
What is charge polarization?
Charge polarization occurs when an electric field distorts the negative cloud of electrons around positive atomic nuclei in a direction opposite the field. The slight separation of charge makes one side of the atom somewhat positive and the opposite side somewhat negative. Home Study Guides Science
Which charge should polarize the metal sphere?
In each case, the tube (in pink) is charged. Its charge should polarize the metal sphere. This is not shown in A; so A can be ruled out. In B, C and D the sphere is polarized. But in B and C, the diagram shows the separation of charge in a manner that would indicate an attraction between like charges.
What is the space charge?
The space charge, or interfacial polarization, is produced by the separation of mobile positively and negatively charged particles under an applied field, which form positive and negative space charges in the bulk of the material or at the interfaces between different materials. These space charges, in turn, modify the field distribution.
What is the polarization of an atom?
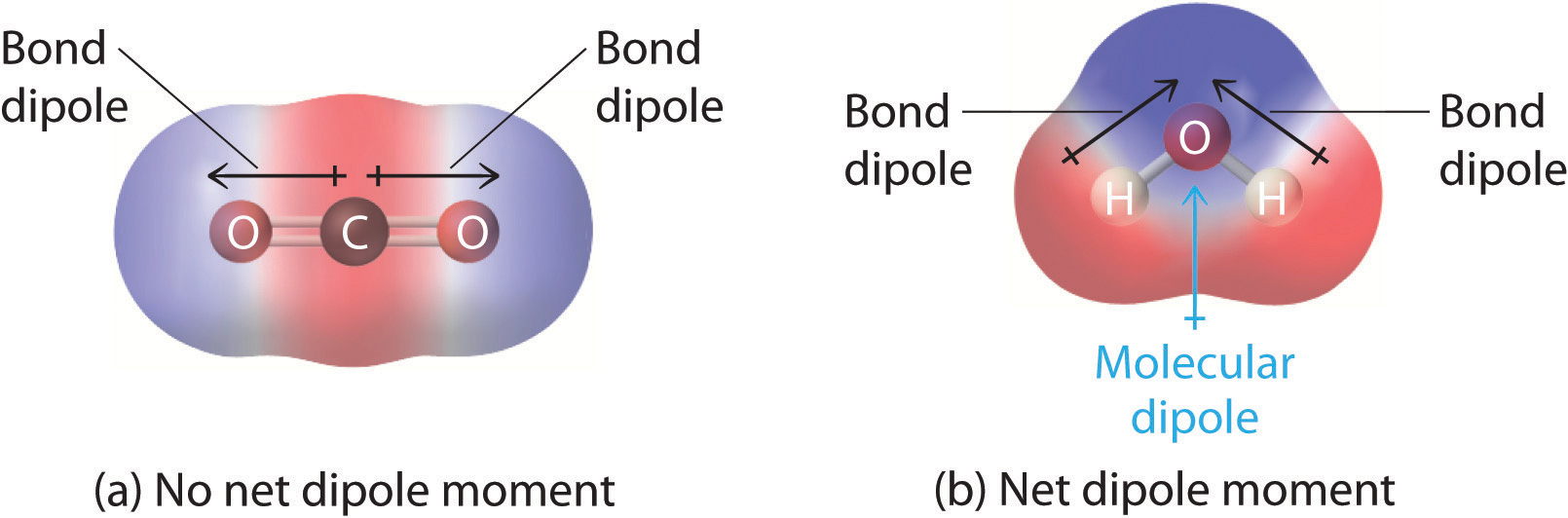
As such, there is a polarization of the atom as the centers of positive and negative charge are no longer located in the same location. The atom is still a neutral atom; it has just become polarized. The discussion becomes even more complex (and perhaps too complex for our purposes) when we consider molecules - combination of atoms bonded together.
What does charge polarization mean?
Polarization occurs when an electric field distorts the negative cloud of electrons around positive atomic nuclei in a direction opposite the field. This slight separation of charge makes one side of the atom somewhat positive and the opposite side somewhat negative.
In which medium space charge polarization occurs?
Space Charge (or Interfacial) Polarization: In ceramics, this phenomenon arises from extraneous charges that come from contaminants or irregular geometry in the interfaces of the polycrystalline solids. These charges are partly mobile and migrate under an applied field, causing this extrinsic type of polarization.
What is polarization in terms of electric charges?
Electric polarization refers to the separation of center of positive charge and the center of negative charge in a material. The separation can be caused by a sufficiently high-electric field.
What are the different types of dielectric polarization?
There are three main polarisation mechanisms that can occur within a dielectric material: electronic polarisation, ionic polarisation (sometimes referred to as atomic polarisation) and orientational polarisation.
What do you mean by space charge?
space charge, electrical charge distributed through a three-dimensional region. In an electron tube, for example, a negative charge results because electrons that are emitted from the cathode do not travel instantaneously to the plate (anode) but require a finite time for the trip.
What is called polarization?
polarization, property of certain electromagnetic radiations in which the direction and magnitude of the vibrating electric field are related in a specified way.
What is the difference between polarization and charging by induction?
This charging process depends upon a charged object to induce polarization within a neutral object. While charging by induction includes polarization as one of its steps, polarization is still NOT a charging process.
How does Polarisation occur?
Polarization also occurs when light is scattered while traveling through a medium. When light strikes the atoms of a material, it will often set the electrons of those atoms into vibration. The vibrating electrons then produce their own electromagnetic wave that is radiated outward in all directions.
How many types of polarization are there?
Following are the three types of polarization depending on the transverse and longitudinal wave motion: Linear polarization. Circular polarization. Elliptical polarization.
What is the effect of dielectric polarization?
Dielectric Polarization occurs when an external electric field is applied to a dielectric substance. When an electric field is applied, it causes charges (both positive and negative) to be displaced. The primary goal of dielectric polarisation is to connect macroscopic and microscopic characteristics.
What is dielectric and electric polarisation?
Solution. Dielectric polarization is the term given to describe the behavior of a material when an external electric field is applied to it. It occurs when a dipole moment is formed in an insulating material because of an externally applied electric field. Concept: Dielectrics and Electric Polarisation.
What is an electric polarization of a dielectric?
When an insulator or a dielectric is placed in an external electric field, the electric field causes the positive and the negative charges to move in the opposite direction in the insulator. This is called electric polarization.
What is space charge?
Space charge is a concept in which excess electric charge is treated as a continuum of charge distributed over a region of space (either a volume or an area) rather than distinct point-like charges.
Why is space charge useful?
On the other hand, space charge was useful in some tube applications because it generates a negative EMF within the tube's envelope, which could be used to create a negative bias on the tube's grid. Grid bias could also be achieved by using an applied grid voltage in addition to the control voltage.
What is it called when a metal is heated to incandescence?
This is called thermionic emission.
How does space charge affect shot noise?
Space charge tends to reduce shot noise. Shot noise results from the random arrivals of discrete charge; the statistical variation in the arrivals produces shot noise. A space charge develops a potential that slows the carriers down. For example, an electron approaching a cloud of other electrons will slow down due to the repulsive force. The slowing carriers also increases the space charge density and resulting potential. In addition, the potential developed by the space charge can reduce the number of carriers emitted. When the space charge limits the current, the random arrivals of the carriers are smoothed out; the reduced variation results in less shot noise.
Where do space charges occur?
Space charges can also occur within dielectrics. For example, when gas near a high voltage electrode begins to undergo dielectric breakdown, electrical charges are injected into the region near the electrode, forming space charge regions in the surrounding gas.
Is space charge positive or negative?
The sign of the space charge can be either negative or positive . This situation is perhaps most familiar in the area near a metal object when it is heated to incandescence in a vacuum. This effect was first observed by Thomas Edison in light bulb filaments, where it is sometimes called the Edison effect.
What is the process of polarization?
The polarization process always involves the use of a charged object to induce electron movement or electron rearrangement. In the above diagram and accompanying discussion, electrons within a conducting object were induced into moving from the left side of the conducting can to the right side of the can.
What does it mean to be polarized?
In general terms, polarization means to separate into opposites. In the political world, we often observe that a collection of people becomes polarized over some issue. For instance, we might say that the United States has become polarized over the issue of the death penalty.
What happens when electrons move away from a repulsive balloon?
Being present within a conducting material, the electrons are free to move from atom to atom. As such, there is a mass migration of electrons from the balloon's side of the aluminum can towards the opposite side of the can.
How do electrons move across the surface of an insulator?
In a conducting object, electrons are induced into movement across the surface of the conductor from one side of the object to the opposite side . In an insulator, electrons merely redistribute themselves within the atom or molecules nearest the outer surface of the object.
What happens if a rubber balloon is charged?
If a rubber balloon is charged by rubbing it with animal fur, the balloon can subsequently be stuck to the surface of a wooden cabinet or a whiteboard. Quite surprisingly, this interaction between a neutral object and any charged object can be explained using our usual rules of opposites attract and likes repel.
What is the process of separating opposite charges within an object?
In the context of electricity, polarization is the process of separating opposite charges within an object.
What is the attraction between a charged object and a neutral object?
Polarization. In an earlier section of Lesson 1, it was stated that an electrical attraction would be observed between a charged object and a neutral object. If a charged plastic tube is held near to neutral paper bits, the attraction between the paper and the plastic would be sufficient to raise the paper off the table.
What is ionic polarization?
Ionic polarization: The ionic polarization is due to the displacement of cation and anions when an electric field is applied to a dielectric material. The ionic polarization occurs in ionic solids. when an electric field is applied to the ionic crystal positive ions are displaced through distance x1 and negative ions are displaced by ...
What is orientational polarization?
Orientational polarization is the charecterstic feature of polar dielectric materials. In polar dielectric materials, positive and negative charges do not coincide with in the molecule. Hence they possess permanent dipole moment.
What is the dipole moment of orientation?
The electric dipole moment due to orientation is. This polarization is dependent of temperature. In the case of electronic and ionic polarization, Lorentz force is balanced by restoring force and coulomb attractive force, but for orientational polarization dipole moment is due to thermal agitation of the molecules.
What is the dipole moment?
When the specimen is placed in DC electric field, it is polarized. Therefore, The dipole is developed in each atom and the dipole moment is proportional to electric field strength. Expression for Electronic polarisability :
What is the cloud of charges?
Accumulation of charges in a particular region is referred to as space charge. The space in which the charges concentrate can be either free space or a dielectric. Further, this cloud of charges might be mobile or immobile in nature. Let us try to understand better with the help of examples.#N#Example 1: Now, consider the case where we have brought a p-type semiconductor in contact with an n-type semiconductor. As is well known, n-type semiconductor material has excess electrons while the p-type material is depleted of them. Thus, when these two kind of materials are brought in-contact, the electrons will start moving from n-type to p-type.
How does space charge affect a thermionic converter?
The space charge effect poses a challenge by affecting the conversion efficiency and the output power of thermionic converters. This is because when such an electron cloud is present around the metal surface, it poses an additional barrier for the electrons which are supposed to reach their final point. This inhibition for the movement of electrons is experienced in the form of repulsion for the emitted electrons from the electrons which are present in the cloud.#N#The space charge effect which occurs in the dielectrics also leads to the breakdown of electrical components like capacitors. This is because, when high voltages are applied, the electric charges emitted from the electrode get trapped within the gas surrounding it. The same effect is also seen to cause the failure of power cables which carry high voltages.#N#However, space charge effect is also seen to be advantageous in certain scenarios. For example, the presence of space charge region creates a negative EMF on certain tubes which is analogous of providing a negative bias to it. This is inturn meritorious as it helps the engineers to have a better control over the process of amplification, thus improving its efficiency.#N#Yet another example noteworthy of being mentioned is that the space charge has a tendency to reduce the shot noise. This is because, basically the space charge affects the easy movement of charges along their path. This inturn reduces the number of charges which arrive randomly, thereby reducing their statistical variation which is nothing but the shot noise.
What is the inhibition of electrons?
This inhibition for the movement of electrons is experienced in the form of repulsion for the emitted electrons from the electrons which are present in the cloud. The space charge effect which occurs in the dielectrics also leads to the breakdown of electrical components like capacitors.
What is interfacial polarization?
Interfacial polarization, also known as the Maxwell–Wagner–Sillars effect, occurs in heterogeneous systems and is favored when the electrical characteristics (i.e., permittivity and conductivity) of the constituent phases vary significantly .
Is interfacial polarization dependent on orientation?
The interfacial polarization, however, is dependent on the orientation of the field due to the alignment of the individual dipoles within the particle and medium with the field , which can collectively be described by a single particle dipole that produces an effective dipole moment.
What is polarization in electrical?
Polarization is actually the alignment of the dipole moments of the fixed or induced dipole in the direction of the peripheral electric field. The mechanism of polarization deals with how a molecule or atom is reacting to a peripheral ...
What is the mechanism of polarization?
The mechanism of polarization deals with how a molecule or atom is reacting to a peripheral electric field. Simply we can say that it leads to the positioning of dipoles. There are fundamentally four divisions of polarization mechanisms. They are Electronic polarization, dipolar or Orientation polarization, Ionic polarization ...
Why do we have no method for computing the charges present in interfacial polarization?
When we go through the four polarization mechanism, we can see that the volume of the drifted entities is different for each of them . It can be seen that the gradual increase in mass happens from electronic to orientation polarization.
What is the term for the shifting of electrons in a neutral atom?
Electronic Polarization . Here, the neutral atoms get polarized and it results in the shifting of electrons. It is also known as atomic polarization. We can simply say that with respect to the nucleus, the center of electrons is shifted. Hence, a dipole moment is formed as represented below.
What is dipolar polarization?
It is also known as dipolar polarization. Due to the thermal equilibrium of the molecules, in normal state the dipoles will be randomly alig ned. When a peripheral electric field is implemented, it results in polarization. Now, the dipoles will align to some degree as represented in figure 2. E.g.:
Can polarization occur in all materials?
However, in most of the cases more than one polarization will be present in one material. Electronic polarization happens in almost all materials. So for us, the dielectric characterisation of real materials can be really difficult.
What is the effect of polarization on an atom?
Electronic Polarization: This effect occurs in all atoms under the application of an electric field. The nucleus of the atom and the center of its electron cloud shift away from each other, creating a tiny dipole with very small polarization effect.
What is ionic polarization?
Ionic Polarization: In ionic solids such as ceramic materials, the ions are symmetrically arranged in a crystal lattice with a net zero polarization. Once an electric field is applied, the cations and anions are attracted to opposite directions.
What is the effect of frequency on polarization?
The frequency at which a dielectric is used has an important effect on the polarization mechanisms, notably the relaxation time displayed by the material when following field reversals in an alternating circuit.
What is the dipole of a solid?
Dipole (or Orientation) Polarization: Certain solids have permanent molecular dipoles that, under an electric field, rotate themselves in the direction of the applied field, creating a net average dipole moment per molecule. Dipole orientation is more common in polymers since their atomic structure permits reorientation.
What happens if the relaxation time for polarization is much longer and slower than the field reversals?
Case 1: If the relaxation time for polarization is much longer and slower than the field reversals, the ions cannot follow the field at all and losses are small. Case 2: If the relaxation time is much faster than the field reversals, the polarizing processes can easily follow the field frequency and losses are small.
Why does polarization affect capacitors?
Since charges are not free to move in an insulator, the polarization effect that opposes the applied field draws charges onto the electrodes, thus storing energy in the capacitor. The more easily a material be polarized, the greater the amount of charge can be stored in the capacitor.
How many degrees out of phase is an AC capacitor?
In an AC circuit, the voltage and current across an ideal capacitor are 90 degrees out of phase. However, real-world dielectrics are not perfect, and therefore the lag or “relaxation time” of the polarization mechanisms with frequency generates dielectric losses. The angle by which the capacitor’s current is out of phase from ...

Overview
Space charge is an interpretation of a collection of electric charges in which excess electric charge is treated as a continuum of charge distributed over a region of space (either a volume or an area) rather than distinct point-like charges. This model typically applies when charge carriers have been emitted from some region of a solid—the cloud of emitted carriers can form a space charge region if they are sufficiently spread out, or the charged atoms or molecules left behind in the so…
Cause
When a metal object is placed in a vacuum and is heated to incandescence, the energy is sufficient to cause electrons to "boil" away from the surface atoms and surround the metal object in a cloud of free electrons. This is called thermionic emission. The resulting cloud is negatively charged, and can be attracted to any nearby positively charged object, thus producing an electric current which passes through the vacuum.
Occurrence
Space charge is an inherent property of all vacuum tubes. This has at times made life harder or easier for electrical engineers who used tubes in their designs. For example, space charge significantly limited the practical application of triode amplifiers which led to further innovations such as the vacuum tube tetrode.
On the other hand, space charge was useful in some tube applications because it generates a n…
Space-charge-limited current
First proposed by Clement D. Child in 1911, Child's law states that the space-charge-limited current (SCLC) in a plane-parallel vacuum diode varies directly as the three-halves power of the anode voltage and inversely as the square of the distance d separating the cathode and the anode.
For electrons, the current density J (amperes per meter squared) is written:
Shot noise
Space charge tends to reduce shot noise. Shot noise results from the random arrivals of discrete charge; the statistical variation in the arrivals produces shot noise. A space charge develops a potential that slows the carriers down. For example, an electron approaching a cloud of other electrons will slow down due to the repulsive force. The slowing carriers also increases the space charge density and resulting potential. In addition, the potential developed by the space charge c…
See also
• Thermionic emission
• Vacuum tube
• Grid leak
Inducing The Movement of Charge
How Can An Insulator Be Polarized?
- Polarization can occur within insulators, but the process occurs in a different manner than it does within a conductor. In a conducting object, electrons are induced into movement across the surface of the conductor from one side of the object to the opposite side. In an insulator, electrons merely redistribute themselves within the atom or molecules nearest the outer surfac…
How Does Polarization Explain The Balloon and The Wall Demonstration?
- A complete discussion of the world of atoms, molecules and chemical bonds is beyond the scope of The Physics Classroom. Nonetheless, a model of the atom as a distortable cloud of negative electrons surrounding a positive nucleus becomes essential to understanding how an insulating material can be polarized. If a charged object is brought near an insulator, the charges on that o…
Polarization Is Not Charging
- Perhaps the biggest misconception that pertains to polarization is the belief that polarization involves the charging of an object. Polarization is not charging! When an object becomes polarized, there is simply a redistribution of the centers of positive and negative charges within the object. Either by the movement of electrons across the surface...