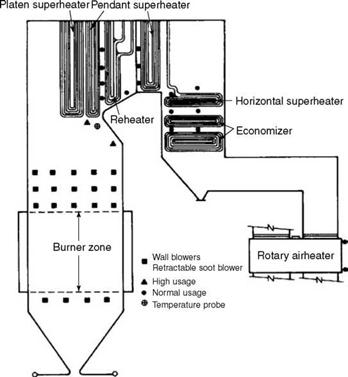
SOOT BLOWERS AND THEIR IMPORTANCE IN POWER PLANT A soot blower is a system for removing the soot that is deposited on the furnace tube of a boiler during Combustion. Various types of soot blowers such a wall blowers, long retractable blowers and air heater blowers are used for cleaning.
What is A sootblower?
A sootblower is a device for removing the soot that is deposited on the internal furnace tubes of a boiler during combustion to prevent plugging of the gas passes and maintain boiler efficiency. Types of soot blowers: Wall Blowers also known as IRs (Insertable Rotating) Long Retractable Soot Blower (LRSB) or IK (Insertable Kinetic)
How many soot blowers are there in a thermal power plant?
A large coal fired Thermal power plant will have around two hundred soot blowers of both types arranged to cover all the area of the boiler. This will be programmed to automatically operate to a required sequence. Intelligent soot blower systems calculate the trends in the temperature increase in different sections of a boiler.
How does a rotary soot blower work?
As the element rotates, the blowing medium removes soot from a large portion of the boiler. High-performing rotary soot blowers can provide blowing arcs between 30 and 360 degrees. Manual operation, where an employee activates the soot blower after inspection of the boiler, is inefficient and can lead to infrequent or too frequent cleaning.
Can a soot blower be used in a superheater?
Even though most high-quality rotary blowers use heat-resistant and durable materials, the inability to retract excludes them from high-temperature regions of your boiler, like the combustion chamber. You can typically find rotary soot blowers in the superheater, economizer, and air heater.

What is soot in power plant?
Soot deposited on the heating surfaces of a boiler acts as a heat insulator. The result is that less heat is transferred to the water to raise steam and more heat is wasted up the chimney. This leads to higher fuel consumption and/or poor steaming.
Where are soot blowers located?
Soot blowers are placed in the flue gas path to clean some portion of the tube. When blowing is starting this high pressure steam comes out at high velocity from the nozzle of blower. This high velocity steam clean the soot deposits on the tube. The blower rotates by 360 degree by means of electrical motor.
What is soot in boilers?
Soot is the inevitable result of burning fossil fuels, and boilers that run on gas or oil produce soot simply by doing their job. However, excessive soot buildup can indicate that your furnace is not running at peak efficiency.
What is retractable soot blower?
Function of Long Retractable Soot Blower (LRSB) is to remove soot deposited on Coils / Tubes in High temperature Zone (e.g. Superheater Coils). To avoid sagging of Lance Element from High temperature of Flue Gases, LRBS is parked outside the Boiler.
How does soot blower work?
A soot blower blasts air, steam or water (or a combination) to remove soot and ash from the interior walls of the boiler heating surfaces. The soot blower can be set to operate automatically at timed intervals or be controlled manually.
What are types of soot?
There are two types of soot blowers. These are rotary soot blowers (RSB) and long retractable soot blowers (LRSB) . Rotary soot blowers rotate at a fixed position. In long retractable soot blowers the lancer enters into flue gas path and also rotates like rotary blowers.
What causes soot?
Soot is a byproduct of burning fossil fuels, particularly coal. It is emitted by a variety of sources, including burning coal for electricity or industrial fuel, manufacturing, oil refining, and motor vehicles. Soot is released into the air as either extremely small particles or liquid droplets.
How can soot be reduced?
We can switch away from diesel fuels, or use more efficient, low-emission diesel engines. And there are other measures that can help reduce the volume of soot released into the atmosphere. “You can certainly put on particle traps on vehicles, off road equipment, passenger vehicles and buses, trucks.
Is soot a good insulator?
“Soot deposits are particularly effective at reducing heat transfer as they insulate extremely well.
What are the preparations before soot blowing?
Check and clean the flame eye cover glass. Check and clean inspection peep hole glass cover. Clean fuel oil fitter. Check the fuel oil pressure.
What is the recommended air pressure for soot blowing the boiler?
135 to 260 psigNormal ranges are from 135 to 260 psig at the nozzle of the blower. Pressure is related to the cleaning energy (PIP) required for a given area and cooling requirements.
Why should boiler soot blower normally only be operated in the correct sequence?
Soot blowers should be used frequently and in proper sequence to prevent the accumulation of heavy deposits of soot since they interfere with heat transfer and are a fire hazard. The process of using the soot blowers is called “blowing tubes.”
How do I clean soot from my boiler?
Use your cleaning brushes to clean soot, dust and carbon from the tubes to the base of the heater. Next, clean the vent stack and then use clean water to wash the burner tubes, and then let them dry. Once the tubes are dry, vacuum the bottom and outside of the boiler to clean the area up.
What causes soot in a furnace?
As the furnace in your house burns fuel to create heat, especially natural gas, there are remnants left over after the process is completed. This is called “incomplete combustion.” One of the combustion byproducts is carbon, the primary ingredient in black soot, which is sent up the heat exchanger and out of the house.
What is soot HVAC?
Excessive soot: Soot is a problem that can occur with gas-fired and oil furnaces. Excessive furnace soot causes the heat that the appliance produces to go up into the chimney instead of into the home. Excessive soot also poses a fire hazard and increases the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Why is my oil boiler sooting up?
The boiler is producing smoke and/or soot A smokey or sooty boiler may be due to a clogged flue pipe or cracked heat exchanger. We recommend that you inspect the flue pipe, especially where it connects to the chimney, and remove any dirt and debris that may have clogged the pipe.
What is a soot blower?from sciencedirect.com
A sootblower is a device for removing the soot that is deposited on the internal furnace tubes of a boiler during combustion to prevent plugging of the gas passes and maintain boiler efficiency. Types of soot blowers: Wall Blowers also known as IRs (Insertable Rotating)
How does a sootblower work?from en.wikipedia.org
A sootblower may be operated manually or by a remotely controlled motor. The soot, which is removed from the heating surfaces, will be blown out with the flue gases. If the boiler is equipped with a dust collector, it will trap the soot. Otherwise, the soot will be ejected into the outside air through the chimney stack .
What is a retractable soot blower?from sciencedirect.com
Retractable soot blowers are used for air heaters having large diameters of about 10 meters and above. (ii) Stationary and multinozzle soot blowers are used for small package air heaters. (iii) Soot blowers with nozzles mounted on a swinging arm are used for air heaters as a popular choice.
How to improve heat transfer in a steam generator?from sciencedirect.com
Several methods are used in the industry for improving heat transfer inside a steam generator. Soot blowers can be used to keep heat exchanger surfaces in steam generators clean and thus to achieve increased efficiencies through improved heat transfer effectiveness. Specifically, coal flow dampers and soot blowers can reduce slagging to improve heat absorption in the lower furnace and decrease superheater attemperation spray flows. Fluidized bed combustion (FBC) also leads to heat transfer improvement. In FBC, crushed coal particles are injected in a bed of fine inert particles (e.g., sand, ash, limestone) fluidized by combustion air. Water tubes submerged in this fluidized combustion zone achieve high rates of heat transfer. FBC also allows for relatively low combustion temperatures (820–870°C) that are well below the ash fusion temperature, so fireside slagging is minimized. The higher efficiencies for FBC compared with normal combustion are in large part due to the high volumetric heat release rates and high heat transfer coefficients in the combustion zone. However, as the flame temperature tends to increase with load, the exergy-efficiency difference between FBC and normal combustion decreases as load increases [19].
What is a swinging soot blower?from sciencedirect.com
Swinging soot blowers are large and equipped with an electric power-driven source with a single- or double-nozzle arrangement. The nozzle assembly moves slowly over the face of the heat transfer surface. The nozzle arm simultaneously swings in an arc across the face of the heat transfer surface.
What is the best medium for AH soot blowing?from sciencedirect.com
However, as per experience, dry superheated steam is found to be the most effective medium of AH soot blowing than either compressed air or saturated steam. The temperature and pressure value of steam are required to be maintained around 70°C superheat and 15 kg/cm 2 for an efficient end result.
What media is used for soot blowing?from sciencedirect.com
There are two widely accepted media available for air heater soot blowing. One of the blowing media is obviously the high-pressure dry superheated steam and the other is high-pressure (around 12 kg/cm 2) or compressed air , with both being equally applicable. The selection normally depends upon the availability and reliability along with the cost factor, as discussed in brief in Section 12.6.2.5 of this chapter.
The Problems Caused by Soot Buildup
The longer a boiler or furnace has been running, the more deposits it will have on all heating surfaces. Soot inside a furnace or other burning equipment reduces efficiency and is also a fire hazard.
What is a Soot Blower?
A soot blower blasts air, steam or water (or a combination) to remove soot and ash from the interior walls of the boiler heating surfaces. The soot blower can be set to operate automatically at timed intervals or be controlled manually.
Soot Blowers Protect Furnace Tubes and Shells
A soot blower can minimize the risk of a soot fire. Such a fire can cause hotspots to appear in the furnace tubes, which can then reach a temperature to weaken the structural integrity of the tubes. The dangers and potential damage of a weakened furnace structure are extreme.
Soot Blowers Improve Operational Efficiency
Soot is a heat insulator. The more there is inside equipment, the more energy will be needed to get the equipment up to optimal operating temperature. No company wants to waste energy. It’s too expensive.
What is a soot blower?
A sootblower is a device for removing the soot that is deposited on the internal furnace tubes of a boiler during combustion to prevent plugging of the gas passes and maintain boiler efficiency. Types of soot blowers: Wall Blowers also known as IRs (Insertable Rotating)
How does a sootblower work?
A sootblower may be operated manually or by a remotely controlled motor. The soot, which is removed from the heating surfaces, will be blown out with the flue gases. If the boiler is equipped with a dust collector, it will trap the soot. Otherwise, the soot will be ejected into the outside air through the chimney stack .
Why is soot bad for boilers?
A soot fire can be damaging to a boiler because it can cause localized hotspots to occur in the tubes. These hotspots may reach temperatures that weaken the materials of the tubes. Sootblowers reduce the risk of soot fires and their resulting damage.
What is the effect of soot on a boiler?
Soot deposited on the heating surfaces of a boiler acts as a heat insulator. The result is that less heat is transferred to the water to raise steam and more heat is wasted up the chimney. This leads to higher fuel consumption and/or poor steaming.
Why is steam used as a medium?
Steam is normally used as a medium for blowing away the soot since capital cost of steam pressure reducing equipment and drain is less than the cost of com pressors, motors and control of air systems.
What happens when a soot blower is used?
When steam is used as a cleaning medium and a soot blower starts is blowing cycle , there normally is a temperature differential between the soot blower and the steam. When this happens, steam condenses and slugs of water are ejected from the soot blower nozzle. After repeated cycles, the slugs may erode the tubes in the boilers requiring plugging ...
What kind of air do soot blowers use?
Generally speaking, soot blower manufacturer’s lances, with some modifications, will handle either cleaning media steam or compressed air .
How much pressure drop is required for a soot blower?
The overall pressure drop may be as high as 100 psig from the compressor discharge to the soot blower nozzle. Approximately 50 psig maybe lost in the control valve at the entrance to the lance. This is often recoverable.
How many scfm does a wall blower use?
Wall blowers are used to clean the furnace walls and will probably use approximately 2,200 to 2,300 scfm. Wall blowers normally operate in one or more pairs depending on the overall cycle. Their basic job is to reduce slag that has accumulated on the pipes in the upper levels of the boiler, and superheated region.
Why is a high pressure compressor so inefficient?
Often because the large horsepower high pressure compressors cannot easily be shut off and also have to run the low pressure (100 psig) plant, service and instrument air is taken from the high pressure receiver that is regulated down to the low pressure. This is very inefficient compared to running a dedicated low pressure compressor.
How long does a wall blower cycle take?
The time for a wall blower cycle is approximately three to six minutes and the period of zero flow between wall blower flow to no-flow to flow can be as high as 1 _ minutes in a normal sequence. This may be reduced if cycle time needs to be reduced by overlapping.
What is the relationship between fluid horsepower and surface soot removal?
This fluid horsepower relates equated kinetic energy at the point of impact to relate to the surface soot removal. This relationship is called “peak impact pressure.”
How many soot blowers are there in a coal fired power plant?
A large coal fired Thermal power plant will have around two hundred soot blowers of both types arranged to cover all the area of the boiler. This will be programmed to automatically operate to a required sequence.
How many types of soot blowers are there?
There are two types of soot blowers.
What is the ash that sticks to the heat transfer surface?
In coal fired boilers, the furnace area gets covered by slag which is molten ash. The ash also sticks to the heat transfer surface in the other heat transfer areas. These ash accumulations reduce heat transfer and increase the tube metal temperatures leading to failure of the tubes.
What is a soot blower?
Large Boilers in power plants are fitted with soot blowers, which are tools to keep the outside surface of the tubes clean and free from material or ash that would have a detrimental effect on the heat transfer surface. The blowing fluid is generally steam and the frequency of operation depends upon the type of fuel being used.
What is a stationary soot blower?
A stationary soot blower, as the name implies, is a fixed tube with holes. The holes are positioned to blow steam between the tubes. Retractable soot blowers – the lance is operated by electric motors. One motor rotates the lance at a constant speed while a two-speed motor handles the travel.
Why does soot blowing cause a temperature drop?
There is a disadvantage to this in that during soot blowing, a temperature reduction occurs because the steam used for soot blowing cools the tubes and therefore the blowing could cause quite a drop in steam production at an inconvenient time.
Why is a soot blower slow?
A slow speed is used when the lance is going in and a much faster speed is used as it retracts .This is to save time and steam. One method of operation of the retractable soot blower is on automatic control of flue gas temperature.
What are the different types of soot blowers?
There are two types of soot blowers: 1 Fixed or stationary soot blowers 2 Retractable soot blowers.
How often should you check soot blowers?
The heating surfaces within the blowing area of the soot blowers are to be visually checked at regular intervals within the first period after commissioning .
What is Soot?
Soot is a carbon-based compound that accumulates as a byproduct of combustion and sticks to the walls and surfaces of your boiler. Soot is a natural insulator, which means it does not conduct heat efficiently. By reducing the conductivity of heat in the boiler, soot can reduce the efficiency of your system.
How Does a Rotary Soot Blower Work?
Unlike other soot blowers that retract from the boiler when not in use, the blowing tube/element of a rotary soot blower remains inside the boiler at all times. This blowing tube includes nozzles placed along its length, and element bearings attached to the boiler tubes support its weight.
Which Soot Blower is Right for You?
At Industrial Boilers America, we are leading the way to zero waste by developing, deploying, and licensing superior soot blowers manufactured at a fraction of the cost of our competitors.
Overview
A sootblower is a device for removing the soot that is deposited on the internal furnace tubes of a boiler during combustion to prevent plugging of the gas passes and maintain boiler efficiency.
Types of soot blowers:
1. Wall Blowers also known as IRs (Insertable Rotating)
Benefits of Sootblowers
• Increased plant availability
• Improved boiler and fired heater efficiency
• Controlled deposit build-up
• Reduced CO2 emissions
Problems caused by soot
Soot deposited on the heating surfaces of a boiler acts as a heat insulator. The result is that less heat is transferred to the water to raise steam and more heat is wasted up the chimney. This leads to higher fuel consumption and/or poor steaming.
A soot fire can be damaging to a boiler because it can cause localized hotspots to occur in the tubes. These hotspots may reach temperatures that weaken the materials of the tubes. Sootblo…
Operation
A sootblower may be operated manually or by a remotely controlled motor. The soot, which is removed from the heating surfaces, will be blown out with the flue gases. If the boiler is equipped with a dust collector, it will trap the soot. Otherwise, the soot will be ejected into the outside air through the chimney stack.
Industries
A sootblower can make an important contribution for an optimised, more efficient and low-emission operation supporting clean energy generation in many industries, including:
• Power Industry
• Petrochemical Industry
• Waste-to Energy Plants
See also
Boiler Monitoring / Cameras - Allows plant operators to accurately view and monitor internal furnace and process applications.
SMART Clean
External links
• Marine Engineer World
• [1] Boiler Efficiency - Clyde Bergemann (cbpg.com)