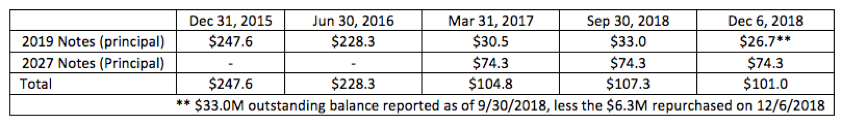
The short/current long-term debt is a separate line item on a balance sheet account. It outlines the total amount of debt that must be paid within the current year—within the next 12 months. Both creditors and investors use this item to determine whether a company is liquid enough to pay off its short-term obligations.
Is short term debt the same as current liabilities?
Is short-term debt the same as current liabilities? Yes, short-term debts and current liabilities are the same due to expected to be paid off within 1 year such as accounts payable, banks payable, taxes payable, etc. It is measured by analysts by using a liquidity ratio that helps to evaluate the creditworthiness of the company.
What are some examples of long term debt?
What is Long Term Debt?
- Long-Term Debt Example. Below is a long-term debt example of Starbucks. ...
- Advantages. ...
- Pepsi’s Long-Term Debt Example. ...
- Oil & Gas Companies Example. ...
- The Negative Impacts of high Long-Term Debt. ...
- Important Note for Investors. ...
- Conclusion. ...
- Recommended Articles. ...
Are long term or short term bonds riskier?
Long-term bonds are riskier than short-term bonds, and so interest rates on long-term bonds are usually lower than interest rates on short-term bonds. riskier than short-term bonds, and so interest rates on long-term bonds are usually higher than interest rates on short-term bonds.
What is a good long term debt ratio?
What is a good long-term debt ratio? A long-term debt ratio of 0.5 or less is considered a good definition to indicate the safety and security of a business. This means that the company's assets should be at least twice more than its long-term debts.
What Is the Short/Current Long-Term Debt?
What is short term debt?
What is a short term liability account?
When is debt due to be paid off?
How long does it take for ABC to pay back a $100 million bond?
See 2 more
About this website
What is short term and long term debt?
Short-term debt is any debt that is due within one year, while long-term debt is any debt that is due after one year. This repayment period can have a big impact on the interest rate that you'll pay. Short-term debt typically has a higher interest rate than long-term debt, because it's seen as a higher risk by lenders.
What is current long term debt?
The current portion of long-term debt (CPLTD) is the amount of unpaid principal from long-term debt that has accrued in a company's normal operating cycle (typically less than 12 months). It is considered a current liability because it has to be paid within that period.
How do you find short current long term debt?
0:303:16Short-Current Long Term Debt on the Balance Sheet - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe short current long-term debt will be found on a company's balance sheet for this example we'reMoreThe short current long-term debt will be found on a company's balance sheet for this example we're looking at Walmart stores incorporated the balance sheet moving on down here to the liabilities.
What is the difference between current debt and long term debt?
Current liabilities are those a company incurs and pays within the current year, such as rent payments, outstanding invoices to vendors, payroll costs, utility bills, and other operating expenses. Long-term liabilities include loans or other financial obligations that have a repayment schedule lasting over a year.
What are examples of long term debt?
Some common examples of long-term debt include:Bonds. These are generally issued to the general public and payable over the course of several years.Individual notes payable. ... Convertible bonds. ... Lease obligations or contracts. ... Pension or postretirement benefits. ... Contingent obligations.
Is long term debt current liabilities?
Long-term liabilities, also called long-term debts, are debts a company owes third-party creditors that are payable beyond 12 months. This distinguishes them from current liabilities, which a company must pay within 12 months. On the balance sheet, long-term liabilities appear along with current liabilities.
Where is short and long term debt on financial statements?
The short/current long-term debt is a separate line item on a balance sheet account. It outlines the total amount of debt that must be paid within the current year—within the next 12 months. Both creditors and investors use this item to determine whether a company is liquid enough to pay off its short-term obligations.
What are examples of short-term liabilities?
Examples of short-term liabilities are as follows:Trade accounts payable.Accrued expenses.Taxes payable.Dividends payable.Customer deposits.Short-term debt.Current portion of long-term debt.Other accounts payable.
Are all current liabilities short-term debt?
Short-term debts are also referred to as current liabilities. They can be seen in the liabilities portion of a company's balance sheet. Short-term debt is contrasted with long-term debt, which refers to debt obligations that are due more than 12 months in the future.
Is a bank loan short or long term?
A bank loan is a long term source of finance. It is a fixed amount of money that is given to a business by the bank that has to be repaid over time with interest , usually in monthly instalments.
Why is long term debt better than short term debt?
Diversifies Capital Portfolio – Long-term financing provides greater flexibility and resources to fund various capital needs, and reduces dependence on any one capital source. It also enables companies to spread out their debt maturities.
What is the difference between short term finance and long term debt finance?
The primary difference between long-term and short-term financing is in the length of time the debt obligation remains outstanding. Short-term financing involves a loan term that is typically less than one year. Conversely, long-term financing is any debt obligation with a loan term that is greater than one year.
What is long term debt in balance sheet?
Long Term Debt (LTD) is any amount of outstanding debt a company holds that has a maturity of 12 months or longer. It is classified as a non-current liability on the company's balance sheet.
How do you record long term debt?
If the debt is payable in more than one year, record the debt in a long-term debt account. This is a liability account. If the debt is in the form of a credit card statement, this is typically handled as an account payable, and so is simply recorded through the accounts payable module in the accounting software.
How do you find long term debt on a balance sheet?
Financial lenders or business leaders may look at a company's balance sheet to factor in the debt ratio to make informed decisions about future loan options. They calculate the debt ratio by taking the total debt and dividing it by the total assets.
What are the two major forms of long term debt?
The main types of long-term debt are term loans, bonds, and mortgage loans. Term loans can be unsecured or secured and generally have maturities of 5 to 12 years. Bonds usually have initial maturities of 10 to 30 years. Mortgage loans are secured by real estate.
What is the difference between short-term and long-term debt?
When you enter a long-term loan into your LivePlan forecast, you may notice that it appears on your Balance Sheet and Cash Flow statements in two ways: as both Short-Term and Long-Term Debt.. To explain why a loan is split this way, let's begin with a definition of each type of debt:
Accounting Examples of Long-Term vs. Short-Term Debt
Most businesses carry long-term and short-term debt, both of which are recorded as liabilities on a company's balance sheet. (Your broker can help you find these.
Is the current portion of long term debt adjusted monthly?
A monthly adjustment to the current portion of long term debt is necessary when: 1. the company issues monthly balance sheets, and 2. the amount to be paid on a loan's principal balance during the next 12 months is different from the amount presently shown as a current liability. The amount repor...
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Debt | Bizfluent
Generally, interest rates on short-term loans are lower than rates for long-term loans, but rates can vary with changing economic conditions. This is because lenders consider long-term loans riskier since payments are stretched over several years, and the possibility exists that the company could go out of business before the loan is repaid.
FASB Changes to Debt Classification: What You Need to Know
Understand the key rule changes and key terms when it comes to debt classification under the new FASB rules.
What is short term debt?
Short-Term Debt is any financing that will be paid back within the current 12 months. If you've entered a loan in your forecast that will last for 12 months or less, the entire loan is short-term debt. If, on the other hand, you've entered a loan that will be paid back over multiple years, then the part you'll pay back within ...
Why do we have a long term debt line?
By the same token, the Long-Term Debt line on your balance sheet helps you see how much debt your business will be carrying in future years. That's a useful view to have if you're considering taking out additional loans or lines of credit.
How long is a $1000.00 loan?
Then, each month another $1000.00 of the long-term debt rolls into short-term debt. Short-term debt will always be 12 months' worth of a loan, until the point where the loan has less than a year left on it.
Why break a loan into short term and long term segments?
Breaking a loan into both short-term and long-term segments is useful in planning for cash flow, and it helps you maintain a picture of the future health of your business.
Is a loan that will be paid back over multiple years considered short term debt?
If, on the other hand, you've entered a loan that will be paid back over multiple years, then the part you'll pay back within the current 12 months is short-term debt. Similarly, if you've entered a line of credit in your forecast, the portion that will be paid back within the current 12 months is also considered short-term debt:
Does LivePlan show long term debt?
When you enter a long-term loan into your LivePlan forecast, you may notice that it appears on your Balance Sheet and Cash Flow statements in two ways: as both Short-Term and Long-Term Debt.
What is a long term debt?
Long-term liabilities include loans or other financial obligations that have a repayment schedule lasting over a year. Eventually, as the payments on long-term debts come due within the next one-year time frame, these debts become current debts, and the company records them as the CPLTD.
What Is the Current Portion of Long-Term Debt?
The current portion of long-term debt (CPLTD) refers to the section of a company's balance sheet that records the total amount of long-term debt that must be paid within the current year. For example, if a company owes a total of $100,000, and $20,000 of it is due and must be paid off in the current year, it records $80,000 as long-term debt and $20,000 as CPLTD.
What happens to the CPLTD amount at the beginning of each tax year?
At the beginning of each tax year, the company moves the portion of the loan due that year to the current liabilities section of the company's balance sheet. For example, if the company has to pay $20,000 in payments for the year, the long-term debt amount decreases, and the CPLTD amount increases on the balance sheet for that amount.
What is CPLTD in financial statements?
When reading a company's balance sheet, creditors and investors use the current portion of long-term debt (CPLTD) figure to determine if a company has sufficient liquidity to pay off its short-term obligations. Interested parties compare this amount to the company's current cash and cash equivalents to measure whether the company is actually able to make its payments as they come due. A company with a high amount in its CPLTD and a relatively small cash position has a higher risk of default, or not paying back its debts on time. As a result, lenders may decide not to offer the company more credit, and investors may sell their shares.
Why is CPLTD separated out?
The CPLTD is separated out on the company's balance sheet because it needs to be paid by highly liquid assets, such as cash. The CPLTD is an important tool for creditors and investors to use to identify if a company has the ability to pay off its short-term obligations as they come due. 1:10.
What happens if a company has a high CPLTD?
A company with a high amount in its CPLTD and a relatively small cash position has a higher risk of default, or not paying back its debts on time. As a result, lenders may decide not to offer the company more credit, and investors may sell their shares.
What is a business's debt?
Businesses classify their debts, also known as liabilities, as current or long term. Current liabilities are those a company incurs and pays within the current year, such as rent payments, outstanding invoices to vendors, payroll costs, utility bills, and other operating expenses. Long-term liabilities include loans or other financial obligations that have a repayment schedule lasting over a year. Eventually, as the payments on long-term debts come due within the next one-year time frame, these debts become current debts, and the company records them as the CPLTD.
When is short term debt due?
Short-term debt is defined as the portion of a company’s total debts that are due to be paid within either the next 12 months or within the company’s current fiscal year.
What are some examples of short term debt?
Examples of Short-Term Debt. Short-term debt may exist in several different forms. Some of the most common examples of short-term debt include: Accounts Payable – Accounts payable. Accounts Payable Accounts payable is a liability incurred when an organization receives goods or services from its suppliers on credit.
What are the two types of debt?
Types of Debt. The debt obligations of a company are commonly divided into two categories – financing debt and operating debt. Financing debt refers to debt obligations that arise from a company borrowing money to fund the expansion of its business. An example of financing debt may be taking out a large bank loan or issuing bonds ...
What is capital expenditure?
Capital Expenditure A capital expenditure (“CapEx” for short) is the payment with either cash or credit to purchase long term physical or fixed assets used in a. , such as the construction of a new plant. Financing debt is typically long-term debt since the amount of debt incurred is usually too large for a company to be able to reasonably repay in ...
What is debt security?
Debt Security A debt security is any debt that can be bought or sold between parties in the market prior to maturity. Its structure represents a debt owed. Due to Account Due to Account is an accounting term that denotes a liability account. It is the amount of funds due to another party and is found in the.
What are the two ratios used to determine a company's short term debt?
Two commonly used ratios that focus on a company’s short-term debt obligations are the current ratio and the working capital ratio .
What is current ratio?
Current ratio is calculated as the company’s current assets divided by its current liabilities. It indicates the company’s ability to meet its short-term debt obligations with relatively liquid assets.
What is the current portion of long term debt?
The current portion of long-term debt is the amount of principal and interest of the total debt that is due to be paid within one year’s time. Current Debt On a balance sheet, current debt is debts due to be paid within one year (12 months) or less. It is listed as a current liability and part of. , which is debt with a maturity ...
What is debt schedule?
Debt Schedule A debt schedule lays out all of the debt a business has in a schedule based on its maturity and interest rate. In financial modeling, interest expense flows.
How to Calculate Current Portion of Long Term Debt?
Current Portion of Long-Term Debt can simply be calculated using the information that is present regarding the company’s debt schedule.
Why is the current portion of the long term debt important?
Current Portion of the Long Term Debt mainly shows the real liquidity positon of the company, and if the company would be able to meet its operating expenses in the coming year. In the same manner, current position of the Long Term Debt is also important because it helps investors, as well as creditors assess the short-term risks associated ...
Why is it important to ensure that the Current Portion of Long-Term Debt is classified correctly?
In this regard, it is also important to ensure how the Current Portion of Long-Term Debt is classified correctly so that the users of financial statements can have a clear understanding of the cash flow position of the company.
Why do financial analysts use the debt schedule?
Normally financial analysts utilize the current portion of the long term debt using the debt schedule, because that has all the relevant information present regarding assessing the portion of debt that the company owes.
Why is the long term debt separated from the balance sheet?
The rationale behind the current portion of the long-term debt being separated from the company’s balance sheet is primarily based on the fact that it needs to be paid using highly liquid assets, including cash.
Is risk profile high in long term debt?
In the case where current portion of long term debt is higher than, or marginally equal to the cash and cash equivalents present within the company, then the risk profile is considered to be high. Hence, creditors and other miscellaneous investors might be reluctant to invest on those grounds.
Is a long term loan a non-current liability?
When the company takes on long term loan, it is classified as a Non-Current Liability because of the reason that it is due at a period that is more than one year. However, in the year when this long-term debt needs to be repaid, it is important to consider the fact that these portions need to be repaid at a certain interval.
What Is the Short/Current Long-Term Debt?
The short/current long-term debt is a separate line item on a balance sheet account. It outlines the total amount of debt that must be paid within the current year—within the next 12 months. Both creditors and investors use this item to determine whether a company is liquid enough to pay off its short-term obligations.
What is short term debt?
The short/current long-term debt outlines the total amount of debt that must be paid within the current year. Debts due for payment after the next 12 months are held in the long-term debt account. Because of the structure of some corporate debt, companies often have to pay back part of the principal to debt holders over the life of the debt.
What is a short term liability account?
The current liability account or short-term debt entry is for debt that is to be paid off within the next 12 months, including short-term bank loans and accounts payable items. In some cases, the short-term liability may be due to be paid within the current fiscal year. If the account is larger than the company's current cash and cash equivalents, it may be a sign that the company could be in poor financial health because it has insufficient cash to repay its short-term debts.
When is debt due to be paid off?
Any debt due to be paid off at some point after the next 12 months is held in the long-term debt account. These debts may include financing or leasing obligations. Because of the structure of some corporate debt—both bonds and notes —companies often have to pay back part of the principal to debt holders over the life of the debt.
How long does it take for ABC to pay back a $100 million bond?
Let's suppose company ABC issues a $100 million bond that matures in 10 years with the covenant that it must make equal repayments over the life of the bond. In this situation, the company is required to pay back $10 million, or $100 million for 10 years, per year in principal.
What Is Short-Term Debt?
What Is Long-Term Debt?
The Difference Between Short-Term and Long-Term Debt
When to Use Short-Term Debt
When to Use Long-Term Debt
The Bottom Line
- Short-term debt and long-term debt are two options that businesses have for borrowing money. The main difference between the two is the repayment period. Short-term debt is any debt that is due within one year, while long-term debt is any debt that is due after one year. Interest rates on short-term debt are typically higher than on long-term debt,...
What Is Short-Term Debt?
What Is Long-Term Debt?
- Long-Term Debtis the portion of a loan that will not be paid back within the current 12 months. So, for example, if you enter a 60-month (or 5-year) loan into your forecast, the part you'll pay back in the first year becomes short-term debt, while the amount you'll pay back in Years 2-5 is long-term debt:
Why Do We Need Both?
Why Doesn't The Short-Term Debt Amount Change as I Make Payments?
What Is The Current Portion of Long-Term Debt?
Current Portion of Long-Term Debt Explained
Current Debt vs. Long-Term Debt
Special Considerations
Recording The CPLTD
Types of Debt
Examples of Short-Term Debt
- Short-term debt may exist in several different forms. Some of the most common examples of short-term debt include: 1. Accounts Payable – Accounts payableincludes all the money a company owes through ordinary credit purchases from suppliers, such as purchases from wholesalers to stock its products. It also includes monthly bills, such as utility bil...
Assessing A Company’S Debt
More Resources