What type of soil is spongy?
Peaty soil is a darker soil and feels damp and spongy due to its higher levels of peat. It is an acidic soil which slows down decomposition and leads to the soil having fewer nutrients. The soil heats up quickly during spring and can retain a lot of water which usually requires drainage.
What is the function of mesophyll?
This way, you have different layers of the leaf. The primary and the absolute most important role of the mesophyll is its role in photosynthesis. Photosynthesis, as you may know, is the process by which a plant takes carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight and creates sugars, which result in the plant having energy.
Does the spongy mesophyll contain any chloroplasts?
The spongy mesophyll contains irregularly shaped cells with wide gaps between them in order to facilitate carbon dioxide diffusion and gas exchange via the stomata. Spongy mesophyll also contains chloroplasts responsible for photosynthesis.
What is the spongy palisade function?
What Is The Main Function Of The Spongy Layer? The palisade layer contains a few chloroplasts, and although they tend to be little more than temporary protein storage, they apparently play an important role in the chemical composition. Furthermore, when leaves are grown, both the environment and the leaf are more readily exposed to air.
.PNG)
What is spongy mesophyll cell?
Spongy mesophyll tissue is packed loosely for efficient gas exchange. The spongy mesophyll cells are covered by a thin layer of water. Gases dissolve in this water as they move into and out of the cells.
What is spongy mesophyll simple?
n. A leaf tissue consisting of loosely arranged, chloroplast-bearing cells, often located on the lower side of the leaf.
What is the difference between mesophyll and spongy mesophyll?
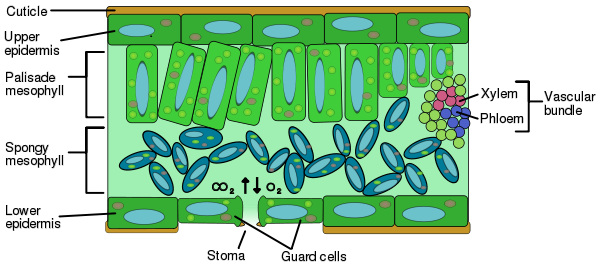
Palisade mesophyll cells are elongate and form a layer beneath the upper epidermis, whereas spongy mesophyll cells are internal to the lower epidermis. Mesophyll cells in monocotyledonous leaves are often highly lobed.
What is the function of the palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll?
The palisade mesophyll layer is where most of the photosynthesis occurs in the leaf. The palisade cells contain a lot of chloroplasts to help them perform this photosynthesis. The palisade cells are closely packed together to maximize light absorption.
What is spongy mesophyll made of?
The spongy mesophyll contains calcium oxalate, mainly in the form of single and twin prisms, but clusters and microsphenoidal crystals are also present (Fig.
What does the spongy layer do?
Spongy layer Although they contain a few chloroplasts, their main function seems to be the temporary storage of sugars and amino acids synthesized in the palisade layer. They also aid in the exchange of gases between the leaf and the environment.
Is spongy mesophyll a plant cell?
Many plant leaves have two layers of photosynthetic tissue: the palisade and spongy mesophyll. Whereas palisade mesophyll consists of tightly packed columnar cells, the structure of spongy mesophyll is not well characterized and often treated as a random assemblage of irregularly shaped cells.
What is the function of the mesophyll?
The most important role of the mesophyll cells is in photosynthesis. Mesophyll cells are large spaces within the leaf that allow carbon dioxide to move freely.
What is the role of mesophyll cells?
There are two types of mesophyll cells in the leaves namely palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll. Mesophyll cells are provided with a large number of chloroplast. Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast. Hence mesophyll cells of leaves are the principal centre of photosynthesis.
Where is the spongy mesophyll located?
The spongy mesophyll layer is located directly below the palisade mesophyll layer. It consists of irregularly-shaped cells that are loosely packed with air spaces in between.
Does photosynthesis occur in spongy mesophyll?
There's still photosynthesis occurring in the spongy mesophyll, but there are large spaces left between the cells. These large spaces allow these layers to help carbon dioxide move around the leaf.
Does spongy mesophyll have chloroplasts?
Spongy mesophyll – have very few chloroplasts and a large surface area to increase the diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen. Intercellular air spaces within the spongy mesophyll layer – they allow the diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
Is spongy mesophyll a plant cell?
Many plant leaves have two layers of photosynthetic tissue: the palisade and spongy mesophyll. Whereas palisade mesophyll consists of tightly packed columnar cells, the structure of spongy mesophyll is not well characterized and often treated as a random assemblage of irregularly shaped cells.
Where is the spongy mesophyll located?
Spongy parenchyma, or spongy mesophyll, represents the second cell type found in plant leaves. This layer of cells is located just below the palisade parenchyma tissue and directly above the lower epidermis in dicots.
What is the function of mesophyll in plants?
The most important role of the mesophyll cells is in photosynthesis. Mesophyll cells are large spaces within the leaf that allow carbon dioxide to move freely.
What is normally inside the spongy mesophyll of a leaf?
structure in plant leaves (veins) are embedded in the mesophyll, the tissue that includes all of the cells between the upper and lower epidermis. The cells of the mesophyll contain the photosynthetic pigments.
What is the spongy mesophyll?
Similar hairs are found on the stems. The spongy mesophyll contains calcium oxalate, mainly in the form of single and twin prisms, but clusters and microsphenoidal crystals are also present (Fig. 26.7B,D ).
What are the enzymes that make black cherry seeds cyanogenic?
47–51 The kernels of black cherry seeds contain large quantities of the cyanogenic diglucoside ( R )-amygdalin ( 12) and three catabolic enzymes: the diglucosidase amygdalin hydrolase; the monoglucosidase, prunasin hydrolase; and an α-hydroxynitrile lyase, ( R )- (+)-mandelonitrile lyase. These enzymes first appear in the seeds about 6 weeks after flowering. The two β-glucosidases are restricted to protein bodies in the procambium, whereas the hydroxynitrile lyase occurs primarily in protein bodies in the cotyledonary parenchyma cells, which is also the location of the cyanogenic diglucoside, amygdalin ( 12 ). Thus, in black cherry, cyanogenesis in intact tissues of the developing seed is prevented by segregation of the first degrading enzyme, amygdalin hydrolase, and amygdalin ( 12) in different tissues.
What are the structures of henbane leaf?
26.7A ). Both surfaces have a smooth cuticle, epidermal cells with wavy walls, stomata of both anisocytic and anomocytic types, and a large number of hairs, which are particularly abundant on the midrib and veins. The hairs are up to 500 μm long; some are uniseriate and two to six cells long, while others have a uniseriate stalk and a large, ovoid, glandular head, the cuticle of which is often raised by the secretion ( Fig. 26.7E). Similar hairs are found on the stems. The spongy mesophyll contains calcium oxalate, mainly in the form of single and twin prisms, but clusters and microsphenoidal crystals are also present (Fig. 26.7B,D ). The broad midrib contains a vascular bundle, distinctly broader than that of stramonium, showing the usual bicollateral arrangement, which is also to be seen in the stems. The mesophyll of the midrib is made up of two thin zones of collenchyma immediately within the epidermi and a ground mass of colourless parenchyma showing large, intercellular air spaces and containing prisms or, occasionally, microsphenoidal crystals of calcium oxalate.
What are the cells of spongy mesophyll?
The cells of spongy mesophyll are loosely packed with many intercellular spaces in between. These cells are covered with a thin layer of water. Gases enter through stomata and get dissolved in this water for exchange. Stomata are some tiny pores that are present on the surface of the leaf. Stomata can be present on both epidermal layers or are limited to lower epidermis only. Stomata allow the exchange of gases between internal tissues of plant and atmosphere.
What is the mesophyll tissue of a leaf?
The mesophyll tissue is called the ground tissue of the leaf. It is composed of parenchyma cells. Parenchyma is a primary permanent simple tissue. These parenchyma cells contain chloroplast. Its primary function is photosynthesis in plants.
Is mesophyll tissue heterogeneous or homogeneous?
It is present between two epidermal layers. It can be homogenous or heterogeneous . One of the factors used in the classification of leaves is the presence of mesophyll tissue. The leaves that are heterogeneous consist of two types of mesophyll cells and are known as dorsiventral of dicot leaf. The leaves which are homogenous, i.e. consisting of only one type of mesophyll cell are known as isobilateral or monocot leaf.
Is mesophyll heterogeneous?
In leaves of the dicotyledonous plant, mesophyll tissue is heterogeneous. The mesophyll layer is composed of two types of parenchyma cells viz. Palisade parenchyma and Spongy parenchyma.
Where are mesophylls located?
Spongy mesophyll and palisade mesophyll are types of cells involved in the the processes leading up to photosynthesis as well as photosynthesis itself and are located in the leaves of vascular plants.
Which leaves have mesophyll?
Monocot leave s usually have 1 type of mesophyll; however, eudicots tend to have 2 types of mesophyll - the spongy and palisade. These cells, as can be deduced, contain chloroplast.
Why is spongy mesophyll packed loosely?
Spongy mesophyll tissue is packed loosely for efficient gas exchange. The spongy mesophyll cells are covered by a thin layer of water. Gases dissolve in this water as they move into and out of the cells. When the plant is photosynthesising during the day, these features allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into the spongy mesophyll cells, ...
Which layer of the leaf absorbs light?
The palisade mesophyll layer of the leaf is adapted to absorb light efficiently. The cells:
What is the structure of a leaf?
The structure of a leaf. Plant leaves are adapted for photosynthesis, and the exchange of gases required for the process. The structure of the tissues is related to their functions in the plant.
What are the organelles of spongy mesophyll cells?
Like palisade cells, spongy mesophyll cells also contain such organelles as a nucleus, a vacuole, a cell membrane as well as chloroplasts among a few others. The number of chloroplasts in these cells, however, is less compared to the number of chloroplasts found in palisade cells.
What are the cells that make up the mesophyll layer?
In the leaves of dicotyledonous plants, this layer is composed of two types of cells, namely, the spongy and palisade cells. These cells also house chloroplasts thus making the mesophyll the site of photosynthesis. ...
Why do chloroplasts move?
When the amount of light is too high, they have been shown to move to regions of the cell so that they are not overly exposed. The capacity of chloroplasts to move (moved by specific structural proteins) within the cell is made possible by the fact that the elongated shape of palisade cells provide sufficient room for them to move and adjust their position with changes in light intensity.
Why are palisade cells arranged in close proximity to each other?
In addition to these features, palisade cells are also well positioned to absorb more light required for photosynthesis.
How many types of cells are in the mesophyll layer?
As already mentioned, the mesophyll layer is composed of two types of cells.
Which cells contain crystal inclusions?
Whether in palisade or spongy cells, mesophyll cells that contain crystal inclusion (e.g. druse crystals) are shorter/smaller compared to the other cells in this region of the leaf. * The thickness of the spongy parenchyma is between 1.5 and 2 times that of palisade tissue.
Which part of the cell restricts chloroplasts to the area along the cell membrane?
Large vacuole - Although the shape of palisade cells allows them to move when need be, the large vacuole located at the central part of the cell restricts chloroplasts to the area along the cell membrane. This ensures that light easily reaches the chloroplasts for photosynthesis to take place.
