What is route in nursing?
A route of drug administration is the path by which a drug or other substance is brought into contact with the body. Drugs are introduced into the body by several routes. When administering a drug, the nurse should ensure that the pharmaceutical preparation is appropriate for the route specified. Route.
What is the meaning of IV route?
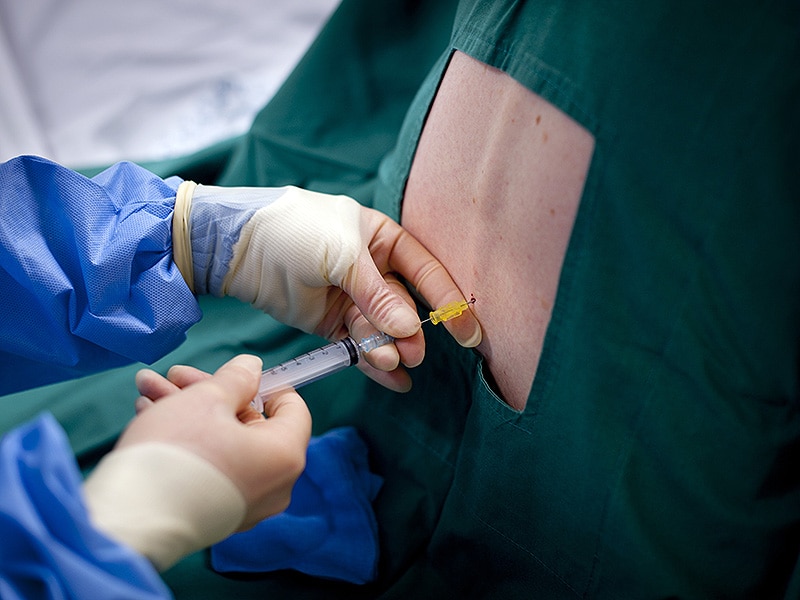
Some medications must be given by an intravenous (IV) injection or infusion. This means they're sent directly into your vein using a needle or tube. In fact, the term “intravenous” means “into the vein.”
What is the route for injection?
Administration by injection (parenteral administration) includes the following routes: Subcutaneous (under the skin) Intramuscular (in a muscle) Intravenous (in a vein)
What is the route of tablet?
The oral route of administration is the safest, most economical and the most convenient way of giving medicines. The dosage forms of the oral route include Tablets, Capsules, Powders, Mixtures, Emulsions and Gels. Most drugs are absorbed from small intestine but some are absorbed from stomach and colon.
Which route is best IV or IM?
Intravenous Administration. The intravenous route is the most effective. An infusion over 30–60 minutes of antivenom diluted in isotonic fluid may be easier to control than a slow intravenous 'push' injection of reconstituted but undiluted antivenom given over 10–20 minutes.
What are the 3 main types of IV fluids?
There are three types of IV fluids:Isotonic.Hypotonic.Hypertonic.
What are the 5 routes of medication?
Techniques involved in each route of medication administration are different, and some of the important points are summarized as follows:Intravenous Route. ... Intramuscular Route. ... Subcutaneous Route. ... Rectal Route. ... Vaginal Route. ... Inhaled Route.
What are the 5 routes of injection?
There are five commonly used routes of parenteral (route other than digestive tract) administration: subcutaneous (SC/SQ), intraperitoneal (IP), intravenous (IV), intrader- mal (ID), and intramuscular (IM).
What are the 8 routes of medication?
Anesthetics and analgesics (such as morphine) are sometimes given this way.Sublingual and buccal routes. ... Rectal route. ... Vaginal route. ... Otic route. ... Nasal route. ... Cutaneous route. ... Transdermal route.
What route is paracetamol?
For increasing its beneficial effects on pain relief, paracetamol can be given as a rectal, oral, or intravenous preparation [13]; however, the route of administration can lead to different levels of effectiveness because of the differences in absorption and the time to reach peak plasma levels.
What is ibuprofen route?
Ibuprofen (Oral Route)
What is route in pharmacy?
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
What type of route is IV?
An intravenous route directly administers the medications to the systemic circulation. It is indicated when a rapid drug effect is desired, a precise serum drug level is needed, or when drugs are unstable or poorly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
Why do we use IV route?
IV injection is the introduction of a medication into the veins using a needle, and it is used when rapid absorption is called for, when fluid cannot be taken by mouth, or when the medication to be administered is too irritating to be injected into the skin or muscles.
What are the IV routes of drug administration?
Administering a drug through the intravenous (IV) route involves the introduction of a drug solution directly into the blood through the vein using a syringe through a needle or a needleless port on an existing IV line or a saline lock (short venous access device).
What is the meaning of IP and IV?
Intravenous (IV) and intraperitoneal (IP) injections were two most widely used administration routes. IP was often considered to be an effective route for tumor therapy1–5, although it was not as commonly used as IV.
What are the different types of ADHD medications?
If you decide to go down the medication route, there are five types licensed for the treatment of ADHD: methylphenidate, dexamfetamine, lisdexamfetamine, atomoxetine and guanfacine.
What is the route of administration of a drug?
The route of administration is chosen according to the speed of absorption desired and the site of action of the medication . Some medications are formulated for a specific route only and must be given in that manner. It is important that medicines be administered as directed by the manufacturer. Various routes of administration used are as follows:
Which route of administration is the nasal route?
Mucosal routes of administration other than the above include absorption through the nasal mucosa, the buccal mucosa, sublingually, or the bronchioles, the latter usually achieved through inhalation of an aerosol. Vaginal and rectal administration are also mucosal routes of medication.
Can oral and enteral administration be used if a patient is vomiting?
It is too slow if rapid absorption is required, and cannot be used if the patient is vomiting. Rectal administration in the form of liquids or suppositories circumvents this problem in enteral administration.
When is parenteral administration used?
Parenteral administration is used when a drug cannot be given by mouth. The speed of absorption varies greatly with the specific route used, which may be subcutaneous, intravenous, intramuscular, intra-arterial, intraperitoneal, intrathecal, intracardiac, or intrasternal.
Why so Many Administration Routes for Back Pain?
Other routes of administration pain-relieving drugs may take include injection into the epidural space or surgically implanted drug pumps. And this is not a complete list, either.
Why is naltrexone sequestered?
Sequestered naltrexone is used to achieve the resistance to tampering, and most ADF opioid products are extended-release formulation.
How many opioids are on the ADF label?
As of February 2018, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has granted ADF labeling permissions to fewer than twelve opioid formulations, but the authors project that the number will rise in the near future.
How do you repurpose an opioid?
But instead of taking opioids as prescribed, some patients who develop opioid use disorder re-purpose the active ingredient by changing the route of administration, usually to inhaling or injecting.
What is ADF in pain medicine?
A 2018 study published in the Journal of Pain Research, discusses ADF, or abuse-deterrent formulation of opioid products. Such products, the study authors say, are tamper-resistant as well as "designed to resist abuse by those who want to smoke, inhale, or inject the active agent.".
Why does it take longer to take a pill or tablet?
Because the ingredients of a tablet or pill must go through the digestive process before it can start working — and before you realize the benefits of the drug — the oral route may take longer than those that directly introduce the medication into the intended target area.
What is the route of administration?
A route of administration is the way in which a drug enters your system. Aside from taking a medication by mouth, also called the oral route, you might have an injection into a muscle, as sometimes is the case with painful trigger points. Wearing a patch on your skin and inhaling the drug through your nose are two other common routes ...
What is medication route?
A medication administration route is often classified by the location at which the drug is administered, such as oral or intravenous. The choice of routes in which the medication is given depends not only on the convenience and compliance but also on the drug’s pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic profile. Therefore it is crucial to understand the characteristics of the various routes and techniques associated with them. Many interprofessional healthcare team members are involved in the administration of medications to patients.
What is medication administration route?
A medication administration route is often classified by the location at which the drug is applied, such as oral or intravenous. The choice of routes in which the medications are applied depends not only on the convenience but also on the drug’s properties and pharmacokinetics. This activity describes medication administration routes ...
What is lubricant used for?
A lubricant can be utilized in rectal or vaginal administration of medication to reduce friction and discomfort. Personnel.
How is inhaled medication delivered?
An inhaled medication is delivered rapidly across the large surface area of the respiratory tract epithelium. Drugs absorbed into the pulmonary circulation enter directly into the systemic circulation via the pulmonary vein, bypassing the first-pass metabolism. The particle size of the inhaled medication is usually 1 to 10 µm for effective delivery. The efficacy of drug delivery to the lungs depends not only on the drug particle size and morphology but also on the patient’s respiratory physiology, such as tidal volume and tracheal inspiration velocity. [4]
Where to administer intravenous medication?
Intravenous injection is the most common parental route of medication administration and has the benefit of bypassing the first-pass metabolism by the liver. Given their superficial location on the skin, peripheral veins provide easy access to the circulatory system and are often utilized in the parenteral administration of medications. The upper extremity is usually the preferred site for intravenous medication as it has a lower incidence of thrombophlebitis and thrombosis than the lower limbs. The median basilic or cephalic veins of the arm or the metacarpal veins on the hand's dorsum are commonly used. In the lower extremity, the dorsal venous plexus of the foot can be used.
Why is nitroglycerin sublingual?
For instance, nitroglycerin is cleared more than 90% during a single pass through the liver; therefore, it is given as a sublingual form. The sublingual and buccal routes also have advantages of rapid absorption, convenience, and low infection incidence.
How to use lubricant for vaginal mucosa?
A lubricant can be used to reduce friction against the vaginal mucosa as the medication is administered. Gently separate labial folds with the non-dominant gloved hand while with the dominant gloved index finger, insert the lubricated suppository to about 8-10 cm along the posterior vaginal wall. Inhaled Route.
What is the name of the medication that nurses administer?
This is the most common route nurses administer medications like capsules, tablet, and liquids. Nitroglycerin is a drug given this route that treats chest pain. Includes certain opioid pain meds, smoking cessation products etc.
What is the name of the route a nurse administers medications?
Medications can be administered through various routes, and it’s important the nurse is familiar with each route. It’s also important the nurse if familiar with the “lingo” or abbreviations used to describe each routes. For example, the term P.O. is used a lot in nursing to describe medications that are taken via the mouth, or IM, subQ, and IV are terms used to describe routes nurses administer medications by injection.
What does P.O. mean in nursing?
For example, the term P.O. is used a lot in nursing to describe medications that are taken via the mouth, or IM, subQ, and IV are terms used to describe routes nurses administer medications by injection. However, it’s important that when using abbreviations with documenting or taking orders, that the nurse uses approved abbreviations set by ...
What is the name of the drug that is given to chest pain?
Nitroglycerin is a drug given this route that treats chest pain.
What is an ETT in emergency?
Medications that can be given through an ETT: L idocaine, A tropine, N aloxone, E pinephrine, D iazepam “ Laned ” .
Where is medication injected?
Medication is injected in the dermis which is found in between the epidermis and hypodermis. A “wheal” is created on the skin. Used in allergy test or Mantoux TB skin test that checks for tuberculosis. Medication is injected in the subcutaneous fat/hypodermis.
How many IV lines are hung?
Two IV lines are hung and connect into some type of IV access.
What does "perineural" mean?
Perineural; administration surrounding a nerve or nerves.
What does "nasal" mean?
Nasal; administration to the nose; administered by way of the nose.
What is diffuse infiltration?
Infiltration; administered in a diffuse pattern to multiple sites.
What does "intra-arterial" mean?
Intra-arterial; administration within an artery or arteries.
What is the auricular part of the ear?
Auricular (Otic); administration to or by way of the ear. Buccal; referring to the inside lining of the cheeks and is part of the lining mucosa.
Where is intrathecal injection administered?
Intrathecal; administration within the cerebrospinal fluid at any level of the cerebrospinal axis, including injection into the cerebral ventricles.
What are the advantages of intravenous route?
Advantages of the Intravenous Route. Immediate effect (suitable for emergencies) Can be given to unconscious patients. Avoids first-pass metabolism. Achieves predictable and precise control over drug plasma levels compared to other routes.
What is IV drug?
A drug administered by the intravenous (IV) route is given directly into a vein as direct injection or infusion.
Where is buccal route administered?
The buccal route is administered by placing the buccal dosage form between the gum and the inner cheek. The drug is rapidly absorbed from the buccal mucosa and enters the systemic circulation, thus avoiding first-pass metabolism. In addition, this route can also be used for a local effect (e.g. hydrocortisone muco-adhesive buccal tablet for the treatment of aphthous ulceration of the mouth).
What is the most commonly used route for drug administration?
Oral Route. The drug is administered to or by way of the mouth. 1 A drug given via this route is absorbed into the systemic circulation from the gastrointestinal tract. The oral route is the most frequently used route for drug administration.
How long do you have to stay on your side after instilling ear drops?
This route may be considered time-consuming by the patient as they need to remain on their side/tilt the ear for a few minutes after instillation of ear drops
What is variable drug absorption dependent upon?
Variable drug absorption dependent upon the muscle group used and the blood flow to the muscle
How is a drug destroyed?
The drug may be destroyed by digestive enzymes and/or stomach acid
What does PT stand for in medical terms?
73. PT: Physical therapy, a type of treatment to help patients move and feel better.
What is a NICU?
69. NICU: Neonatal intensive care unit, a specialized unit that cares for premature infants.
What does BMI stand for?
57. BMI: Body mass index, a measure of body fat based on height and weight.
What does "pulmon/o" mean?
50. Pulmon/o: Refers to the lungs.
What is the meaning of the word "cardio"?
43. Cardi/o: Related to the heart.
What does "a" mean in medical terminology?
You likely know some of these from words outside the realm of medicine. 25. A-, an-: Lack of or without. 26. -ation: Indicates a process.
What are the medical terms used in medical charts?
You might even know some of them by a different name. 1. Abrasion: A cut or scrape that typically isn’t serious. 2. Abscess: A tender, fluid-filled pocket that forms in tissue, usually due to infection. 3.
