What determines the amount of rhodopsin bleached in RCS?
In both RCS and normal rats the fraction of rhodopsin bleached is always directly proportional to the photon content of the light, I.t, where I is the light intensity in effective quanta (500 nm) cm-2 sec-1 and t is the duration of the bleaching exposure in seconds. 3.
What happens to rhodopsin when it is destroyed?
The fading of colour was later attributed to the destruction of rhodopsin, via a process known as bleaching. Bleaching and the subsequent regeneration of rhodopsin are major steps in the visual cycle—the series of biochemical reactions that is critical for vision in low light. Human Body: Fact or Fiction?
What is the history of rhodopsin?
Rhodopsin was discovered in 1876 by German physiologist Franz Christian Boll, who observed that the normally reddish purple frog retina turned pale in bright light. The fading of colour was later attributed to the destruction of rhodopsin, via a process known as bleaching. Bleaching and the subsequent regeneration...
Does urea-bleached rhodopsin work in the dark?
Urea acts on cattle rhodopsin to produce a urea-bleached product ( Kito and Takezaki, 1966 ). We have demonstrated that this process occurs not only in the light but also in the dark, and shows a marked dependence on urea concentration.

What is photobleaching in the eye?
If the eye is exposed to bright light all the rhodopsin splits at once (a process called photobleaching). When subsequently exposed to darkness there is therefore no rhodopsin to split and the eye cannot detect light properly.
Will rhodopsin be bleached in the dark?
Rhodopsin, the pigment of the retinal rods, can be bleached either by light or by high temperature.
What is bleaching of the pigment?
the change in the photopigment rhodopsin that occurs when it absorbs photons. The color of the pigment changes from purple (visual purple) to a transparent light yellow (visual yellow).
What does bleach of the pigment mean and when does it happen?
When the rod photopigments are exposed to light they undergo a process called bleaching. It is called bleaching because the photopigment color actually become almost transparent. In the dark when they regenerate and regain their pigmentation again.
What happens when light hits rhodopsin?
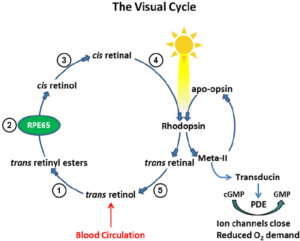
When light strikes rhodopsin, the G-protein transducin is activated, which in turn activates phosphodiesterase. Phosphodiesterase converts cGMP to GMP, thereby closing sodium channels. As a result, the membrane becomes hyperpolarized. The hyperpolarized membrane does not release glutamate to the bipolar cell.
What Happens When rhodopsin is exposed to light?
When the eye is exposed to light, the 11-cis-retinal component of rhodopsin is converted to all-trans-retinal, resulting in a fundamental change in the configuration of the rhodopsin molecule.
What does bleach do to melanin?
Unlike colouring hair, where pigments are deposited into the hair shaft, bleach causes the natural melanin of the hair shaft to break down or dissolve.
Does bleach remove melanin?
How skin bleaching works. Skin bleaching reduces the concentration or production of melanin in the skin. Melanin is a pigment produced by cells called melanocytes.
What happens to rod cells in darkness?
In the dark, cGMP levels in the rod outer segment are high. This cGMP mediates a standing sodium current. At rest, in the dark, sodium ions flow into the rod outer segment. This high resting level of sodium permeability results in a relatively high resting potential for rod cells, about −40 mV.
What is the process of bleaching?
Bleaching, a process of whitening fabric by removal of natural colour, such as the tan of linen, is usually carried out by means of chemicals selected according to the chemical composition of the fibre. Chemical bleaching is usually accomplished by oxidation, destroying colour by…
What is the ultimate result of bleaching of the pigment?
What is the ultimate result of "bleaching of the pigment"? The ultimate result is a series of regions resulting in an action potential being generated from the ganglion cells & impulse traveling down the optic nerve.
How does rhodopsin work in the eye?
The rhodopsin protein is attached (bound) to a molecule called 11-cis retinal, which is a form of vitamin A. When light hits this molecule, it activates rhodopsin and sets off a series of chemical reactions that create electrical signals. These signals are transmitted to the brain, where they are interpreted as vision.
How does rhodopsin work in the dark?
Once in the dark, rhodopsin regenerates and the sensitivity of the retina increases over time (this can take approximately one hour). During these adaptation process reflexive changes occur in the pupil size.
How does rhodopsin help you see in the dark?
Rhodopsin is what allows the rods in our eyes to absorb photons and perceive light, making it essential to our vision in dim light. As rhodopsin absorbs a photon, it splits into a retinal and opsin molecule and slowly recombines back to into rhodopsin at a fixed rate.
Does rhodopsin help us see in the dark?
Rhodopsin is the photopigment used by the rods and is the key to night vision. Intense light causes these pigments to decompose reducing sensitivity to dim light. Darkness causes the molecules to regenerate in a process called “ dark adaptation” in which the eye adjusts to see in the low lighting conditions.
What happens when rhodopsin doesn't work?
In retinitis pigmentosa, mutations in the gene for rhodopsin result in an abnormal version of the protein that doesn't work correctly and eventually causes the rod cells to die. Over time, the loss of the rod cells causes cone cells to die as well, resulting in blindness.
What is the structure of rhodopsin?
Structure. Rhodopsin consists of two components, a protein molecule also called scotopsin and a covalently -bound cofactor called retinal. Scotopsin is an opsin, a light-sensitive G protein coupled receptor that embeds in the lipid bilayer of cell membranes using seven protein transmembrane domains.
What happens when rhodopsin absorbs light?
When rhodopsin absorbs light, its retinal cofactor isomerizes from the 11-cis to the all-trans configuration, and the protein subsequently undergoes a series of relaxations to accommodate the altered shape of the isomerized cofactor.
What is the color of the rods that absorbs light?
Rhodopsin of the rods most strongly absorbs green-blue light and, therefore, appears reddish-purple, which is why it is also called "visual purple". It is responsible for monochromatic vision in the dark. Bovine rhodopsin. Visual cycle.
What is the name of the protein that makes a human see purple?
Wikidata. View/Edit Human. View/Edit Mouse. Rhodopsin (also known as visual purple) is a light -sensitive receptor protein involved in visual phototransduction. It is named after ancient Greek ῥόδον ( rhódon) for rose, due to its pinkish color, and ὄψις ( ópsis) for sight.
How long does it take for rhodopsin to regenerate?
When rhodopsin is exposed to light, it immediately photobleaches. In humans, it is regenerated fully in about 30 minutes, after which rods are more sensitive. Rhodopsin was discovered by Franz Christian Boll in 1876.
What is the name of the protein that is responsible for visual phototransduction?
Rhodopsin. This article is about the visual rhodopsin of vertebrates. For other types of rhodopsin , see Retinylidene protein. Rhodopsin (also known as visual purple) is a light -sensitive receptor protein involved in visual phototransduction.
Which organisms express rhodopsin ion pumps?
Many other pro- and eukaryotic organisms (in particular, fungi such as Neurospora) express rhodopsin ion pumps or sensory rhodopsins of yet-unknown function. Very recently, microbial rhodopsins with guanylyl cyclase activity have been discovered.
Information About Rhodopsin
While this part of the human eye is extremely important, many people don’t know that much about it. If you wish to learn more about rhodopsin and exactly what it does, you can speak with your eye doctor in Miami and do some research on it yourself.
What to do if You Have Night Blindness
If you are having troubles seeing at night, then you may need to get a pair of eyeglasses in Miami Beach from your doctor. If this does not solve the problem, then you may need to begin Vitamin A therapy.
What happens to the contralateral pupil after rhodopsin bleach?
5. After a full rhodopsin bleach, the contralateral pupil size recovered its full dark value along a curve which followed the regeneration of rhodopsin.
Is rod bleaching normal?
8. Therefore, rod bleaching signals are normal in such retinas but rod signals evoked by real lights are not functional. This supports Rushton's concept as to how bleaching signals influence retinal sensitivity as opposed to the view of Barlow.
Is rhodopsin in rods?
3. However, there is the normal amount of rhodopsin in their rods with normal kinetics.

Overview
Structure
Rhodopsin consists of two components, a protein molecule also called scotopsin and a covalently-bound cofactor called retinal (11-cis-retinal). Scotopsin is an opsin, a light-sensitive G protein coupled receptor that embeds in the lipid bilayer of cell membranes using seven protein transmembrane domains. These domains form a pocket where the photoreactive chromophore, retinal, lies hori…
General
Rhodopsin of the rods most strongly absorbs green-blue light and, therefore, appears reddish-purple, which is why it is also called "visual purple". It is responsible for monochromatic vision in the dark.
Several closely related opsins differ only in a few amino acids and in the wavelengths of light that they absorb most strongly. Humans have including rhodopsin nine opsins , as well as cryptochro…
Phototransduction
Rhodopsin is an essential G-protein coupled receptor in phototransduction.
In rhodopsin, the aldehyde group of retinal is covalently linked to the amino group of a lysine residue on the protein in a protonated Schiff base (-NH =CH-). When rhodopsin absorbs light, its retinal cofactor isomerizes from the 11-cis to the all-trans configuration, and the protein subsequently undergoes a series of …
Retinal disease
Mutation of the rhodopsin gene is a major contributor to various retinopathies such as retinitis pigmentosa. In general, the disease-causing protein aggregates with ubiquitin in inclusion bodies, disrupts the intermediate filament network, and impairs the ability of the cell to degrade non-functioning proteins, which leads to photoreceptor apoptosis. Other mutations on rhodopsin lead to X-linked congenital stationary night blindness, mainly due to constitutive activation, when the …
Microbial rhodopsins
Some prokaryotes express proton pumps called bacteriorhodopsins, archaerhodopsins, proteorhodopsins, heliorhodopsins and xanthorhodopsins to carry out phototrophy. Like animal visual pigments, these contain a retinal chromophore (although it is an all-trans, rather than 11-cis form) and have seven transmembrane alpha helices; however, they are not coupled to a G protein. Prokaryotic halorhodopsins are light-activated chloride pumps. Unicellular flagellate algae contain
Further reading
• See also bacteriorhodopsin, used in some halobacteria as a light-driven proton pump.
• Humphries P, Kenna P, Farrar GJ (May 1992). "On the molecular genetics of retinitis pigmentosa". Science. 256 (5058): 804–8. Bibcode:1992Sci...256..804H. doi:10.1126/science.1589761. PMID 1589761.
• Edwards SC (July 1995). "Involvement of cGMP and calcium in the photoresponse in vertebrate photoreceptor cells". The Journal of the Florida Medical Association. 82 (7): 485–8.
• See also bacteriorhodopsin, used in some halobacteria as a light-driven proton pump.
• Humphries P, Kenna P, Farrar GJ (May 1992). "On the molecular genetics of retinitis pigmentosa". Science. 256 (5058): 804–8. Bibcode:1992Sci...256..804H. doi:10.1126/science.1589761. PMID 1589761.
• Edwards SC (July 1995). "Involvement of cGMP and calcium in the photoresponse in vertebrate photoreceptor cells". The Journal of the Florida Medical Association. 82 (7): 485–8. P…
External links
• Rhodopsin at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
• Kolb H, Fernandez E, Nelson R, Jones BW (1 March 2010). "Webvision Home Page: The organization of the retina and visual system". University of Utah.
• The Rhodopsin Protein