: either of a pair of membrane bones of the roof of the skull between the frontal and occipital bones that are large and quadrilateral in outline, meet in the sagittal suture, and form much of the top and sides of the cranium.
What does sagittal suture mean?
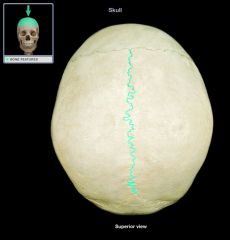
The sagittal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint between the two parietal bones of the skull. The term is derived from the Latin word sagitta, meaning arrow. In forensic anthropology, the sagittal suture is one method used to date human remains.
What are the 4 major sutures of the skull?
What are the 4 major sutures of the skull?
- Sagittal Suture - the joint between the two parietal bones.
- Coronal Suture - the joint between the frontal bone and the parietal bones.
- Squamous Suture - the joint between the parietal and temporal bones.
- Lambdoidal Suture - the joint between the parietal bones and the occipital bone.
How is sagittal used in a sentence?
sagittal in a sentence The sagittal suture joins together the two parietal bones of skull. The two most common types of craniosynostosis are sagittal and bicoronal. Any plane parallel to the median plane is a sagittal plane. The bones of the lambdoid, and one sagittal suture. The bilaterally ...
Does the sagittal suture connect the parietal bones?
The sagittal suture joins the two parietal bones to each other. The lambdoid suture joins the parietal bones to the occipital bone. The squamous suture joins the parietal bones to the temporal bones. Although the skull appears to be one large bone, there are actually several major bones thatare connected together.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/sagittal-suture/DrtLislQUAQFUQovvLDeA_Sagittal_suture_02.png)
What is the function of the sagittal suture?
…and the newborn child, the sagittal suture, which separates the right and left halves of the roof of the skull, is quite wide and markedly so at its anterior and posterior ends. This enables one of the halves to glide over the other during the passage of the child through…
Where is the sagittal suture?
Sagittal suture. This extends from the front of the head to the back, down the middle of the top of the head. The 2 parietal bone plates meet at the sagittal suture.
What is sagittal suture in anatomy?
Anatomical Parts The sagittal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint between the two parietal bones of the skull. The term is derived from the Latin word Sagitta, meaning "arrow".
Where is the sagittal suture and when does it close?
Sagittal synostosis– The sagittal suture runs along the top of the head, from the baby's soft spot near the front of the head to the back of the head. When this suture closes too early, the baby's head will grow long and narrow (scaphocephaly).
Why is it called sagittal suture?
The sagittal suture, also known as the interparietal suture and the sutura interparietalis, is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint between the two parietal bones of the skull. The term is derived from the Latin word sagitta, meaning arrow. Human adult skull from above. Human adult skull from above.
Which bones are joined by the sagittal suture?
The sagittal suture connects the two parietal bones. The lambdoid connects the two parietal bones to the occipital bone. The squamous sutures connect the parietal bones to the temporal bones.
What age does the sagittal suture fused?
The sagittal and lambdoid sutures do not usually begin to fuse before 18 years of age. However, more sagittal sutures are fused before age 18 than expected given the currently accepted prevalence of craniosynostosis.
What is the purpose of sutures in the skull?
The sutures and fontanelles are needed for the infant's brain growth and development. During childbirth, the flexibility of the sutures allows the bones to overlap so the baby's head can pass through the birth canal without pressing on and damaging their brain.
How many sutures are in a skull?
three suturesThe sutures are a type of fibrous joint, found in between many of the bones that make up the skull. Today we're going to take a look at three sutures; the coronal suture, the sagittal suture and the lambdoid suture.
What is the weakest suture location of the skull?
pterionThe pterion is known as the weakest part of the skull. The anterior division of the middle meningeal artery runs underneath the pterion. Consequently, a traumatic blow to the pterion may rupture the middle meningeal artery causing an epidural haematoma.
At what age does the skull stop growing?
By age 5, the skull has grown to over 90% of the adult size. All sutures remain open until adulthood, except for the metopic suture which usually closes between 6 and 12 months of age. A baby will have a misshapen head when one or more of the sutures closes too early.
What are the 4 sutures of skull?
The main sutures of the skull are the coronal, sagittal, lambdoid and squamosal sutures.
At what age does the sagittal suture close?
Normal Development of the Skull Base and Cranial Sutures The sagittal suture is the first to close, typically at around 22 years of age; the coronal suture closes at around 24 years; and the lambdoid and squamosal sutures close at around 26 and 60 years, respectively (2).
Where are sutures found?
In anatomy, a suture is a fairly rigid joint between two or more hard elements of an organism, with or without significant overlap of the elements. Sutures are found in the skeletons or exoskeletons of a wide range of animals, in both invertebrates and vertebrates.
What is the weakest suture location of the skull?
pterionThe pterion is known as the weakest part of the skull. The anterior division of the middle meningeal artery runs underneath the pterion. Consequently, a traumatic blow to the pterion may rupture the middle meningeal artery causing an epidural haematoma.
Where is the coronal suture located?
The coronal suture is a dense and fibrous association of connection tissue located in between the frontal and parietal bones of the skull.
What is subcuticular suture?
subcuticular suturea method of skin closure involving placement of stitches in the subcuticular tissues parallel with the line of the wound.
Where is buried suture placed?
buried sutureone placed within the tissues and concealed by the skin.
What is vertical mattress suture?
vertical mattress suturea suture whose stitches are at right angles to the edges of the wound, taking both deep and superficial bites of tissue; the superficial ones achieve more exact apposition of the cutaneous margins. When the suture material is pulled tight, the wound edges evert.
What is retention suture?
retention suturea reinforcing suture made of exceptionally strong material such as wire, and including large amounts of tissue in each stitch. Used to relieve pressure on the primary suture line and to decrease the potential for wound dehiscence.
What is a purse string suture?
purse-string suturea type of suture commonly used to bury the stump of the appendix, a continuous running suture being placed about the opening, and then drawn tight.
What is a lock stitch suture?
lock-stitch suturea continuous hemostatic suture used in intestinal surgery, in which the needle is, after each stitch, passed through the loop of the preceding stitch.
What is double armed suture?
double-armed sutureone made with suture material threaded through a needle at each end. Called also cobbler's suture.
What is the sagittal suture?
The sagittal suture is the midline articulation that joins the two parietal bones. premature fusion of the sagittal suture results in scaphocephaly. normal fusion of the sagittal suture occurs at approximately 22 years of age.
Which articulation joins the parietal bones?
The sagittal suture is the midline articulation that joins the two parietal bones.
When does a sagittal suture start fusing?
Sagittal suture, endocranially starts fusing at the age of 20-29 years.
What is subcuticular suture?
subcuticular suturea method of skin closure involving placement of stitches in the subcuticular tissues parallel with the line of the wound.
What is vertical mattress suture?
vertical mattress suturea suture whose stitches are at right angles to the edges of the wound, taking both deep and superficial bites of tissue; the superficial ones achieve more exact apposition of the cutaneous margins. When the suture material is pulled tight, the wound edges evert.
What is retention suture?
retention suturea reinforcing suture made of exceptionally strong material such as wire, and including large amounts of tissue in each stitch. Used to relieve pressure on the primary suture line and to decrease the potential for wound dehiscence.
What is a purse string suture?
purse-string suturea type of suture commonly used to bury the stump of the appendix, a continuous running suture being placed about the opening, and then drawn tight.
What is a lock stitch suture?
lock-stitch suturea continuous hemostatic suture used in intestinal surgery, in which the needle is, after each stitch, passed through the loop of the preceding stitch.
What is double armed suture?
double-armed sutureone made with suture material threaded through a needle at each end. Called also cobbler's suture.
Which suture separates the right and left halves of the roof of the skull?
…and the newborn child, the sagittal suture, which separates the right and left halves of the roof of the skull, is quite wide and markedly so at its anterior and posterior ends. This enables one of the halves to glide over the other during the passage of the child through…
What is the groove of the superior longitudinal venous sinus?
…front to back, along the sagittal suture, the seam between the two parietal bones, is a shallow depression—the groove for the superior longitudinal venous sinus, a large channel for venous blood. A number of depressions on either side of it mark the sites of the pacchionian bodies, structures that permit…
What is the name of the fusion of the sagittal suture?
Sagittal craniosynostosis describes a fusion of the sagittal suture, which runs from the front of the head to the back. This is the most common type of craniosynostosis, and is usually visible at birth or shortly after. 2
How to diagnose sagittal craniosynostosis?
Sagittal craniosynostosis is usually diagnosed with a physical exam. The abnormality is often spotted at birth because the skull malformation can be very pronounced.
What is the name of the condition that causes the bones in a baby's head to fuse prematurely?
Sagittal craniosynostosis is a type of craniosynostosis, a common birth defect that causes the bones in a baby’s head to fuse prematurely. The bones in your child’s skull are connected by joints called sutures. These sutures usually stay flexible until your little one’s second birthday, giving their brain room to grow.
Which type of craniosynostosis causes one side of the head to be flat?
Lambdoid craniosynostosis: This rare type of craniosynostosis affects the lambdoid suture. This suture runs along the back of the head, and premature fusing causes one side of the head to appear flat and one ear to be higher than the other.
Is sagittal craniosynostosis a genetic disorder?
Sagittal craniosynostosis may also be a symptom of a genetic disorder. Genetic disorders associated with sagittal craniosynostosis include: 2
Can sagittal craniosynostosis cause birth defects?
While we still do not understand the exact causes of sagittal craniosynostosis, some risk factors appear to raise a baby’s risk of having this birth defect.
Can a child with sagittal craniosynostosis survive surgery?
Fortunately, most babies with sagittal craniosynostosis have success with surgery and go on to live healthy lives without complications. Despite this hopeful prognosis, the diagnostic and treatment period can feel grueling for parents.
What is the growth of the sagittal suture?
The sagittal suture runs lengthwise along the top of the skull from front to back, therefore the growth at this suture gives the skull its width. When the sagittal suture is closed the skull can’t widen, so the remaining open sutures must create more bone to make room for the growing brain.
How is Pediatric Sagittal Craniosynostosis (Scaphocephaly) treated?
There is no one operation that works well for all patients. In general, the treatment strategy depends on the age of the patients at the time of diagnosis.
What helmet do you put a baby in after surgery?
After surgery, we place the baby in a custom-fit molding helmet. This helmet fits up against the forehead and back of the head and does not apply pressure. Instead, it resists growth in these directions. The skull then grows to a more normal shape because the brain takes the path of least resistance and widens pushing the bones as it expands.
How to remodel cranial vault?
In general, the skull bones are removed in the areas of abnormal restricted and compensatory growth and repositioned to over correct the head shape and increase the space in the skull. In general, for sagittal suture craniosynostosis the surgeries are aimed at restoring normal dimensions in the width, height and length of the skull. Rarely, surgeons use cranial vault distraction.
Where do sutures meet in the brain?
In the front of the skull, the sutures meet in the large soft spot (fontanel) on top of the head. The anterior fontanel is the soft spot you feel just behind your baby's forehead.
What is the name of the fusion of multiple sutures?
There are several types of craniosynostosis. Most involve the fusion of a single cranial suture. Some complex forms of craniosynostosis involve the fusion of multiple sutures. Most cases of multiple suture craniosynostosis are linked to genetic syndromes and are called syndromic craniosynostosis.
What type of suture causes craniosynostosis?
The term given to each type of craniosynostosis depends on what sutures are affected. Types of craniosynostosis include: Sagittal (scaphocephaly). Premature fusion of the sagittal suture that runs from the front to the back at the top of the skull forces the head to grow long and narrow.
What are the bones that hold the bones of a baby's skull together?
Cranial sutures and fontanels. Joints made of strong, fibrous tissue (cranial sutures) hold the bones of your baby's skull together. The sutures meet at the fontanels, the soft spots on your baby's head. The sutures remain flexible during infancy, allowing the skull to expand as the brain grows. The largest fontanel is at the front (anterior).
What is the name of the fusion that gives the forehead a triangular appearance?
Premature fusion gives the forehead a triangular appearance and widens the back part of the head. This is also called trigonocephaly. Lambdoid. Lambdoid synostosis is a rare type of craniosynostosis that involves the lambdoid suture, which runs along the back of the head.
Where is the fontanel in a baby's skull?
The next largest is at the back (posterior). Each side of the skull has a tiny fontanel. Craniosynostosis usually involves premature fusion of a single cranial suture, but can involve more than one of the sutures in your baby's skull (multiple suture craniosynostosis). In rare cases, craniosynostosis is caused by certain genetic syndromes ...
