What are the symptoms of Sinding Larsen Johansson syndrome?
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome is a temporary injury to the growth plate in the knee. It affects kids and teens ages 10 to 14 and is almost always caused by overuse from playing sports. It will usually heal with rest, ice and over-the-counter medicine. Kids will need to avoid sports or intense physical activity while their tendon heals.
What causes Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome?
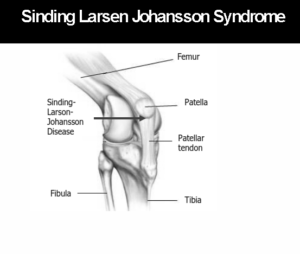
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson (SLJ) syndrome is pain at the bottom of the kneecap (patella). It is caused by swelling and irritation of the growth plate there. A growth plate is a layer of cartilage near the end of a bone where most of the bone's growth happens. It is weaker and more at risk for injury than the rest of the bone.
What is Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome (distal patella apophysitis)?
Oct 25, 2018 · Sinding-Larsen-Johansson, or SLJ, syndrome is a debilitating knee condition that most commonly affects teens during periods of rapid growth. The kneecap, or patella, is attached to the shinbone, or tibia, from the patellar tendon. The tendon connects to an expansion plate at the bottom of the kneecap throughout growth.
What is the prognosis of Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome (SLJ)?
Jan 07, 2021 · Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome involves pain in the lower part of the kneecap that occurs when practicing physical activity. The area becomes inflamed, and the individual experiences extreme pain upon touching the area. It was described by Sinding-Larsen in 1921, and Johansson in 1922. This syndrome consists of a mechanical overload, similar to …
How long does Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome last?
Mild cases can be resolved with a slight reduction in activity level, whereas moderate to severe cases may require significantly reduced activity (12-16 weeks) and even immobilization (cast/brace) at times.
How is Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome treated?
How Can I Deal With SLJ Syndrome?Stop doing an activity if knee pain or swelling comes back. Then, try to limit your activity until the pain or swelling goes away.If possible, avoid or limit activities that put a lot stress on the knees, such as walking up and down stairs, lifting heavy objects, and squatting.
What body part is affected by Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome?
Sinding Larsen Johansson Syndrome (SLJS) is a juvenile osteochondrosis and traction epiphysitis affecting the extensor mechanism of the knee which disturbs the patella tendon attachment to the inferior pole of the patella.
What signs or symptoms distinguish Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome?
Athletes complain of a dull, aching pain at the bottom of the kneecap. This pain may become worse when walking up stairs, kneeling or squatting, running or jumping. They may have swelling or a bump at the bottom of the kneecap.
Is Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome serious?
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome is a temporary injury to the growth plate in the knee. It affects kids and teens ages 10 to 14 and is almost always caused by overuse from playing sports. It will usually heal with rest, ice and over-the-counter medicine.Mar 11, 2022
What causes Larsen syndrome?
Causes. Larsen syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder, caused by a mutation in a gene that is important to normal skeletal development before birth, called FLNB (filamin B).
Does patellar tendonitis affect growth?
In growing children, the patellar tendon attaches to the growth plate of the kneecap, and repetitive stress on the tendon can irritate and injure the growth plate.Feb 5, 2013
What muscle causes Osgood-Schlatter?
When a child is active, the quadriceps muscles pull on the patellar tendon which, in turn, pulls on the tibial tubercle. In some children, this repetitive traction on the tubercle leads to inflammation of the growth plate. The prominence, or bump, of the tibial tubercle may become very pronounced.
Is Osgood Schlatters disease hereditary?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is an osteochondrosis, which is a group of disorders of the growth plates that occur when the child is growing rapidly. Doctors are not sure what causes osteochondrosis, but the disorders do seem to run in families.
How common is a patellar tendon rupture?
Overall, patellar tendon rupture is the third most common injury to the extensor mechanism of the knee, following patellar fracture and quadriceps tendon rupture.Mar 30, 2021
Where does Osgood-Schlatter disease occur?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a condition that causes pain and swelling below the knee joint, where the patellar tendon attaches to the top of the shinbone (tibia), a spot called the tibial tuberosity. There may also be inflammation of the patellar tendon, which stretches over the kneecap.
What is similar to Osgood-Schlatter?
Sinding-Larsen–Johansson disease is another common cause of anterior knee pain in children and adolescents. It is similar to Osgood-Schlatter disease, except that Sinding-Larsen–Johansson disease occurs at the inferior pole of the patella.Feb 1, 2011
What is SLJ in medical terms?
Sinding Larsen Johansson Syndrome (SLJ) is a juvenile osteochondrosis and traction epiphysitis affecting the extensor mechanism of the knee which disturbs the patella tendon attachment to the inferior pole of the patella.
What is the syndrome of tenderness at the inferior pole of the patella?
This is the Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease (SLJD), and has been used as an umbrella term for the syndrome that causes pain of the inferior pole of the patella accompanied by fragmentation of the pole or a calcification at the pole.
How to treat tendinopathy?
An adjunct treatment that has been proven beneficial for tendinopathy or tenosynovitis problems is the ASTYM system.#N#A safe progression back to sports or high-level activities may happen when each of the following happens in this specific order: 1 The lower kneecap is no longer tender and there is no swelling. 2 The injured knee can be fully straightened and bent without pain. 3 The knee and leg have regained normal strength compared to the uninjured knee and leg 4 Ability to jog straight ahead without limping. 5 Ability to sprint straight ahead without limping. 6 Ability to do 45-degree cuts. 7 Ability to do 90-degree cuts. 8 Ability to do 20-yard figure-of-eight runs. 9 Ability to do 10-yard figure-of-eight runs. 10 Ability to jump on both legs without pain and hop on the injured leg without pain.
What is the avulsion of the patellar ligament?
The Sinding-Larsen Johansson Syndrome is a rupture or avulsion of the patellar ligament at the distal point of the patella caused by traction. The patellar ligament or tendon is the distal part of the tendon of the M. Rectus Femoris, part of the quadriceps femoris, which is a continuation of it. It goes over the patella and is attached to the tibial tuberosity. It’s other attachment is the spina iliaca anterior inferior. The most superficial fibers originate from the rectus femoris, the deepest layer from the vastus intermedius and the intermediate layer from the vastus lateralis and vastus medialis.
What is the condition of the kneecap?
Sinding Larsen Johansson syndrome is an inflammation of the bone at the bottom of the patella (kneecap), where the tendon from the shin bone (tibia) attaches. It is an overuse knee injury rather than a traumatic injury. The syndrome usually appears in adolescence, during the growth spurt.
What is PFP in sports?
Patellofemoral pain (PFP) is one of the most common disorders between adolescent athletes and is multifactorial in nature. The Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome usually appears in children after a period of rapid growth.
What is Physioplus course?
Physioplus is an approved course provider of the Australian Physiotherapy Council (APC). Ireland (CORU) Ireland Physioplus meets the CPD standards of the Health and Social Professions Council of Ireland (CORU).
How old is Sinding Larsen?
Unlike "jumper's knee" which is seen at any age, Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease is seen in active adolescents, typically between 10-14 years of age 1. Children with cerebral palsy are also prone to Sinding-Larsen-Johansson 4.
What is SLJ syndrome?
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson, or SLJ, syndrome is a debilitating knee condition that most commonly affects teens during periods of rapid growth. The kneecap, or patella, is attached to the shinbone, or tibia, from the patellar tendon. The tendon connects to an expansion plate at the bottom of the kneecap throughout growth.
Why do I have knee pain?
Knee pain is a well-known symptom which can occur due to a variety of knee injuries and/or conditions, including sports injuries. The knee is one of the most complex joints in the human body as it is made-up of the intersection of four bones, four ligaments, various tendons, two menisci, and cartilage. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, the most common causes of knee pain include patellar subluxation, patellar tendinitis or jumper’s knee, and Osgood-Schlatter disease. Although knee pain is most likely to occur in people over 60 years old, knee pain can also occur in children and adolescents. Knee pain can be treated at home following the RICE methods, however, severe knee injuries may require immediate medical attention, including chiropractic care.
What is the muscle group at the front of the upper leg called?
The large muscle group at the front of the upper leg is known as the quadriceps. When straightening the leg, the quadriceps pull to deliver the leg forward. This puts pressure on the growth plate at the bottom of the kneecap. During rapid growth, the bones and muscles don’t always grow at precisely the same rate.
What sports cause knee pain?
Sports that involve a lot of running and jumping, such as field and track or other sports such as football, gymnastics, basketball, lacrosse, and field hockey, can place stress on the knees. Increased or incorrect physical activity can add strain on the knees.
What is the pain at the bottom of the knee?
Symptoms demonstrating the presence of�Sinding-Larsen-Johansson, or SLJ, syndrome include: pain at the front of the knee or near the bottom of the kneecap, as this is the main symptom of SLJ; swelling and tenderness around the kneecap; pain that increases with physical activities like jogging, climbing stairs, or leaping; pain that becomes more acute when kneeling or squatting; and a swollen or bony bump at the bottom of the kneecap.
What is SLJ in medical terms?
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson, or SLJ, syndrome is medically referred to as a juvenile osteochondrosis which affects the patella tendon in the kneecap which attaches to the inferior pole of the patella in the shinbone. Commonly characterized by knee pain and inflammation, SLJ is considered an overuse knee injury rather than a traumatic injury.
Diagnosing Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome
Clinical evaluation is typically enough to make a diagnosis. The pain can cause loss of function in the individual. This usually manifests as being unable to jump, unable to kick the ball hard, etc. Cold weather usually makes it worse, and the condition improves with warm weather.
Treatment for SLJ syndrome
The goal of treatment is to alleviate pain while maintaining normal activities as much as possible. This is usually done through a combination of stretches, icing the area, and anti-inflammatory medications.
When can I resume physical activity?
You can do strengthening and balance exercises once the pain has subsided to try to prevent the pain from returning. Doctors recommend practicing alternative training, or doing activities like cycling or swimming, which don’t require running or jumping.
How old is Sinding Larsen?
Unlike "jumper's knee" which is seen at any age, Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease is seen in active adolescents, typically between 10-14 years of age 1. Children with cerebral palsy are also prone to Sinding-Larsen-Johansson 4.
What is the name of the disease that affects the proximal end of the patellar tendon?
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease. Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease , also known as Sinding-Larsen disease or Larsen-Johansson syndrome, affects the proximal end of the patellar tendon as it inserts into the inferior pole of the patella .
Is a thickening of the proximal patellar tendon seen?
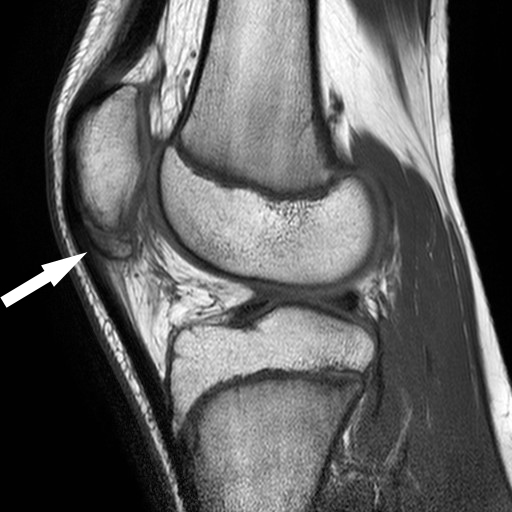
Early findings are subtle or absent. Thickening of the proximal patellar tendon may be seen with possible stranding of the adjacent portions of Hoffa's fat pad. Dystrophic calcification and/or ossification may eventually occur.
What causes knee pain in children?
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson lesion or syndrome is one of a group of injuries known as osteochondroses which cause knee pain in children. Other similar injuries include: 1 Osgood’s Schlatter disease – is a chronic stress injury to the bottom of the kneecap. 2 Sever’s disease – causes pain at the back of the heel.
What causes a jumper's knee?
It is caused by a combination of excessive traction on the patella from the patella tendon and usually a period of rapid growth. This condition is described as the adolescent equivalent to Jumper’s knee or patella tendinopathy. Other alternative diagnoses include Osgood Schlatter disease and a bipartite patella.
What causes pain in the back of the knee?
Other similar injuries include: Osgood’s Schlatter disease – is a chronic stress injury to the bottom of the kneecap. Sever’s disease – causes pain at the back of the heel. It usually affects young boys, up ...
What is bipartite patella?
A bipartite patella occurs when the patella has a natural split in it and is not the result of a fracture. Cases of Sinding-Larsen-Johansson usually correct themselves once the skeleton matures.
Growth plates
Up until we are fully grown, we have so-called growth plates located at the ends of long bones such as the shinbone (tibia) and thighbone (femur). These growth plates consist of cartilage to which tendons of muscles are attached. When the body grows, the tendons can pull on and irritate the cartilage.
Better with time
Osgood-Schlatter and Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndromes are self-limiting conditions that improve with time, but it can take up to 1 year to be symptom-free.
Causes
Osgood-Schlatter and Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndromes are common in athletes who participate in sports with lots of sprinting and jumping, for example, athletics, football, volleyball, and basketball. They may be a result of repeated jumping and landing with volleyball and basketball players, or repeated long kicks with football players.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made on the basis of symptoms. An experienced doctor or physiotherapist will make an accurate diagnosis. These conditions can often be confused with patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), which has some similarities but is more common in girls than boys.
Treatment
Both are treated the same. When symptoms flare up, ice can be an effective way to reduce pain, but the most important measure is to adjust the level of activity. This might involve refraining from certain activities which cause a lot of pain for a while so that the symptoms can subside.
Be honest!
Ignoring your symptoms is not recommended. Pushing through the pain or masking symptoms by taking painkillers like NSAIDs will in most cases prolong the rehabilitation period.

Definition/Description
Classification
- Medlar and Lyne classified the condition in four stages based on the radiographs. The following stages were proposed: stage I when the patella has a normal appearance, stage II if there are irregular calcifications in the distal pole, stage III with coalescence of calcifications, stage IV-a when the calcifications are coalescing into the distal pole, and stage IV-b is a calcified ossicle di…
Epidemiology
- Unlike "Jumper's Knee" which is seen at any age, SLJS is seen in active adolescents, typically between 10-14 years of age. 1. Children with cerebral palsy are also prone to SLJS.
Etiology
- SLJS is caused by traction on the patellar ligament, causing inflammation at the insertion of the proximal ligament into the inferior pole of the patella. The extensor mechanism of the knee comprises the quadriceps tendon and muscles, patella, patellar ligament and the supporting retinaculum. Injuries can occur from direct trauma, overuse, degenerative disease. The most co…
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation
- Physical examination is important for the diagnosis of SLJS, as with most conditions. Most will have tenderness at the inferior pole of the patella and there may be some tenderness along the patellar tendon. Resisted knee extension may elicit pain and there may be some localized soft tissue swelling. A joint effusion should not be present with this condition and may be present wit…
Differential Diagnosis
- Differential considerations include: 1. Osgood-Schlatter disease: occurs at the inferior attachment of the patellar tendon onto the tibial tuberosity 1. Jumper's knee: same location and similar pathology, but seen in adults (some authors do not distinguish between Sinding-Larsen-Johansson and jumper's knee). 2. Patellar sleeve fractures: same age group; avulsion of inferior …
Diagnostic Procedures
- The physiotherapist performs a physical examination of the knee and reviews the patient’s symptoms. In case of anterior knee pain there are three important tests to perform. In all tests the patient is in supine position. 1. Patellar Grind Test;Tester places thumb web-space just above the patella, then asks to contract their quad forcefully. The test is positive if there is pain or grinding…
Outcome Measures
- The Kujala anterior knee pain scale and the Lower extremity functional scalecan be used for both an initial screening tool as well as to detect changes with treatment and as outcome measures.
Treatment
- Initial treatment consists of relieving the pain by resting for a few days and strengthening exercises with modification of activities. There is no definite protocol or treatment algorithm that exists for SLJS. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be necessary, and in severe cases a cast is used for maintaining immobility. This is usually done for up to 4 weeks, but mos…
Physical Therapy Treatment
- The physical therapist must educate the patient on activity modification. Kneeling, jumping, squatting, stair climbing, and running on the affected knee should be avoided at least for the short term. Lower extremity strength needs to be tested, especially at the ankle and the hip to find any muscle weaknesses that may be contributing to the overuse syndrome. Core strengthening sho…