Common Causes
The shoulder muscles serve a variety of functions, including:
- Holding the bones of your shoulder joint in place.
- Moving your arms up, down, forward and backward.
- Protecting your shoulder joint.
- Rotating your shoulder joint.
Related Conditions
the shoulder joint is built for mobility. list three factors that contribute to the large range of motion at the shoulder. 1) scapula makes no posterior bones attachment. 2) ball and socket. 3) glenoid cavity is shallow. 4) articular capsule is loose. articulations. 1) hold the bones together.
What is the function of the shoulder joint?
Movements As a ball and socket synovial joint, there is a wide range of movement permitted: Extension (upper limb backwards in sagittal plane) – posterior deltoid, latissimus dorsi and teres major. Flexion (upper limb forwards in sagittal plane) – pectoralis major, anterior deltoid and coracobrachialis.Biceps brachii weakly assists in forward flexion.
What shoulder joint is built for mobility?
What are the Symptoms and Causes of Shoulder Joint Pain?
- Arthritis. *All individuals are unique. ...
- Shoulder Instability. *All individuals are unique. ...
- Bursitis. The shoulder joints and other joints all around the body are filled with small sacs commonly known as Bursae.
- Tendinitis. This condition that primarily affects the shoulder joints is caused of wearing down of the tendon. ...
- Tendon Tears. ...
What movements does the shoulder joint allow?
What are symptoms of shoulder joint pain?

Where is the shoulder joint?
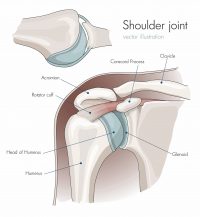
The shoulder joint is where the humerus (upper arm bone) meets the scapula (shoulder blade). Muscles and ligaments help make up the joint. They attach to the shoulder blade and upper arm bone. At the top of the shoulder blade are two bony knobs called the acromion and coracoid process.
What is the shoulder joints function?
Your shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint that allows you to perform a wide range of movements. You use these muscles for actions from throwing a ball to reaching an item on a shelf. Also called the glenohumeral joint, it has more range of motion than any other joint in your body.
What are the 5 shoulder joints?
Comprising numerous ligamentous and muscular structures, composed of the clavicle, scapula, humerus and sternum, and an intricately designed combination of four joints, the Glenohumeral (GH) Joint, the Acromioclavicular (AC) Joint and the Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint, and a "floating joint", known as the Scapulothoracic ...
What is called shoulder?
In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, and the head sits in the glenoid cavity. The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint. Shoulder. Capsule of shoulder-joint (distended). Anterior aspect.
What is a shoulder bone called?
Scapula: Another name for this bone is the shoulder blade. There are 17 muscles that attach to the scapula! Much of your shoulder motion is between the scapula and the chest.
What are the 7 movements of the shoulder?
This mobility provides the upper extremity with tremendous range of motion such as adduction, abduction, flexion, extension, internal rotation, external rotation, and 360° circumduction in the sagittal plane. Furthermore, the shoulder allows for scapular protraction, retraction, elevation, and depression.
What are the 4 main ligaments of the shoulder?
Ligaments in the shoulder are essential for a healthy shoulder.Glenohumeral Ligaments.Coraco-acromial Ligament.Coraco-clavicular Ligaments.Transverse Humeral Ligament.
What are the 4 joints that make up the shoulder?
The shoulder girdle is composed of the clavicle and the scapula, which articulates with the proximal humerus of the upper limb. Four joints are present in the shoulder: the sternoclavicular (SC), acromioclavicular (AC), and scapulothoracic joints, and glenohumeral joint.
What is shoulder size?
The official way to measure your shoulder width is to measure joint-to-joint from shoulder tip to shoulder tip. This can be done with your back facing your friend who holds up a measuring tape.
How many bones are in the shoulder?
three bonesThe shoulder is a ball and socket joint made up of three bones, namely the humerus, scapula, and clavicle. The end of the humerus or upper arm bone forms the ball of the shoulder joint.
What is the shoulder muscle called?
The primary muscle group that supports the shoulder joint is the rotator cuff muscles. The four rotator cuff muscles include the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis.
What are the 4 joints of the shoulder?
Four major shoulder joints help to achieve a complex range of motion: the glenohumeral joint, the acromioclavicular joint, the scapulothoracic joint, and the sternoclavicular joint. Joints are where 2 or more bones meet.
What is the function of the hip joint?
The hip joint is a complex ball-and-socket joint that supports the weight of the body and is responsible for movement of the upper leg. It consists of two main parts: a ball (femoral head) at the top of the thighbone (femur) that fits into a rounded socket (acetabulum), sometimes referred to as the cup, in the pelvis.
What is the shoulder joint an example of?
The glenohumeral joint is structurally a ball-and-socket joint and functionally is considered a diarthrodial, multiaxial, joint.
What type of joint is the shoulder joint quizlet?
What type of joint is the shoulder? What bones articulate to form the joint? The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint.
What is the condition of the shoulder?
Arthritis in the shoulder joint. Bone spurs in the shoulder area. Bursitis, which is inflammation of a fluid-filled sac (bursa) that normally protects the joint and helps it move smoothly. Broken shoulder bone. Dislocation of the shoulder.
What is shoulder pain?
Definition. Shoulder pain is any pain in or around the shoulder joint.
Why does my shoulder hurt?
The most common cause of shoulder pain occurs when rotator cuff tendons become trapped under the bony area in the shoulder. The tendons become inflamed or damaged. This condition is called rotator cuff tendinitis or bursitis. Shoulder pain may also be caused by: Arthritis in the shoulder joint. Bone spurs in the shoulder area.
What is frozen shoulder?
Shoulder separation. Frozen shoulder, which occurs when the muscles, tendons, and ligaments inside the shoulder become stiff, making movement difficult and painful. Overuse or injury of nearby tendons, such as the bicep muscles of the arms. Tears of the rotator cuff tendons.
What tests are needed to diagnose shoulder pain?
Blood or imaging tests, such as x-rays or MRI, may be ordered to help diagnose the problem. Your provider may recommend treatment for shoulder pain, including: If you have a rotator cuff problem, your provider will likely suggest self-care measures and exercises.
How to get shoulder pain to go away?
Here are some tips for helping shoulder pain get better: Put ice on the shoulder area for 15 minutes, then leave it off for 15 minutes. Do this 3 to 4 times a day for 2 to 3 days. Wrap the ice in cloth. Do not put ice directly on the skin because this can result in frostbite. Rest your shoulder for the next few days.
What does it mean when your left shoulder hurts?
Sudden left shoulder pain can sometimes be a sign of a heart attack. Call 911 if you have sudden pressure or crushing pain in your shoulder, especially if the pain runs from your chest to the left jaw, arm or neck, or occurs with shortness of breath, dizziness, or sweating. Go to the hospital emergency room if you have just had a severe injury ...
What is the glenohumeral joint?
Glenohumeral joint (Articulatio glenohumeralis) The glenohumeral, or shoulder, joint is a synovial joint that attaches the upper limb to the axial skeleton. It is a ball-and-socket joint, formed between the glenoid fossa of scapula (gleno-) and the head of humerus (-humeral). Acting in conjunction with the pectoral girdle, ...
Where does blood come from in the shoulder?
Blood supply to the shoulder joint comes from the anterior and posterior circumflex humeral, circumflex scapular and suprascapular arteries.
What is the inferior glenohumeral ligament?
The inferior glenohumeral ligament is a sling-like ligament extending between the glenoid labrum and the inferomedial part of the humeral neck. It is split into anterior and posterior bands, between which sits the axillary pouch. This is the strongest of the three GH ligaments, being thicker and longer than the other two. Both bands stabilize the humeral head when the arm is abducted above 90°. The anterior band limits external rotation of the arm, while the posterior band limits internal rotation.
What is the articulation between the spherical head of the humerus and the conca?
The glenohumeral joint is the articulation between the spherical head of the humerus and the concave glenoid fossa of the scapula. Being a synovial joint, both articular surfaces are covered with hyaline cartilage. The glenoid fossa is a shallow pear-shaped pit on the superolateral angle of scapula.
How do the four muscles of the glenoid fossa work together?
All four muscles are firmly attached around the joint in such a way that they form a sleeve (rotator capsule). Individually, each muscle has its own pulling axis that results in a certain movement (prime mover), while together they create a concavity compression. This is a stabilizing mechanism in which compression of the humerus into the concavity of glenoid fossa prevents its dislocation by translating forces.
Which ligament extends horizontally between the tubercles of the humerus?
The transverse humeral ligament extends horizontally between the tubercles of the humerus. It covers the intertubercular sulcus and the long head tendon of the biceps brachii muscle, preventing displacement of the tendon from the sulcus. The coracohumeral ligament extends between the coracoid process of the scapula to the tubercles of the humerus and the intervening transverse humeral ligament, supporting the joint from its superior side. It acts to limit inferior translation and excessive external rotation of the humerus.
Which ligaments connect the subscapular bursa to the glenohumeral joint?
Between the superior and middle glenohumeral ligaments, via which the subscapular bursa communicates with the glenohumeral joint cavity.
What is the shoulder joint?
The shoulder is a ball-and-socket type of joint that permits a wide range of movement. Its bony structures includes the upper arm bone (the humerus) and the shallow cavity (the glenoid) of the shoulder blade. The ball of the humerus (humeral head) is meant to stay close to the socket, like a ball bearing in a holder. The humeral head is held into the socket by the lining of the joint (the capsule), thickenings of the capsule called ligaments and a cartilage rim (the labrum) (Figure 1).
How to help a shoulder that is swollen?
Typically, the exercise program is done in conjunction with a trained physical therapist. Applying cold packs or ice bags to the shoulder before and after exercise can help reduce the pain and swelling.
How is shoulder instability diagnosed?
A complete history and physical examination should be done by a physician. The examination includes palpation to check for points of tenderness as well as a determination of range of motion and strength. The degree of shoulder looseness or laxity of the shoulder joint can also be assessed by specific tests during the examination. X-rays are usually done to obtain information about the possible causes of the instability and to rule out other causes of shoulder pain, such as a fracture.
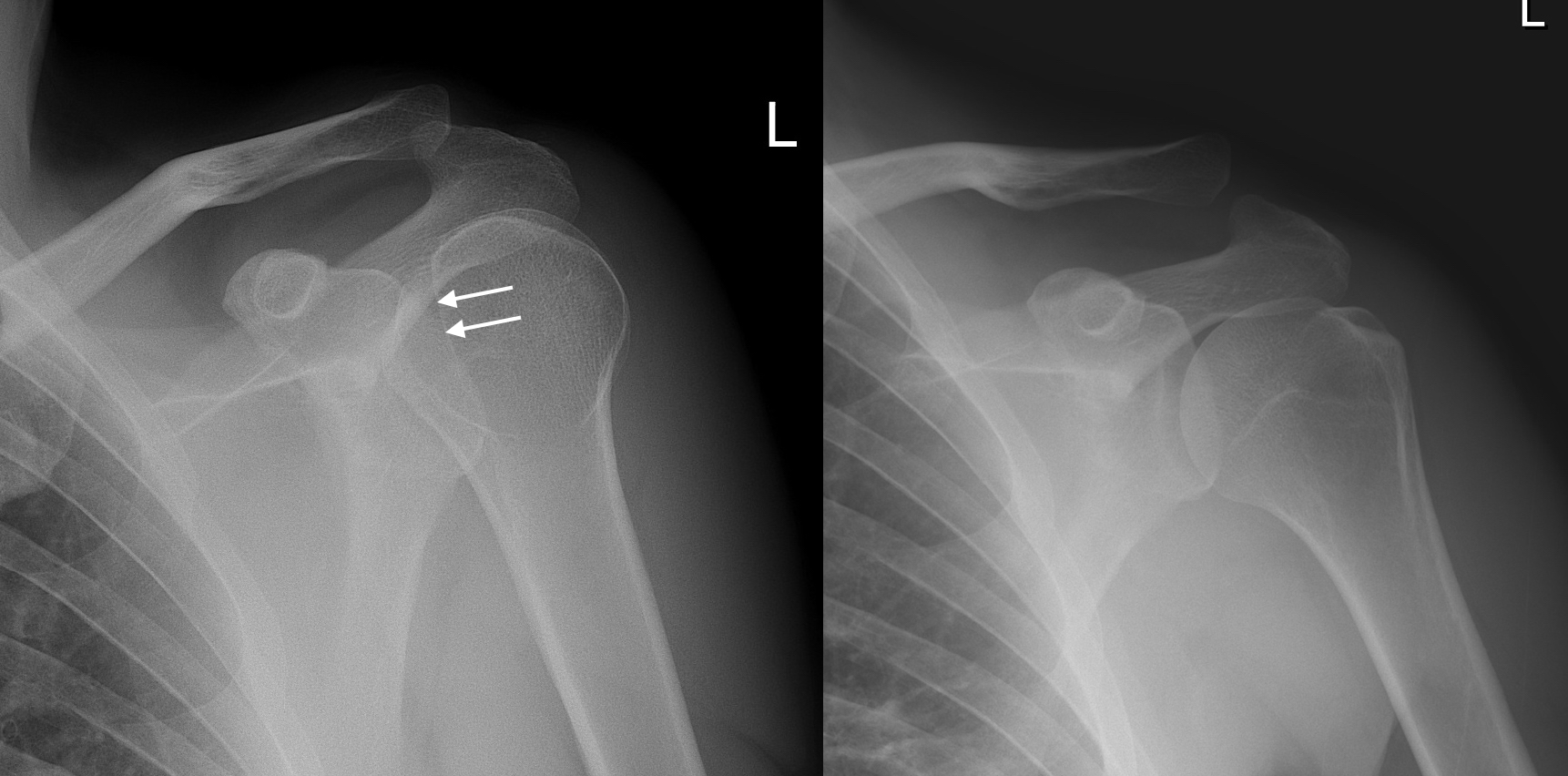
What happens when the humerus comes out of the glenoid?
Shoulder dislocations occur when the humerus comes all the way out of the glenoid (Figure 3). It may fall back into place after time or may need to be put back into place with medical assistance. The capsule, ligaments or labrum can be stretched, torn or detached from the bone during shoulder subluxation and dislocation.
What is the ball of the humerus?
The ball of the humerus (humeral head) is meant to stay close to the socket, like a ball bearing in a holder . The humeral head is held into the socket by the lining of the joint (the capsule), thickenings of the capsule called ligaments and a cartilage rim (the labrum) (Figure 1).
Can you be born with a loose shoulder?
Some people are born with somewhat loose shoulder ligaments (they have a loose or spacious capsule). For these people, instability can occur without any trauma or following relatively minor injury. Some patients may also have a genetic condition that causes looseness in the joints and predisposes them to develop shoulder instability or weakness.
Can you have a reverse total shoulder replacement?
Johns Hopkins shoulder surgeon Dr. Uma Srikumaran explains how this technology can be used to treat people who are not candidates for normal total shoulder replacement.
What is shoulder replacement?
Shoulder replacement removes damaged areas of bone and replaces them with parts made of metal and plastic (implants). This surgery is called shoulder arthroplasty (ARTH-row-plas-tee).
What is the replacement of the ball and socket in shoulder replacement?
In an anatomic total shoulder replacement, the ball and the socket are replaced with implants that resemble the natural shape of the bones.
What is the top of the arm bone?
The top of the arm bone fits into a socket on the shoulder blade. In a typical shoulder replacement, a plastic lining is attached to the socket to allow smooth movement. The surgeon removes the top of the arm bone and inserts a metal stem with a ball on the end. However, if the rotator cuff is severely damaged, the joint may not be stable or work properly.
What is the rotator cuff?
Rotator cuff injuries. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint. Rotator cuff injuries sometimes can result in damage to cartilage and bone in the shoulder joint.
How does a surgeon put a bone in the arm?
As seen before, the surgeon exposes the joint, prepares the top of the arm bone and inserts a metal stem with a ball on the end. If the socket is worn out, the surgeon smooths and reshapes it. The arm bone is then put back in place.
What is the cause of rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory disorders. Caused by an overactive immune system, the inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis can damage the cartilage and occasionally the underlying bone in the joint.
Why do you need shoulder replacement surgery?
Shoulder replacement surgery is done to relieve pain and other symptoms that result from damage to the shoulder joint.
What is frozen shoulder?
Frozen shoulder. Frozen shoulder. Frozen shoulder occurs when the connective tissue enclosing the joint becomes thickened and tight. Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in your shoulder joint.
How long does a frozen shoulder last?
Frozen shoulder typically develops slowly, and in three stages. Each stage can last a number of months. Freezing stage. Any movement of your shoulder causes pain, and your shoulder's range of motion starts to become limited. Frozen stage.
Why is my shoulder frozen?
One of the most common causes of frozen shoulder is the immobility that may result during recovery from a shoulder injury, broken arm or a stroke. If you've had an injury that makes it difficult to move your shoulder, talk to your doctor about exercises you can do to maintain the range of motion in your shoulder joint. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What is the best treatment for a frozen shoulder?
Treatment for frozen shoulder involves range-of-motion exercises and, sometimes, corticosteroids and numbing medications injected into the joint capsule.
Can frozen shoulder recur in the same shoulder?
In a small percentage of cases, arthroscopic surgery may be indicated to loosen the joint capsule so that it can move more freely. It's unusual for frozen shoulder to recur in the same shoulder, but some people can develop it in the opposite shoulder.
Does shoulder pain diminish at night?
Pain may begin to diminish during this stage. However, your shoulder becomes stiffer, and using it becomes more difficult. Thawing stage. The range of motion in your shoulder begins to improve. For some people, the pain worsens at night, sometimes disrupting sleep.
Can you get frozen shoulder from immobility?
People who've had prolonged immobility or reduced mobility of the shoulder are at higher risk of developing frozen shoulder. Immobility may be the result of many factors, including:
How to help shoulder pain?
But if you have general, mild shoulder pain, try adjusting your activities, taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and performing mild stretches to see if the pain improves on its own. However, if the pain doesn't go away after a few weeks, you should consult your doctor.
How to stretch your arm and shoulder?
Movement: Keeping your shoulders down and back, lift your right elbow up toward the ceiling to the point of tightness. Feel the stretch in the back of your upper right arm and shoulder. Hold. Return to the starting position. Repeat on the other side. This is one rep.
What is the pain of a rotator cuff tear?
Rotator cuff tears. A tear in the rotator cuff will produce pain that is similar to an impingement but has one additional differentiating feature. "If the pain is associated with weakness, it is likely caused by a tear, and if you just have pain, it may only be a rotator cuff impingement," says Dr. Ramappa.
Why does my shoulder freeze?
Frozen shoulder can occur after a rotator cuff impingement, a tendon tear, or even minor injury. But why some people go on to develop a frozen shoulder is not clear, says Dr. Ramappa. Someone with shoulder pain may hesitate to move the arm as a result of those problems, which then leads to additional pain and stiffness.
What are the problems with the rotator cuff?
Suspect a rotator cuff problem if you have pain or stiffness in your shoulder when you lift your arm above your head to brush your hair or when you reach behind your back.
Why does my rotator cuff hurt?
Calcific tendinitis. Pain from calcific tendinitis comes from calcium deposits embedded within the rotator cuff tendons. While it's unclear exactly what causes these deposits to form, some experts believe they may result from a healing process in the ligament gone awry. The condition causes sudden, severe pain that often starts in the morning. It's more common in middle-aged and older adults and those who have diabetes.
What is the rotator cuff?
Your rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that help tether your shoulder into the socket and allow you to move it in a circular motion. Some two million people visit a doctor each year for rotator cuff–related issues, according to the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgery (AAOS).
What is the bursae in the shoulder?
In the shoulder, the subacromial bursae cushion the area between the rotator cuff tendons and the acromion (the highest point of the shoulder blade or scapula). Bursae allow the tendons and bones to glide without friction when you move and lift your arms. Injuries or overuse can cause fluid to collect in bursae, causing bursitis.
What is shoulder bursitis?
Shoulder bursitis is the most common type of bursitis. It occurs when excess fluid builds up in a bursa, the cushioning pad between bones and tissue in joints. Many people with shoulder bursitis also have shoulder tendinitis. The conditions cause pain and can affect arm mobility.
What is the bursae?
The bursae (bur-SEE) are potential fluid-filled sacs that are part of the skeletal system. They cushion the space between bones and connective tissue, allowing tendons, muscle and bone to move together. In the shoulder, the subacromial bursae cushion the area between the rotator cuff tendons and the acromion ...
What causes redness in the shoulder?
Infectious (septic): In rare cases, bacterial infections like staph infections cause infectious (septic) shoulder bursitis. The shoulder may look red or purple and feel warm to the touch. In this rare case, you may have a fever and feel sick. You may have severe shoulder pain.
Can bursitis cause shoulder pain?
Most people who get shoulder bursitis also have shoulder tendinitis (damage to rotator cuff tendons). Both conditions cause shoulder pain, inflammation and stiffness. These conditions can also affect shoulder mobility and cause shoulder pain: Bone spurs or calcific tendinitis. Dislocated shoulder.
Can bursitis affect shoulder mobility?
Chronic shoulder bursitis and repeated flare-ups can damage the bursae. Over time, this may affect shoulder mobility. Bacteria that cause infectious (septic) shoulder bursitis can spread to organs and other parts of the body. In severe cases, sepsis can be life-threatening.
Who is more prone to shoulder bursitis?
Certain professionals and athletes who do a lot of repetitive shoulder movements are more prone to this problem. These include painters, carpenters and builders, and people who play football, softball or lacrosse. You may be more prone to shoulder bursitis if you have: Arthritis or gout. Diabetes.