Interesting Facts about Transition Metals
- The transition metal group is called the "d-block" of the periodic table. There are 35 elements located in the d-block.
- Sometimes the elements of column twelve of the periodic table (zinc, cadmium, mercury, copernicium) are not included as part of the transition metal group.
- Iron, cobalt, and nickel are the only three elements that produce a magnetic field.
What are the most common transition metals?
- Scandium.
- Titanium.
- Vanadium.
- Chromium.
- Manganese.
- Iron.
- Cobalt.
- Nickel.
How do transition metals differ from other metals?
• Transition metals are less reactive compared to other metals. • Transition metals can form colored compounds. • Transition metals can have various oxidation states within compounds, but other metals can have limited number of oxidation states (most of the time one state).
What are three examples of transition metals?
List of Elements That Are Transition Metals
- Scandium
- Titanium
- Vanadium
- Chromium
- Manganese
- Iron
- Cobalt
- Nickel
- Copper
- Zinc
What are the common properties of transition metals?
What are the characteristic properties of transition elements?
- Complex ion formation
- Formation of coloured compounds
- Variable oxidation states
- Catalytic activity

What are the special characteristics of transition elements?
The transition elements' general properties are as follows:They are typically metals with a high melting point.They have a variety of oxidation states.They usually combine to form coloured compounds.They are frequently paramagnetic.They have a high charge/radius ratio.High density and hardness.More items...
What is significant about the transition metal atoms?
General properties of the group Many of the elements are technologically important: titanium, iron, nickel, and copper, for example, are used structurally and in electrical technology. Second, the transition metals form many useful alloys, with one another and with other metallic elements.
What are 3 facts about transition metals?
Transition metals are generally good conductors of heat and electricity, malleable and ductile. Their compounds are often brightly colored in solution and when hydrated, and can exhibit multiple positive oxidation states. They are hard solids, with high melting points and boiling points.
What is the most important characteristic of the transition metals?
Solution : The general characteristics of transition elements are : (1) Most of the transition elements are hard metals. (2) They have high boiling and melting points. (3) They form metal alloys with transition and other metals. (4) They are very good conductors of heat and electricity.
Why are they called transition metals?
Transition metals are placed between s−block and p−block elements in periodic table. They are termed as d-block elements. These metals are unstable and exhibit transitional behavior between s block and p block elements, hence the name transition metals.
Are transition metals highly reactive?
Compared with the alkali metals in group 1 and the alkaline Earth metals in group 2, the transition metals are much less reactive. They don't react quickly with water or oxygen, which explains why they resist corrosion. Other properties of the transition metals are unique.
Why are transition metals good conductors?
Transition metals have free electrons in outer energy levels because d-orbitals shields poorly and due to this they acts as good conductor of electricity.
What are transition metals in simple terms?
noun. : any of various metallic elements (such as chromium, iron, and nickel) that have valence electrons in two shells instead of only one.
Are transition metals good conductors?
Except for mercury, the transition metals have high melting points and high densities. They are good conductors of heat and electric current, and are very malleable.
Why do transition metals make good catalysts?
Transition metals are particularly good catalysts, thanks to incompletely filled d-orbitals that enable them to both donate and accept electrons from other molecules with ease.
Why are transition metals not very reactive?
A transition metal does not attain stable electron configuration of nearest noble gas by loss of one or two electrons. Hence, transition metals are less reactive and do not lose electrons as readily as alkali or alkaline earth metals.
Why are transition elements used?
Transition metals have a wide variety of uses, with some of the main ones listed below: Iron is often made into steel, which is stronger and more easily shaped than iron on its own. It is widely used in construction materials, tools, vehicles and as a catalyst in the manufacture of ammonia.
What are transition elements and why are they called transition elements?
Transition elements (also known as transition metals) are elements that have partially filled d orbitals. IUPAC defines transition elements as an element having a d subshell that is partially filled with electrons, or an element that has the ability to form stable cations with an incompletely filled d orbital.
What are transition metal complexes used for?
Transition metal complexes are important in catalysis, materials synthesis, photochemistry, and biological systems. Medicinal inorganic chemistry can exploit the unique properties of metal ions for the design of new drugs. The use of metals and their salts for medicinal purposes has been present throughout history.
Why do transition metals have similar properties?
To answer your first question, there are 10 transition metals in the 3rd period and they account for the filling of the 3rd shell d orbitals (which can accommodate 10 electrons). As they all have electrons in the 3 d shell, they all have similar properties.
Why do transition metals have multiple oxidation states?
Transition metals can have multiple oxidation states because of their electrons. The transition metals have several electrons with similar energies, so one or all of them can be removed, depending the circumstances. This results in different oxidation states.
What Is a Transition Metal?
According to the IUPAC, a transition metal is any element with a partially filled d electron sub-shell. This describes groups 3 through 12 on the periodic table, although the f-block elements (lanthanides and actinides, below the main body of the periodic table) are also transition metals. The d-block elements are called transition metals, while the lanthanides and actinides are called "inner transition metals".
Why are transition metals considered a metal?
Because they possess the properties of metals, the transition elements are also known as the transition metals. These elements are very hard, with high melting points and boiling points. Moving from left to right across the periodic table, the five d orbitals become more filled. The d electrons are loosely bound, which contributes to the high electrical conductivity and malleability of the transition elements. The transition elements have low ionization energies. They exhibit a wide range of oxidation states or positively charged forms. The positive oxidation states allow transition elements to form many different ionic and partially ionic compounds. The formation of complexes causes the d orbitals to split into two energy sublevels, which enables many of the complexes to absorb specific frequencies of light. Thus, the complexes form characteristic colored solutions and compounds. Complexation reactions sometimes enhance the relatively low solubility of some compounds.
Why are transition metals called transition metals?
The elements are called "transition" metals because the English chemistry Charles Bury used the term in 1921 to describe the transition series of elements, which referred to the transition from an inner electron layer with a stable group of 8 electrons to one with 18 electrons or the transition from 18 electrons to 32.
What are the transition metals in the periodic table?
The d-block elements are called transition metals, while the lanthanides and actinides are called "inner transition metals".
What are the d electrons in transition elements?
The d electrons are loosely bound, which contributes to the high electrical conductivity and malleability of the transition elements. The transition elements have low ionization energies. They exhibit a wide range of oxidation states or positively charged forms.
What is the positive oxidation state?
The positive oxidation states allow transition elements to form many different ionic and partially ionic compounds. The formation of complexes causes the d orbitals to split into two energy sublevels, which enables many of the complexes to absorb specific frequencies of light.
Where are transition metals located?
The transition elements are located in groups IB to VIIIB of the periodic table. In other words, the transition metals are elements: Another way to view it is that the transition metals include the d-block elements, plus many people consider the f-block elements to be a special subset of transition metals.
Why are transition metals important?
Transition metals are incredibly important for the role they play in the global economy, technology, and infrastructure. Metals, like iron, titanium, chromium and manganese, are necessary components of building materials. Tungsten and cobalt are used for manufacturing processes that require high temperatures.
What are the properties of transition metals?
Transition metals show similar properties by column and by row. In general, transition metals are lustrous, silvery, hard, and good conductors of heat and electricity. Properties between individual elements may vary greatly. For instance, mercury is a liquid at room temperature, whereas tungsten does not melt until 3,400 degrees Celsius.
What are elements that lose electrons easily?
Elements that lose electrons easily, that are lustrous and malleable, and that are good conductors of heat and electricity are known as metals. Metal elements can be broken down into several categories, one of which is the category of transition metals. A transition metal is defined as a metal with inner d or f orbitals being filled.
Why do transition metals have multiple types of cations?
Chemical reactivity of the transition metals varies greatly. Some metals will react to form compounds, while others prefer to remain in their pure form.
How many transition metals are there?
There are nearly 100 transition metals, so it would take a little too long to list them all in this video. However, it might be useful to you to remember that transition metals include:
Where are transition metals found?
Transition metals which are found in columns 3-12 on the periodic table, contain electrons in the 'd' or 'f' orbitals. Learn the concept of transition metals, see an extensive list of examples, and properties that cause various chemical reactions. Updated: 09/22/2021
Which group of the periodic table contains transition metals?
B. The six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table are all transition metals.
What is a transition metal?
Transition Metals Definition - The d-block elements are called transition metal. The d-block consists of the elements that are lying in between the s and p blocks. The position of this block is between groups 2 and 13 in the periodic table. It starts from the fourth period onwards. In these elements, the outermost shell contains one or two electrons in their s-orbital but the last electron enters the last but one d subshell (n-1) d. The properties of the elements of this block generally lie between the elements of s block and p block.
What is the first transition element?
The first transition element is scandium, in scandium, the 3d orbital starts filling up and its electronic configuration is A r 4s2 3d1. As we move from scandium onwards, 3d orbitals get filled up more and more till the last element, zinc, in which the 3d orbitals are completely filled A r 4s2 3d10.
What is the second transition series?
The 2nd transition series consists of elements from yttrium, Y (Z = 39) to cadmium, Cd (Z = 48), i.e., yttrium, zirconium, niobium, molybdenum, technetium, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver and cadmium. This series involves the filling of 4d-orbitals.
Which transition element is liquid at room temperature?
Except for mercury which is liquid at room temperature, other transition elements have typical metallic structures.
Which element has the highest ionization energy?
The ionization energy of chromium and copper have an exceptionally higher energy than those of their neighbours.
What are transition metals used for?
Several transition metals have catalytic properties that are very useful in the industrial production of some chemicals. For example, iron is used as a catalyst in the Haber process of preparing ammonia. Similarly, vanadium pentoxide is used as a catalyst in the industrial production of sulfuric acid.
What are the characteristics of transition metals?
The transition metals exhibit typical metallic properties such as malleability, ductility, high tensile strength, and metallic lustre. They are generally good conductors of heat and electricity and tend to crystallize in BCC (body-centred cubic), CCP (cubic close-packed), or HCP (hexagonally close-packed) structures.
What are Transition Elements?
Transition elements (also known as transition metals) are elements that have partially filled d orbitals. IUPAC defines transition elements as an element having a d subshell that is partially filled with electrons, or an element that has the ability to form stable cations with an incompletely filled d orbital.
What are the properties of transition elements?
General Properties of Transition Elements 1 These elements form coloured compounds and ions. This colour is explained by the d-d transition of electrons. 2 There is a relatively low gap in energy between the possible oxidation states of these elements. The transition elements, therefore, exhibit many oxidation states. 3 Many paramagnetic compounds are formed by these elements, because of the unpaired electrons in the d orbital. 4 A large variety of ligands can bind themselves to these elements. Due to this, a wide variety of stable complexes are formed by transition elements. 5 These elements have a large ratio of charge to the radius. 6 Transition metals tend to be hard and they have relatively high densities when compared to other elements. 7 The boiling points and the melting points of these elements are high, due to the participation of the delocalized d electrons in metallic bonding. 8 This metallic bonding of the delocalized d electrons also causes the transition elements to be good conductors of electricity.
How is ionization energy related to atomic radius?
In a way, the ionization energy of an element is closely related to its atomic radius. Atoms with smaller radii tend to have greater ionization enthalpies than those with relatively larger radii. The ionization energies of the transition metals increase while moving along the row (due to the increase in atomic number).
What is the configuration of electrons in transition elements?
The list of the first two rows of transition elements with their corresponding electronic configurations is tabulated below. It can be noted that in some of these elements, the configuration of electrons corresponds to (n-1)d 5 ns 1 or (n-1)d 10 ns 1. This is because of the stability provided by the half-filled or completely filled electron orbitals.
Why do radii decrease in transition elements?
The atomic and ionic radii of the transition elements decrease from group 3 to group 6 due to the poor shielding offered by the small number of d-electrons. Those placed between groups 7 and 10 have somewhat similar atomic radii and those placed in groups 11 and 12 have larger radii.
What are the transition metals?
The transition metals are the metallic elements that serve as a bridge, or transition, between the two sides of the table. The lanthanides and the actinides at the bottom of the table are sometimes known as the inner transition metals because they have atomic numbers that fall between the first and second elements in the last two rows ...
What are the transition metals in the periodic table?
The elements in the periodic table are often divided into four categories: (1) main group elements, (2) transition metals, (3) lanthanides, and (4) actinides. The main group elements include the active metals in the two columns on the extreme left of the periodic table and the metals, semimetals, ...
What is the difference between transition metals and main group metals?
The transition metals are more electronegative than the main group metals, for example, and are therefore more likely to form covalent compounds. Another difference between the main group metals and transition metals can be seen in the formulas of the compounds they form. The main group metals tend to form salts (such as NaCl, Mg 3 N 2, ...
What happens when manganese is oxidized?
When the manganese atom is oxidized, it becomes more electronegative. In the +7 oxidation state, this atom is electronegative enough to react with water to form a covalent oxide, MnO 4-.
How many oxidation states are there in transition metals?
Most transition metals form more than one oxidation state.
Why are oxidation states common?
Some of these oxidation states are common because they are relatively stable. Others describe compounds that are not necessarily stable but which react slowly. Still others are common only from a historic perspective. Common Oxidation States of the First Series of Transition Metals.
When are electrons removed from the valence shell?
In general, electrons are removed from the valence-shell s orbitals before they are removed from valence d orbitals when transition metals are ionized.
What is transition metal?
One definition of a transition metal, is any metal that has at least one unpaired d electron in one of their stable ions. Unpaired d electrons are more likely to participate in chemical reactions. This definition excludes scandium, since the Sc+3 ion does not have unpaired d electrons.
Why are transition metals colored?
Transition metal compounds are often highly colored, due to d to d electron transitions. They often form paramagnetic compounds because of their unpaired d electrons. In their elemental form, they often act as catalysts.
Why are they so colorful?
It is because of their unfilled d orbitals, and something called “d to d electronic transitions”. When a transition metal forms an ion, its electrons can absorb light and move between d orbitals. The d orbitals are normally degenerate, meaning they are all at the same energy level. But when a transition metal forms a complex with a ligand, such as H 2 O or NH 3, the d orbitals develop different energy levels. For example, Cu +2 is colorless, but Cu (H 2 0) 6+2 is a blue color. Depending on the energy difference between those d orbitals, different wavelengths of light will be absorbed and reflected. As expected, ions with no d-orbital electrons, like Sc +3, or a full d orbital, like Zn +2, are colorless.
What Is A Transition Metal?
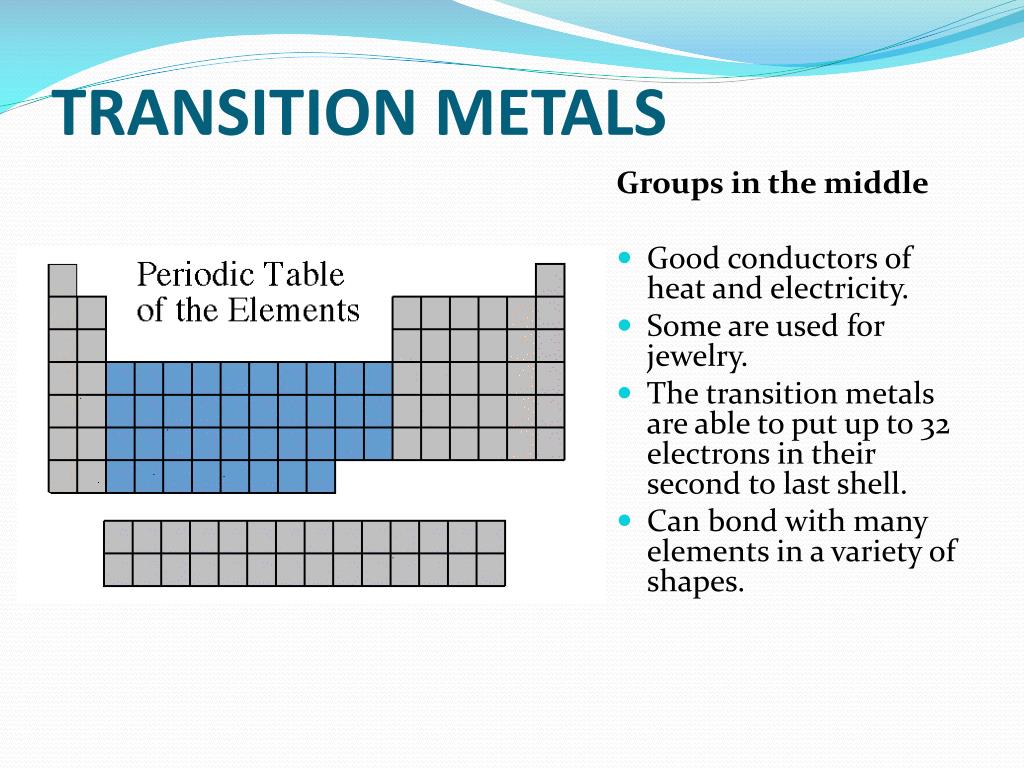
Location of The Transition Metals on The Periodic Table
- The transition elements are located in groups IB to VIIIB of the periodic table. In other words, the transition metals are elements: 1. 21 (scandium) through 29 (copper) 2. 39 (yttrium) through 47 (silver) 3. 57 (lanthanum) through 79 (gold) 4. 89 (actinium) through 112 (copernicium) - which includes the lanthanides and actinides Another way to view it is that the transition metals includ…
Overview of Transition Metal Properties
- Because they possess the properties of metals, the transition elements are also known as the transition metals. These elements are very hard, with high melting points and boiling points. Moving from left to right across the periodic table, the five d orbitals become more filled. The d electrons are loosely bound, which contributes to the high elect...
Quick Summary of The Transition Metal Properties
- Low ionization energies
- Positive oxidation states
- Multiple oxidation states, since there is a low energy gap between them
- Very hard
Transition Elements List
- The transition elements list contain the metals that have incompletely filled d-subshells in their ground state or any one of their oxidation states. Metals included in the transition elements list are: 1. Scandium (first transition element). 2. Titanium. 3. Vanadium. 4. Chromium. 5. Manganese. 6. Iron. 7. Cobalt. 8. Nickel. 9. Copper. 10. Zinc. 11...
First Transition Series
- The first transition series consists of elements from scandium, Sc (Z = 21) to zinc, Zn (Z = 30) i.e scandium, titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, and zinc. The first transition element is scandium, in scandium, the 3d orbital starts filling up and its electronic configuration is Ar 4s23d1. As we move from scandium onwards, 3d orbitals get filled up more …
Second Transition Series
- The 2nd transition series consists of elements from yttrium, Y (Z = 39) to cadmium, Cd (Z = 48), i.e., yttrium, zirconium, niobium, molybdenum, technetium, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver and cadmium. This series involves the filling of 4d-orbitals.
Third Transition Series
- This series consists of elements of lanthanum and from hafnium to mercury i.e., lanthanum, hafnium, tantalum, tungsten, rhenium, osmium, iridium, platinum, gold, and mercury. In between Lanthanum and Hafnium there are fourteen elements called lanthanides which involve the filling of 4f-orbitals and do not belong to this series. The elements of the d-block third series involve th…
Fourth Transition Series
- It involves the filling of a 6d subshell starting from actinium (Z=89); which has the configuration 6d17s2. This fourth transition series in periodic table is incomplete as given in the table below:
Did You Know?
- The fundamental difference in the electronic configuration of transition elements and representative elements is that in the representative elements the valence electrons are present only in the ou...
- The ionization energy of chromium and copper have an exceptionally higher energy than those of their neighbours.
What Are Transition elements?
Electronic Configuration of Transition Elements
- The list of the first two rows of transition elements with their corresponding electronic configurations is tabulated below. It can be noted that in some of these elements, the configuration of electrons corresponds to (n-1)d5 ns1 or (n-1)d10 ns1. This is because of the stability provided by the half-filled or completely filled electron orbitals. It can be observed that t…
General Properties of Transition Elements
- As discussed earlier, the elements zinc, cadmium, and mercury are not considered transition elements since their electronic configurations are different from other transition metals. However, the rest of the d-block elements are somewhat similar in properties and this similarity can be observed along each specific row of the periodic table. These properties of the transition eleme…
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the General Characteristics of Transition Elements?
The d-block elements are known for their: 1. Large charge: radius ratios 2. High melting points and boiling points 3. High densities and hardness. 4. Formation of paramagnetic compounds 5. Formation of coloured ions/compounds 6. Ability to form stable complexes These elements als… - What are the Metallic Qualities of the Transition Metals?
The transition metals exhibit typical metallic properties such as malleability, ductility, high tensile strength, and metallic lustre. They are generally good conductors of heat and electricity and tend to crystallize in BCC (body-centred cubic), CCP (cubic close-packed), or HCP (hexagonally close …