
: a complex tissue in the vascular system of higher plants that consists mainly of sieve tubes and elongated parenchyma cells usually with fibers and that functions in translocation and in support and storage — compare xylem.
What is sieve tubes and its function?
Sieve tube is an integral component of the phloem which is composed of several sieve tube elements which join end to end to form a channel for conduction. The main function of the sieve tube is the transport of carbohydrates, primarily sucrose, in the plant.
What is sieve tube cells in biology?
In plant anatomy, sieve tube elements, also called sieve tube members, are a specialised type of elongated cell in the phloem tissue of flowering plants. The ends of these cells are connected with other sieve tube members, and together they constitute the sieve tube.
What is a sieve in biology?
sieve element, in vascular plants, elongated living cells of the phloem, the nuclei of which have fragmented and disappeared and the transverse end walls of which are pierced by sievelike groups of pores (sieve plates). They are the conduits of food (mostly sugar) transport from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
What is sieve tube made of?
A sieve tube is a tube made up of sieve-tube elements joined end-to-end. Therefore, it is a series of cells forming a tube through which the photosynthate materials flow through. Each cell is referred to as sieve-tube element (or sieve-tube member).
Why are sieve tubes called so?
In gymnosperms and pteridophytes, sieve tubes are not organized in linear rows and thus are known as sieve cells. The conducting structure of the phloem is sieve tubes. These are organized end to end in linear rows along with septa found between two sieve tube structures. Sieve pores are found in the sieve plate.
Why is sieve tube living?
Solution : Sieve tubes are considered as living cells without nucleus because, the nucleus of companion cells control their functional activities.
Does sieve tubes have DNA?
Mature sieve elements contain structural phloem specific proteins (P-proteins), mitochondria, ER, and sieve elements plastids. In plants, sieve tube cells lose their nuclei at maturity (just like our RBCs), and thus lose their chromosomal DNA, but they don't lose their mitochondria.
What is the difference between sieve cells and sieve tubes?
Sieve cells are long elongated cells found in gymnosperms and other seedless vascular plants. Sieve tubes are short specialised cells that are found only in angiosperms. Long cells with narrow pores. Short cells with wider pores.
Is sieve tube a dead cell?
The sieve tube members are living cells (which do not contain a nucleus) that are responsible for transporting carbohydrates throughout the plant.
Are sieve cells living?
Sieve elements are living cells, as opposed to water-conducting xylem vessel elements, which are dead when mature. They are unique in that they do not have a nucleus when they reach maturity.
Is the sieve tube a cell?
The sieve tube members are living cells (which do not contain a nucleus) that are responsible for transporting carbohydrates throughout the plant.
What are sieve cells Class 9?
Sieve cells: These are the primitive types of conducting elements in the phloem found in pteridophytes (pteridophytes produce neither flowers nor seeds: It is reproduced and disperse via spores) and gymnosperms (Non-flowering plants). These are long, conducting cells in the phloem that do not form sieve tubes.
1. What is a Sieve Plate?
A sieve plate is a sieve tube element that forms from the maturity of plasmodesmata, the connection between sieve tubes and companion cells. You wi...
2. What is the Prime Function of Sieve Tubes?
The prime function of the sieve tubes is to maintain support and aid the material transport system in phloem and to maintain the connection between...
3. What is the Basic Sieve Plate Function?
Sieve plates are the connection between the adjacent tissue cells of phloem. They help in passing food and other important organic materials to the...
What is a sieve tube?
Sieve tube, in flowering plants, elongated living cells (sieve-tube elements) of the phloem, the nuclei of which have fragmented and disappeared and the transverse end walls of which are pierced by sievelike groups of pores (sieve plates). They are the conduitsof food (mostly sugar) transport.
What is the name of the strands of cytoplasm that are traversed by sieve cells?
The small pores of sieve cells and the larger ones of sieve elements are traversedby strands of cytoplasm called P-protein. It is not known whether P-protein is active in transport or merely serves as a seal against leakage in case of injury. See alsophloem.
Do vascular plants have sieve tubes?
In nonangiospermous vascular plants—e.g.,gymnosperms and ferns—rows of sieve cells, showing more primitive structural features, perform the same function. Sieve-tube elements are almost always adjacentto nucleus-containing companion cells, which have been produced as sister cells with the sieve element from the same mother cell.
How are sieve tubes connected?
Sieve tube members and companion cells are connected through plasmodesmata. Plasmodesmata consists of channels between cell walls of adjacent plant cells for transport and cell to cell recognition. Structurally, the walls of sieve tubes tend to be dispersed with plasmodesmata grouped together and it is these areas of the tube walls and plasmodesmata that develop into sieve plates over time. Sieve tube members tend to be found largely in angiosperms. They are very long and have horizontal end walls containing sieve plates. Sieve plates contain sieve pores which can regulate the size of the openings in the plates with changes in the surroundings of the plants. These sieve plates are very large which means that there is a greater surface area for material transport.
What is the function of a sieve element?
Sieve elements are specialized cells that are important for the function of phloem, which is a highly organized tissue that transports organic compounds made during photosynthesis. Sieve elements are the major conducting cells in phloem. Conducting cells aid in transport of molecules especially for long-distance signaling.
Why do we need callose in sieve cells?
Sieve pores are very common in the areas that have overlapping sieve cells. Callose levels are measure in order to observe the activity of sieve cells. Callose acts as a block to the sieve pores that are present in both of these sieve elements. A lack callose suggests that the sieve elements are more active and therefore can regulate their pores more actively in response to environmental changes.
How do sieve elements help plants?
Because the plant vascular system is vital in growth and development of plant cells and the organs within the plant, the role of sieve elements in the transport of necessary carbohydrates and macromolecules is largely expanded. This can be applied to agriculture to observe the way resources are distributed to various parts of the plant. Plasmodesmata connect companion cells to sieve elements and parenchyma cells can connect the sieve tubes to various tissues within the plant. This system between the plasmodesmata, companion cells, and sieve tubes allow for the delivery of necessary metabolites. The yield of agricultural product could potentially be increased to maximize the delivery system of these specialized cells within the phloem in a way that diffusion can be maximized. It has been discovered that the angiosperm phloem can use the sieve tubes as a way to transport various forms of RNA to sink tissues which can help alter transcriptional activity. Sink tissues are tissues that are in the process of growth and need nutrients. Having Sieve elements transport additional nutrients to sink tissues can speed up the growth process, which can affect plant growth and development. Over time, rapid growth has the potential of leading to greater agricultural output.
Why are sieve cells flanked with albuminous cells?
Similar to how Sieve Tube members are associated with companion cells, sieve cells are flanked with albuminous cells in order to aid in transporting organic material.
Why do sieve pores connect with parenchyma?
They connect parenchyma with mature sieve cells to help participate in transport of cells. There can be many of these albuminous cells that belong to one sieve cell, depending on the function of the tissue or organ. Sieve pores are very common in the areas that have overlapping sieve cells.
What are sieve elements?
Sieve elements elongate cells containing sieve areas on their walls. Pores on sieve areas allow for cytoplasmic connections to neighboring cells, which allows for the movement of photosynthetic material and other organic molecules necessary for tissue function. Structurally, they are elongated and parallel to the organ or tissue ...
Why do plants not have sieve cells?
All plants have sieve cells, but not all plants have sieve tube elements because they evolved after the plant family tree had started to branch. Only angiosperms have sieve tube elements.
Do plant cells have sieve tubes?
They still have all their organelles, and are long and thin. Some plants, such as seedless plants and gymnosperms, don't have any sieve tube elements and rely solely on sieve cells for nutrient transport.
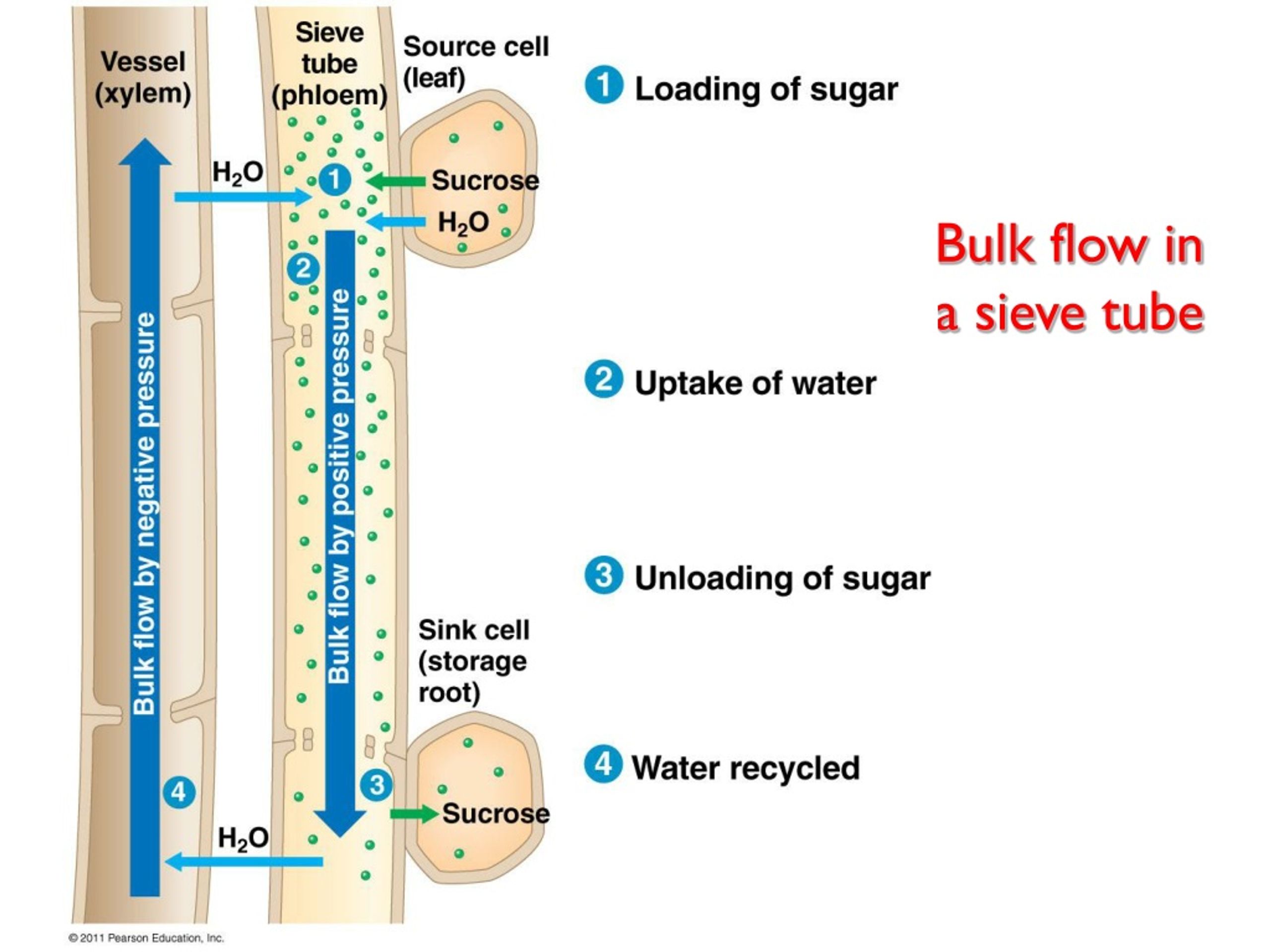
Overview
Sieve tube members
There are two categories of sieve elements: sieve cells and sieve tube members. The main functions of sieve tube members include maintaining cells and transporting necessary molecules with the help of companion cells. The sieve tube members are living cells (which do not contain a nucleus) that are responsible for transporting carbohydrates throughout the plant. Sieve tube me…
Discovery
Sieve elements were first discovered by the forest botanist Theodor Hartig in 1837. Since this discovery, the structure and physiology of phloem tissue has been emphasized more as there has been greater focus on its specialized components such as the sieve cells. Phloem was introduced by Carl Nägeli in 1858 after the discovery of sieve elements. Since then, multiple studies have been conducted on how sieve elements function in phloem in terms of working as a transport m…
Sieve cells
Sieve cells are long, conducting cells in the phloem that do not form sieve tubes. The major difference between sieve cells and sieve tube members is the lack of sieve plates in sieve cells. They have a very narrow diameter and tend to be longer in length than sieve tube elements as they are generally associated with albuminous cells. Similar to how Sieve Tube members are associated with companion cells, sieve cells are flanked with albuminous cells in order to aid in t…
Further applications in agriculture
Because the plant vascular system is vital in growth and development of plant cells and the organs within the plant, the role of sieve elements in the transport of necessary carbohydrates and macromolecules is largely expanded. This can be applied to agriculture to observe the way resources are distributed to various parts of the plant. Plasmodesmata connect companion cells to sieve elements and parenchyma cells can connect the sieve tubes to various tissues within the …
See also
• Vascular tissue