
What is the technological difference in the Ricardian model of trade?
The technological difference is essentially supply side difference between the two countries involved in international trade. The Ricardian model assumes all other factors to be similar across the countries. The Labor Theory of Value forms the basis of the Ricardian model of trade.
What is the role of demand in the Ricardian model?
According to the Ricardian model of trade, the demand side conditions come in handy in determining the trade compositions and gains from trade, after trade opens up. Demand plays a crucial role in the determination of international terms of trade in the Ricardian model only after opening up of trade.
What are the limitations of the Ricardian model?
The Ricardian Model concludes therefore that international trade benefits all participants. The model is limited in several ways: 1. Having only 1 factor of production is way too simplistic a view of manufacturing. 2. In real world, almost no country produces only the goods in which they have a comparative advantage.
What are Ricardian and Heckscher-Ohlin models?
There are several models that are used to analyze the dynamics of international trade. Two such models are Ricardian and Heckscher-Ohlin models. Let's look at each of them in detail. The focus is on comparative advantage. The model suggests that the countries specialize in producing goods and services that they can do best.
Why is Ricardian model important?
The Ricardian model helps us understand a few basic facts about trade: Trade is defined by comparative advantage. Trade between countries diminishes with distance. Large countries trade less relative to GDP, but trade relatively more in absolute terms.
What are the assumptions of Ricardian theory of international trade?
The Ricardian doctrine of comparative advantage is based on the following assumptions: (1) There are only two countries, say A and B. (2) They produce the same two commodities, X and Y (3) Tastes are similar in both countries. (4) Labour is the only factor of production.
What are the limitations of the Ricardian model?
The model is limited in several ways: 1. Having only 1 factor of production is way too simplistic a view of manufacturing. 2. In real world, almost no country produces only the goods in which they have a comparative advantage.
What are the two theories of international trade?
There are 6 economic theories under International Trade Law which are classified in four: (I) Mercantilist Theory of trade (II) Classical Theory of trade (III) Modern Theory of trade (IV) New Theories of trade.
How many are the assumptions of the theory of record?
The three main assumptions we will deal with are – going concern, consistency, and accrual basis.
What is the only factor of production in Ricardian theory of international trade?
In Ricardo's theory, which was based on the labour theory of value (in effect, making labour the only factor of production), the fact that one country could produce everything more efficiently than another was not an argument against international trade.
On which of the following assumptions the comparative cost theory of trade is based on?
The theory of comparative costs is based on the assumption that labour is used in the same fixed proportions in the production of all commodities.
What is the main difference between Heckscher-Ohlin theory and Ricardian theory?
Unlike Ricardian Model, the model suggested by Heckscher-Ohlin assumes that there are two factors of production, namely, labor and capital. One country has comparative advantage over the other because of the differences in relative amounts of each factor.
Who developed the Ricardian model of trade?
Introduction. The Ricardian Model of Trade is developed by English political economist David Ricardo in his magnum opus On the Principles of Political Economy and Taxation (1817).
What is the Ricardian model?
1. There are only 2 countries. 2. They produce 2 goods. 3.
How does trade benefit both countries?
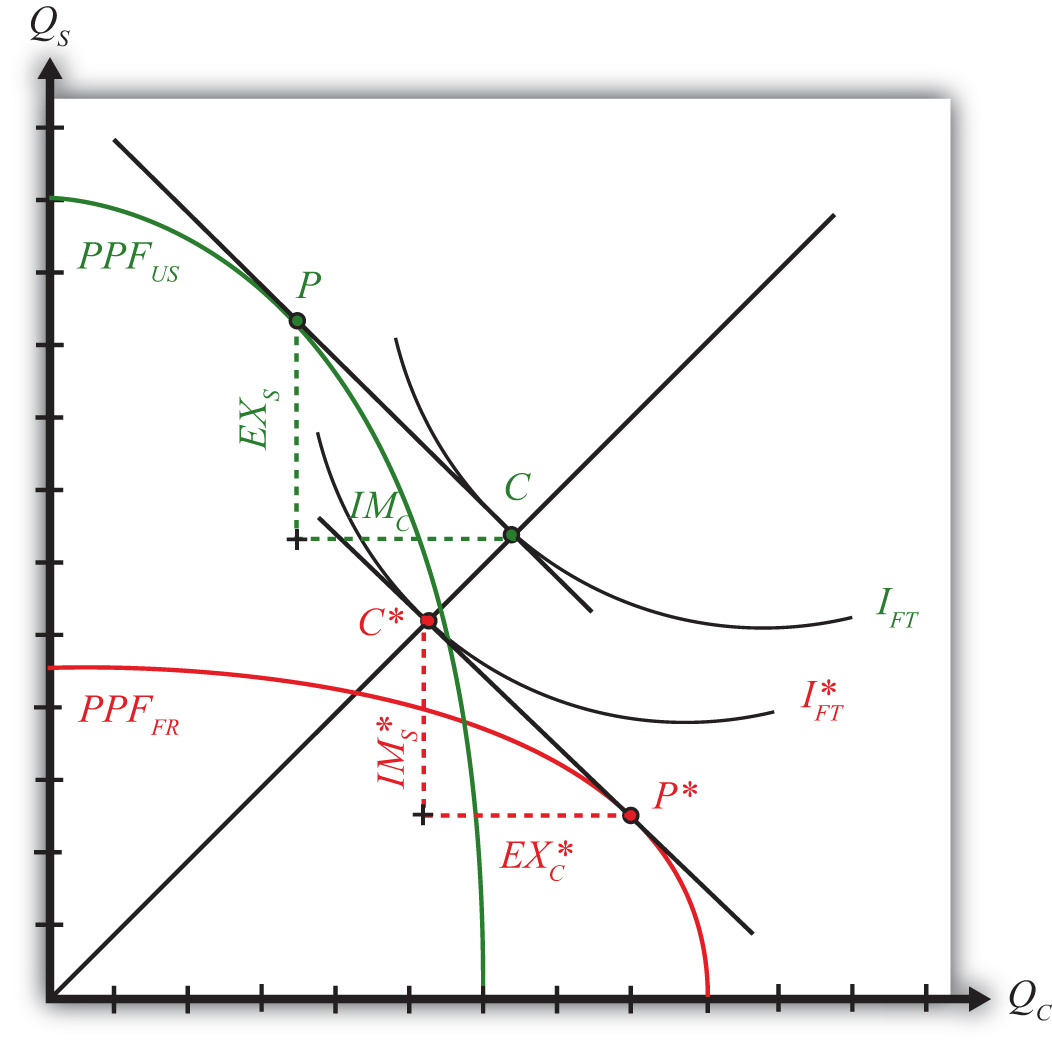
Under autarky condition (no trade), each of the two countries produces some combination of the 2 goods. Once trade becomes possible, they are motivated to specialize fully in the production of the good in which they have a comparative advantage, thus allocating their scarce resources (labor) to its most productive uses. In the aggregate, people in both countries end up consuming more of both goods than they did in the absence of trade. Since more consumption means greater satisfaction (using economic jargon, equilibrium shifts to a higher indifference curve), trade allow both countries to improve their welfare. The Ricardian Model concludes therefore that international trade benefits all participants.
Why is the model limited?
The model is limited in several ways: 1. Having only 1 factor of production is way too simplistic a view of manufacturing . 2. In real world, almost no country produces only the goods in which they have a comparative advantage. 3. Opportunity costs between goods are unlikely to be constant, but should rather be increasing. 4. Most significantly, the model does not explain the source of comparative advantage: why can some countries produce some goods more cheaply than other countries?
Which model allows multiple factors of production and explains the source of comparative advantage by relative abundance of resources?
In addressing these problems, scholars of international trade after Ricardo would make adjustments on his model to come up with better models, the most notable being the Heckscher-Ohlin Model ), which allows multiple factors of production and explains the source of comparative advantage by relative abundance of resources.
Question
What is the Ricardian model of international trade? What factors of production are addressed with this model?
International trade
The trade between different countries of different goods and services is International trade. It is the export and import of goods and services across the boundaries of different countries.
Answer and Explanation: 1
The Ricardian model of international trade is based on the concept of comparative advantage and is based on two countries, two goods and one factor of production- labour.
What is the Ricardian model of international trade?from economywatch.com
The Ricardian model of international trade attempts to explain the difference in comparative advantage on the basis of technological difference across the nations. The technological difference is essentially supply side difference between the two countries involved in international trade. The Ricardian model assumes all other factors ...
How does trade benefit both countries?from mediawiki.middlebury.edu
Under autarky condition (no trade), each of the two countries produces some combination of the 2 goods. Once trade becomes possible, they are motivated to specialize fully in the production of the good in which they have a comparative advantage, thus allocating their scarce resources (labor) to its most productive uses. In the aggregate, people in both countries end up consuming more of both goods than they did in the absence of trade. Since more consumption means greater satisfaction (using economic jargon, equilibrium shifts to a higher indifference curve), trade allow both countries to improve their welfare. The Ricardian Model concludes therefore that international trade benefits all participants.
Why is the model limited?from mediawiki.middlebury.edu
The model is limited in several ways: 1. Having only 1 factor of production is way too simplistic a view of manufacturing . 2. In real world, almost no country produces only the goods in which they have a comparative advantage. 3. Opportunity costs between goods are unlikely to be constant, but should rather be increasing. 4. Most significantly, the model does not explain the source of comparative advantage: why can some countries produce some goods more cheaply than other countries?
What is trading bloc?from analystprep.com
Trading Blocs A trading bloc is defined as a number of nations within... Read More
Why is Ricardo's comparative advantage a profit maximizing solution for capitalists?from analystprep.com
Ricardo’s comparative advantage proves to be a profit-maximizing solution for capitalists because of infrastructures and goods requiring different factors of production. However, all nations will not see the need to trade with each other.
Which model allows multiple factors of production and explains the source of comparative advantage by relative abundance of resources?from mediawiki.middlebury.edu
In addressing these problems, scholars of international trade after Ricardo would make adjustments on his model to come up with better models, the most notable being the Heckscher-Ohlin Model ), which allows multiple factors of production and explains the source of comparative advantage by relative abundance of resources.
Why is Ricardian model important?
The Ricardian model helps us understand a few basic facts about trade: Trade is defined by comparative advantage. Trade between countries diminishes with distance. Large countries trade less relative to GDP, but trade relatively more in absolute terms.
What are the assumptions of Ricardian theory of international trade?
Assumptions of the Theory: The Ricardian doctrine of comparative advantage is based on the following assumptions: (1) There are only two countries, say A and B. (2) They produce the same two commodities, X and Y (3) Tastes are similar in both countries. (4) Labour is the only factor of production.
What is Ricardo theory of value?
Classical economist David Ricardo's labor theory of value holds that the value of a good (how much of another good or service it exchanges for in the market) is proportional to how much labor was required to produce it, including the labor required to produce the raw materials and machinery used in the process.
What insights about international trade came from Adam Smith and David Ricardo?
Later economists deviated from Adam Smith in developing new lines of inquiry, but retained his insights. Inspired by The Wealth of Nations, David Ricardo developed the theory of comparative advantage, which shows that nations should specialize and then trade, which led to greater prosperity.
What is Ricardo famous for?
David Ricardo (1772–1823) was a classical economist best known for his theory on wages and profit, the labor theory of value, the theory of comparative advantage, and the theory of rents.
Who gains from trade in the Ricardian model?
That is, in US each worker (person) gets 1/600 of the higher consumption basket; in Mexico each gets 1/2000). Because workers in each country are identical in productivity and income changes, all share equally in the gains from trade.
Which is necessary for a country to gain from trade in the Ricardian model?
The Ricardian model predicts the direction of trade: each country exports its comparative advantage good. ... In the Ricardian model, the condition for gains from trade is equivalent to saying a country gains whenever it becomes completely specialized in its comparative advantage good.
