What are the side effects of too little sodium?
When You Stop Eating Salt, This Is What Really Happens To Your Body
- Your blood pressure drops when you stop eating salt. ...
- When you stop eating salt, your kidneys function better. ...
- Your risk of kidney stones drops when you stop eating salt. ...
- You'll feel less bloated after you stop eating salt. ...
- You'll feel more energetic when you stop eating salt. ...
- If you stop eating salt, your palate will change. ...
What happens if you don't consume enough sodium?
Insufficient sodium can cause hyponatremia, characterized by the following symptoms:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Confusion
- Loss of energy
- Fatigue
- Restlessness and irritability
- Muscle weakness, spasms or cramps
What does high sodium serum level mean?
What Causes High Sodium Levels in Blood? High sodium levels in the blood indicate a condition called hypernatremia, which is caused by dehydration, medications, endocrine diseases, excessive consumption of salt and hyperventilation, according to Chemocare.
What are the signs of too much sodium?
These include:
- dehydration
- vomiting
- kidney disease
- uncontrolled diabetes
- diabetes insipidus
- extreme diarrhea
- dementia
- fever
- delirium
- certain medications
What is sodium serum levels?
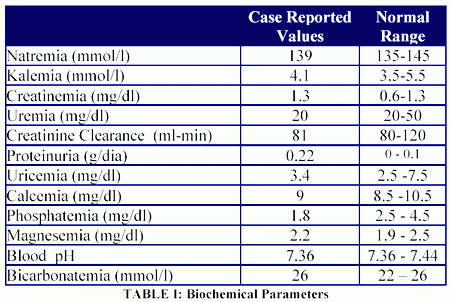
A normal blood sodium level is between 135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). Hyponatremia occurs when the sodium in your blood falls below 135 mEq/L.
What happens if serum sodium is low?
Low blood sodium is common in older adults, especially those who are hospitalized or living in long-term care facilities. Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia can include altered personality, lethargy and confusion. Severe hyponatremia can cause seizures, coma and even death.
What is the difference between sodium and serum sodium?
Serum sodium concentration is the amount of sodium relative to the volume of water in the blood; it does not reflect total body sodium content. Hyponatremic and hypernatremic patients may have decreased, normal, or increased total body sodium.
What happens if serum sodium is high?
Hypernatremia typically causes thirst. The most serious symptoms of hypernatremia result from brain dysfunction. Severe hypernatremia can lead to confusion, muscle twitching, seizures, coma, and death.
Can a person recover from low sodium levels?
Hyponatremia can result from multiple diseases that often are affecting the lungs, liver or brain, heart problems like congestive heart failure, or medications. Most people recover fully with their doctor's help.
How do you fix low sodium?
TreatmentIntravenous fluids. Your doctor may recommend IV sodium solution to slowly raise the sodium levels in your blood. ... Medications. You may take medications to manage the signs and symptoms of hyponatremia, such as headaches, nausea and seizures.
Which organ is most affected by hyponatremia?
Hyponatremia occurs when your blood sodium level goes below 135 mEq/L. When the sodium level in your blood is too low, extra water goes into your cells and makes them swell. This swelling can be dangerous especially in the brain, since the brain cannot expand past the skull.
What causes sodium levels to be low?
The term for low sodium levels in the blood is hyponatremia. And there are many different causes, such as changes in kidney function, blood pressure medicines, or conditions like heart or liver failure. The seriousness of hyponatremia depends on how low sodium levels are and how quickly they change.
What is a critical sodium level?
Any value below 135 mEq/L is considered to be a low sodium level, a condition medically referred to as hyponatremia. As sodium levels drop to 125 mEq/L, the situation becomes more serious. And when the sodium level drops to 115 mEq/L or below, the situation is critical and requires immediate treatment.
What causes sodium levels to be high?
A high sodium level in the blood (hypernatremia) often means there is not enough water in the body rather than too much salt. A high sodium level can happen when you are dehydrated and not drinking enough water. But there are other medical conditions that can affect your sodium level as well.
How is high sodium treated?
Hypernatremia is treated by replacing fluids. In all but the mildest cases, dilute fluids (containing water and a small amount of sodium in carefully adjusted concentrations) are given intravenously. The sodium level in blood is reduced slowly because reducing the level too rapidly can cause permanent brain damage.
What are symptoms of too much sodium?
The immediate symptoms of eating too much salt include: Increased thirst. Swollen feet or hands. Headache (in some cases)...This is why, over time, eating too much salt comes with long-term health consequences, including:High blood pressure (hypertension)Heart disease.Stroke.Kidney disease.Kidney stones.
What causes sodium levels to drop?
Kidney problems So, the most common reason for low sodium is a kidney problem. When the kidneys are not functioning normally, which can be seen in chronic kidney disease or even temporary dehydration, the body holds too much water. And the proportion of sodium compared to water in the body lowers the sodium level.
What is a critical sodium level?
Any value below 135 mEq/L is considered to be a low sodium level, a condition medically referred to as hyponatremia. As sodium levels drop to 125 mEq/L, the situation becomes more serious. And when the sodium level drops to 115 mEq/L or below, the situation is critical and requires immediate treatment.
What level of sodium is too low?
How low is too low? Your blood sodium level is normal if it's 135 to 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). If it's below 135 mEq/L, it's hyponatremia. Your doctor will be able to tell you whether your level is too low.
What happens if your sodium level is 120?
Hyponatremia is the most common electrolyte abnormality in hospitalized patients, and it increases the likelihood of a hospital death (1–5). Inpatient mortality rates as high as 50% or more have been reported for patients with serum sodium concentrations (sNa) <120 mEq/L (6–9).
Why do we need a sodium blood test?
A sodium blood test will measure your sodium level, because too little or too much can cause problems.
Why is sodium important?
Sodium is key to helping send electrical signals between cells and controlling the amount of fluid in your body. Your body needs it for your cells to work the right way. Most foods have sodium in them. The most common form is sodium chloride, found in table salt.
What does it mean when your sodium level is too low?
If the levels are too low, that’s called hyponatremia. You may not need to worry about one slightly high or low sodium blood test. Your doctor will look at how the results relate to other tests, your overall health, and medical history. It’s possible that they’ll repeat the test.
What does it mean when your sodium is too high?
If your sodium levels are too high for the amount of water in your body, it’s called hypernatremia. If the levels are too low, that’s called hyponatremia.
How do you know if your sodium level is too high?
You might be confused, forgetful, or have problems with reasoning. Other symptoms your doctor may watch for include: Muscle cramps or twitching. Problems walking.
Where to draw blood for sodium?
For the test, a technician will draw blood, usually from the inside of the elbow area or back of the hand.
What causes sodium to go out of balance?
Any number of things can cause your sodium levels to get out of whack. They include: Surgery, an injury, or a serious illness. Eating or drinking too much salt or liquids -- or too little of them. Getting IV fluids. Taking a class of medications called diuretics, which lower the amount of fluid in your body.
What is the reference range for sodium?
The reference range for serum sodium is 135-147 mmol/L, [ 1] although different assays establish their own reference ranges, which may differ slightly.
What is the method used to measure sodium in water?
Other methods, such as direct ISE, gas electrodes, or freezing-point depression method , measure sodium in the water phase and are thus not subject to the electrolyte exclusion effect.
How much sodium is needed for renal failure?
The body requires only 1-2 mmol/d of sodium intake, and average daily intake in adults ranges from 90-250 mmol/d.
Can serum be collected in plastic bottles?
Container - Serum can be collected into glass or plastic bottles, with or without gel barriers; for plasma, lithium heparin is an acceptable anticoagulant; sodium heparin should be avoided. Collection method - Standard venipuncture technique.
What is sodium blood test?
A sodium blood test is a routine test that allows your doctor to see how much sodium is in your blood. It’s also called a serum sodium test. Sodium is an essential mineral to your body. It’s also referred to as Na+. Sodium is particularly important for nerve and muscle function. Your body keeps sodium in balance through a variety of mechanisms.
Why do you need a sodium test?
Sometimes it’s needed because you may be on certain medications that affect the sodium levels in your blood. Other times it may be part of a general health checkup. Either way it’s important to know how much sodium in your blood. Keeping it at the optimum level is good ...
What does it mean when your sodium is high?
Abnormally high levels. Hypernatremia means high levels of sodium in the blood. It’s defined as levels that exceed 145 mEq/L. Symptoms of hypernatremia include: thirst. fatigue. swelling in hands and feet. weakness. insomnia. rapid heartbeat.
What is the blood sodium panel?
Blood sodium can also be part of an electrolyte panel. Electrolytes are substances that carry an electrical charge. Potassium and chloride are other electrolytes. This test may be ordered if you have: eaten large amounts of salt. not eaten enough or had enough water. a serious illness, or gone through surgery.
How does sodium get into your blood?
Sodium gets into your blood through food and drink. It leaves the blood through urine, stool, and sweat. Having the right amount of sodium is important for your health. Too much sodium can raise your blood pressure. A lack of sodium can cause symptoms such as: nausea. vomiting. exhaustion. dizziness.
Why do older people have hypernatremia?
Causes of hypernatremia include: not drinking enough water. drinking salty water. eating too much salt. excessive sweating. diarrhea. low levels of hormones such as vasopressin. high levels of aldosterone.
Is sodium a metabolic panel?
The sodium blood test is often part of a basic metabolic panel. This is a group of related tests. The basic metabolic panel includes tests for: Blood sodium can also be part of an electrolyte panel. Electrolytes are substances that carry an electrical charge. Potassium and chloride are other electrolytes.
What is sodium blood test?
A sodium blood test is used to measure the amount of sodium found in your bloodstream. It is used to determine unusual concentrations of sodium, including high sodium and low sodium. This is often used as a part of a basic metabolic panel or electrolyte panel.
What does it mean when you have a sodium test?
Conclusion. A sodium blood test may be recommended by your doctor if you are manifesting symptoms of too little or too much sodium in your blood. You need to maintain normal sodium levels in your blood. If you don’t have a normal sodium level in the blood, then it can indicate a certain condition.
Why does sodium imbalance occur?
Sodium imbalances may also be caused by kidney problems and diabetes. It may be due to an injury, serious illness, or surgery. This can also be as a result of certain medications such as diuretics since it lowers the fluid in your body. This can also be due to the medicines you are taking, such as hormone aldosterone.
Why is sodium high?
High sodium levels are an indication of hypernatremia. Sodium imbalances may also be caused by kidney problems and diabetes. It may be due to an injury, serious illness, or surgery. This can also be as a result of certain medications such as diuretics since it lowers the fluid in your body.
Why is sodium important?
Sodium is needed by your body for it to work properly. Normal sodium levels help in the function of muscles and nerves. It allows the fluid in your body to maintain the right balance. Your kidneys are responsible for controlling the sodium in your body. Too high or too low sodium in your blood can be detrimental to your entire well-being, ...
What does it mean when you have a high sodium level?
A high level of sodium may mean that you have hypernatremia, and this is common in infants and adults, especially those who are bedridden. A low level of sodium may mean that you have hyponatremia , and this is more common in adults. Dr. Ahmed Zayed.
Why is sodium low in the blood?
People with low sodium levels in the blood can be suffering from hyponatremia. These are usually a problem in the elderly. Here are some causes of low sodium in the blood; Antidepressants. Addison’s disease. Certain pain medications. Diuretics. Kidney disease. Large burns on the skin.
How does sodium affect your body?
Sodium works hard with other electrolyte minerals to maintain an even amount of fluid in and around cells. Without adequate sodium in your body, the fluid concentrations shift. The electrical current that powers your muscles and heart rhythm deteriorates, resulting in an abnormally weak heartbeat.
What is the ideal sodium level?
Somewhere around 135 to 145 milliequivalents per liter, or mEq/L, is the ideal range for serum sodium, reports MedlinePlus. It isn’t common for sodium levels to be low, but once your sodium drops below 135 mEq/L, it can be problematic. Having a level of 125 milliequivalents per liter or less is severely dangerous. Some labs may use slightly different values. Check with your lab technician or physician to see if your sodium level is off.
What happens if your sodium level is too low?
Once your sodium reaches that dangerously low point, you can have seizures or start convulsing uncontrollably as you lose muscle control. Ultimately, as your heart rhythm continues to slow down, you may pass out or slip into a coma, possibly resulting in a fatality. av-override. ‒‒:‒‒. /. ‒‒:‒‒. Replay. Skip.
Why is sodium bad for you?
As your sodium level starts dropping, you’ll begin to feel very tired and unable to perform your usual tasks. Your muscles weaken, you may become confused and headaches might start to set in. You could also feel nauseated or even throw up.
Why is my sodium level low?
Some causes aren’t so obvious, however. An abnormally low sodium level could be a sign of kidney disease, heart failure or cirrhosis of the liver.
Does sodium increase blood pressure?
Excess sodium increases your blood pressure and leads to heart disease if you continuously consume a lot of it. However, sodium does have important functions in your system, such as balancing fluid and conducting electricity for muscle and heart processes. So if your sodium levels get too low, these functions don’t work properly.
What causes low sodium (hyponatremia)?
Hyponatremia, or a low sodium level, is the most common electrolyte problem. Sodium levels in the blood are affected by how much sodium we eat or how much water we drink. However, the body adjusts for variations in our diet in order to maintain normal sodium levels. Below are some of the common causes of hyponatremia.
What are the symptoms of low sodium levels?
The symptoms of hyponatremia are related to the way it causes fluid shifts in the brain. The severity of symptoms depends on both the sodium levels and how fast sodium levels change.
How low is too low?
Hyponatremia is always diagnosed with a blood test, usually a blood electrolyte panel. Your doctor might check your sodium levels routinely if you are on a medication that can cause low sodium. Or it may be discovered on a blood test that is ordered for a different reason.
How do you treat low sodium levels?
The most important treatment for low sodium is treating the underlying cause. Your provider will make sure you are getting the best treatment for your illness while correcting your sodium levels.
The bottom line
Sodium is a vital mineral that plays an important role in many bodily functions. So, when levels get too low, it can cause some problems — particularly with fluid levels, blood pressure, and brain function.

Discussion
- Serum sodium changes tend to be affected more by changes in fluid balance, body waterand functional issue such as adrenal dysfunction, than by changes in sodium/salt balance. Urinary sodium is considered to be a more sensitive indicator of altered sodium/salt balance than blood. Mechanisms for maintaining a constant and steady level of plasma and e...
Patient Preparation
- Food or fluid is not restricted.
- Factors which can cause increased levels
Clinical Implications
- Ranges:The following are the reference ranges for this lab. However, lab ranges can vary by laboratory and country. High levels indicate: 1. Adrenal hyperfunction 2. Cushing's disease 3. Dehydration 4. Other conditions: water softeners, high salt intake, licorice, calcium, fluorides, and iron, renal insufficiency, diabetes insipidus, primary aldosteronism Low levels indicate: 1. Adrena…
Associated Tests
- BUN, Creatinine, Serum Potassium, Chloride, CO2, anion gap, uric acid, salivary and plasma cortisol.
References
- ↑ Pagana Kathleen D, Pagana Timothy J (1998) Mosby's Manual of Diagnostic and Laboratory Tests, Mosby, Inc
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weatherby Dicken, Ferguson Scott (2002) Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis: Clinical Laboratory Testing from a Functional Perspective, Bear Mountain