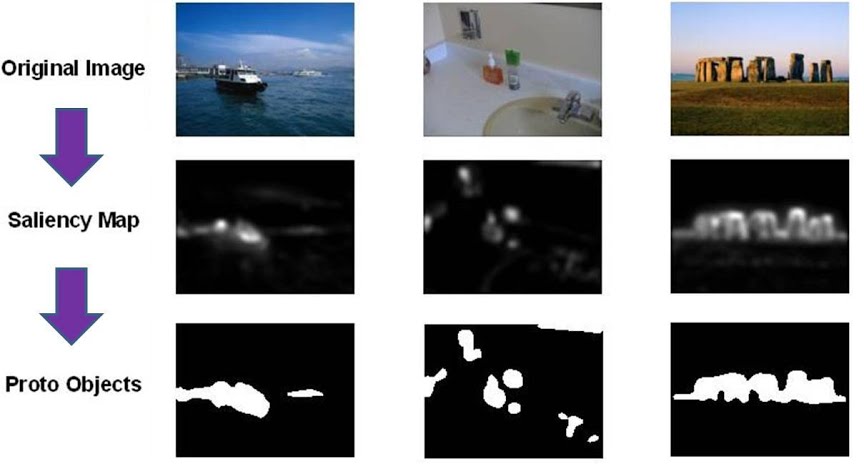
Saliency detection is generally described as the automatic estimation of significant (salient) objects and regions of images without any prior assumption or knowledge. Saliency usually is described as difference between a pixel and its surrounding neighborhood [ 2 ].
How is saliency measured?
What are the issues with artificially modelling saliency detection?
What is salience in psychology?
Why is a brand considered salient?
Why do we need limited cognitive resources?
What are some examples of things that stand out more than others?
Why do we hone in on something?
See 2 more

What is salience detection?
The salience of a stimulus is the state of being noticeable or important. Saliency detection is a key brain mechanism that facilitates learning and survival by enabling organisms to focus their limited attention resources on the most important event.
What is a salient object detection?
Salient object detection aims at simulating the visual characteristics of human beings and extracts the most attractive regions from images or videos. The content in these saliency areas is what we call salient objects.
What is saliency method?
A saliency map is a way to measure the spatial support of a particular class in each image. It is the oldest and most frequently used explanation method for interpreting the predictions of convolutional neural networks. The saliency map is built using gradients of the output over the input.
What is saliency in image processing?
Saliency refers to unique features (pixels, resolution etc.) of the image in the context of visual processing. These unique features depict the visually alluring locations in an image. Saliency map is a topographical representation of them.
What is an example of salience?
Salience is a critical low level cognitive ability that supports situational awareness. For example, a driver going at 40 miles per hour who is able to quickly focus on relevant things such as pedestrians, bicycles, vehicles and traffic lights from a fast moving stream of visual information.
How many types of object detection are there?
7 Types of Sensors for Object Detection.
What is salience and why is it important?
Salience is the way researchers understand what information will most likely capture one's attention in a given situation and have the greatest influence on one's cognitions about the stimuli.
Why is salience used?
Salience is also used in cognitive linguistics to explain an array of information–theoretical concepts drawn from cognitive psychology to account for attentional processes.
Why do we use salience?
Understanding stakeholder saliency is useful because it helps you identify how to spend your limited resources. You have limited time, and you can make the most of that by applying different levels of stakeholder engagement to different people.
What is the salience of an image?
Salience: the part of the image that grabs your attention first. Salience is created by different features such as the size, sharpness or focus of people or objects; colour; placement of figures or object in the foreground.
What is the effect of saliency?
The Salience Effect explores the why, when and how of which elements are “salient” for different individuals - meaning which elements we are most drawn to and will focus our attention on.
What is a salient feature in an image?
Christine Roman-Lantzy. Salient visual features are the defining elements that distinguish one target from another. They are key pieces of distinct information that facilitate the recognition of an image, object, environment, or person.
What is video salient object detection?
Video salient object detection aims to find the most visually distinctive objects in a video. To explore the temporal dependencies, existing methods usually resort to recurrent neural networks or optical flow. However, these approaches require high computational cost, and tend to accumulate inaccuracies over time.
What are the methods for object detection?
1| Fast R-CNN.2| Faster R-CNN.3| Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG)4| Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks (R-CNN)5| Region-based Fully Convolutional Network (R-FCN)6| Single Shot Detector (SSD)7| Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP-net)8| YOLO (You Only Look Once)
Which method is best for object detection?
– RetinaNet is currently one of the best methods for object detection in a number of different tasks. It can be used as a replacement for a single-shot detector for a multitude of tasks to achieve quick and accurate results for images.
What is the difference between object detection and recognition?
Object recognition models are given an image or video, with the task of identifying all the relevant objects in it. Object detection models are given an image or video as well as an object class, with the task of identifying all the occurrences of that object (and only that object).
Image saliency detection - Digital Scientists
To automatically identify the most relevant or salient visual elements within thousands of images, we used a process called image saliency, which enables its user to detect logos, branding, and other key design elements in websites.
Xiaodi Hou's Homepage
Xiaodi Hou's Homepage
Saliency Detection - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
There has been quite a surge of interest in saliency detection since the early works. The context aware saliency is grounded in psychology [Goferman12] (learning from human vision is invariably a good idea). The approach uses colour images, and the colour representation is the CIE Lab (to be covered later in Chapter 11) as it is known to be the closest system to human colour vision.
OpenCV Static Saliency Detection in a Nutshell
On-center and off-center ganglion cells and their approximation on computational models of visual saliency. Source: B. Wang and P. Dudek “A Fast Self-tuning Background Subtraction Algorithm”, in proc of IEEE Workshop on Change Detection, 2014
What is FES algorithm?
A free energy inspired saliency (FES) algorithm was proposed in [44]. FES was motivated by the fact that the free energy principle directly relates free energy level to the amount of “surprise” of a given scene. AR and bi-lateral filtering was used as the generative model.
What is the overall saliency?
The overall saliency is then the average of the saliency over the number of scales NS
How to determine saliency at point A?
Again, the value for K can be chosen by experiment. The saliency at point a is determined by averaging the best K dissimilarities over patches b as
Why are cosegmentation methods limited?
Generally, several state-of-the-art cosegmentation methods still have some limitations because they required the co-labeling of multiple images simultaneously , which caused high computational cost mainly for large diverse datasets. For that, authors proposed in Jerripothula, Cai, and Yuan (2016) a binary image cosegmentation method for a given image set. In fact, they exploited multiple existing saliency extraction methods to obtain diverse salient maps of each image independently, in order to be then fused using the association of similar images, for the purpose of boosting up common foreground saliency and suppressing background saliency. Nevertheless, when one foreground object is extremely salient in all the saliency maps and the other one is not very salient in any of the saliency maps, this leads to only segment out the foreground object while missing the other. Moreover, when part region of the foreground object is not so salient, this method fails to extract correctly the foreground objects and this is mainly the case of faces where shoulders are missing.
What is the grey level of an image?
Grey level images use a single value per pixel that it is called intensity or brightness . As presented in Chapter 2, the intensity represents the amount of light reflected or emitted by an object, and it is dependent on the object's material properties as well as on the sensitivity of the camera sensors. Historically, image processing and computer vision have mainly used grey level images since colour sensors were very expensive and the computer processing was very limited. Also, grey level images have less noise, so they are adequate for locating low-level features like edges and corners. However, as devices have increased processing power and with the development of inexpensive colour sensors of high quality, colour images are now ubiquitous. So image processing is now commonly used to process colour information and not only to develop algorithms for image understanding and scene representation, but also to create images that appeal to humans. Thus, colour image processing has become increasingly necessary, as seen in superpixels (Section 8.2.3). Besides, it is evident that some processes like the localisation and identification of objects can obtain clear advantage by incorporating colour information, as we have already seen in saliency detection. For example, colour is an important clue in traffic sign recognition.
What is a low-rank tensor?
The low-rank structure also exists in tensor. Tensor is a higher dimensional generalization of the matrix that attracts great attention recent years. Low-rank tensor recovery aims to recover the low-rank tensor M ∈ R N 1 × … × N n from a limited number of observations, where A: R N 1 × … × N n → R M (typically M ≪ ∏ i = 1 n N i ). The corresponding prior information J ( ·) = rank ( M), where rank ( M) denotes some form of tensor rank. One popular approach is to use tensor nuclear norm ∥ M ∥ *, which is a convex combination of the nuclear norms of all matrices unfolded along different modes [27]. There also exists nonconvex method, for example, in [28], Chen et al. propose an empirical Bayes method that has state-of-the-art performance in sparse and low-rank matrix recovery.
What are the different types of color models?
In this chapter, we distinguish four types of colour models. The first type of model is based on perception. Perception models sort out colours according to the similarities we perceive , and they were developed by experiments aimed at establishing measurable links between colours. The second type of model describes colours according to the way they are used in reproduction systems (e.g. printing and displaying). The third type of model looks for separating the brightness from the hue (pigment). These models were created by the practical necessity of video transmission and have become very popular for video encoding. The last type of colour model creates a perceptual organisation by rearranging the colour of other models by using a colour transformation. The aim is to create an arrangement that is more intuitive and easy to interpret. The chapter is summarised in Table 11.1.
U 2 -Net: Going Deeper with Nested U-Structure for Salient Object Detection
In this paper, we design a simple yet powerful deep network architecture, U 2 -Net, for salient object detection (SOD).
Pyramid Feature Attention Network for Saliency detection
To solve this problem, we propose Pyramid Feature Attention network to focus on effective high-level context features and low-level spatial structural features.
Uncertainty Inspired RGB-D Saliency Detection
Our framework includes two main models: 1) a generator model, which maps the input image and latent variable to stochastic saliency prediction, and 2) an inference model, which gradually updates the latent variable by sampling it from the true or approximate posterior distribution.
Real Time Image Saliency for Black Box Classifiers
In this work we develop a fast saliency detection method that can be applied to any differentiable image classifier.
Sanity Checks for Saliency Maps
We find that reliance, solely, on visual assessment can be misleading.
Time-Series Anomaly Detection Service at Microsoft
At Microsoft, we develop a time-series anomaly detection service which helps customers to monitor the time-series continuously and alert for potential incidents on time.
CAGNet: Content-Aware Guidance for Salient Object Detection
Beneficial from Fully Convolutional Neural Networks (FCNs), saliency detection methods have achieved promising results.
Authors
Get the week's most popular data science and artificial intelligence research sent straight to your inbox every Saturday.
I Introduction
aims at identifying the visually interesting object regions that are consistent with human perception. It is intrinsic to many computer vision tasks such as image cropping
Iii Joint Salient Edge and Saliency Detection
To highlight salient edges as well as better detect salient objects of diverse scales, we reformulate saliency detection as a three-category dense labeling task and jointly learn salient edge and saliency map within our end-to-end framework. Furthermore, to handle the imbalance in labeling, we propose a new loss function.
Iv Integrating Deep and Handcrafted Features
Deep learning based saliency detection methods predict saliency maps by exploiting large scale labeled saliency datasets, which could be biased by the training datasets.
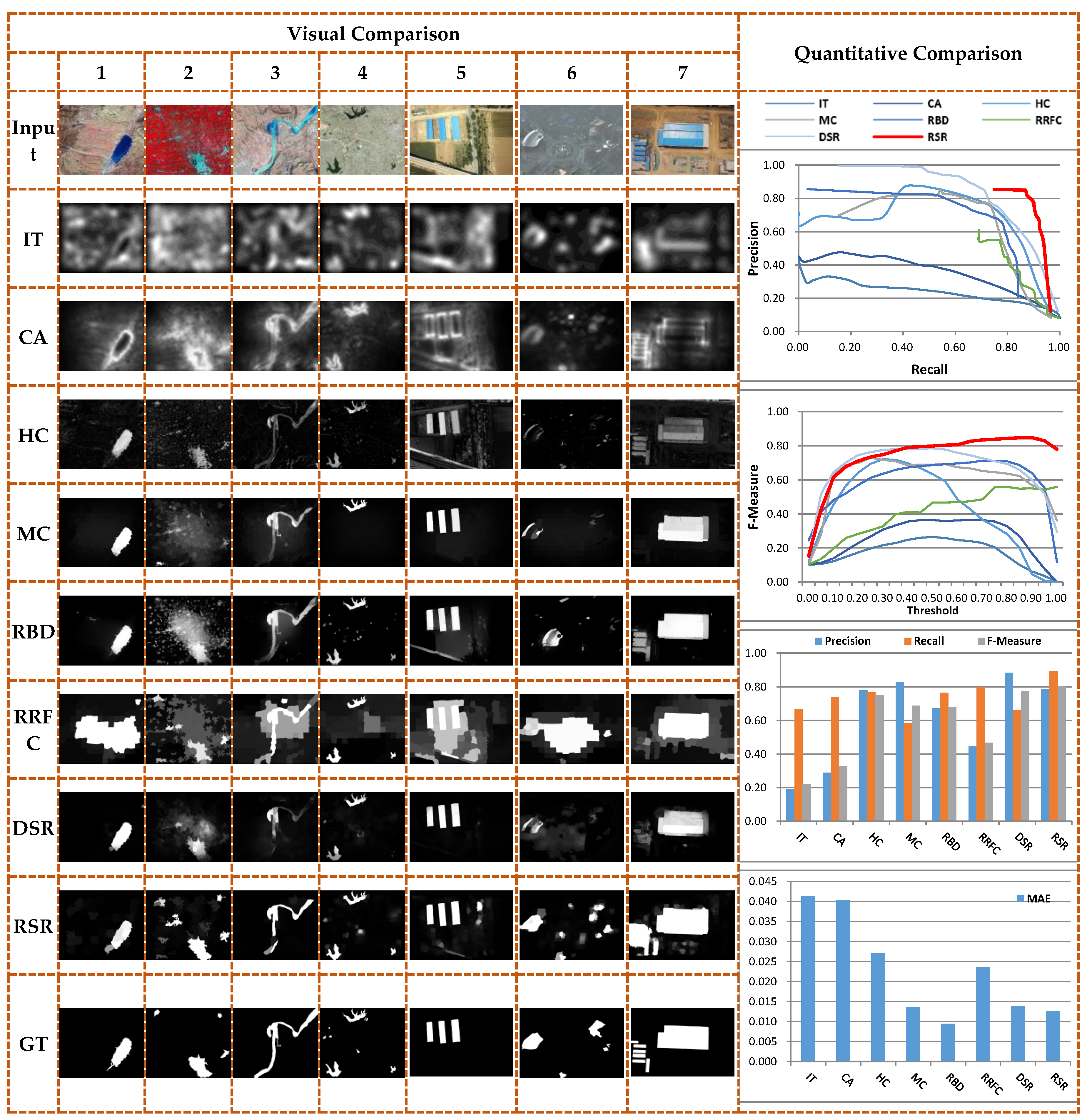
V Experimental Results
Dataset: We have evaluated the performance of our proposed model on 10 saliency benchmarking datasets.
Vi Conclusions
We reformulated saliency detection as a three-category dense labeling problem and introduced an edge-aware model. We demonstrated that with saliency edges as constraints in our formulation, we achieved more accurate saliency map and preserve salient edges.
What is salience in biology?
The salience (also called saliency) of an item is the state or quality by which it stands out from its neighbors. Saliency detection is considered to be a key attentional mechanism that facilitates learning and survival by enabling organisms to focus their limited perceptual and cognitive resources on the most pertinent subset ...
What are the limitations of saliency detection?
A key limitation in many such approaches is their computational complexity leading to less than real-time performance, even on modern computer hardware. Some recent work attempts to overcome these issues at the expense of saliency detection quality under some conditions. Other work suggests that saliency and associated speed-accuracy phenomena may be a fundamental mechanisms determined during recognition through gradient descent, needing not be spatial in nature.
What is the primary visual cortex?
The primary visual cortex (V1) generate s a bottom-up saliency map from visual inputs to guide reflexive attentional shifts or gaze shifts. According to V1 Saliency Hypothesis, the saliency of a location is higher when V1 neurons give higher responses to that location relative to V1 neurons' responses to other visual locations. For example, a unique red item among green items, or a unique vertical bar among horizontal bars, is salient since it evokes higher V1 responses and attracts attention or gaze. The V1 neural responses are sent to the superior colliculus to guide gaze shifts to the salient locations. A fingerprint of the saliency map in V1 is that attention or gaze can be captured by the location of an eye-of-origin singleton in visual inputs, e.g., a bar uniquely shown to the left eye in a background of many other bars shown to the right eye, even when observers cannot tell the difference between the singleton and the background bars.
Which nucleus modulates physical/perceptual salience in attentional selection?
The pulvinar nuclei (in the thalamus) modulate physical/perceptual salience in attentional selection.
How to mimic bottom up saliency?
One way is based on the spatial contrast analysis: for example, a center-surround mechanism is used to define saliency across scales, which is inspired by the putative neural mechanism. The other way is based on the frequency domain analysis. While they used the amplitude spectrum to assign saliency to rarely occurring magnitudes, Guo et al. use the phase spectrum instead. Recently, Li et al. introduced a system that uses both the amplitude and the phase information.
What is the NAC and VTA?
The NAc and VTA are central components of the circuitry underlying reward and memory of reward. As previously mentioned, the activity of dopaminergic neurons in the VTA appears to be linked to reward prediction. The NAc is involved in learning associated with reinforcement and the modulation of motoric responses to stimuli that satisfy internal homeostatic needs. The shell of the NAc appears to be particularly important to initial drug actions within reward circuitry; addictive drugs appear to have a greater effect on dopamine release in the shell than in the core of the NAc.
What is the reward circuitry of addictive drugs?
The brain reward circuitry that is targeted by addictive drugs normally mediates the pleasure and strengthening of behaviors associated with natural reinforcers, such as food, water, and sexual contact. Dopamine neurons in the VTA are activated by food and water, and dopamine release in the NAc is stimulated by the presence of natural reinforcers, such as food, water, or a sexual partner. ...
What does salient mean in photography?
Salient means “most noticeable or important”. So, salient object detection is the detection of the most noticeable/important object in an image.
What are the two dominant colors of circles?
Out of those circles, identify circles with two dominant colors- red and white .
How many ways are there to track an object?
There are two sets of ways to “track” an object.
What is labelbox?
Labelbox helps take artificial intelligence and machine learning initiatives from the research & development phase all the way to production. The platform allows AI & ML teams to(Continue reading)
Why do we use dense method of tracking?
Because we are processing all the pixels of the video snap many times, these kind of algorithms come under dense method of tracking.
Is sparse method of tracking faster?
As we are processing the pixels which are near to the area where we are estimating object to be , this is sparse method of tracking. Also, it is faster (processing of less pixels)
Can you identify stop signs in an image?
If you have a list of objects that satisfy all of the above, it is possible that you were able to identify all stop signs in your image. therefore you have implemented a stop sign detector.
How To Create Saliency Maps?
This section presents the steps generally considered in creating saliency maps for learning algorithms such as neural networks. For this, the saliency model created by Itti is borrowed for explanation purposes. The model considers three features in an image, namely colours, intensity and orientations. These combinations are presented in the saliency map. The model uses a winner-takes-it-all neural network for working with the saliency map.
How are saliency maps created?
Saliency maps are created based on the traffic light condition in the images through an illumination algorithm.
What is saliency map?
Saliency refers to unique features (pixels, resolution etc.) of the image in the context of visual processing. These unique features depict the visually alluring locations in an image. Saliency map is a topographical representation of them.
How has deep learning changed the way visual problems are addressed in machine learning?
Deep learning has changed the way visual problems are addressed in machine learning. Elements such as convolutional neural networks (CNN) have now become the standard architecture for areas like image recognition and computer vision. Research in these areas has unveiled scores of new theoretical concepts and innovative practical implementations. A plethora of concepts are available to achieve these futuristic technologies.
How many angles does the orientation feature have?
The orientation feature is converted using Gabor filters with respect to four angles.
Who created the feature extraction map?
These maps were first proposed by neuroscientists Laurent Itti, Christof Koch and Ernst Niebur in their study on feature extraction in images. They give a detailed description which is given below.
How is saliency measured?
It has taken a long time to develop methods for assessing the saliency of images.
What are the issues with artificially modelling saliency detection?
Issues with artificially modelling saliency detection include the fact that current models use low- level saliency cues. These may include contrast and colour.
What is salience in psychology?
Saliency is the aspect of any stimulus that makes it stand out from the crowd. The reason a particular stimulus has such salience may be due to contrast i.e. a white line on a black background or as a result of emotional or cognitive factors.
Why is a brand considered salient?
The reason a brand may be salient stems from the science behind saliency itself. Not only must the brand be visually appealing but memory and past experience can also inform saliency. If you previously had a positive experience with a product and spot it in the supermarket. It is much more likely to “jump out at you”.
Why do we need limited cognitive resources?
Our limited cognitive resources require a way to identify the most relevant stimuli for learning and or survival.
What are some examples of things that stand out more than others?
If you find yourself gazing over a city from a height for example, you may be drawn to a nearby skyscraper, a flashing light or even a red coat someone is wearing below.
Why do we hone in on something?
For example, we may hone in on something because we are actively looking for it or because it triggers something in our past or memory.