
In animals, there are two types of defenses against foreign invaders: specific and nonspecific. Specific immune responses can distinguish among different invaders. The response is different for each invader. With nonspecific defenses, the protection is always the same, no matter what the invader may be.
What is the second line of non specific defense?
The second line of defense is nonspecific resistance that destroys invaders in a generalized way without targeting specific individuals: Phagocytic cells ingest and destroy all microbes that pass into body tissues. For example macrophages are cells derived from monocytes (a type of white blood cell). Click to see full answer.
What does the non specific defense system do?
Nonspecific Mechanisms of Defense The body possesses many mechanisms that impart nonspecific defense. The objectives of these mechanisms are to prevent microorganisms from gaining a foothold in the body and to destroy them if they penetrate to the deeper tissues. Mechanical barriers.
Which of these is a nonspecific defense of the body?
immunity: Nonspecific Defenses Nonspecific defenses include physical and chemical barriers, the inflammatory response, and interferons. Physical barriers include the intact skin and mucous membranes. These barriers are aided by various antimicrobial chemicals in tissue and fluids.
What is a non specific immune defense?
Non specific immunity refers to the action of structures and substances that are naturally present. Both responses involve white blood cells Both responses have the mean of killing invading bacteria and parasites The specific immune system is antigen specific and reacts only with the organism that made the response happen.
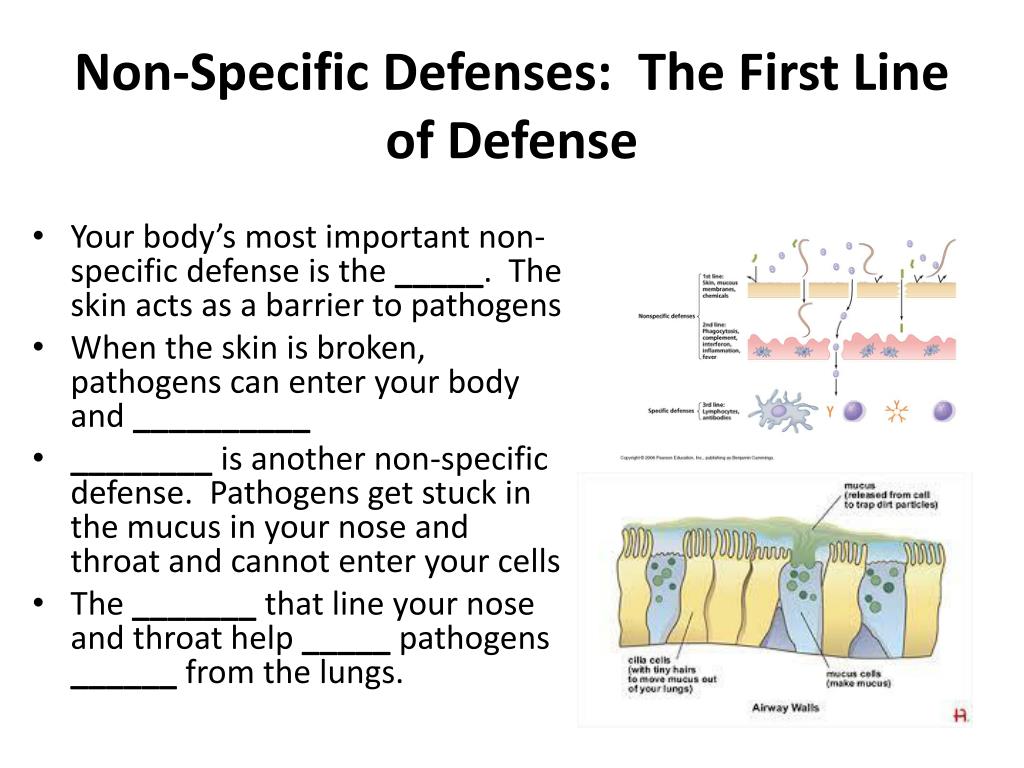
What is specific and non specific defense?
Nonspecific protective mechanisms repel all microorganisms equally, while the specific immune responses are tailored to particular types of invaders. Both systems work together to thwart organisms from entering and proliferating within the body.
What is meant by specific defense?
Specific Defense. Specific defense (sometimes called adaptive immunity) recognizes and coordinates attacks against specific pathogens. The system can also remember pathogens and produce a powerful response the next time a pathogen enters the body.
What's the difference between specific and nonspecific?
Immunity is categorized into two types; Specific or nonspecific immunity. Specific immunity is the production of antibodies against a particular antigen. Nonspecific immunity, on the other hand, is the immunity directed against all types of antigens without selecting a specific type.
What is a specific defense example?
It may be a toxin (injected into the blood by the sting of an insect, for example), a part of the protein coat of a virus, or a molecule unique to the plasma membranes of bacteria, protozoa, pollen, or other foreign cells.
Which are examples of non specific defenses?
Nonspecific defense mechanisms include the skin, mucous membranes, secretions, excretions, enzymes, inflammatory responses, genetic factors, hormonal responses, nutritional status, behavior patterns, and the presence of other diseases.
What are the 2 types of specific immune defenses?
The immune system is made up of two parts: the innate, (general) immune system and the adaptive (specialized) immune system. These two systems work closely together and take on different tasks.
What is the difference between nonspecific and specific immunity quizlet?
nonspecific immunity are things that protect the body from various bacterias, viruses, and pathogens. These include the first and second line of defense, such as the skin, fever( body gets hot as an attempt to kill the pathogen). Specific immunity are things that protect the body from specific pathogens.
What is non specific Defence mechanism?
Nonspecific defenses include anatomic barriers, inhibitors, phagocytosis, fever, inflammation, and IFN. Specific defenses include antibody (more...) Although interferon was first recognized as an extraordinarily potent antiviral agent, it was found subsequently to affect other vital cell and body functions.
What is a nonspecific response?
The non-specific response is a generalized response to pathogen infections involving the use of several white blood cells and plasma proteins. Non-specific immunity, or innate immunity, is the immune system with which you were born, made up of phagocytes and barriers.
How do specific defenses work?
Specific immune responses are triggered by antigens. Antigens are usually found on the surface of pathogens and are unique to that particular pathogen. The immune system responds to antigens by producing cells that directly attack the pathogen, or by producing special proteins called antibodies.
Is skin specific or nonspecific?
NON SPECIFIC DEFENSES: Skin and Mucous membranes, antimicrobial chemicals, natural killer cells, phagocytosis, inflammation and fever.
Are vaccines specific or nonspecific?
Vaccination is based on the adaptive immune responses that provide protection against a specific pathogen. Safe and controlled activation of the immune system results in a specific memory in the vaccinated hosts and protects them from secondary infection with the same pathogen (Chang et al., 2014).
What is specific defense quizlet?
Specific defense system. immune system- antibodies target and destroy specific pathogens.
What does non specific defense mean?
Non-specific defenses are the body's first line of defense against diseases. They are not directed against a particular pathogen. Non-specific defenses guard against all infections, regardless of their cause. It is also called as innate immunity (Fig.
What are the specific defense mechanisms?
Specific defense mechanism is the ability of the body to develop immunity against specific pathogens, toxins or foreign things. This is possible by a special immune system that produces antibodies and/or activated lymphocytes that attack and destroy specific invading organisms or toxins.
Which of the following are key characteristics of the specific defenses?
Terms in this set (15)The four general characteristics of specific defenses include. specificity. ... Cellular immune response. - Cytotoxic T cells (aka CD8, MHC I dependent): Recognize and kill altered self-cells. ... Tc Cells: ... Th cells: ... Antibody-Mediated immunity. ... Active immunity. ... Passive immunity. ... Active: Gets sick, then better.More items...
What is specific immunity and nonspecific immunity?
Non-specific immunity is generalized immunity that all humans are born with, including barriers, like skin, chemicals, like stomach acid and tears,...
Is skin an example of specific immunity?
No. Skin is an example of non-specific immunity. Non-specific immunity is the body's generalized and ongoing defense system to protect from pathogens.
What are the four types of specific immunity?
The four types of specific immunity are vaccine acquired, disease acquired, naturally acquired, and curative. Natural immunity is passed down gener...
What are nonspecific defenses?
Most viral infections are limited by nonspecific defenses, which (1) restrict initial virus multiplication to manageable levels, (2) initiate recovery from established infections that is then completed by a combination of these early nonspecific and subsequent antigen-specific immune ...
Why do multiple defenses have complexity?
These multiple defenses function with great complexity because of their interactions with one another. This complexity is compounded by the varying effectiveness of the defenses that results from the diversity of viruses, hosts, and sites and stages of infection.
Where do nonspecific inhibitors occur?
Nonspecific Inhibitors. A number of viral inhibitors occur naturally in most body fluids and tissues. They vary chemically (lipids, polysaccharides, proteins, lipoproteins, and glycoproteins) and in the degree of viral inhibition and types of viruses affected.
What is NCBI bookshelf?
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Is phagocytosis effective against viruses?
The limited information available suggests that phagocytosis is less effective against viral infections than against bacterial infections. However, few of the factors that control uptake of virions or infected cells by phagocytes and their digestion by lysosomal enzymes have been studied systemically. Different viruses are affected differently by the various phagocytic cells. Some viruses are not engulfed, whereas others are engulfed but may not be inactivated. In fact, some viruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), may even multiply in the phagocytes (e.g., macrophages), which may serve as a persistent reservoir of virus (Fig. 49-1). The virulence of several strains of HIV and herpesviruses correlates with their ability to multiply in macrophages. Infected macrophages may carry virus across the blood-brain barrier. Interestingly, cytomegalovirus has been reported to replicate in granulocytes. Macrophages seem to be more effective against viruses than are granulocytes, and some viruses seem to be more susceptible to phagocytosis than others. Macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes can afford important protection by markedly reducing the viremia caused by virus strains susceptible to phagocytosis.
What is the difference between specific and nonspecific immunity?
Difference Between Specific and Nonspecific Immunity. Specific immunity is the immune response generated against a particular antigen using the production of antibodies while nonspecific immunity is the initial immune response against the vast array of foreign antigens using nonspecific antibodies and immune cells.
What is non-specific immunity?
Non-specific immunity, as the name suggests, is not specific to a certain group of micro-organisms. These defense mechanisms act against each and every invader of the body. It is very important to understand that this non-specific immune response is so formidable that only a minute amount of infections penetrates this first line of defense.
What are the two types of immune responses?
Specific and Nonspecific immunity are two types of immune responses.
What are the two types of immunity?
Immunity is categorized into two types; Specific or nonspecific immunity. Specific immunity is the production of antibodies against a particular antigen. Nonspecific immunity, on the other hand, is the immunity directed against all types of antigens without selecting a specific type. Specific immunity occurs via lymphocytes; T cells and B cells, antibodies while nonspecific immunity occurs in many ways such as inflammation, fever, skin, mucous membrane, phagocytic white blood cells, antimicrobial substances, etc. Thus, this is the difference between specific and nonspecific immunity.
What is the immune response?
The immune response is the complex series of mechanisms that act against invasions by harmful microorganisms. Without this defense, the body is vulnerable to a whole host of infections. Furthermore, immunity can be categorized into two sections as specific and non-specific immunity.
Which type of defenses are nonspecific?
Examples of nonspecific defenses include physical barriers, protein defenses, cellular defenses, inflammation, and fever.
What are some examples of nonspecific cellular defenses?
Natural killer cells and macrophages are examples of nonspecific cellular defenses. Natural killer cells are a class of lymphocytes that recognize abnormal cells (such as cancerous cells or virus-infected cells), attach to them, and release chemicals that destroy them.
What are the two types of defenses that animals have against foreign invaders?
In animals, there are two types of defenses against foreign invaders: specific and nonspecific. Specific immune responses can distinguish among different invaders. The response is different for each invader. With nonspecific defenses, the protection is always the same, no matter what the invader may be.
What are the proteins that help prevent infection?
Interferons send a warning to nearby cells. They help prevent infection by stimulating the production of antiviral proteins. Interferons also stimulate natural killer cells and macrophages.
How do organisms defend themselves against invasion?
One way for an organism to defend itself against invasion is through barriers that separate the organism from its environment. Physical barriers such as the skin and mucous membranes mechanically regulate what enters the body. Secretions provide protection at the barrier as well. Mucus, for example, can trap potential invaders. Also, skin secretions are slightly acidic , inhibiting bacterial growth. Many body secretions (such as mucus, tears, and saliva) contain an enzyme called lysozyme that destroys bacteria.
What are the secretions that protect the body?
Also, skin secretions are slightly acidic , inhibiting bacterial growth. Many body secretions (such as mucus, tears, and saliva) contain an enzyme called lysozyme that destroys bacteria.
What are the substances secreted by cells invaded by viruses that stimulate neighboring cells to produce proteins that help them?
Interferons (IFNs) are substances secreted by cells invaded by viruses that stimulate neighboring cells to produce proteins that help them defend against the viruses. Certain IFNs (such as gamma‐IFN) also amplify the activity of macrophages and NK cells.
What is the inflammatory response?
The inflammatory response is a series of nonspecific events that occur in response to pathogens. The response typically produces redness, swelling, heat, and pain in the target area, and often the area is disabled.
Which cells bind to self-antigens are destroyed?
2. B cells that bind to self-antigens are destroyed
What is the name of the cell that attacks the body's own tissues as if they were foreign?
1. Killer T Cells or Antibodies attack the body’s own tissues as if they were foreign

Barriers
Proteins
Cellular Defenses
Inflammation
- Non-specific immunity is a set of defenses effective against all the invaders while specific immunity is a highly focused and targeted response. Non-specific immunity is the first line of defense whereas specific immunity is the second line of defense. Moreover, non-specific immunity includes effector cells like white blood cells and macrophages wh...
Fever
Bibliography
- One way for an organism to defend itself against invasion is through barriers that separate the organism from its environment. Physical barriers such as the skin and mucous membranes mechanically regulate what enters the body. Secretions provide protection at the barrier as well. Mucus, for example, can trap potential invaders. Also, skin secretions are slightly acidic , inhibiti…