Explore
are scored. Score 1 only if a clear-cut asymmetry, including quadrantanopia, is found. If patient is blind from any cause, score 3. Double simultaneous stimulation is performed at this point. If there is extinction, patient receives a 1, and the results are used to respond to item 11. 0 = No visual loss. 1 = Partial hemianopia. 2 = Complete hemianopia.
How to score hemianopia?
While hemianopsia cannot be directly treated with medications or surgery. Instead, the causes and symptoms of hemianopsia can be rehabilitated by an occupational therapist, low vision specialist, or driving specialist. Occupational and Vision Therapy
Can hemianopsia be treated?
Left Homonymous Hemianopia: This results from lesions to the optic tract in route towards the lateral geniculate body of the thalamus (location 3) as well as lesions right after the radiating fibers leave the lateral geniculate body (location 5). These lesions are often caused by strokes or neoplasms.
What causes left homonymous hemianopsia?
What is a complete hemianopia? Hemianopia which is also sometimes referred to as Hemianopsia, is a visual disorder in which half of the visual field is affected and the person is able to see only half the things in his visual field and has complete blindness or decreased vision in the other half.
What does complete hemianopia mean?

What causes right homonymous Hemianopsia?
Any type of intracranial lesion in the appropriate location can cause a homonymous hemianopia; however, vascular causes (cerebral infarction and intracranial hemorrhage) are the most frequent in adults, ranging from 42 to 89 percent, followed by brain tumors, trauma, surgical interventions, and other central nervous ...
What is right sided hemianopia?
Hemianopia means loss of half of your vision. In other words, the right half or the left half of your vision is missing from each eye.
What stroke causes right homonymous hemianopia?
3 Homonymous hemianopia is a loss of the right or left halves of the visual field of both eyes (Figure 1a, 1b) and usually occurs as a result of a middle cerebral or posterior cerebral artery stroke affecting either the optic radiation or visual cortex of the occipital lobe (Figure 2).
Where is the lesion in right homonymous Hemianopsia?
Homonymous hemianopia (HH) involves vision loss on the same side of the visual field in both eyes. This type of visual field loss is indicative of a lesion involving the visual pathway posterior to the chiasm.
Can someone with homonymous hemianopia drive?
Individuals with homonymous hemianopia (HH) are permitted to drive in some jurisdictions. They could compensate for their hemifield vision loss by scanning toward the blind side.
How is hemianopsia treated?
How is hemianopia treated?wearing prismatic correction glasses to help with double vision.getting vision compensatory training to help you use your remaining vision more efficiently.undergoing vision restoration therapy to improve visual information processing.
What does a homonymous hemianopia person see?
Homonymous hemianopsia is a condition in which a person sees only one side ― right or left ― of the visual world of each eye. The person may not be aware that the vision loss is happening in both eyes, not just one.
Can you drive with visual field loss?
Driving is challenging and potentially hazardous for those with visual field loss, because the road is a dynamic environment. The impact of visual field loss on driving will depend upon a combination of factors, such as extent of defect, location and ability to compensate.
What does homonymous hemianopia mean?
Homonymous hemianopsia (or homonymous hemianopia, HH) is a field loss deficit in the same halves of the visual field of each eye. This condition most commonly results from stroke for adults, or tumors/lesions for patients under the age of 18.
Can you recover from hemianopia?
Patients can spontaneously recover from HH, but the probability of such recovery is proportional to the time that has elapsed since the lesion occurred. Reported recovery rates range from 7% to 86% (for a review, see: Sabel and Kasten, 2000).
How long does it take to get your vision back after a stroke?
The Rochester team found that survivors of occipital strokes—strokes that occur in the occipital lobe of the brain and affect the ability to see—may retain some visual capabilities immediately after the stroke, but these abilities diminish and eventually disappear permanently after approximately six months.
How do you manage homonymous hemianopia?
The final treatment modality used in patients with homonymous hemianopia is cognitive rehabilitation techniques. This involves strategies such as compensatory oculomotor training to enhance a patient's ability to scan into their blind field. Computerized saccadic training is often beneficial for this.
What is left sided hemianopia?
Left hemianopia, which causes a loss of vision in the left half of each eye. Superior hemianopia, which causes a loss of vision in the upper half of each eye. Inferior hemianopia, which causes a loss of vision in the lower half of each eye.
Can you recover from hemianopia?
Patients can spontaneously recover from HH, but the probability of such recovery is proportional to the time that has elapsed since the lesion occurred. Reported recovery rates range from 7% to 86% (for a review, see: Sabel and Kasten, 2000).
What does hemianopsia look like?
Hemianopsia, or hemianopia, is a visual field loss on the left or right side of the vertical midline. It can affect one eye but usually affects both eyes....Homonymous hemianopsiaCausesbrain bleed, brain inflammation, brain tumor, dementia, epilepsy, lymphoma, other kinds of brain injuries, and stroke5 more rows
Can you read with hemianopia?
Patients with hemianopia can read, but they tend to be much slower at it than individuals without this type of reading problem.
What is the right hemispheric damage?
Right Hemispheric Damage. Right Hemispheric damage may not only produce a left homonymous hemianopsia or quadranopsia, but it may also produce a severe attention disorder to the left side called left hemispatial inattention or visual neglect.
Why do people not receive adequate visual rehabilitation?
Unfortunately many of these patients fail to receive adequate visual rehabilitation services because they do not present with the severe debilitating problems of the hemiparesis, confusion, or speech problems that typically lead the patient into rehabilitative services. These patients may have had no hospital stay that might have lead to rehabilitative services.
Can left hemispheric damage cause right hemianopsia?
Left hemispheric damage may produce a right hemianopsia or quadranopsia, but may also impact mood and behavior. Some patients may appear compulsive, disorganized and easily frustrated. Patients may demonstrate problems in memory, speech, writing, and cognitive processing.
Can left brain damage cause paralysis?
Left brain damage results in problems on the right side of the body including paralysis. Reading ability may be impaired at a cognitive level. Often this loss of reading and speech can be rehabilitated with speech therapy, but in some cases this loss is permanent.
Can hemianopsia be a stroke?
Some patients present with damage localized to a specific area of one lobe, thus reducing the number of associated problems. The most common being a small area of stroke isolated to the occipital lobe. This may create a homonymous hemianopsia without cognitive impairment, paralysis, visual neglect, or impaired eye movements. Some of these patients may be candidates to return to higher level functioning including driving with the right rehabilitation.
What is a homonymous hemianopia?
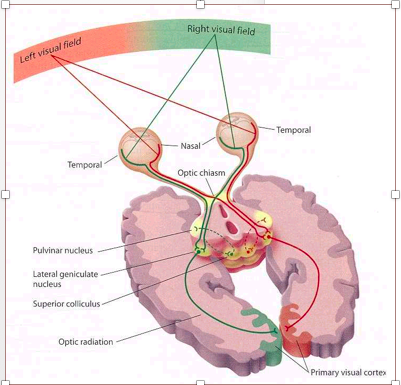
Homonymous hemianopsia (or homonymous hemianopia, HH) is a field loss deficit in the same halves of the visual field of each eye. This condition most commonly results from stroke for adults, or tumors/lesions for patients under the age of 18.[1] Often, the cause of HH is located at the occipital lobe, followed by an injury to the optic radiations or optic tract.[1] HH can also be characterized as contralateral hemianopsia (unilateral involvement at the optic tract, lateral geniculate nucleus, optic radiations, or occipital cortex opposite to the side of field loss) in contrast to bitemporal hemianopsia (involvement at the optic chiasm).
What is the most common cause of homoonymous hemianopsia?
Homonymous hemianopsia frequently results from vascular injury. In adults, cerebral infarcts and intracranial hemorrhages being the most common (42% to 89%). They are followed by tumors, trauma, iatrogenic events, and neurologic disease.[2] Pediatric cases often originate from neoplasms (39%), stroke (25%), and trauma (19%). [3]
What are the most common homonymous hemianopsia deficits?
The most common homonymous hemianopsia deficits are from occipital lobe lesions. These deficits typically present without other associated neurologic symptoms. However, the patterns may vary. Often these lesions include macular sparing as a result of the dual blood supply and bilateral macular representation at the occipital cortex. At the occipital pole, most posteriorly, homonymous scotomas are produced. Most anteriorly, temporal crescent loss and other similar peripheral vision patterns occur. If the lesion extends anteriorly enough to involve the left corpus callosum, patients may present with alexia without agraphia (if the lesion spares the angular gyrus). Bilateral occipital lobe lesions will produce bilateral homonymous hemianopsia of various types. Most notably is Anton’s syndrome involving a complete bilateral homonymous hemianopsia (cortical blindness) with which the patient also experiences anosognosia, being unaware of their blindness. With bilateral occipital lesions, it is possible that visual acuity may be impacted. [1][19][20]
What is the term for a loss of the temporal crescent?
Temporal crescent-sparing or unilateral lossinvolves varying field loss of about 30 degrees of the farthest peripheral temporal field, which is not overlapped by the contralateral eye’s nasal field (the temporal crescent). Unilateral loss is the only mentioned defect thus far that involves retrochiasmal lesions and presents as a monocular field defect (the others are bilateral and homonymous). Temporal crescent-sparing homonymous hemianopsia is hemianopsia with the temporal crescent of the contralateral eye field being spared, often caused by injury to the occipital cortex with preservation of the anterior portion of the cortex. [16]
How long does it take for hemianopsia to improve?
Even with reported differences in spontaneous improvement, after six months from the incident, it is unlikely that the patient will experience a spontaneous recovery. However, improvement in underlying diseases has shown to provide visual field improvement even after such time (eg., multiple sclerosis). [26][27]
What imaging is used to diagnose homonymous hemianopsia?
In addition to identifying the field deficit, all patients experiencing homonymous hemianopsia should undergo further imaging, such as an MRI, to identify the cause of such symptomatology.
Can homonymous hemianopsia cause nausea?
In addition to the visual field deficit, patients experiencing homonymous hemianopsia may feel disoriented and complain of dizziness, vertigo, or nausea. These symptoms all increase the risk of trauma. Patients are more likely to fall as a result of their field loss.
What is homonymous hemianopsia?
What homonymous hemianopsia (HH) can be defined as is when an individual is reduced to only being able to see one side of the visual world from each eye. HH is commonly caused by a stroke and will cause a person to bump into objects or fail to see objects or people.
What side of the brain is affected by homonymous hemianopsia?
It is the brain that is the issue in homonymous hemianopsia, rather than the eyes themselves. When the left side of the brain is injured, there is loss to the right half of the visual world of each eye. An injury to the right brain could potentially cause a loss to the left half of the visual world of each eye.
What is hemianopsia MRI?
Your eyes may also be checked to see if the retina, macula, and optic nerve are healthy and not causing problems. An MRI of the brain can diagnose the location of a brain injury that may be causing homonymous hemianopsia.
What percentage of strokes have homonymous hemianopsia?
About eight to 10 percent of stroke victims have homonymous hemianopsia. Other leading causes of homonymous hemianopsia include brain injury (14 percent of cases) and tumors (11 percent). Legions from the optic tract to the visual cortex can be the cause of homonymous hemianopsia.
How long does it take to recover from a homonymous hemianopsia?
A severe brain injury does not have a good likelihood of complete recovery. Total recovery of homonymous hemianopsia occurs within four weeks in 17 to 19 percent of those who experience symptoms due to a stroke.
Can homonymous hemianopsia cause hallucinations?
Those with right homonymous hemianopsia will find reading takes a lot longer, since we read from left to right. Visual hallucinations are a common symptom of homonymous hemianopsia. Hallucinations can take the form of recognizable objects, or they can be unformed lights, shapes, or geometric figures.
What causes homonymous hemianopsia?
Causes. Homonymous hemianopsia can be congenital, but is usually caused by brain injury such as from stroke, trauma, tumors, infection, or following surgery. Vascular and neoplastic (malignant or benign tumours) lesions from the optic tract, to visual cortex can cause a contralateral homonymous hemianopsia. Injury to the right side of the brain ...
What is a prism for hemianopsia?
Prisms or "field expanders" that bend light have been prescribed for decades in patients with hemianopsia. Higher power Fresnel ("stick-on") prisms are commonly employed because they are thin and lightweight, and can be cut and placed in different positions on a spectacle lens.
What is the name of the visual field loss on the left side of the midline?
Homonymous hemianopsia. Hemianopsia, or hemianopia, is a visual field loss on the left or right side of the vertical midline. It can affect one eye but usually affects both eyes. Homonymous hemiano psia (or homonymous hemianopia) is hemianopic visual field loss on the same side of both eyes. Homonymous hemianopsia occurs because the right half ...
What happens if you have a cerebral lesion on the right side of the brain?
Injury to the right side of the brain will affect the left visual fields of each eye. The more posterior the cerebral lesion, the more symmetric (congruous) the homonymous hemianopsia will be. For example, a person who has a lesion of the right optic tract will no longer see objects on his left side. Similarly, a person who has a stroke ...
What causes macular sparing hemianopia?
Infarction of occipital cortex typically causes macular sparing hemianopias due to dual blood supply from both posterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery. Occlusion of the calcarine artery that results in infarction of the superior part of the occipital lobe causes a lower peripheral visual field defect.
Can hemianopia affect both eyes?
It can affect one eye but usually affects both eyes. Homonymous hemianopsia (or homonymous hemianopia) is hemianopic visual field loss on the same side of both eyes. Homonymous hemianopsia occurs because the right half of the brain has visual pathways for the left hemifield of both eyes, and the left half of the brain has visual pathways for ...
Can homonymous hemianopsia cause mobility problems?
Signs and symptoms. Mobility can be difficult for people with homonymous hemianopsia. "Patients frequently complain of bumping into obstacles on the side of the field loss, thereby bruising their arms and legs.". People with homonymous hemianopsia often experience discomfort in crowds.
What causes homonymous hemianopia?
Stroke is the most common cause of homonymous hemianopia (HH) in adults, followed by trauma and tumors. Associated signs and symptoms, as well as visual field characteristics such as location and congruity, can help determine the location of the causative brain lesion. HH can have a significant effect on quality of life, ...
Which lesions are more likely to cause inferior visual field defects with sloping borders superiorly?
In contrast, parietal lesions are more likely to cause inferior visual field defects with sloping borders superiorly. Lesions isolated to the upper, cuneus gyrus or the lower, lingual gyrus result in an inferior or superior quadrantanopia, respectively (Figure 1D).
What is HH in medical terms?
Homonymous hemianopia (HH) involves vision loss on the same side of the visual field in both eyes. This type of visual field loss is indicative of a lesion involving the visual pathway posterior to the chiasm.
How sensitive is confrontation visual field testing?
Confrontation visual field testing is not sensitive at detecting visual field loss , but it may be the only method available. Kerr et al29evaluated 332 eyes prospectively to compare seven types of confrontation visual field tests. Finger counting was the least sensitive method, finding 0% of mild defects and 49% of severe defects. Overall, the most sensitive individual method of confrontation visual field testing is kinetic testing using a 5 mm red bead. This picks up 43% of mild defects and 89% of severe defects. The overall sensitivity using the kinetic red bead is 74%, but this improves to 78% when combined with static finger wiggle testing. Formal perimetry is necessary if there is a strong suspicion of visual field loss.
What is the most common cause of HH?
The potential causes of HH are dependent on the age of the patient. The most common cause of HH in adults is stroke. Approximately 8%–10% of stroke patients have permanent HH, and 52%–70% of hemianopias are caused by stroke. 1,2As the population ages and stroke patients live longer, the incidence of stroke and resultant HH is likely to increase.3.
How many states require a binocular vision field?
A binocular visual field of at least 110° is required in 27 states.37Despite this, some continue to drive illegally,38,39and 12 states have no minimum visual field requirement for driving. Therefore, it is important to be familiar with safety concerns as well as available options for these patients.
What causes HH?
Other common causes of HH include traumatic brain injury (14% of HH cases) and tumors (11% of HH cases).1,4Less common causes of HH are shown in Table 1.4–13
What are the symptoms of hemianopia?
The main symptom of hemianopia is losing half of your visual field in one or both eyes. But it can also cause a range of other symptoms, including:
How is hemianopia diagnosed?
Hemianopia is usually first detected during a routine eye exam that includes a visual field exam. This will help your doctor determine how well your eyes can focus on specific objects.
What is hemianopia in the eyes?
What is hemianopia? Hemianopia, sometimes called hemianopsia, is partial blindness or a loss of sight in half of your visual field. It’s caused by brain damage, rather than a problem with your eyes. Depending on the cause, hemianopia may be permanent or temporary.
Why is hemanopia so frustrating?
Hemianopia can be a frustrating condition because it often makes everyday things, such as reading or walking, difficult.
How do you know if you have hemianopia?
For many people with hemianopia, their symptoms become more noticeable when they try to read or focus their eyes on something.
Where does hemianopia originate?
Remember, hemianopia originates in your brain, not your eyes. Ruling out any issues with your eyes will help your doctor reach a diagnosis.
What are the two halves of hemianopia?
What are the types of hemianopia? There are a few types of hemianopia, depending on the parts of the brain involved. Your brain contains two halves: Left side. This half receives information from both eyes, processes it, and sends signals that allow you to see the right side of your visual world. Right side. This half receives information ...

Overview
Hemianopsia, or hemianopia, is a visual field loss on the left or right side of the vertical midline. It can affect one eye but usually affects both eyes.
Homonymous hemianopsia (or homonymous hemianopia) is hemianopic visual field loss on the same side of both eyes. Homonymous hemianopsia occurs because the right half of the brain has visual pathways for the left hemifield of both eyes, and the left half of the brain has visual pathw…
Signs and symptoms
Mobility can be difficult for people with homonymous hemianopsia. "Patients frequently complain of bumping into obstacles on the side of the field loss, thereby bruising their arms and legs."
People with homonymous hemianopsia often experience discomfort in crowds. "A patient with this condition may be unaware of what he or she cannot see an…
Causes
Homonymous hemianopsia can be congenital, but is usually caused by brain injury such as from stroke, trauma, tumors, infection, or following surgery.
Vascular and neoplastic (malignant or benign tumours) lesions from the optic tract, to visual cortex can cause a contralateral homonymous hemianopsia. Injury to the right side of the brain will affect the left visual fields of each eye. The more posterior the cerebral lesion, the more symmetric (co…
Diagnosis
Homonymous hemianopsia secondary to posterior cerebral artery occlusion – may result in syndromes of memory impairment, opposite visual field loss (homonymous hemianopsia), and sometimes hemisensory deficits. The PCA supplies the occipital lobe and the medial portion of the temporal lobe.
Infarction of occipital cortex typically causes macular sparing hemianopias due to dual blood su…
Management
Prisms or "field expanders" that bend light have been prescribed for decades in patients with hemianopsia. Higher power Fresnel ("stick-on") prisms are commonly employed because they are thin and lightweight, and can be cut and placed in different positions on a spectacle lens.
Peripheral prism spectacles expand the visual field of patients with hemifield visual defects and have the potential to improve visual function and mobility. Prism spectacles incorporate higher …
Etymology
Homonymous hemianopsia can be broken down as follows:
• Homonymous: (Greek >ομόνυμος = όμοιος + όνομα (same + name) (having the same name or designation) or standing in the same relation
• hemi: ημι-, half
• anopsia: α(ν)+όψις = without + sight; blindness
See also
• Binasal hemianopsia
• Bitemporal hemianopsia
• Blindsight
• Vision restoration therapy