What is the basic Keynesian model?
The main plank of Keynes's theory, which has come to bear his name, is the assertion that aggregate demand—measured as the sum of spending by households, businesses, and the government—is the most important driving force in an economy.
What are the assumptions of simple Keynesian model?
Like any economic theory, Keynesian economics relies on a set of fundamental assumptions. The three most noted assumptions are rigid or flexible prices',500,400)">inflexible prices, effective demand, and important savings and investment determinants other than the interest rate.
What is simple Keynesian model of income determination?
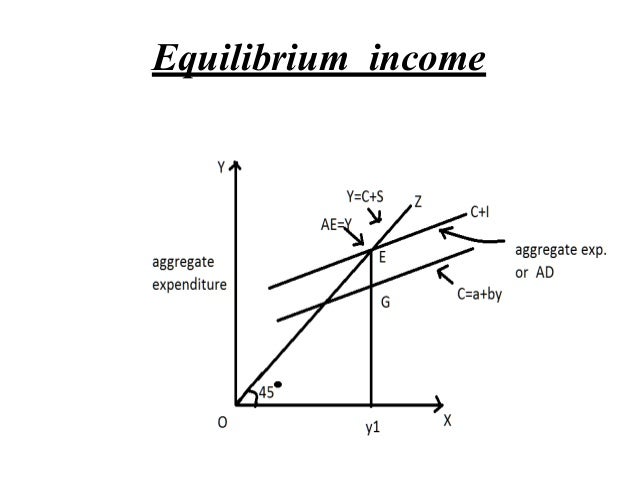
According to Keynesian model, the equilibrium level of national income is determined at a point where the aggregate demand curve intersects the aggregate supply curve. The 45° helping line represents aggregate supply. By definition, output equals income on each point of aggregate supply curve.
Why is the model called a Keynesian model?
The other model is called the Keynesian Model, named after the famous economist John Maynard Keynes. This is a newer model.
What is the simple condition model?
The Simple Keynesian Model emphasizes that a decrease in aggregate demand can lead to a stable equilibrium with substantial unemployment. It is also known as the Keynesian Cross. You can read about the Monetary System – Types of Monetary System (Commodity, Commodity-Based, Fiat Money) in the given link.
What are the stability condition of simple Keynesian model?
The stability condition in the SKM is that the MPC(b) should lie in-between zero and one. It has to be greater than zero and less than one. We may now rigorously demonstrate the income path in SKM with a lagged consumption function. We know that the Keynesian consumption function is linear.
What is simple income determination?
It shows how an equilibrium level of income is determined in a simple. economy in which there are only three basic activities - investment. expenditure, consumption expenditure and saving. There are two ways of approaching the problem: (I) Income-expenditure.
How does Keynesian model determine income and employment?
“In the Keynesian analysis, the equilibrium level of employment and income is determined at the point of equality between saving and investment. Saving is a function of income, i.e. S=f (Y). It is defined as the excess of income over consumption, S=Y-C and income is equal to consumption plus investment.
When was Keynesian economics used?
Keynesian economics, as part of the neoclassical synthesis, served as the standard macroeconomic model in the developed nations during the later part of the Great Depression, World War II, and the post-war economic expansion (1945–1973).
What is the difference between classical and Keynesian model?
While classical economists believe the economy is, for the most part, self-correcting, John Maynard Keynes thought the government and economists should help the economy occasionally. The Classical Model involves economic growth in the long run, while the Keynesian Model involves economic growth in the short run.
What are the importance of Keynesian economics?
Keynesian economics focus on demand-side solutions to recessionary periods. The intervention of government in economic processes is an important part of the Keynesian arsenal for battling unemployment, underemployment, and low economic demand.
What are the 3 major theories of economics?
The 3 major theories of economics are Keynesian economics, Neoclassical economics, and Marxian economics.
What are the underlying assumptions of a Keynesian cross model?
An assumption commonly made in this model is that even if income were zero, people would have to consume something. In this example, consumption would be $600 even if income were zero. Then, the MPC is 0.8 and the MPS is 0.2. Thus, when income increases by $1,000, consumption rises by $800 and savings rises by $200.
What is not the assumption of Keynesian theory?
Answer and Explanation: Which of the following is not an assumption of the Keynesian model? d. Prices and wages are flexible. Flexible prices and wages were an assumption of Adam Smith's original classical model of the economy.
Which of the following is an assumption of the Keynesian view of economics quizlet?
What is a key assumption of a Keynesian Model? Prices are STICKY in the short run so that output is determined by shifts in demand in the goods market.
What are the assumption of classical economics?
The three key assumptions underlying the classical study of macroeconomics are flexible prices, Say's law, and saving-investment equality. These three assumptions ensure that the macroeconomy would continue to produce the quantity of aggregate output that fully employs available resources.
What is the Keynesian model?
The Keynesian model calls for fiscal policy where governments increase spending at times when the economy is in a slowdown. This involves a theory described as the multiplier. This states that if government spends to create jobs, the employed people will have more money to spend.
Who developed the Keynesian model?
John Lister. John Maynard Keynes. The Keynesian model is a set of economic theories pioneered by John Maynard Keynes. The model works on the belief that the private sector does not always produce the most efficient results for the economy as a whole.
What are the criticisms of the Keynesian model?
Instead, critics back monetary policy, which backs measures such as controlling interest rates to influence how much money is made available to both consumers and businesses in loans . Most governments today use a combination of the fiscal policy and monetary policy.
What is the theory of Keynesian economics?
Keynesian economics is a theory that says the government should increase demand to boost growth. 1 Keynesians believe consumer demand is the primary driving force in an economy.
What is the difference between Keynesian and classical economics?
Keynesian Versus Classical Economic Theories. The classical economic theory promotes laissez-faire policy. It says the free market allows the laws of supply and demand to self-regulate the business cycle. It argues that unfettered capitalism will create a productive market on its own.
What distinguishes Keynesian economic theory from supply-side economics?
Keynesian economic theory is essentially the opposite of supply-side economics, which emphasizes business growth and deregulation. 11 Keynesian economics promotes government intervention to promote consumer demand. 1
What do the proponents of trickle down economics say?
Proponents of trickle-down economics say that all fiscal policy should benefit the wealthy. Since the wealthy are business owners, benefits to them will trickle down to everyone. 13. Monetarists claim that monetary policy is the real driver of the business cycle.
What was Keynes' theory of employment, interest, and money?
Keynes described his premise in “The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money.”. Published in February 1936, it was revolutionary. 7 First, it argued that government spending was a critical factor driving aggregate demand. That meant an increase in spending would increase demand.
Why do socialists criticize Keynesianism?
Socialists criticize Keynesianism because it doesn't go far enough. They believe the government should take a more active role to protect the common welfare. This role means owning some factors of production. Most socialist governments own the nation's energy, health care, and education services. 15
What are the factors that determine the economics of a business?
These four factors are entrepreneurship, capital goods, natural resources, and labor. In this theory, business owners use the most efficient practices to maximize profit. Classical economic theory also advocates for a limited government. It should have a balanced budget and incur little debt.
What Is Keynesian Economics?
Keynesian economics is a macroeconomic economic theory of total spending in the economy and its effects on output, employment, and inflation. Keynesian economics was developed by the British economist John Maynard Keynes during the 1930s in an attempt to understand the Great Depression. Keynesian economics is considered a "demand-side" theory that focuses on changes in the economy over the short run. Keynes’s theory was the first to sharply separate the study of economic behavior and markets based on individual incentives from the study of broad national economic aggregate variables and constructs.
What are the primary tools recommended by Keynesian economists to manage the economy and fight unemployment?
Activist fiscal and monetary policy are the primary tools recommended by Keynesian economists to manage the economy and fight unemployment.
What did Keynes advocate for?
Based on his theory, Keynes advocated for increased government expenditures and lower taxes to stimulate demand and pull the global economy out of the depression . Subsequently, Keynesian economics was used to refer to the concept that optimal economic performance could be achieved—and economic slumps prevented—by influencing aggregate demand through activist stabilization and economic intervention policies by the government.
Why does Keynesian economics argue that lower wages can restore full employment?
For example, Keynesian economics disputes the notion held by some economists that lower wages can restore full employment because labor demand curves slope downward like any other normal demand curve. Instead he argued that employers will not add employees to produce goods that cannot be sold because demand for their products is weak. Similarly, poor business conditions may cause companies to reduce capital investment, rather than take advantage of lower prices to invest in new plants and equipment. This would also have the effect of reducing overall expenditures and employment.
When lowering interest rates fails to deliver results, Keynesian economists argue that other strategies must be employed,?
When lowering interest rates fails to deliver results, Keynesian economists argue that other strategies must be employed, primarily fiscal policy. Other interventionist policies include direct control of the labor supply, changing tax rates to increase or decrease the money supply indirectly, changing monetary policy, or placing controls on the supply of goods and services until employment and demand are restored.
What is Keynes' theory of inflation?
Keynesian economics represented a new way of looking at spending, output, and inflation. Previously, what Keynes dubbed classical economic thinking held that cyclical swings in employment and economic output create profit opportunities that individuals and entrepreneurs would have an incentive to pursue, and in so doing correct the imbalances in the economy. According to Keynes’s construction of this so-called classical theory, if aggregate demand in the economy fell, the resulting weakness in production and jobs would precipitate a decline in prices and wages. A lower level of inflation and wages would induce employers to make capital investments and employ more people, stimulating employment and restoring economic growth. Keynes believed that the depth and persistence of the Great Depression, however, severely tested this hypothesis.
Why did Keynes see excessive saving as dangerous?
He saw it as dangerous for the economy because the more money sitting stagnant, the less money in the economy stimulating growth. This was another of Keynes's theories geared toward preventing deep economic depressions.
Why is the Simple Keynesian Model important?
The Simple Keynesian Model is important not so much for its ability to capture the details of recessions, but for its ability to demonstrate the possibility of a stable equilibrium at less than full employment. While the real wage rate adjusts in the Classical Model to move the economy to full employment, the real wage rate does not appear in the Simple Keynesian Model and equilibrium is achieved by adjustments in aggregate demand, which equals aggregate income. The equilibrium aggregate income need not imply full employment.
What is the Keynesian Cross?
That point is that a decrease in aggregate demand can lead to a stable equilibrium with substantial unemployment.
Which theory of national income determination states that aggregate income is always equal to consumption and savings?
According to Keynes theory of national income determination, the aggregate income is always equal to consumption and savings.
What are the two sectors of economy?
Comprises only two sectors, namely, households and businesses . The households are the owners of factors of production and provide factor services to businesses to earn their livelihood in the form of wages, rents, interest, and profits. In addition the households are the consumers of final goods and services produced by businesses. On the other hand, businesses purchase factor services from households to produce goods and services and sell it to households.
What is the difference between a two sector and a three sector economy?
The two-sector model of economy involves households and businesses only, while three-sector model represents households businesses, and government. On the other hand, the four-sector model contains households, businesses, government, and foreign sector.Let us discuss these three types of models of income determination given by Keynes.
What are the two major factors that determine the national income of a country?
These two factors are Aggregate Supply (AS) and Aggregate Demand (AD) of goods and services.
