Common Causes
It is a type of reduced vision that occurs in one eye. The condition is called a lazy eye because the stronger eye works best. Amblyopia is the most common cause of visual impairment in children. The eye condition usually occurs between birth and seven years of age.
Related Conditions
In many cases, a scotoma affecting one eye is only noticeable when you close your other eye The term “scotomata” sometimes is used to describe multiple scotomas. A central scotoma is a blind spot directly in the center of your vision (directly in your line of sight).
What is amblyopia?
For visual scotomas, the primary pathogenesis may occur at the level of the receptors, retinal arterial tree, short posterior ciliary arteries, ophthalmic artery, optic nerve, carotid artery, vertebrobasilar artery or cerebral hemisphere.
What is the difference between a scotoma and a scotomata?
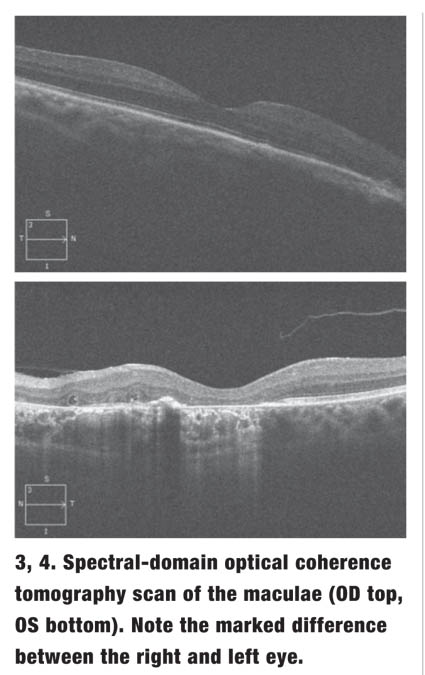
Causes of central scotomata include macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy or diabetic macular edema. [Read more about diabetic eye disease .] Eye infections and injuries that affect the macula of the retina also can cause a central scotoma.
What is the pathophysiology of visual scotoma?
What causes central scotomata in the eye?

What is a scotoma?
A scotoma is an aura or blind spot that obstructs part of your vision. Scintillating scotomas are blind spots that flicker and waver between light and dark.
What causes a scotoma?
Common causes of scotomas include demyelinating disease such as multiple sclerosis (retrobulbar neuritis), damage to nerve fiber layer in the retina (seen as cotton wool spots) due to hypertension, toxic substances such as methyl alcohol, ethambutol and quinine, nutritional deficiencies, vascular blockages either in ...
What is an example of scotoma?
A paracentral scotoma is a blind spot slightly off-center in your vision. For example, if you have a paracentral scotoma, you can probably see the words on road signs clearly, but there are spots near the sign that are dark or blurry.
Can scotoma be cured?
If the scotoma is on the outer edges of your vision, it usually does not cause severe vision problems. If you have a scotoma in your central vision, it cannot be corrected or treated with glasses, contact lenses, or surgery. Your provider will recommend that you use aids to support your decreased vision.
How is a scotoma diagnosed?
Scotomas generally are detected and monitored using an automated visual field test (sometimes called a Humphrey visual field test). This test typically is supervised by a trained assistant in your eye doctor's office. During the visual field test, you will be seated in front of a large, bowl-shaped instrument.
How long do scotomas last?
Symptoms typically appear gradually over 5 to 20 minutes and generally last less than 60 minutes, leading to the headache in classic migraine with aura, or resolving without consequence in acephalgic migraine.
Can a eye doctor see scotoma?
An eye doctor can help you find out where the scotomas are. Then you will know if they are central or peripheral. If you have central scotomas, it may help to make things bigger. The easiest way to make things bigger is to get close to them.
How do you treat scotoma?
Can a scotoma be treated? Temporary scotomas, such as those caused by a migraine, usually don't need to be treated. Permanent or fixed scomtomas aren't able to be corrected with glasses or surgery, but often treating the underlying cause (such as high blood pressure) can prevent new blind spots from forming.
How do people live with scotoma?
Some tips to help one “see around” the scotoma include using more and better lights, utilizing contrast to enhance light against dark or dark against light, and magnifying your reading with magnifiers, ebook readers or magnifying software.
Can you drive with scotoma?
Central visual field loss, a scotoma or blind area in central vision, is found most commonly in patients with age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Patients with AMD may drive provided their visual acuity at least meets the requirements for a restricted license.
How to tell if you have a scotoma?
If you suddenly notice a scotoma or other vision disturbances, see an optometrist or ophthalmologis t immediately. Urgent medical care is especially needed if you also experience any of these signs or symptoms along with a scotoma: 1 Feeling confused or disoriented 2 Dizziness or nausea 3 Muscle weakness 4 Sudden extreme headache 5 Numbness in your limbs or face 6 Slurred speech or difficulty speaking 7 Scotomas following a head or eye injury
What is a central scotoma?
Central scotoma. A central scotoma is a blind spot directly in the center of your vision (directly in your line of sight). Central scotomas are some of the most devastating visual field defects because they can make reading, driving and recognizing faces difficult or impossible. Causes of central scotomata include macular degeneration ...
How long does it take for a scotoma to go away?
Scotomas associated with migraine headaches typically are temporary and go away without treatment within 30 minutes or so.
How long does a scintillating scotoma last?
Most scintillating scotomas are temporary and last anywhere from a few seconds to up to 30 minutes. Often, they are associated with migraine headaches (and therefore are sometimes called a migraine scotoma ). But scintillating scotoma can occur without head pain as well.
What is the name of the scotoma that is arc shaped?
In the case of glaucoma, the scotoma may be arc-shaped and therefore called an arcuate scotoma. A paracentral scotoma may occur by itself or there may be more than one of these blind spots in your vision.
How are scotomas detected?
Scotomas generally are detected and monitored using an automated visual field test (sometimes called a Humphrey visual field test). This test typically is supervised by a trained assistant in your eye doctor’s office. During the visual field test, you will be seated in front of a large, bowl-shaped instrument.
Where does scintillating scotoma occur?
A scintillating scotoma is a visual disturbance that usually occurs on the paracentral or mid-peripheral portion of your visual field. However, this type of scotoma also may move across your field of view rather than staying in just one spot.
What is a visual scotoma?
The definition of visual scotoma is similar to that of visual aura. The differentials for scotoma likewise include migraine and seizure, but the term is more appropriately linked to ischemia, retinal degenerations and inflammations, paraneoplastic syndromes and other neurologic disorders. For visual scotomas, the primary pathogenesis may occur ...
What causes a negative scotoma?
As a rule, optic nerve disease produces unformed scotomas that are negative and rarely positive.2 Embolic disease blocking the central retinal artery or immediately at the bifurcation produces a negative scotoma that is either diffuse or altitudinal, respectively.
What is optic nerve disease?
At the level of the optic nerve, non-migrainous vision loss may occur with disorders associated with central retinal artery or short posterior artery disease. In addition, optic nerve drusen or papilledema may also be associated with aura.
What is the ERG test for photopsia?
Patients complaining about difficulties with both day and nighttime vision require multifocal ERG testing, which may reveal dysfunction even with the absence of visual aura. Photopsias are simply related to vitreoretinal interaction. Optic Nerve Disease.
Can cone disease cause night vision problems?
Patient complaints of glare and (acquired) photophobia are common with cone disease. Rod disease, however, is associated with night vision difficulties (nyctalopia).
Can migraines cause scotoma?
Retinal migraine may result in the same type of visual deficit (negative aura); however, positive scotoma or blindness is also possible. Note that retinal migraines are often, but not always, associated with headache on the same side as the visual deficit within an hour.
What is a scotoma?
Joana Rodrigues/EyeEm/Getty Images. A scotoma is an aura or blind spot that obstructs part of your vision. Scintillating scotomas are blind spots that flicker and waver between light and dark. Scintillating scotomas are typically not permanent. But they can be an indicator of an underlying health condition.
What is a scintillating scotoma?
Like other types of scotoma, scintillating scotomas appear as floaters, dots, or blind spots in your field of vision. Scotomas smear and obscure what you see, but they aren’t pieces of dust or dirt that have landed in your eye. Instead, scotomas are related to the neurological signals being sent from your eye to your brain.
What does it mean when you have a headache and a scotoma?
headache and scotomas following an accident or injury. numbness in your face, arms, or legs. disorientation or confusion. If you’re getting severe migraine for the first time or if your headache symptoms have changed from your typical experience, schedule an appointment to discuss it with your primary physician.
How long does it take for a scotoma to heal?
Typically, scintillating scotomas don’t require treatment. In most cases, the blind spot will resolve on its own within about an hour. Lying down to rest, closing your eyes, drinking water, and taking an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may help to relieve mild symptoms of scotomas.
Can a scintillating scotoma resolve on its own?
The scotoma will most likely resolve on its own. There are some symptoms that, when they occur with scintillating scotoma, will need to be addressed by a medial professional. Seek medical attention right away if you experience the following: sudden, severe headache. muscle weakness.
Can scintillating scotomas cause headaches?
Headache pain may occur along with scintillating scotomas, or you may feel no pain at all. Scintillating scotomas can happen before or during a migraine or because of an underlying condition, such as glaucoma or multiple sclerosis (MS).
How to treat amblyopia?
The treatment of amblyopia may include vision therapy techniques, such as occlusion therapy. Occlusion therapy for a lazy eye involves wearing an eye patch. The patch covers the better eye for several hours a day.
Can glasses correct amblyopia?
Glasses can correct existing refractive errors in childrens’ eyes. Refractive errors include nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. In children with amblyopia, one eye is often more nearsighted or farsighted than the other.
