers and you can monitor the reaction in real time.
What is RFLP in DNA?
RFLP is simply a description of regions of DNA that do (or don't) have restriction sites for restriction endonuclease enzymes. It has lots of potential applications (forensics, DNA fingerprinting, crop breeding, genotyping, etc.). It's pretty easy to learn, I even use it with my undergrads.
Is qPCR a sensitive test?
qPCR is a very sensitive way to measure DNA (or cDNA) copy numbers. Again, it has LOTS of potential applications (disease diagnosis, gene expression, etc.). It's HARD to master and you'll spend much longer trouble-shooting than actually doing your experiment.
How It Works
- SNPsor INDELscan create or abolish restriction endonuclease (RE) recognition sites, thus affecting quantities and length of DNA fragments resulting from RE digestion.
Developing RFLP Probes
- Total DNA is digested with a methylation-sensitive enzyme (for example, PstI), thereby enriching the library for single- or low-copy expressed sequences (PstI clones are based on the suggestion tha...
- The digested DNA is size-fractionated on a preparative agarose gel, and fragments ranging from 500 to 2000 bp are excised, eluted and cloned into a plasmid vector (for example, pUC1…
- Total DNA is digested with a methylation-sensitive enzyme (for example, PstI), thereby enriching the library for single- or low-copy expressed sequences (PstI clones are based on the suggestion tha...
- The digested DNA is size-fractionated on a preparative agarose gel, and fragments ranging from 500 to 2000 bp are excised, eluted and cloned into a plasmid vector (for example, pUC18).
- Digests of the plasmids are screened to check for inserts.
- Southern blots of the inserts can be probed with total sheared DNA to select clones that hybridize to single- and low-copy sequences.
PCR-RFLP
- Isolation of sufficient DNA for RFLP analysis is time consuming and labor intensive. However, PCR can be used to amplify very small amounts of DNA, usually in 2-3 hours, to the levels required for RFLP analysis. Therefore, more samples can be analyzed in a shorter time. An alternative name for the technique is Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequence (CAPS)assay.
Resources
- "Polymorphism, Restriction Fragment Length"[MAJR]in PubMed Note: [MAJR] is a Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) tag for Major Heading. The tag is used to limit the search to articles for which major subjects are represented by terms included in the NLM MeSH database.
Disclaimer
- Mention of specific products or vendors on this website does not constitute an endorsement by the U.S. government.
Overview
In molecular biology, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is a technique that exploits variations in homologous DNA sequences, known as polymorphisms, in order to distinguish individuals, populations, or species or to pinpoint the locations of genes within a sequence. The term may refer to a polymorphism itself, as detected through the differing locations of restriction enzyme sites, or to a related laboratory technique by which such differences can be illustrated. I…
Alternatives
The technique for RFLP analysis is, however, slow and cumbersome. It requires a large amount of sample DNA, and the combined process of probe labeling, DNA fragmentation, electrophoresis, blotting, hybridization, washing, and autoradiography can take up to a month to complete. A limited version of the RFLP method that used oligonucleotide probes was reported in 1985. The results of the Human Genome Project have largely replaced the need for RFLP mapping, and the identificati…
RFLP analysis
The basic technique for the detection of RFLPs involves fragmenting a sample of DNA with the application of a restriction enzyme, which can selectively cleave a DNA molecule wherever a short, specific sequence is recognized in a process known as a restriction digest. The DNA fragments produced by the digest are then separated by length through a process known as agarose gel electrophoresis and transferred to a membrane via the Southern blot procedure. Hybridization of t…
Applications
Analysis of RFLP variation in genomes was formerly a vital tool in genome mapping and genetic disease analysis. If researchers were trying to initially determine the chromosomal location of a particular disease gene, they would analyze the DNA of members of a family afflicted by the disease, and look for RFLP alleles that show a similar pattern of inheritance as that of the disease (see genetic linkage). Once a disease gene was localized, RFLP analysis of other families could r…
See also
• Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP)
• RAPD
• STR analysis
External links
• https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/genome/probe/doc/TechRFLP.shtml