Does secretion occur in the kidney?
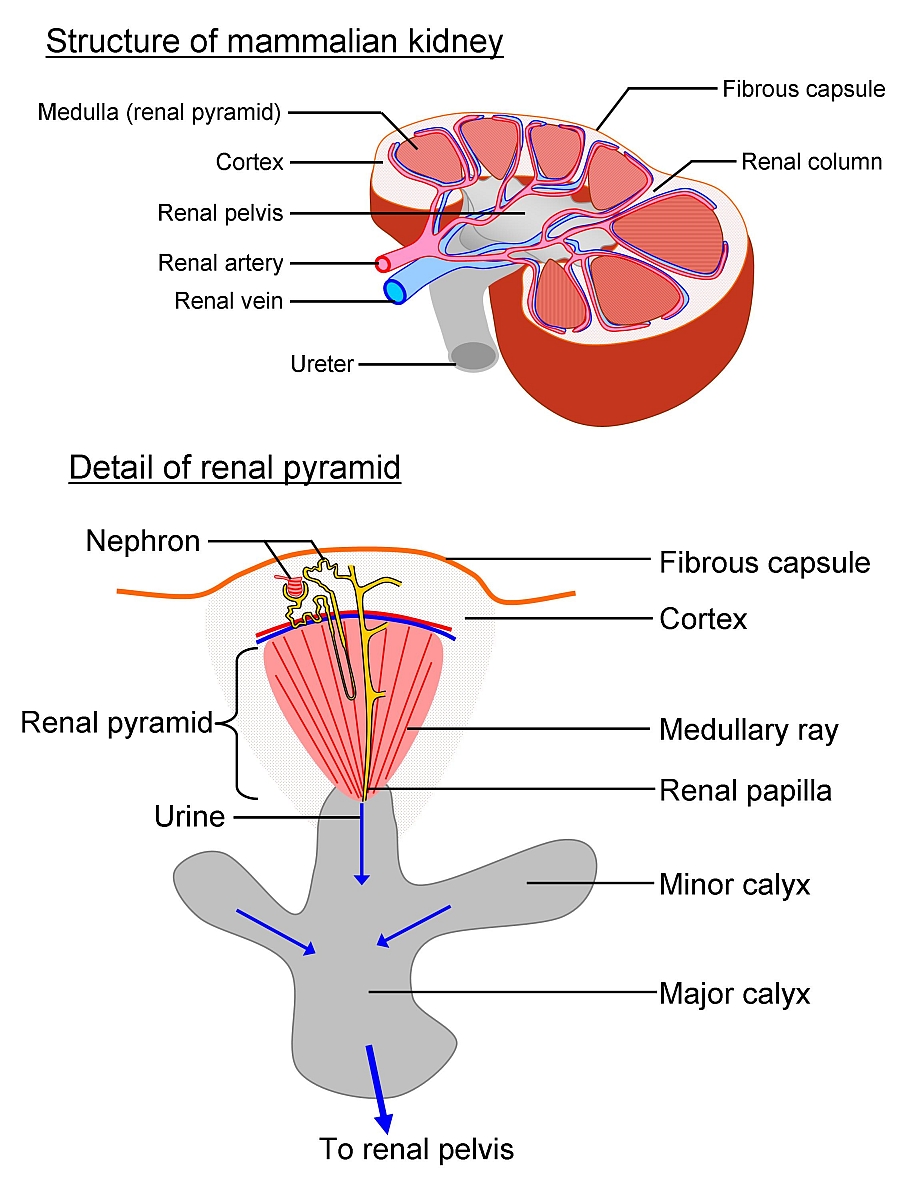
Location of Tubular Secretion In humans, and other vertebrates, tubular secretion occurs in the kidneys, where the blood is filtered in specialized structures known as nephrons. These structures consist of a long tubule surrounded by extensive capillaries. Also, why is tubular secretion important?
What enzymes are secreted by the kidneys?
filter body fluid; dispose of wastes and excesss ions; regulate blood volume and chemical makup; convert vitamin D to its active form. renin. enzyme produced by kidneys that helps regulate blood pressure. erythropietin. hormone secreted by kidneys that stimulates RBC production. urinary system.
Do lysosomes help in secretion?
This work is also important due to the recent revelation that conventional lysosomes are also capable of secretion, which blurs the distinction between the two populations of lysosomes. However, it is now apparent that secretory lysosomes use some unique components in their secretion machinery.
What is secreted by the kidneys during hypoxia?
The kidneys secrete a variety of hormones, including erythropoietin, calcitriol, and renin. Erythropoietin is released in response to hypoxia (low levels of oxygen at tissue level) in the renal circulation. It stimulates erythropoiesis (production of red blood cells) in the bone marrow.
See more

Where does secretion occur in the kidney?
proximal tubuleSecretion, which occurs in the proximal tubule section of the nephron, is responsible for the transport of certain molecules out of the blood and into the urine. Secreted substances include potassium ions, hydrogen ions, and some xenobiotics.
Why is secretion important in the kidney?
The secretion of small molecules by the proximal tubules of the kidneys represents a vital homeostatic function for rapidly clearing endogenous solutes and medications from the circulation.
What is the difference between secretion and reabsorption?
First of all reabsorption and secretion are two different processes. Reabsorption → back movement of stuff from glomerular filtrate into blood. Secretion → movement of contents from blood enter into nephron.
What is the difference between filtration and secretion?
Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. ... Secretion involves the transfer of hydrogen ions, creatinine, drugs, and urea from the blood into the collecting duct, and is primarily made of water.
Which cells function in the kidneys for secretion?
Figure 7. Intercalated cells are involved in K+ secretion in the collecting duct.
What is the difference between secretion and excretion in the kidney?
Both these processes involve the movement of materials in the body. But the difference between excretion and secretion is that excretion is the removal of waste from the body, whereas secretion involves the movement of materials within the body.
What is happen during secretion process in urine formation?
The next step in urine formation is tubular secretion. Here, tubular cells secrete substances like hydrogen ions, potassium ions, etc into the filtrate. Through this process, the ionic, acid-base and the balance of other body fluids are maintained. The secreted ions combine with the filtrate and form urine.
What happens during reabsorption and secretion?
Glomerular filtration produces ultrafiltrate of plasma, i.e. without proteins. Some substances are reabsorbed almost entirely and returned to circulation while others are secreted to remove substances from the peritubular capillary blood.
What are the roles of reabsorption and secretion in kidneys?
The filtrate absorbed in the glomerulus flows through the renal tubule, where nutrients and water are reabsorbed into capillaries. At the same time, waste ions and hydrogen ions pass from the capillaries into the renal tubule. This process is called secretion.
What is the role of the kidney in osmoregulation?
Kidneys regulate the osmotic pressure of a mammal's blood through extensive filtration and purification, in a process known as osmoregulation. Kidneys filter the blood; urine is the filtrate that eliminates waste from the body via the ureter into the bladder.
What are the 3 main functions of the kidneys?
The kidneys are powerful chemical factories that perform the following functions: remove waste products from the body. remove drugs from the body. balance the body's fluids.
What is the function of the kidneys in the endocrine system?
The kidney has multiple endocrine roles; it secretes various hormones and humoral factors: the hormones of the renin- angiotensin system (RAS), erythropoietin (EPO), and 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D3. It also produces enzymes, such as kallikreins, which produce hormones in other, distant sites.
How does ADH affect kidney function?
Certain hormones and hormonelike substances are intimately related to renal function. Some of these, such as ADH , are produced outside the kidney and travel to the kidney via the blood as chemical messengers. Others are produced within the kidney and appear to exert only a local effect. The role of ADH in controlling diuresis has already been discussed. ADH regulates water excretion by increasing the permeability of the collecting ducts to water and salt and by accelerating water and ion transfer in a direction determined by the osmotic gradient. The receptors at the base of the brain form part of the feedback mechanism that stimulates ADH output if the osmotic concentration of extracellular fluid is high, so as to concentrate the urine, and reduces ADH output and so dilutes the urine if osmotic concentration of ECF and of plasma falls.
What hormone is released into the blood when sodium levels fall?
Aldosterone ,a hormone secreted by the kidneys, regulates the transfer of sodiumfrom the nephron to the blood. When sodium levels in the blood fall,aldosterone is released into the blood, causing more sodium to passfrom the nephron to the blood. This causes water to flow into theblood by osmosis. Renin is released into the blood to control aldosterone.
What hormone is responsible for red blood cell production?
Erythropoietin is an essential hormone for red blood cell production. Without it, definitive erythropoiesis does not take place. Under hypoxic conditions, the kidney will produce and secrete erythropoietin to increase the production of red blood cells by targeting CFU-E, pro erythroblast and basophilic erythroblast subsets in the differentiation. Erythropoietin has its primary effect on red blood cell progenitors and precursors by promoting their survival through protecting these cells from apoptosis, or cell death.
Where does the filtrate go in the kidney?
This process is called secretion. The secreted ions combine with the remaining filtrate and become urine. The urine flows out of the nephron tubule into a collecting duct. It passes out of the kidney through the renal pelvis, into the ureter, and down to the bladder.
How does the body use waste?
As blood flows through the body it picks up waste and carries this to the kidneys using the kidney arteries. The waste in your blood comes from the normal breakdown of active tissues and from the food you eat. Your body uses food for energy and selfrepair. After the body has taken what it needs, from the food, the waste is sent to the blood. The kidneys filter out the waste products and excess fluids from the body and dispose of them in the form of urine, via the bladder. The clean blood flows back to the other parts of the body. If your kidneys did not remove this waste, it would build up in the blood and cause damage to your body.
How does blood flow into the kidney?
Blood flows into your kidney through the renal artery. This large blood vessel branches into smaller and smaller blood vessels until the blood reaches the nephrons. In the nephron, your blood is filtered by the tiny blood vessels of the glomeruli and then flows out of your kidney through the renal vein.
Where does filtering happen?
The actual filtering occurs in tiny units inside your kidneys called nephrons. Each kidney contains about a million nephrons. In the nephron, a glomerulus intertwines with a urine collecting tube called tubules. A complicated chemical exchange takes place, as waste materials and water in your blood enter your urinary system.
What are the two hormones that the kidneys secrete?
The kidney also secretes two hormones, renin and erythropoietin.
Why is calcitriol important?
Calcitriol is essential for bone health, calcium absorption, cell growth, muscle function, and immunity. People with chronic kidney disease sometimes require calcitriol supplementation – there is no point in giving them the inactive form of vitamin D as it is the kidneys that turn the inactive form into the active form.
How many nephrons are there in the human body?
Nephrons are individual filtering systems; the average human kidney contains between 200,000 and more than 2.5 million nephrons. No new nephrons are formed from around the 36 th week of gestation.
How big is a kidney bean?
Named after a vital organ. Human kidneys are approximately ten centimeters in length and five in width.
What are the organs that protect the kidneys?
Each kidney is protected by the rib cage, perirenal (perinephric) fat, renal capsule, and the muscles of the back. These vital organs do not lie within the abdominal cavity but sit behind the peritoneum – they are retroperitoneal.
Where does the kidney begin?
Kidney anatomy begins at the renal hilus, also called the renal hilum or pedicle. This is the indentation that produces the bean-like form. It is where the renal arteries, renal veins, and the hollow, muscled tube of the ureter access the inner tissue.
How long does a kidney injury last?
Acute kidney injuries develop quickly, perhaps through trauma, untreated infection, and last for a few hours to a few days. Even so, it is often necessary to take over the filtration function of the kidney for this period by way of hemodialysis.
What is the letter for secretion of the kidney?
In the image above, a simplified drawing of a nephron (right) within the kidney (left) is shown. Secretion is indicated by the letter S , which involves specific waste products moving from the blood in the capillaries (in red and purple) into the nephron tubule (in yellow).
What is the process of filtration of blood to produce urine?
Tubular secretion is one of many steps in the process of filtering blood to produce liquid waste in the form of urine. Within the excretory system of many organisms, this is important for both waste removal and acid-base balance.
How does the kidney secrete tubular secretions?
Many substances filtered in the kidney move between the different regions of the nephron via diffusion and osmotic gradients, but tubular secretion occurs via active transport. Several different types of transporter proteins exist in the membrane of the tubular cells making up the transport epithelium.
Where does tubular secretion occur?
In humans, and other vertebrates, tubular secretion occurs in the kidneys, where the blood is filtered in specialized structures known as nephrons. These structures consist of a long tubule surrounded by extensive capillaries. The secreted substances come from the blood in peritubular capillaries and pass through the interstitial fluid before going through the wall of the tubule (known as the transport epithelium) into the inside of the tubule (known as the lumen). Different aspects of secretion occur in the proximal or distal portions of each tubule, but not in the region between known as the loop of Henle.
Where does the secreted substance come from?
The secreted substances come from the blood in peritubular capillaries and pass through the interstitial fluid before going through the wall of the tubule (known as the transport epithelium) into the inside of the tubule (known as the lumen).
Where are drugs secreted?
Drugs and toxins are secreted into the proximal tubule. In both proximal and distal tubule regions, H + is also transported to maintain ideal pH. One example of a transporter important for this is the Na + – H + exchanger (NHE3). Within the distal tubule, K + is also transported at varied levels depending on the amount in excess of the body’s need. Ultimately, these secreted substances make their way into urine and are removed from the body.
What are the processes of the kidneys?
Processes of the Kidneys. There are four basic processes in the formation of urine starting with plasma. Filtration. Filtration is the mass movement of water and solutes from plasma to the renal tubule that occurs in the renal corpuscle.
What is the main cause of filtration?
Filtration is primarily driven by hydraulic pressure (blood pressure) in the capillaries of the glomerulus. Note that the kidneys filter much more fluid than the amount of urine that is actually excreted (about 1.5 liters per day).