Quota Sampling
- Methods of sampling are used to choose accurate samples from a population so as to represent its characteristics.
- There are two types of sampling techniques - probability and non-probability sampling.
- Probability sampling is used for hypothesis testing in quantitative research.
- Non-probability sampling is used to gather an initial understanding of the population for qualitative research.
What are some examples of sampling techniques?
Real world examples of simple random sampling include:
- At a birthday party, teams for a game are chosen by putting everyone's name into a jar, and then choosing the names at random for each team.
- On an assembly line, each employee is assigned a random number using computer software. ...
- A restaurant leaves a fishbowl on the counter for diners to drop their business cards. ...
What are the two types of sampling methods?
Sampling methods can be broadly categorised into two types – random or probability sampling methods and non-random or non-probability sampling methods. Random or probability sampling methods can be further sub-divided into 2 types, i.e. restricted or simple random sampling and unrestricted random sampling.
What are the different sampling techniques in statistics?
Sampling Methods | Types and Techniques Explained
- The Purpose of Sampling. In psychological research we are interested in learning about large groups of people who all have something in common.
- Random Sampling. ...
- Stratified Sampling. ...
- Opportunity Sampling. ...
- Systematic Sampling. ...
What are the types of random sampling methods?
Types of Random Sampling Methods
- Simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is the randomized selection of a small segment of individuals or members from a whole population.
- Systematic sampling. Systematic sampling is the selection of specific individuals or members from an entire population. ...
- Stratified sampling. ...
- Cluster sampling. ...

What is the definition of sampling techniques?
A sampling technique is the name or other identification of the specific process by which the entities of the sample have been selected.
What do you mean by sample and sampling?
Sampling is a process in statistical analysis where researchers take a predetermined number of observations from a larger population. The method of sampling depends on the type of analysis being performed, but it may include simple random sampling or systematic sampling.
What is sample size and sampling techniques?
Number of elements in the population is the size of the population. Sample is the subset of the population. The process of selecting a sample is known as sampling. Number of elements in the sample is the sample size.
What is sample and sampling in statistics?
A sample refers to a smaller, manageable version of a larger group. It is a subset containing the characteristics of a larger population. Samples are used in statistical testing when population sizes are too large for the test to include all possible members or observations.
What are the 4 types of samples?
There are 4 types of random sampling techniques:Simple Random Sampling. Simple random sampling requires using randomly generated numbers to choose a sample. ... Stratified Random Sampling. ... Cluster Random Sampling. ... Systematic Random Sampling.
What is the purpose of sampling?
The primary goal of sampling is to create a representative sample, one in which the smaller group (sample) accurately represents the characteristics of the larger group (population). If the sample is well selected, the sample will be generalizable to the population.
What are the 5 different sampling techniques explain each?
There are five types of sampling: Random, Systematic, Convenience, Cluster, and Stratified. Random sampling is analogous to putting everyone's name into a hat and drawing out several names. Each element in the population has an equal chance of occuring.
What are the 5 basic sampling methods?
Five Basic Sampling MethodsSimple Random.Convenience.Systematic.Cluster.Stratified.
What is a sample in research?
In research terms a sample is a group of people, objects, or items that are taken from a larger population for measurement. The sample should be representative of the population to ensure that we can generalise the findings from the research sample to the population as a whole.
What are the different type of sampling?
Table of Contents:Definition.Types.Probability Sampling Methods. Simple random sampling. Systematic sampling. Stratified sampling. Clustered sampling.Non-probability Sampling Methods. Convenience sampling. Consecutive sampling. Quota sampling. Purposive or Judgmental sampling. ... Probability vs Non-probability Sampling.FAQs.
What are the 4 sampling strategies?
Four main methods include: 1) simple random, 2) stratified random, 3) cluster, and 4) systematic. Non-probability sampling – the elements that make up the sample, are selected by nonrandom methods. This type of sampling is less likely than probability sampling to produce representative samples.
What are characteristics of sampling?
It should not lack in any characteristic of the population. It must be unbiased and must be obtained by a probability processor random method. It must make the research work more feasible and has the practicability for the research situation.
What do you mean by sample in research?
In research terms a sample is a group of people, objects, or items that are taken from a larger population for measurement. The sample should be representative of the population to ensure that we can generalise the findings from the research sample to the population as a whole.
What is the difference between sample and sampling unit?
In the context of market research, a sampling unit is an individual person. The term sampling unit refers to a singular value within a sample database. For example, if you were conducting research using a sample of university students, a single university student would be a sampling unit.
What is the difference between sample and sampling frame?
The sampling frame lies between the population and sample. Ideally, the sampling frame should match the population, but rarely does because the population is not usually small enough to list all members of the population. Sample: Those individuals or objects who provide the data to be collected.
What is the difference between sample and sampling distribution?
The sampling distribution considers the distribution of sample statistics (e.g. mean), whereas the sample distribution is basically the distribution of the sample taken from the population.
What is sample in research?
The sample is the group of individuals who will actually participate in the research. To draw valid conclusions from your results, you have to carefully decide how you will select a sample that is representative of the group as a whole. There are two types of sampling methods:
What is a sampling frame?
The sampling frame is the actual list of individuals that the sample will be drawn from. Ideally, it should include the entire target population (and nobody who is not part of that population).
How to determine how many people should be sampled from each subgroup?
Based on the overall proportions of the population, you calculate how many people should be sampled from each subgroup. Then you use random or systematic sampling to select a sample from each subgroup.
What is the best way to conduct a random sample?
1. Simple random sampling. In a simple random sample, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. Your sampling frame should include the whole population. To conduct this type of sampling, you can use tools like random number generators or other techniques that are based entirely on chance.
How does cluster sampling work?
Cluster sampling also involves dividing the population into subgroups, but each subgroup should have similar characteristics to the whole sample. Instead of sampling individuals from each subgroup, you randomly select entire subgroups.
What is stratified sampling?
Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into subpopulations that may differ in important ways. It allows you draw more precise conclusions by ensuring that every subgroup is properly represented in the sample.
What is probability sampling?
Probability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that are representative of the whole population, probability sampling techniques are the most valid choice.
Which method of sampling is the easiest?
Convenience sampling is the easiest method of sampling and the participants are selected based on availability and willingness to participate in the survey. The results are prone to significant bias as the sample may not be a representative of population.
What is a sample in a study?
The sample is the group of elements who participated in the study.
How to select a random sample?
One possible method of selecting a simple random sample is to number each unit on the sampling frame sequentially and make the selections by generating numbers from a random number generator.
How does systematic random sampling work?
In systematic random sampling, the researcher first randomly picks the first item from the population. Then, the researcher will select each nth item from the list . The procedure involved in systematic random sampling is very easy and can be done manually. The results are representative of the population unless certain characteristics of the population are repeated for every nth individual.
Why is probability sampling important?
Probability sampling is normally preferred when conducting major studies, especially when a population frame is available, ensuring that we can select and contact each unit in the population. Probability sampling allows us to quantify the standard error of estimates, confidence intervals to be formed and hypotheses to be formally tested.
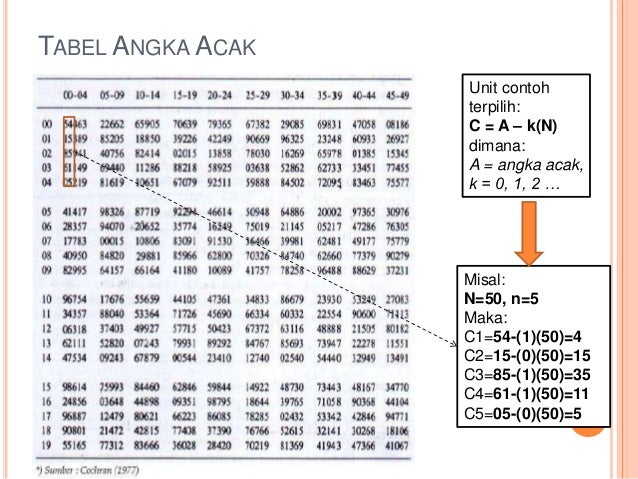
What is quota sampling?
Quota sampling can be divided into two groups-. Controlled quota sampling involves introduction of certain restrictions in order to limit researcher’s choice of samples. Uncontrolled quota sampling resembles convenience sampling method in a way that researcher is free to choose sample group members.
What is the process of selecting a group of individuals from a population to study them and characterize the population as?
Sampling is the process of selecting a group of individuals from a population to study them and characterize the population as a whole. The population includes all members from a specified group, all possible outcomes or measurements that are of interest. The exact population will depend on the scope of the study.
What are the sampling methods or Sampling Techniques?
In Statistics, the sampling method or sampling technique is the process of studying the population by gathering information and analyzing that data. It is the basis of the data where the sample space is enormous.
What are the two types of sampling methods?
In Statistics, there are different sampling techniques available to get relevant results from the population. The two different types of sampling methods are:: 1 Probability Sampling 2 Non-probability Sampling
What is Non-Probability Sampling?
The non-probability sampling method is a technique in which the researcher selects the sample based on subjective judgment rather than the random selection. In this method, not all the members of the population have a chance to participate in the study.
What are the different types of probability sampling?
Probability Sampling methods are further classified into different types, such as simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and clustered sampling. Let us discuss the different types of probability sampling methods along with illustrative examples here in detail.
How is stratified sampling done?
In a stratified sampling method, the total population is divided into smaller groups to complete the sampling process. The small group is formed based on a few characteristics in the population. After separating the population into a smaller group, the statisticians randomly select the sample.
What is the method of chance selection?
In simple random sampling technique , every item in the population has an equal and likely chance of being selected in the sample. Since the item selection entirely depends on the chance, this method is known as “ Method of chance Selection ”. As the sample size is large, and the item is chosen randomly, it is known as “ Representative Sampling ”.
What is snowball sampling?
The snowball sampling is also known as chain-referral sampling technique. In this method, the samples have traits that are difficult to find. So, each identified member of a population is asked to find the other sampling units. Those sampling units also belong to the same targeted population.
What is the purpose of sampling?
Sampling is a method that allows us to get information about the population based on the statistics from a subset of the population (sample), without having to investigate every individual.
What is the first step in the sampling process?
Step 1. The first stage in the sampling process is to clearly define the target population. So, to carry out opinion polls, polling agencies consider only the people who are above 18 years of age and are eligible to vote in the population.
Why do we need Sampling?
I’m sure you have a solid intuition at this point regarding the question.
Why is probability sampling used?
Generally, probability sampling methods are used because every vote has equal value and any person can be included in the sample irrespective of his caste, community, or religion. Different samples are taken from different regions all over the country.
What is clustered sample?
In a clustered sample, we use the subgroups of the population as the sampling unit rather than individuals. The population is divided into subgroups, known as clusters, and a whole cluster is randomly selected to be included in the study:
What is a sampling frame?
Sampling Frame – It is a list of items or people forming a population from which the sample is taken.
Why is convenience sampling prone to bias?
Convenience sampling is prone to significant bias, because the sample may not be the representation of the specific characteristics such as religion or, say the gender, of the population.
What is the process of selecting a sample?
Sample is the subset of the population. The process of selecting a sample is known as sampling. Number of elements in the sample is the sample size.
Why is sampling important in research?
Sampling Techniques. Sampling helps a lot in research. It is one of the most important factors which determines the accuracy of your research/survey result. If anything goes wrong with your sample then it will be directly reflected in the final result. There are lot of techniques which help us to gather sample depending upon the need and situation.
What is random sampling?
This Sampling technique uses randomization to make sure that every element of the population gets an equal chance to be part of the selected sample. It’s alternatively known as random sampling.
How is the population divided into small subgroups?
This technique divides the elements of the population into small subgroups (strata) based on the similarity in such a way that the elements within the group are homogeneous and heterogeneous among the other subgroups formed. And then the elements are randomly selected from each of these strata. We need to have prior information about the population to create subgroups.
When to use simple random sampling?
It is used when we don’t have any kind of prior information about the target population.
Is selection random or systematic?
Here the selection of elements is systematic and not random except the first element. Elements of a sample are chosen at regular intervals of population. All the elements are put together in a sequence first where each element has the equal chance of being selected.
Is random sampling biased?
It does not rely on randomization. This technique is more reliant on the researcher’s ability to select elements for a sample. Outcome of sampling might be biased and makes difficult for all the elements of population to be part of the sample equally. This type of sampling is also known as non-random sampling.
What is the definition of a sample?
Definition: Choose members of a population that are readily available to be included in the sample. Example: A researcher stands in front of a library during the day and polls people that happen to walk by. Drawback: Location and time of day will affect the results.
What is the first class of sampling methods?
The first class of sampling methods is known as probability sampling methods because every member in a population has an equal probability of being selected to be in the sample.
What are the drawbacks of sampling bias?
Because initial subjects recruit additional subjects, it’s likely that many of the subjects will share similar traits or characteristics that might be unrepresentative of the larger population under study. Thus, findings from the sample can’t be extrapolated to the population.
Why is non probability sampling used?
This type of sampling method is sometimes used because it’s much cheaper and more convenient compared to probability sampling methods.
Why is cluster random sampling useful?
Benefit: Cluster random samples get every member from some of the groups, which is useful when each group is reflective of the population as a whole.
What are the drawbacks of a voluntarily responding sample?
Drawback: People who voluntarily respond will likely have stronger opinions (positive or negative) than the rest of the population , which makes them an unrepresentative sample. Using this sampling method, the sample is likely to suffer from nonresponse bias – certain groups of people are simply less likely to provide responses.
What is the benefit of random sampling?
Benefit: Simple random samples are usually representative of the population we’re interested in since every member has an equal chance of being included in the sample.
Population vs Sample
Probability Sampling Methods
- Probability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that are representative of the whole population, probability sampling techniques are the most valid choice. There are four main types of probability sample.
Non-Probability Sampling Methods
- In a non-probability sample, individuals are selected based on non-random criteria, and not every individual has a chance of being included. This type of sample is easier and cheaper to access, but it has a higher risk of sampling bias. That means the inferences you can make about the population are weaker than with probability samples, and your conclusions may be more limited…
Why Do We Need Sampling Techniques?
- Research benefits greatly from sampling. It is one of the most crucial elements that affect how accurate your study or survey results are. If your sample contains any errors, the outcome will be affected accordingly. Depending on the situation and necessity, numerous methodologies aid in sample collection. But before diving into the topic, let’s look at some essential statistical terms y…
What Is A Sampling Technique?
- It is seldom possible to gather data from every member of a group of individuals when conducting research on them. So, what do you do? Well, you pick a sample instead. The population that will actually take part in the study is the sample. The sampling technique is the method you employ while choosing a sample from a population. For example, you co...
Non-Probability Sampling Techniques
- In non-probability sampling, participants are chosen at random by the researcher. This type of sampling is not a set or predetermined selection procedure. Due to this, it is challenging to ensure that every component of a population has an equal chance of being represented in a sample. It enables simple data collection. A non-representative sample that cannot yield generalizable con…
Conclusion
- Sampling is a very extensive yet one of the most undermined areas in research and general statistical studies. People don’t realize how important it is to choose suitable sampling methods to achieve the correct results. Most use the same one or two generic approaches, regardless of their use case, resulting in improper results. So, to achieve your research objectives properly, sel…