
How do you determine solubility of a substance?
Write the chemical equation.
- For example, a molecule of PbI 2 splits into the ions Pb 2+, I -, and a second I -. ...
- Write the equation 7.1×10 –9 = [Pb 2+ ] [I -] 2
- The equation is the product solubility constant, which can be found for the 2 ions in a solubility chart. ...
How can solubility help you identify a substance?
Solubility Rules
- Salts containing Group I elements (Li +, Na +, K +, Cs +, Rb +) are soluble . ...
- Salts containing nitrate ion (NO 3-) are generally soluble.
- Salts containing Cl -, Br -, or I - are generally soluble. ...
- Most silver salts are insoluble. ...
- Most sulfate salts are soluble. ...
- Most hydroxide salts are only slightly soluble. ...
What are factors affect the solubility of a substance?
Temperature Affects Solubility
- Solids. The effects of temperature on the solubility of solids differ depending on whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
- Liquids. In the case of liquids, there is no defined trends for the effects of temperature on the solubility of liquids.
- Gases. ...
What does it mean if a substance is a soluble?
Soluble substances are those that easily dissolve in a solvent, such as water, and include sugar, salt, alcohol and some dishwashing detergents. In chemistry, solubility of a substance is a quantitative term that refers to the amount of substance that can dissolve in a given volume of a solvent.
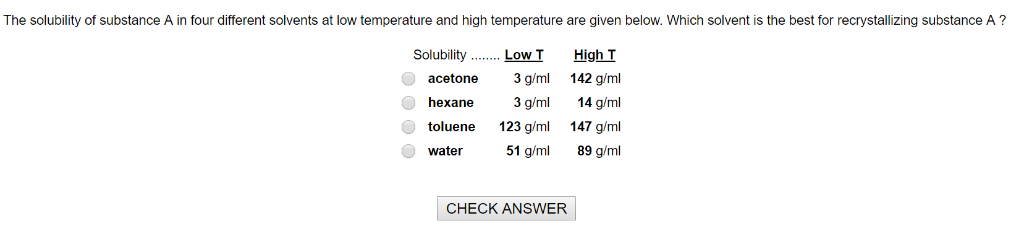
What is solubility of a substance class 9?
What is Solubility? The maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a known quantity of solvent at a certain temperature is its solubility. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of one or more solutes in a solvent.
What is solubility short answer?
Solubility is a property referring to the ability for a given substance, the solute, to dissolve in a solvent.
What does solubility mean example?
Solubility is defined as able to be dissolved. An example of something with solubility is salt in water.
What is solubility of a substance class 12?
Solubility is a physical property of a solution. It can be defined as the measure of maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a quantified amount of solvent.
What is soluble substance?
Substances that dissolve in water are called soluble substances. When you mix sugar with water, the sugar dissolves to make a transparent solution. Salt is soluble in water too. Substances that do not dissolve in water are called insoluble substances. When you mix sand or flour with water, they do not dissolve.
What is the other name of solubility?
Solubility is also a synonym for solvability, or how easy or difficult a particular problem is to solve.
What is insoluble substance?
Definition: An insoluble substance is a substance (solid) that will not dissolve in a solvent even after mixing (eg; sand and water).
What is the principle of solubility?
Solubility is defined as the maximum quantity of a substance that can be completely dissolved in a given amount of solvent, and represents a fundamental concept in fields of research such as chemistry, physics, food science, pharmaceutical, and biological sciences.
1. How is Solubility Related to Concentration Why is it Important to Know the Solubility of a Substa...
Solubility is the amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature. The concentration of a solution is the am...
2. What is the KSP Formula and What are the Factors that Affect Solubility?
In general, MXb(s) ⇔ aM+b(aq) + bX-a(aq) is expressed as Ksp = [M+b]a[X−a]b. These expressions are called solubility product constant expressions b...
3. Do gases also dissolve in water and can we also call them Solute?
Water is an excellent solvent present on Earth. A wide number of substances are Soluble in it. Solid-state substances that can dissolve in water ar...
4. Why are some substances that are Soluble in water not Soluble in other Liquids or vice versa?
Solving ability of any Liquid is determined by the polarity of the molecules of that Liquid. Water molecules are formed by the chemical combination...
5. What is a saturated Solution?
Water and any solvent that has the ability to dissolve a solvent can do so for a certain amount of Solute. This is essentially a function of the de...
6. What are the different factors that affect the Solubility of a Solute in a substance?
There are many that affect the Solubility of a substance in any solvent. By changing these factors we can successfully regulate the concentration o...
7. Where can I find problem questions on Solubility and Solution?
The amount of Solute that is present in a Solution and the various factors that determine it are quantitative in nature. So these factors can be me...
What is the solubility of a solute?
The solubility of a given solute in a given solvent is function of temperature. Depending on the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) of the dissolution reaction, i.e., on the endothermic (ΔG > 0) or exothermic (ΔG < 0) character of the dissolution reaction, the solubility of a given compound may increase or decrease with temperature. The van 't Hoff equation relates the change of solubility equilibrium constant (K sp) to temperature change and to reaction enthalpy change (ΔH). For most solids and liquids, their solubility increases with temperature because their dissolution reaction is endothermic (ΔG > 0). In liquid water at high temperatures, (e.g. that approaching the critical temperature ), the solubility of ionic solutes tends to decrease due to the change of properties and structure of liquid water; the lower dielectric constant results in a less polar solvent and in a change of hydration energy affecting the ΔG of the dissolution reaction.
What is the extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent?
The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is measured as the saturation concentration, where adding more solute does not increase the concentration of the solution and begins to precipitate the excess amount of solute. Insolubility is the inability to dissolve in a solid, liquid or gaseous solvent.
What is the property of a solid, liquid or gaseous chemical substance called?
Solubility is the property of a solid, liquid or gaseous chemical substance called solute to dissolve in a solid, liquid or gaseous solvent. The solubility of a substance fundamentally depends on the physical and chemical properties of the solute and solvent as well as on temperature, pressure and presence of other chemicals ...
How is solubility determined?
The solubility of one substance in another is determined by the balance of intermolecular forces between the solvent and solute, and the entropy change that accompanies the solvation. Factors such as temperature and pressure will alter this balance, thus changing the solubility.
How to separate solubility of a substance?
For example, a mixture of salt ( sodium chloride) and silica may be separated by dissolving the salt in water, and filtering off the undissolved silica. The synthesis of chemical compounds, by the milligram in a laboratory, or by the ton in industry, both make use of the relative solubilities of the desired product, as well as unreacted starting materials, byproducts, and side products to achieve separation.
What is the IUPAC definition of solubility?
According to the IUPAC definition, solubility is the analytical composition of a saturated solution expressed as a proportion of a designated solute in a designated solvent. Solubility may be stated in various units of concentration such as molarity, molality, mole fraction, mole ratio, mass (solute) per volume (solvent) and other units.
What is the threshold for insoluble substances?
The thresholds to describe something as insoluble, or similar terms, may depend on the application. For example, one source states that substances are described as "insoluble" when their solubility is less than 0.1 g per 100 mL of solvent.
What is soluble in chemistry?
Solubility Definition in Chemistry. Solubility is a measure of how well one substance dissolves into another. Ilbusca / Getty Images. Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels.
What is it called when a substance is soluble at all proportions in a specific solvent?
If a substance is soluble at all proportions in a specific solvent, it is called miscible in it or possesses the property called miscibility. For example, ethanol and water are completely misci ble with each other. On the other hand, oil and water do not mix or dissolve in each other. Oil and water are considered to be immiscible .
What is the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent at equilibrium?
Solubility is defined as the maximum quantity of a substance that can be dissolved in another. It is the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent at equilibrium, which produces a saturated solution. When certain conditions are met, additional solute can be dissolved beyond the equilibrium solubility point, which produces a supersaturated solution. Beyond saturation or supersaturation, adding more solute does not increase the concentration of the solution. Instead, the excess solute starts to precipitate out of the solution.
How much insoluble solute is insoluble?
While there is no hard-and-fast limit that defines a substance as insoluble, it's common to apply a threshold where a solute is insoluble if less than 0.1 gram dissolves per 100 milliliters of solvent.
What are the factors that affect the solubility of a solution?
Solubility can be influenced by the presence of other chemical species in a solution, the phases of the solute and solvent, temperature, pressure, solute particle size, and polarity. Cite this Article.
How does ethanol dissolve in water?
For example, when ethanol dissolves in water, it maintains its molecular identity as ethanol, but new hydrogen bonds form between ethanol and water molecules. For this reason, mixing ethanol and water produces a solution with a smaller volume than you would get from adding together the starting volumes of ethanol and water.
What happens when NaCl dissolves in water?
When sodium chloride (NaCl) or another ionic compound dissolves in water, the compound dissociates into its ions. The ions become solvated, or surrounded by a layer of water molecules. Solubility involves dynamic equilibrium, involving opposing processes of precipitation and dissolution.
What is Solubility ?
The maximum amount of Solute that can dissolve in a known quantity of solvent at a certain temperature is its Solubility
What is the solubility product of a compound?
It is the maximum product of the molar concentration of the ions (raised to their appropriate powers) which are produced due to dissociation of the compound. At a given temperature the solubility product is constant.
What is the difference between a saturated and supersaturated solution?
Based on solubility, different types of solution can be obtained. A saturated solution is a solution where a given amount of solute is completely soluble in a solvent at a given temperature. On the other hand, a supersaturated solution is ...
What is the maximum concentration of a solute that dissolves in a known concentration of solvent at a given?
In terms of quantity, solubility is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known concentration of solvent at a given temperature. Based on the concentration of solute dissolves in a solvent, solutes are categorized into highly soluble, sparingly soluble or insoluble .
How does temperature affect soluble properties?
Effect of Temperature on Solubility: By changing the temperature we can increase the soluble property of a solute. Generally, water dissolves solutes at 20° C or 100° C. Sparingly soluble solid or liquid substances can be liquified completely by raising the temperature.
What is the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a known quantity of solvent at a certain temperature?
The maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a known quantity of solvent at a certain temperature is its solubility . A solution is a homogeneous mixture of one or more solutes in a solvent. Sugar cubes added to a cup of tea or coffee is a common example of a solution.
What is the property of sugar molecules to dissolve?
The property which helps sugar molecules to dissolve is known as solubility . Hence, the term solubility can be defined as a property of a substance (solute) to dissolve in a given solvent. A solute is any constituent which can be either solid or liquid or gas liquified in a solvent.
What is the solubility of a solute in a particular solvent?
The solubility of a solute in a particular solvent is the maximum concentration that may be achieved under given conditions when the dissolution process is at equilibrium. Referring to the example of salt in water:
What are the factors that affect the solubility of a substance in a given solvent?
Other factors also affect the solubility of a given substance in a given solvent. Temperature is one such factor, with gas solubility typically decreasing as temperature increases (Figure 6.3. 1 ). This is one of the major impacts resulting from the thermal pollution of natural bodies of water.
How does carbonation affect solubility?
The solubility of a gaseous solute is also affected by the partial pressure of solute in the gas to which the solution is exposed. Gas solubility increases as the pressure of the gas increases . Carbonated beverages provide a nice illustration of this relationship. The carbonation process involves exposing the beverage to a relatively high pressure of carbon dioxide gas and then sealing the beverage container, thus saturating the beverage with CO 2 at this pressure. When the beverage container is opened, a familiar hiss is heard as the carbon dioxide gas pressure is released, and some of the dissolved carbon dioxide is typically seen leaving solution in the form of small bubbles (Figure 6.3. 3 ). At this point, the beverage is supersaturated with carbon dioxide and, with time, the dissolved carbon dioxide concentration will decrease to its equilibrium value and the beverage will become “flat.”
How do gases form supersaturated solutions?
If a solution of a gas in a liquid is prepared either at low temperature or under pressure (or both), then as the solution warms or as the gas pressure is reduced , the solution may become supersaturated. In 1986, more than 1700 people in Cameroon were killed when a cloud of gas, almost certainly carbon dioxide, bubbled from Lake Nyos (Figure 6.3. 5 ), a deep lake in a volcanic crater. The water at the bottom of Lake Nyos is saturated with carbon dioxide by volcanic activity beneath the lake. It is believed that the lake underwent a turnover due to gradual heating from below the lake, and the warmer, less-dense water saturated with carbon dioxide reached the surface. Consequently, tremendous quantities of dissolved CO 2 were released, and the colorless gas, which is denser than air, flowed down the valley below the lake and suffocated humans and animals living in the valley.
What happens when you add salt to a solution?
If we add more salt to a saturated solution of salt, we see it fall to the bottom and no more seems to dissolve. In fact, the added salt does dissolve, as represented by the forward direction of the dissolution equation. Accompanying this process, dissolved salt will precipitate, as depicted by the reverse direction of the equation. The system is said to be at equilibrium when these two reciprocal processes are occurring at equal rates, and so the amount of undissolved and dissolved salt remains constant. Support for the simultaneous occurrence of the dissolution and precipitation processes is provided by noting that the number and sizes of the undissolved salt crystals will change over time, though their combined mass will remain the same.
How to determine the concentration of salt in a solution?
You can repeat this process until the salt concentration of the solution reaches its natural limit, a limit determined primarily by the relative strengths of the solute-solute, solute-solvent, and solvent-solvent attractive forces discussed in the previous two modules of this chapter. You can be certain that you have reached this limit because, no matter how long you stir the solution, undissolved salt remains. The concentration of salt in the solution at this point is known as its solubility.
When a solute's concentration is equal to its solubility, the solution is said to be?
When a solute’s concentration is equal to its solubility, the solution is said to be saturated with that solute. If the solute’s concentration is less than its solubility, the solution is said to be unsaturated. A solution that contains a relatively low concentration of solute is called dilute, and one with a relatively high concentration is called concentrated.
What is the degree to which a substance dissolves in a solvent to make a solution?
Solubility, degree to which a substance dissolves in a solvent to make a solution (usually expressed as grams of solute per litre of solvent). Solubility of one fluid (liquid or gas) in another may be complete (totally miscible; e.g., methanol and water) or partial (oil and water dissolve only slightly).
What is the ability of liquids to dissolve solids, other liquids, or gases?
The ability of liquids to dissolve solids, other liquids, or gases has long been recognized as one of the fundamental phenomena of nature encountered in daily life. The practical importance of solutions and the need to understand their properties have challenged numerous writers since…
What is a solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature and pressure?
A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature and pressure is said to be saturated ( see saturation ). See also Joel Hildebrand.
What does "like dissolves like" mean?
In general, “like dissolves like” (e.g., aromatic hydrocarbons dissolve in each other but not in water). Some separation methods ( absorption, extraction) rely on differences in solubility, expressed as the distribution coefficient (ratio of a material’s solubilities in two solvents).
What is saturation in science?
saturation, any of several physical or chemical conditions defined by the existence of an equilibrium between pairs of opposing forces or of an exact balance of the rates of opposing processes. Common examples include the state of a solution left in contact with the pure undissolved solute until no further…
Do solids dissolve in liquids?
liquid: Solubilities of solids and gases. Since the dissolution of one substance in another can occur only if there is a decrease in the Gibbs energy, it follows that, generally speaking, gases and solids do not dissolve in liquids as readily as do other liquids. To….
What is the solubility limit?
The solubility, which is also known as the solubility limit , of a solute corresponds to the maximum amount of that chemical that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent. Because, based on this definition, a solubility limit is a ratio of the amount of solute that can dissolve, relative to the quantity of solvent that is utilized to prepare ...
What unit is used to measure solubility?
While the amount of a chemical that is contained in a solution can be expressed using any chemically-acceptable unit, the quantities within a solubility limit are typically reported using mass-based units, such as grams.
What happens to the solute particles when the temperature increases?
As a result, solute particles are able to more easily overcome the attractive forces that exist between the solvent molecules and, therefore, temporarily generate "empty" spaces between those particles.
What is the formula for water?
Finally, because the chemical formula for water, H 2 O , is associated with the 100.-gram quantities in the denominators of the solubilities in both Figure 7.9. 1 and Table 7.9. 1, water is the solvent that was used to obtain all of the data that is presented above. As stated in Section 4.12, water is known as the "universal solvent," due to its ability to dissolve more substances than any other chemical. As a result, most solubility experiments that have been performed utilized solutions that were prepared by dissolving a solute in 100. grams, or 100. milliliters, of water.
Why is water considered a universal solvent?
As stated in Section 4.12, water is known as the "universal solvent," due to its ability to dissolve more substances than any other chemical. As a result, most solubility experiments that have been performed utilized solutions that were prepared by dissolving a solute in 100. grams, or 100. milliliters, of water.
How to determine the role of a chemical?
The role of a particular chemical can be assigned by analyzing the relative location in which that substance is written, or, alternatively, the numerical quantity with which that chemical is associated, in a solubility proportion.
Is solubility directly proportional to temperature?
Therefore, the solubility of a solid or a liquid solute is generally directly, or linearly , proportional to its temperature. At higher temperatures, gaseous solute particles are also able to more easily overcome the attractive forces that exist between the solvent molecules.
How to measure solubility?
Solubility is measured in grams of a solute per 100 g of water. If the mass of water is not 100 g, you can scale the solubility values up or down. A saturated solution is one in which no more solid can dissolve in the liquid at a given temperature.
What is the solubility of sodium chloride at 20°C?
The solubility of sodium chloride at 20°C is 40 g/100 g water.
Table of Contents
Solubility Product
- The term solubility product is generally applicable for sparingly soluble salts. It is the maximum product of the molar concentration of the ions (raised to their appropriate powers) which are produced due to dissociation of the compound. At a given temperature the solubility product is constant. Lesser the value of solubility product indicates lower solubility and higher value of sol…
Recommended Videos
- On the basis of solubility, the factors affecting solubility vary on the state of the solute: 1. Liquids In Liquids 2. Solids In Liquids 3. Gases In Liquids
Solubility of Liquids in Liquids
- Water is known as a universal solvent as it dissolves almost every solute except for a few. Certain factors can influence the solubility of a substance. Solubility is the new bond formation between the solute molecules and solvent molecules. In terms of quantity, solubility is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known concentration of solvent at a given temperatur…
Solubility of Solids in Liquids
- It has been observed that solid solubility depends on the nature of the solute as well as the solvent. We often see that substances like sugar, common salt (NaCl), etc readily dissolve in water while substances like naphthalene do not dissolve in water. From the various observations and experimental results, it has been seen that only polar solutes tend to dissolve in the polar so…
Solubility of Gases in Liquids
- Gas solubility in liquids deals with the concept of gas dissolving in a solvent. Let us first define solubility. For any substance, solubility is the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a given solvent at a particular temperature. Now our concern is gas solubility in liquids. The gas solubility in liquids is greatly affected by temperature and pressure as well as the nature of the s…
Factors Affecting Solubility
- It has been found that the gas solubility in liquids increases with increase in pressure. To have a better understanding of the effect of pressure on gas solubility let us consider a system of a g...
Overview
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a saturated solution, one in whic…
Quantification of solubility
The solubility of a specific solute in a specific solvent is generally expressed as the concentration of a saturated solution of the two. Any of the several ways of expressing concentration of solutions can be used, such as the mass, volume, or amount in moles of the solute for a specific mass, volume, or mole amount of the solvent or of the solution.
In particular, chemical handbooks will often express the solubility of a substance in a liquid as gra…
Qualifiers used to describe extent of solubility
The extent of solubility ranges widely, from infinitely soluble (without limit, i. e. miscible ) such as ethanol in water, to essentially insoluble, such as titanium dioxide in water. A number of other descriptive terms are also used to qualify the extent of solubility for a given application. For example, U.S. Pharmacopoeia gives the following terms, according to the mass msv of solvent required to dissolve one unit of mass msu of solute: (The solubilities of the examples are approx…
Molecular view
Solubility occurs under dynamic equilibrium, which means that solubility results from the simultaneous and opposing processes of dissolution and phase joining (e.g. precipitation of solids). The solubility equilibrium occurs when the two processes proceed at equal and opposite rates.
The term solubility is also used in some fields where the solute is altered by solvolysis. For example, many metals and their oxides are said to be "soluble in hydrochloric acid", although in fa…
Factors affecting solubility
Solubility is defined for specific phases. For example, the solubility of aragonite and calcite in water are expected to differ, even though they are both polymorphs of calcium carbonate and have the same chemical formula.
The solubility of one substance in another is determined by the balance of intermolecular forces between the solvent and solute, and the entropy change t…
Solubility of gases
Henry's law is used to quantify the solubility of gases in solvents. The solubility of a gas in a solvent is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas above the solvent. This relationship is similar to Raoult's law and can be written as:
where is a temperature-dependent constant (for example, 769.2 L·atm/mol for dioxygen (O2) in water at 298 K), is the partial pressure (in atm), and is the concentration of the dissolved gas in th…
Polarity
A popular aphorism used for predicting solubility is "like dissolves like" also expressed in the Latin language as "Similia similibus solventur". This statement indicates that a solute will dissolve best in a solvent that has a similar chemical structure to itself, based on favorable entropy of mixing. This view is simplistic, but it is a useful rule of thumb. The overall solvation capacity of a solvent depe…
Rate of dissolution
Dissolution is not an instantaneous process. The rate of solubilization (in kg/s) is related to the solubility product and the surface area of the material. The speed at which a solid dissolves may depend on its crystallinity or lack thereof in the case of amorphous solids and the surface area (crystallite size) and the presence of polymorphism. Many practical systems illustrate this effect, for example in designing methods for controlled drug delivery. In some cases, solubility equilibri…