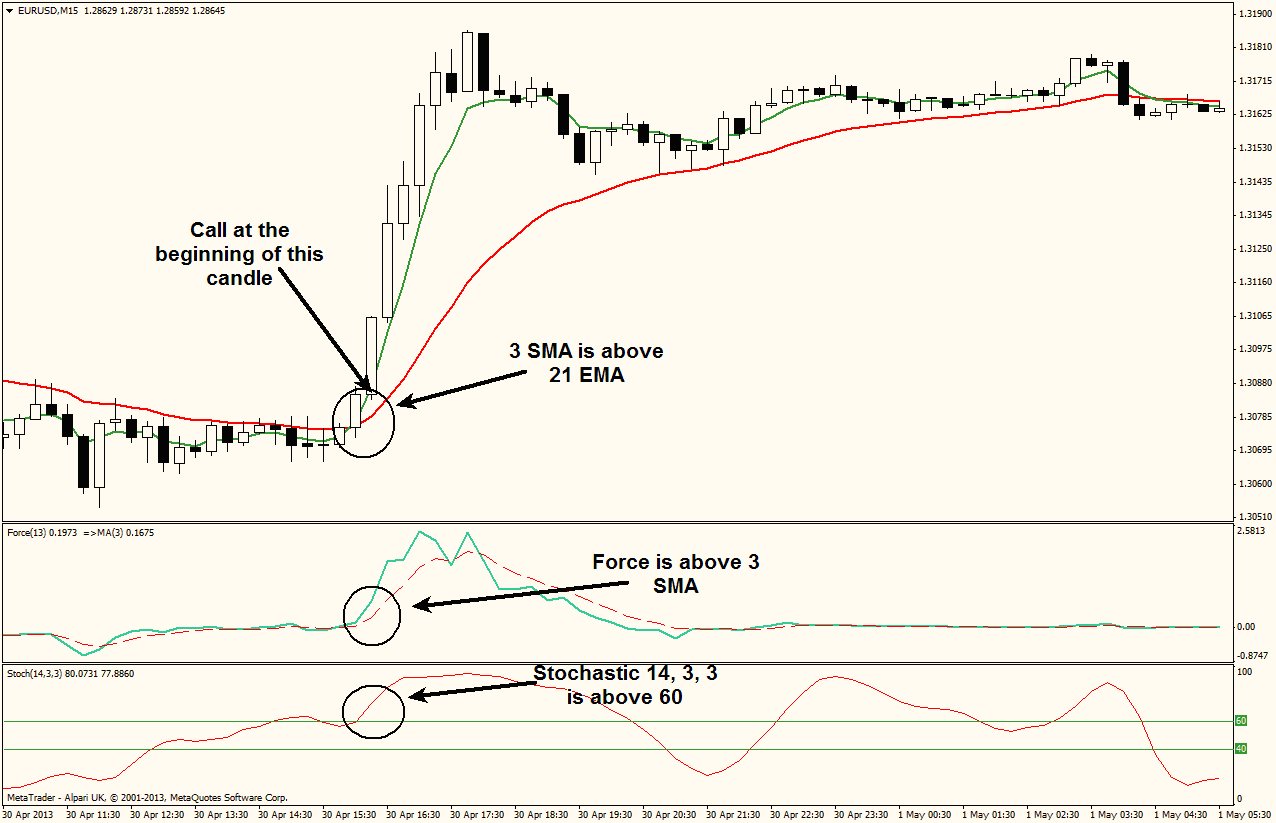
Scarcity is the idea that there are limited resources or goods available. 1 Anything people desire or can’t obtain easily is considered to be scarce. When facing scarcity, you have to make trade-offs, which is one of the underlying principles of economics.
What is scarcity and how does it force tradeoffs?
What is Scarcity, and how does it force tradeoffs? - Scarcity is the condition that results because people have limited resources but unlimited wants. - It forces trade offs by the idea that limited resources force people to make choices and face tradeoffs when they choose.
Why does scarcity lead to trade offs?
Thereof, how does scarcity force trade off? Since consumers' resources such as time, attention, and money are limited, they must choose how to best allocate them by making tradeoffs. The concept of trade-offs due to scarcity is formalized by the concept of opportunity cost. The opportunity cost of a choice is the value of the best alternative forgone.
What are 3 causes of scarcity?
What are the three main causes of water scarcity around the world?
- Climate change.
- Natural calamities such as droughts and floods.
- Increased human consumption.
- Overuse and wastage of water.
- A global rise in freshwater demand.
- Overuse of aquifers and its consequent slow recharge.
What are the reasons for scarcity?
The causes of scarcity can be due to a number of different reasons, but there are four primary ones. Poor distribution of resources, personal perspective on resources, a rapid increase in demand, and a rapid decrease in supply are all potential scarcity causes. The key is to determine what the causes are so that the situation can be corrected.

How does scarcity force trade-off?
Because of scarcity people are forced to make choices. When you choose one item over another you are making a tradeoff. You are trading away – or giving up – one thing that you want so that you can get something that you want even more. Remember, what you gave up (or traded) is your opportunity cost.
What is scarcity forces tradeoffs example?
Scarcity Forces Tradeoff. Limited resources force people to make choice and trade offs when they choose. Scarcity Forces Tradeoffs (example) Boring, high-paying mall job or an internship that is in your high interests. Costs Vs Benefits.
Does scarcity create trade-offs?
Scarcity is the idea that there are limited resources or goods available. 1 Anything people desire or can't obtain easily is considered to be scarce. When facing scarcity, you have to make trade-offs, which is one of the underlying principles of economics.
What is scarcity force?
Scarcity forces all of us to make choices by making us decide which options are most important to us. The principle of scarcity states that there are limited goods and services for unlimited wants. Thus, people need to make choices in order to satisfy the wants that are most important to them.
What is scarcity with example?
What is Scarcity in Economics. In economics, scarcity refers to the limited resources we have. For example, this can come in the form of physical goods such as gold, oil, or land – or, it can come in the form of money, labour, and capital. These limited resources have alternate uses.
What is a trade-off example?
In economics, a trade-off is defined as an "opportunity cost." For example, you might take a day off work to go to a concert, gaining the opportunity of seeing your favorite band, while losing a day's wages as the cost for that opportunity.
How do scarcity trade-offs and opportunity costs related?
This concept of scarcity leads to the idea of opportunity cost. The opportunity cost of an action is what you must give up when you make that choice. Another way to say this is: it is the value of the next best opportunity. Opportunity cost is a direct implication of scarcity.
What is trade-offs in economics?
Economics is all about tradeoffs. A tradeoff is loosely defined as any situation where making one choice means losing something else, usually forgoing a benefit or opportunity. We experience tradeoffs in zero-sum situations when a plus in one area must be a negative in another.
What are the causes of scarcity in economics?
The primary causes of economic scarcity are demand-induced, supply-induced, and structural.
How does scarcity affect your life?
Scarcity of resources can affect us because we can't always have what we want. For example, a lack of money and funds can lead me to not being able to buy the dream computer I want for work. In order to adjust, we have to either earn more money or adjust our dream computer to afford something more realistic.
How are trade offs involved when you make decisions?
Making decisions requires trading off one item against another. In economics, the term trade-off is often expressed as an opportunity cost, which is the most preferred possible alternative. A trade-off involves a sacrifice that must be made to get a certain product or experience.
What is the sentence of scarcity?
Scarcity sentence example. True scarcity is uncommon. Through the resultant scarcity of labor, much land fell out of cultivation. But in a world without scarcity, socialism can't even exist.
What is an example of markets coordinate trade?
Examples of Markets Coordinate Trade :) Foreign foods from Mexico, Thailand, Germany, Belize, France, Alaska, etc. are sold at local grocery stores or food markets for lower prices.
How do scarcity trade offs and opportunity costs related?
This concept of scarcity leads to the idea of opportunity cost. The opportunity cost of an action is what you must give up when you make that choice. Another way to say this is: it is the value of the next best opportunity. Opportunity cost is a direct implication of scarcity.
What is an example of an economic enigma?
-Why do people use a tanning bed when you can tan for free? -Why do people spend more money on name brand products when they can spend less for similar generic products? -Why do people buy fast food even though they know it is bad for their health? -Why do brides spend so much money on a wedding dress that they will ...
What is an example of future consequences count?
Example- An example of Future Consequences Count is when you make a decision today to cut yourself, your consequence today will be harming yourself and being in pain. And your Future consequence is having the scars for the rest of your life and living with having to remember that forever.
What does it mean to focus on what we do well and then trade with others?
By focusing on what we do well and then trading with others, we will end up with more and better choices than by trying to do everything by ourselves
When do people choose something?
people choose something when the benefits of doing so are greater than the cost.
Do markets do better than anyone else?
Markets usually do better than anyone else at coordinating exchanges between buyers and sellers
Do decisions made today have consequences?
Decisions made today have consequences not only for today, but also in the future.
What happens if there is overpopulation?
However, if there is overpopulation or a major drop in population like a famine then the system of provision of goods and services (scarcity) can be disrupted and scarcity not solved. With overpopulation then there will be unemployment and the wages received will fall due to labour compet
Why is there more scarcity in the world?
In our modern world, we have overpopulation and limited resources and availability of productive land, so there will be more scarcity and unemployment. Printing money and increasing credit is of no use, as they create inflation. Instead, people need to be allowed to find new land or sea to produce more goods and services and provide for the increased scarcity in the world. That is why some people and countries are helping Third World nations to be able to trade more fairly and not have taxes on their exports - some nations use tariffs to limit supply and protect their own suppliers - the USA has started doing this again.
What dictates the price of a good?
Scarcity is what basically dictates the PRICE of a good … OPPORTUNITY COST is what you could have bought instead, or what else you could have done with your TIME… they're not necessarily relevant to one another.
What is the net effect of price gouging?
The net effect is that the needed resources rapidly move to the disaster area and those who facilitate this most efficiently are rewarded. But under price controls which make “price gouging” illegal, the motivations to meet the demand no longer exist and the flashlights will go to those first in line, rather than those who most need it. It may not be possible to fund the rapid transport of extra supplies without accruing a loss. Also, people are likely to illegally exchange at rates above the gouging limit anyway.
How can we solve the problem of scarcity?
Economically, to solve the problem of scarcity is to allow the market to operate freely, so that small businesses and individual suppliers can provide for the needs of scarcity. Each person provides for other people from their own hands and owning land. Some of these suppliers can employ labour at a fair wage.
What is the deal in basic economics?
in basic economics the deal is this: people have UN-limited wants, needs, and desires. the Terran World has finite resources. any item has a price point to cover manufacture, distribution, logistics and cost, with profit to those involved ( you want to get paid, no ??). this the system of conservation through price that results in afford-ability .
How do ships turn ocean water into drinking water?
Anyway, that’s my example of scarcity. :-) And how to cope. Oh, and Navy ships turn ocean water into drinking water by using desalinization plants. Human beings are good at coping, usually. :-)
Why is next day shipping important?
Many online companies use the tactic to let consumers know that they have very little time before they lose the opportunity to have their purchases shipped out the following day. It increases urgency on the part of the consumer and encourages her to make purchases.
Why does Amazon use countdowns?
Companies like Amazon take advantage of countdowns to urge consumers to make purchases or else they will not guarantee next day shipping once time runs out. It works because many consumers want their purchases to arrive as soon as possible.
Why do Starbucks have seasonal offers?
Seasonal offers. Seasonal offers are used to create scarcity and encourage sales because seasons and holidays don’t last that long. Actually, this is the reason stores such as Starbucks offer pumpkin-flavored products during the fall.
How does a countdown work?
Countdowns also work in the context of a limited time sales price. A sales price countdown is used to drive urgency and encourage consumers to make purchases before time runs out. It creates scarcity, as well as a buy now mindset, while tapping into what sociologists call loss aversion to encourage consumers to make the purchase immediately instead of later.
What does a timer mean in sales?
A timer within a sales context implies that the sales team is defining scarcity as the key parameter. So how does it increase sales? Once a customer understands how much time she needs to make a decision, she will act with a sense of urgency. Companies like eBay use such a tactic, and it works really well because it drives that last-minute rush to make purchases before time runs out.
Why does scarcity cause the value of commodities to appreciate?
Why? Well, commodities that are in short supply tend to be attractive. It is a common scenario in real life because people sometimes want that which they cannot get.
How to make scarcity work?
Here are a number of tactics that make scarcity really work for marketers: 1. Purchase countdown. A timer within a sales context implies that the sales team is defining scarcity as the key parameter.
What is scarcity in economics?
Scarcity in economics is a term describing finite resources, or the perception of limited resources, when there is not enough to fulfill human needs and wants. It can also refer to how companies decide what and how to produce using the limited resources and how they determine a retail price for the item based on purchase demand.
What are the causes of scarcity in animal products?
Epidemics and pandemics like avian flu, swine flu or mad cow disease can cause a scarcity in animal products, food supplies and imports or exports. In severe instances, they can also lead to a shortage of medical personnel to care for patients.
What are the effects of poor weather on agriculture?
Poor weather can give farmers a low yield, which can cause a scarcity of food for animals and people. Hurricanes, tornados, flooding, tsunamis and other natural disasters can also affect natural resources, imports and exports, food, housing and supplies. Also, harsh climates can experience delayed shipments or deliveries of goods and services, causing temporary scarcities in communities.
What is congestion on roads?
Congestion on roadways can create delivery delays and with a scarcity of land available to build new roadways or railways in certain areas , certain regions or communities can experience reoccurring scarcity .
Why is there a shortage in healthcare?
The healthcare industry experiences shortages through the limited number of hospital beds and healthcare workers, particularly when there is a healthcare crisis or a waiting list for certain operations and procedures. Medical supplies, prescriptions and medications, like the annual flu vaccine, are also prone to scarcity issues.
What are some examples of seasonal shortages?
Another seasonal shortage comes from consumer demand, like purchasing holiday gifts, for example. This can create temporary scarcities for popular consumer items.
Why do we have a scarcity of land?
You can have a land scarcity when there is a shortage of land area for populations to grow food, raise livestock or develop housing and infrastructure. For example, the desertification of the land masses around the world is causing a decline in useful land for farming, and the depletion of forests is leading to a scarcity of wood and building materials in certain countries, causing the reuse of supplies from demolished buildings.