
Silicone Elastomeric Impression materials
- Polydimethyl siloxane (hydroxy terminated)
- Colloidal silica or micro sized metal oxide filler
- putty viscosity – 60-70%
- medium viscosity – 35-75 %
- low viscosity – 5-15%
- color pigments
What is the composition of silicone impression material?
CONDENSATION SILICONES. It was the first type of silicone impression material. Also known as conventional silicones. Setting occurs in room temp , so called as RTV silicones. Composition: Base paste. Polydimethyl siloxane (hydroxy terminated) Colloidal silica or micro sized metal oxide filler; putty viscosity – 60-70%; medium viscosity – 35-75 %
What is the history of silicone impression?
INTRODUCTION 3 CONDENSATION SILICONE IMPRESSION MATERIAL 4. Elastic impression materials were developed from synthetic rubber by S.L. Pearson at the University of Liverpool in 1955. The introduction of rubber-based, polysulfide impression materials was followed by silicone- based materials, both of which are still in use.
What are the types of impression materials in dentistry?
– A number of rubber-like impression materials have been developed for dentistry. impression materials, rubber base materials, elastomers, and others. materials, but they are also more expensive. – They are named based on their polymerization chemistry: polysulfide, condensation silicone, polyether, and addition silicone.
What are the disadvantages of silicon impressions?
The only problem with these impressions is when the dentist can’t have a good moisture control. There are many different types of addition silicones available on the market. The main group of silicon materials is divided in two: condensation and addition. The second ones are mostly used during restorative procedures.
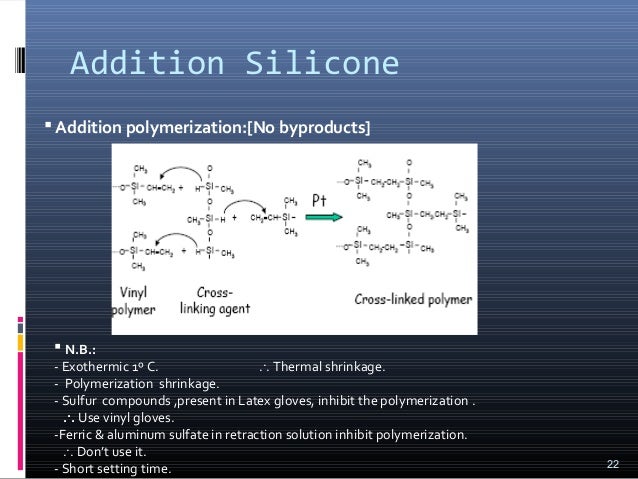
What is silicone impression material used for?
Silicone, being a more elastic material, allows more uses for dentists than alginates. With regard to impressions, for example, silicones are used in root canal cases, soft structures and bone tissues, as well as implants and functional impressions of complete prostheses.
What are the advantages of silicone impression materials?
They are non-rigid and irreversible impression materials. Odourless, clean and easy to mix. They reproduce better the detail, the dimensional stability and have a greater elastic recovery.
What is silicone used for in dentistry?
Condensation silicon is the first silicon material ever used in dentistry. It is commonly used to get impressions in the preparation of crowns, bridges, onlays, and inlays. In some cases, it's used for an impression in the process of preparation for complete dentures.
How do you make silicone impression material?
2:455:52How To Take Impression from Addition Silicone Impression MaterialYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipImmediately fill the prepared tree inject light body with cartridge system onto.MoreImmediately fill the prepared tree inject light body with cartridge system onto.
What material is used for dental impressions?
AlginateAlginate and elastomers are used to impress the oral tissues in partial removable and fixed dentures. Addition-cured silicones and polyether are the most commonly used impression materials in implant prosthodontics.
What is dental putty made of?
Polyvinyl siloxane (PVS), also called poly-vinyl siloxane, vinyl polysiloxane (VPS), or vinylpolysiloxane, is an addition-reaction silicone elastomer (an addition silicone).
Is silicone safe in your mouth?
The bottom line. When used in household products such as cooking utensils, silicone is largely a safe material. However, research suggests that liquid silicone can be dangerous if it gets inside your body through ingestion, injection, absorption, or leakage from an implant.
What are silicone dentures?
Flexible dentures have a soft, clear base that allows your own gums to show through. They're made with a high-tech thermoplastic material and there are no attachments or clips needed to hold them in place, resulting in a denture that's more comfortable and flexible.
Is silicone good for your teeth?
The main benefit of silicone toothbrushes is that they are much more gentle on gums, enabling you to thoroughly clean your teeth and mouth. This may give you added protection against gingivitis. There are studies showing that silicone bristles are more effective against plaque than regular nylon bristles.
What are rubber based impression material?
Rubber Impression Materials Oligomers are long-chain organic molecules that have reactive groups capable of further molecular binding. These oligomers are viscous fluids that can polymerize further through the processes of chain lengthening and cross-linking to form a viscoelastic solid rubber.
What is the difference between extra silicone and condensation silicone?
Addition silicones and condensation silicones are two types of impression materials. The key difference between addition silicone and condensation silicone is that addition silicone forms from an addition chemical reaction, whereas condensation silicone forms from a condensation chemical reaction.
What is agar in dentistry?
Agar is an aqueous impression material used for recording maximum details; for example, as in the production of dies for fixed restorations. Agar is also known as a reversible hydrocolloidal impression material.
What are the advantages of silicone impression materials quizlet?
Using this material ensures stability, accuracy, ease of clean up, and allows the impression to be poured at a later date.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of condensation and addition silicones?
Generally, condensation silicone has a more economical value compared to the addition silicone. Besides, addition silicone provides virtually no shrinkage while condensation silicone has a slight degree of shrinkage.
Which is better condensation or addition silicone?
Conclusion: The addition silicones have better dimensional accuracy and stability than condensation silicones. An impression made from condensation silicone should be poured as soon as possible.
What are advantages of the Automix system for elastomeric impression materials?
Automixing of impression materials has been shown to reduce or eliminate many of the problems associated with spatula-mixing. Contamination is prevented, voids are eliminated, and physical properties are comparable to those of spatula-mixed materials.
What is silicone used for?
With regard to impressions, for example, silicone is used in cases of root canals, soft structures and bone tissues, in addition to implants and functional impressions of full dentures.
Why is it important to take impressions?
In many dental treatments, taking impressions is an important part of the process. It ensures that the tests performed on the patient are correct. In addition to providing more confidence, it provides excellent results. When choosing the materials for the impression, we must take into account:
What are the most commonly used materials?
Due to their uses and characteristics, alginates and silicones are two of the most commonly used materials. We will discuss them in today's article.
Is silicone a material?
Silicone is an elastic material, which allows for shaping with relative ease and is easy to remove it after solidification in the oral cavity. This simplifies the procedure, since it does not permanently deform the mold. Silicone has various classifications and knowing them is important for the choice of products.
Is condensation silicone the same as addition silicone?
Condensation silicone has a different level of density and preparation than addition silicone, so the technique should be used in two steps. There is silicone designed for the impression taking for dentures due to their high density after polymerization.
What are impression materials used for?
A. General Comments. – Impression materials are used to make replicas (models or casts) of teeth and other oral. tissu es. – In dentistry, we take impressions of teeth and their supporting structures. These supporting structures include gingiva, alveolar bone or residual ridge, hard and soft palate, and. frenums, which are muscle attachments.
What is the thickest impression material?
moisture in the area. – Putty materials are the thickest impression materials, but they can still record the details of a fingerprint. – Heavy-body and putty materials are placed in an impression tray, and their high viscosity. reduces running and dripping of the impression material out of the tray and onto the.
What is addition silicone?
Addition Silicones – Addition silicones are the most popular type of elastomeric impression material, especially for crown and bridge impressions. – They are clean and do not have an unpleasant taste or smell. – They are the most accurate, stable, and expensive impression materials.
What is the classification of impression materials?
E. Classification of Impression Materials. 1. Chemical Reaction or Physical Change. – Impression materials set either by a chemical reaction or by a physical change. – Impression materials set by chemical reactions to form elastic rubber materials are called thermoset.
What is an impression tray?
1. Use of Impression Trays. – Impression trays are used to carry the impression material into the mouth, and the handle of the tray is used to remove the impression. – The tray can also support a weak material impression and improve accuracy. – Trays are supplied in a variety of shapes and sizes and are made from several materials.
What are replicas used for?
frenums, which are muscle attachments. – The replicas are used to construct restorations and other appliances. – The impression is a negative reproduction, whereas the replica (model or cast) is a positive reproduction.
Is alginate an acceptable impression material?
-Study models are not considered to be highly accurate reproductions of oral tissues. – Therefore, alginate is an acceptable impression material for study models, but it is.
What is addition silicone?
Addition silicones are among the most popular elastomeric impressions at the moment. They are used mostly for fixed restorations such as crowns and bridges. They are very accurate and stable. Actually, this is the most dimensionally stable impression material.
What are the different types of silicones?
There are many different types of addition silicones available on the market. The main group of silicon materials is divided in two: condensation and addition. The second ones are mostly used during restorative procedures. They were introduced after the condensation and are considered to have better properties than them. They enjoy this widespread use mostly because of the positive experiences that dentists have. Among the many types, the ones that are most commonly used are universal (medium-bodied) with a 35%-75% viscosity, heavy-bodied with a 60%-70% viscosity, light-bodied 5%-15% viscosity. All of these addition silicones have a certain polymerization time, according to the instruction manual. The thing is that they all use the same chemical reaction of polymerization.
What is the viscosity of silicone?
Among the many types, the ones that are most commonly used are universal (medium-bodied) with a 35%-75% viscosity, heavy-bodied with a 60%-70% viscosity, light-bodied 5%-15% viscosity. All of these addition silicones have a certain polymerization time, according to the instruction manual.
Why do dentists use silicone molds?
First of all, these materials provide a very precise impression with a great attention to detail. Most of the fixed and mobile restorations require a very detailed impression so that the final product fits perfectly in the mouth. The second thing why dentists love them so much is the dimensional stability. After the impression is taken, some materials tend to shrink. That is why the mold might not be as precise as needed. With addition silicone materials there is no shrinkage. This leads to the fact that dental technicians can actually get more than one mold from a single impression. This might not be the case with a number of the other materials. Patients have a very high tolerance for this type of dental material.
How long does it take to mix silicone?
The base paste consists of polymethyl hydrogen siloxane, other siloxane prepolymers, and fillers. The acceleration paste includes divinylpolysiloxane, fillers, platinum salt, palladium and more. The general time of mixing is around 45s. The setting time is around 6 minutes. Some brands offer them in special cartridges and are mixed with an automix gun.
What are the disadvantages of adding silicone?
Disadvantages: One of the biggest problems in the past for addition silicones was their hydrophobic character . Due to the way of production, dentists had to be careful and provide a dry area. Today, thanks to advanced technology, dentists are past that problem. These materials can be very costly.
Can you get more than one mold from a dental impression?
That is why the mold might not be as precise as needed. With addition silicone materials there is no shrinkage. This leads to the fact that dental technicians can actually get more than one mold from a single impression.
What are the different types of impression materials?
They can be categorised into either rigid impression materials (zinc oxide eugenol and impression compound) or elastic impression materials (alginate and silicone). Each material is used for different purposes, as some laboratories require a more detailed impression than others. Impression materials are commonly classified by their elastic properties once set. Non-elastic materials are generally not used for taking impressions of crown preparations because of their inability to accurately record undercuts.
What is an impression paste?
Impression paste is a modified form of zinc oxide eugenol. Other properties are added to make it suitable to use as an impression material. It comes in two tubes: one containing a white zinc oxide mixture and the other containing a red eugenol mixture.
What is rigid impression?
Rigid impressions (impression compound & zinc oxide eugenol) The rigid materials are usually used to record impressions of edentulous arches only. Impression compound must be heated in a water bath and then moulded onto the impression tray. It doesn’t flow well and can't record fine detail. It is therefore used for primary impressions ...
Why are impression materials not used for crown preparations?
Non-elastic materials are generally not used for taking impressions of crown preparations because of their inability to accurately record undercuts.
Which is more stable, silicone or alginate?
However, silicones work best in a dry environment and may not be ideal if there is a lot of saliva. Alginate is flexible and flows well.
Why do we take impressions?
There are many reasons for taking an impression to make a model in dentistry for example; To study a case. To diagnose a case. To educate our patients about their dental needs. To treatment plan ( especially for orthodontics ) To construct indirect restorations including; Inlays, onlays, bridges, crowns and dentures.
How to improve mouth impression accuracy?
Its accuracy can be improved by retaking the impression. This is done by adding fresh paste and inserting into the mouth until set.
What is a CD impression?
Clinicians make final impressions of complete dentures (CD) and removable partial dentures (RPD) using different techniques and materials. Applying the correct impression technique and material, based on an individual's oral condition, improves the quality of the prosthesis, which may improve quality of life.
Why is the final impression important?
The final impression is a very important step for ensuring the quality of the denture in terms of satisfaction, comfort, stability of the denture, and chewing ability . There are a number of different techniques and materials used for making the final impression for complete dentures or removable partial dentures.
How many studies have compared single stage impressions with alginate versus two stage two step impressions?
Three studies compared single‐stage impressions with alginate versus two stage‐two step with elastomer (silicone, polysulfide, or polyether) impressions. There was no evidence of a clear difference in the OHIP‐EDENT at one month (MD 0.05, 95% CI ‐2.37 to 2.47; two studies, 98 participants). There was no evidence of a clear difference in participant‐rated general satisfaction with dentures at six months (MD 0.00, 95% CI ‐8.23 to 8.23; one study, 105 participants). We assessed the quality of the evidence as very low.
What is the final impression of dentures?
Clinicians can make the final impression (sometimes referred to as the wash impression) for complete dentures using different techniques and materials (Starcke 1975). These have evolved along with our understanding of the biology of the tissues, and advances in available impression materials. The techniques can be grouped into mucostatic, mucocompressive, selective pressure, functional, and neutral zone impression techniques (Addison 1944; Beresin 1976; Boucher 1943; Cagna 2009; Freeman 1969; Solomon 1973; (Figure 1)). The impression materials used are impression plaster, resinous wax, zinc‐oxide eugenol impression paste, alginate, polysulfide, addition silicone, and polyether (Boucher 1951; Daou 2010; Joglekar 1968; Koran 1977; Mehra 2014; Trapozzano 1939). See Figure 2.
Is silicone better than alginate?
Oral health‐related quality of life measured by the OHIP‐EDENT seemed to be better with silicone (MD 7.20, 95% CI 2.71 to 11.69; 144 participants). The study found no clear differences in participant‐reported quality of the denture (comfort) after a two‐week 'confirmation' period, but reported that silicone was better for stability and chewing efficiency. We assessed the quality of the evidence as low.
Is there evidence of a difference between the techniques and materials compared?
For most comparisons and outcomes, there was no evidence of a clear difference between the techniques or materials compared.
Is there any evidence that one technique or material has a substantial advantage over another for making complete dentures and removable?
We conclude that there is no clear evidence that one technique or material has a substantial advantage over another for making complete dentures and removable partial dentures. Available evidence for the relative benefits of different denture fabrication techniques and final‐impression materials is limited and is of low or very low quality. More high‐quality RCTs are required.
Who made ear impressions?
Ear impressions were used to make earmolds for Astronauts Gordon Cooper, Pete Conrad, Neil Armstrong, and Elliott See . The earmold impressions were made by hearing aid dispenser Stanley G. Barr of Orlando, FL, based on interest generated to the Houston, TX Space Agency by fellow hearing aid specialist Gordon L. Bisel. The earmolds were made by Bruel C. Kent and W.R. Rice at Mid-States Laboratories, Wichita, KS 6. The custom earmolds made from these ear impressions were used in their communications systems, replacing the cumbersome ear sets that the astronauts had been using. Reports indicated that the communication systems involving the earmolds were so successful that the Space Agency ordered earmolds for the astronauts scheduled for the October, 1965 space shots: Ed White, Frank Boorman, Jim Lovell, and Mike Collins.
When were ear impressions first used?
The first report identifying an impression material for the ear (wax) was by Hawksley in 1890.
When did acrylic ear impressions start?
Even though acrylic material was introduced to make ear impressions in about 1946 3, it was still a fairly new technology well into the late 1950s 4. The powder and liquid combination had a long life span in being used to take ear impressions, primarily from the late 1940s and continuing at least into the early 1980s, but with the bulk coming in the 1960s and 1970s.
When did hearing aids start using ear impressions?
Many hearing professionals fail to recognize that even though a variety of ear impression materials had been introduced by the 1960s to make customized earpieces, many dispensers of hearing aids continued to use “stock” earmolds and/or a variety of ear tips when fitting hearing aids. These were commonly used by hearing aid dispensers – ...
