What is the difference between a thoery and a scientific law?
Summary A hypothesis is a tentative explanation that can be tested by further investigation. A theory is a well-supported explanation of observations. A scientific law is a statement that summarizes the relationship between variables. An experiment is a controlled method of testing a hypothesis.
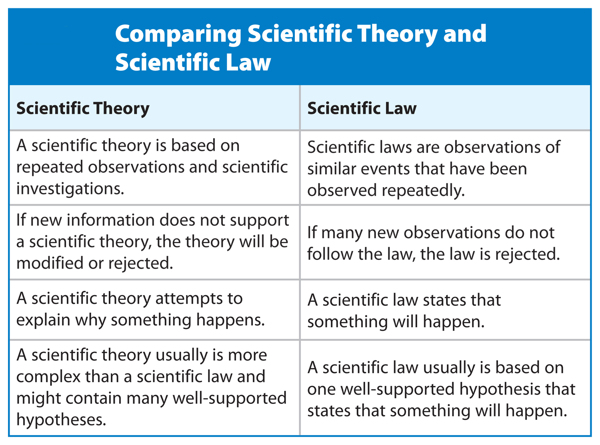
How does a scientific law differ from a theory?
- Newton's law of cooling
- Fourier's law
- Ideal gas law, combines a number of separately developed gas laws; Boyle's law Charles's law Gay-Lussac's law Avogadro's law, into one
What is the difference between science theory and law?
Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups?
- 1,338,028 Views
- 40,968 Questions Answered
- TED Ed Animation
What is the difference between scientific law and legal law?
Scientific Theory vs Law
- English Definition of Theory. ...
- Scientific Definition of Theory. ...
- The Scientific Method. ...
- Scientific Theory vs Scientific Law. ...
- Just A Theory. ...
- Scientific Certainty. ...
- Conclusion. ...

What is scientific theory?
A scientific theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world, based on a body of facts that have been repeatedly confirmed through observation and experiment. Such fact-supported theories are not "guesses" but reliable accounts of the real world.
What is theory and law?
1. A law is an observation; a theory is the explanation of that observation. 2. A theory requires experimentation under various conditions.
What is scientific law example?
An example of a scientific law is Newton's Aecond Law of Motion which states that acceleration (a) happens when a force (F) acts on an object's mass (m). The equation for this law is F = ma.
What is the difference between theory and scientific law give examples?
A scientific law predicts the results of certain initial conditions. It might predict your unborn child's possible hair colors, or how far a baseball travels when launched at a certain angle. In contrast, a theory tries to provide the most logical explanation about why things happen as they do.
What is scientific law?
What Is a Scientific Law? Like theories, scientific laws describe phenomena that the scientific community has found to be provably true. Generally, laws describe what will happen in a given situation as demonstrable by a mathematical equation, whereas theories describe how the phenomenon happens.
How is scientific law different than a scientific theory?
In general, a scientific law is the description of an observed phenomenon. It doesn't explain why the phenomenon exists or what causes it. The explanation for a phenomenon is called a scientific theory. It is a misconception that theories turn into laws with enough research.
What is a theory example?
The definition of a theory is an idea to explain something, or a set of guiding principles. Einstein's ideas about relativity are an example of the theory of relativity. The scientific principles of evolution that are used to explain human life are an example of the theory of evolution.
What are the 5 scientific laws?
What are the five scientific laws? The five most popular scientific laws are Hooke's Law of Elasticity, Archimedes' Principle of Buoyancy, Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures, Bernoulli's Law of Fluid Dynamics and Fourier's Law of Heat Conduction.
How does a theory become a theory?
See if this sounds familiar: Scientists begin with a hypothesis, which is sort of a guess of what might happen. When the scientists investigate the hypothesis, they follow a line of reasoning and eventually formulate a theory. Once a theory has been tested thoroughly and is accepted, it becomes a scientific law.
What is the difference between a scientific theory and a scientific law quizlet?
A theory is an explanation for what has been shown many times. A scientific law is a relationship in nature that has been proved many times and there are no exceptions.
What is the difference between a scientific theory and a scientific law look closely at the definitions of theory and law and try to see what is different?
Scientific Theory vs Scientific Law As previously stated, a scientific theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world. A scientific law is simply an observation of the phenomenon that the theory attempts to explain.
What do scientific theories and laws have in common?
What is a Law? Scientific laws are similar to scientific theories in that they are principles that can be used to predict the behavior of the natural world. Both scientific laws and scientific theories are typically well-supported by observations and/or experimental evidence.
What is scientific theory?
A scientific theory is an explanation of the natural world that can be repeatedly tested and verified using the scientific method and observation....
What is an example of scientific theory?
One of the most popular scientific theories is Einstein's Special Relativity, which explains the relationship between space and time for objects mo...
Is a scientific law more accurate than a scientific theory?
A scientific theory is a verifiable explanation of natural phenomenon. For example, the theory of gravity explains why an apple always falls to the...
What are the five scientific laws?
The five most popular scientific laws are Hooke’s Law of Elasticity, Archimedes’ Principle of Buoyancy, Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures, Bernoull...
What is the difference between a scientific theory and a law?
A scientific theory is a verifiable explanation of natural phenomenon. For example, the theory of gravity explains why an apple always falls to the ground when dropped. A law, on the other hand, is an observation. In simpler terms, a law predicts what happens and a theory explains why.
What is the scientific law?
A scientific law can often be reduced to a mathematical statement, such as E = mc²; it's a specific statement based on empirical data, and its truth is generally confined to a certain set of conditions. For example, in the case of E = mc², c refers to the speed of light in a vacuum.
What did Hubble's law help to quantify?
Hubble and his famous law helped to quantify the movement of the universe's galaxies. © 2018 HowStuffWorks. Let's stick with Edwin Hubble for a second. While the 1920s roared past and the Great Depression limped by, Hubble was performing groundbreaking astronomical research.
What are the elements of the scientific method?
Both laws and theories depend on basic elements of the scientific method, such as generating a hypothesis, testing that premise, finding (or not finding) empirical evidence and coming up with conclusions.
Why is Albert Einstein's theory of relativity important?
Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity remains an important and essential discovery because it permanently altered how we look at the universe. Einstein's major breakthrough was to say that space and time are not absolutes and that gravity is not simply a force applied to an object or mass. Rather, the gravity associated with any mass curves the very space and time (often called space-time) around it.
What are the five laws of science?
The five most popular scientific laws are Hooke’s Law of Elasticity, Archimedes’ Principle of Buoyancy, Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures, Bernoulli’s Law of Fluid Dynamics and Fourier’s Law of Heat Conduction. .
What is the first law of motion?
The first of the three laws states an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. For a ball rolling across the floor, that outside force could be the friction between the ball and the floor, or it could be the toddler that kicks the ball in another direction. Advertisement.
How do scientific laws differ from theories?
A scientific law might explain the relationship between two specific forces or between two changing substances in a chemical reaction. Theories are typically more expansive, and they focus on the how and why of natural phenomena.
What is scientific theory?
What Is a Scientific Theory? A scientific theory is a description of the natural world that scientists have proven through rigorous testing. As understood within the scientific community, a theory explains how nature behaves under specific conditions.
What are the laws of science?
The laws that anchor the world's scientific knowledge include: 1 Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation: Sir Isaac Newton's 1687 law of gravity describes the attractive forces between all forms of matter. This theory of gravity establishes a bedrock for many subsequent theories, as the force of gravity impacts nearly all physical relationships in the universe. 2 Newton’s Laws of Motion: First published in 1687, this set of three laws describes the role that competing forces play on an object at motion or at rest. 3 Boyle's Law: Alternately known as Boyle-Mariotte Law or Mariotte's Law, this describes the relationship between gas volume and gas pressure. Physicists Robert Boyle and Edme Mariotte discovered the law independently in 1662 and 1676, respectively. 4 The Laws of Thermodynamics: This set of four laws concerns thermodynamic work, entropy, heat, temperature, and other forces pertaining to the transfer of energy.
How to turn a hypothesis into a proven theory?
In order to turn a hypothesis into a proven theory, researchers design science experiments to challenge their ideas under the conditions of the natural world. By adhering to the scientific method and working with careful attention to detail, scientists can eventually accumulate enough evidence to prove their hypothesis, ...
What is Newton's law of gravity?
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation: Sir Isaac Newton's 1687 law of gravity describes the attractive forces between all forms of matter. This theory of gravity establishes a bedrock for many subsequent theories, as the force of gravity impacts nearly all physical relationships in the universe.
What is Darwin's theory of evolution?
The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection: Charles Darwin's theory—most succinctly summarized as “survival of the fittest”—explains how gradual changes in populations of organisms over time leads to the emergence of traits that allow those organisms to survive.
Who discovered the laws of thermodynamics?
Physicists Robert Boyle and Edme Mariotte discovered the law independently in 1662 and 1676, respectively. The Laws of Thermodynamics: This set of four laws concerns thermodynamic work, entropy, heat, temperature, and other forces pertaining to the transfer of energy.
What is scientific theory?
A scientific theory summarizes a hypothesis or group of hypotheses that have been supported with repeated testing. A theory is valid as long as there is no evidence to dispute it. Therefore, theories can be disproven. Basically, if evidence accumulates to support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis can become accepted as a good explanation of a phenomenon. One definition of a theory is to say that it's an accepted hypothesis.
What does "theory" mean in science?
Outside of science, you might say something is "just a theory," meaning it's a supposition that may or may not be true. In science, however, a theory is an explanation that generally is accepted to be true.
What is hypothesis in science?
A hypothesis is an educated guess, based on observation. It's a prediction of cause and effect. Usually, a hypothesis can be supported or refuted through experimentation or more observation. A hypothesis can be disproven but not proven to be true.
What happens when evidence accumulates to support a hypothesis?
Basically, if evidence accumulates to support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis can become accepted as a good explanation of a phenomenon. One definition of a theory is to say that it's an accepted hypothesis.
Why do scientists construct models?
Scientists often construct models to help explain complex concepts. These can be physical models like a model volcano or atom or conceptual models like predictive weather algorithms. A model doesn't contain all the details of the real deal, but it should include observations known to be valid.
Is there proof in science?
As you can see, there is no "proof" or absolute "truth" in science. The closest we get are facts, which are indisputable observations. Note, however, if you define proof as arriving at a logical conclusion, based on the evidence, then there is "proof" in science.
What is the difference between a law and a theory?
A law is a description of an observed phenomenon in the natural world that hold true every time it is tested. It doesn't explain why something is true; it just states that it is true. A theory, on the other hand, explains observations that are gathered during the scientific process.
What is the importance of scientific theory?
An important part of scientific theory includes statements that have observational consequences. A good theory, like Newton's theory of gravity, has unity, which means it consists of a limited number of problem-solving strategies that can be applied to a wide range of scientific circumstances. Another feature of a good theory is ...
What is the scientific method based on?
Any scientific theory must be based on a careful and rational examination of the facts. Facts and theories are two different things. In the scientific method, there is a clear distinction between facts, which can be observed and/or measured, and theories, which are scientists' explanations and interpretations of the facts.
What is a theory?
Theory basics. The University of California, Berkley, defines a theory as "a broad, natural explanation for a wide range of phenomena. Theories are concise, coherent, systematic, predictive, and broadly applicable, often integrating and generalizing many hypotheses.". Any scientific theory must be based on a careful and rational examination ...
Why do scientists use theories?
Scientists use theories to develop inventions or find a cure for a disease. Some think that theories become laws, but theories and laws have separate and distinct roles in the scientific method.
What is the process of becoming a scientific theory?
The process of becoming a scientific theory. Every scientific theory starts as a hypothesis. A scientific hypothesis is a suggested solution for an unexplained occurrence that doesn't fit into a currently accepted scientific theory.
Is a theory the end result of the scientific method?
A scientific theory is not the end result of the scientific method; theories can be proven or rejected, just like hypotheses. Theories can be improved or modified as more information is gathered so that the accuracy of the prediction becomes greater over time. Theories are foundations for furthering scientific knowledge and for putting ...
What is scientific law?
A scientific law is different from a theory. A law is a generalization that describes what happens when certain conditions are met. The Oxford dictionary defines law as “A statement of fact, deduced from observation, to the effect that a particular natural or scientific phenomenon always occurs if certain conditions are present”. The American heritage dictionary defines it as “A statement describing a relationship observed to be invariable between or among phenomena for all cases in which the specified conditions are met”.
What is the difference between law and theory?
Although theories and laws explain various concepts in science, there is a definitive difference between theory and law. Theory explains why something happens whereas law describes what happens when certain conditions are present. This is the key difference between theory and ...
What are some examples of scientific laws?
Some examples of scientific laws include Newton’s law of motion, Mendelian laws of heredity, and Boyle’s law. Laws describe how something happens with proof, but they cannot explain why something happens. Laws are universally observable facts; therefore they cannot be challenged or revised. Kepler’s law.
What is the definition of theory?
Definitions of Theory. Theory is a set of verified explanations or statements about a phenomenon. The Oxford Dictionary defines theory as “a supposition or a system of ideas intended to explain something, especially one based on general principles independent of the thing to be explained”. The American heritage defines it as “A set ...
What is a law based on?
As the above definitions explain, laws are typically based on observations, specially repeated experimental observations. To be more specific, it describes what happens when certain conditions are met.
What is a theory?
Characteristics and Examples. As the above definitions indicate, a theory is an explanation that is acquired through scientific methods. A theory is formed after constant observation and repeated experimentation. Einstein’s’ theory of relativity, Darwin’s theory of evolution, Lavoisier’s oxygen theory of combustion, quantum theory, ...
Can theories be revised?
Theory: Theories can be revised or replaced as new evidence comes to light. Law: Laws are not typically revised since they are universally observable. Image Courtesy: “297234” (Public Domain) via Pixabay. “Kepler laws diagram” By Hankwang – Own work (CC BY 2.5) via Commons Wikimedia.
