What is an example of generalization in psychology?
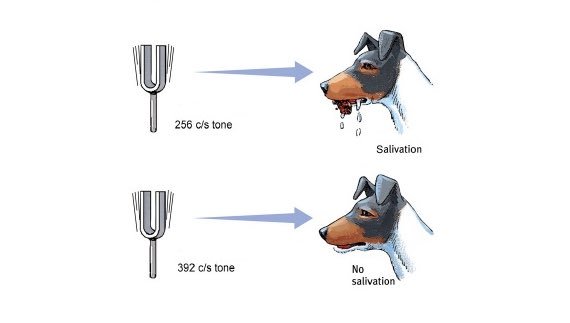
generalization, in psychology, the tendency to respond in the same way to different but similar stimuli. For example, a dog conditioned to salivate to a tone of a particular pitch and loudness will also salivate with considerable regularity in response to tones of higher and lower pitch.
What is spontaneous in psychology?
Spontaneous recovery can be defined as the reappearance of the conditioned response after a rest period or period of lessened response. If the conditioned stimulus and unconditioned stimulus are no longer associated, extinction will occur very rapidly after a spontaneous recovery.
What are the three types of generalization?
Generalization includes three specific forms: Stimulus generalization, response generalization, and maintenance. Stimulus generalization involves the occurrence of a behavior in response to another similar stimulus.
What is an example of stimulus generalization in psychology?
Stimulus generalization is the tendency of a new stimulus to evoke responses or behaviors similar to those elicited by another stimulus. For example, Ivan Pavlov conditioned dogs to salivate using the sound of a bell and food powder.
What is spontaneous and its example?
A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that favors the formation of products at the conditions under which the reaction is occurring. A roaring bonfire is an example of a spontaneous reaction, since it is exothermic (there is a decrease in the energy of the system as energy is released to the surroundings as heat).
What is an example of a spontaneous?
A spontaneous process is one that occurs on its own, without any energy input from the outside. For example, a ball will roll down an incline; water will flow downhill; ice will melt into water; radioisotopes will decay, and the iron will rust.
What are the two types of generalization?
These are inductive generalizing (a reasoning process that begins with observations and subsequently uses them as the basis on which to build a theory) and deductive generalizing (a reasoning process that begins with a theory and subsequently processes or tests it against observations).
What are the two kinds of generalizations?
There are two kinds of generalizations, valid and faulty, and it is your role to determine which generalizations have validity behind them. Broad characterization of cultural groups can serve as a framework for cultural interactions.
What is the most famous example of generalization?
One of the most famous examples of stimulus generalization took place in an early psychology experiment. In the Little Albert experiment, the behaviorist John B. Watson and his assistant Rosalie Rayner conditioned a little boy to fear a white rat.
Which is the best example of stimulus generalization?
Potty training is a good example of stimulus generalization in operant conditioning. When a child is learning to use the toilet, rewards are often used to increase the desired behaviors.
What are examples of stimulus and response generalization?
This is the case of stimuli that occasion novel responses. For example, if Sally learned to pick up a phone and talk on it with a friend, she has response generalization if she can also pick up a walkie talkie and use it to talk to a friend.
What is a good example of generalization?
When you make a statement about all or most of the people or things together, you are making a generalization. For example: – All birds have wings. – Many children eat cereal for breakfast.
What means spontaneous?
Some common synonyms of spontaneous are automatic, impulsive, instinctive, and mechanical. While all these words mean "acting or activated without deliberation," spontaneous implies lack of prompting and connotes naturalness.
What is a spontaneous concept?
Spontaneous concepts are the result of generalization of everyday personal experience in the absence of systematic instruction. Therefore, such concepts are unsystematic, not conscious, and often wrong.
Do organisms react to different stimuli?
In generalization, on the other hand, the organism has the same reaction to different stimuli. To apply this to our previous example, let's say you were too young to understand the differences between cats and dogs at the time you were bitten. Now you get anxious around any kind of animal, even though it was a dog that bit you (and not a cat, or horse, or anything else).
Can discrimination and generalization occur without your knowledge?
In the case described above, discrimination and generalization occur without your knowledge or forethought. These are unconditioned responses. It is possible to condition the discrimination or generalization response to accomplish certain goals.
When dealing with spontaneous recovery, it's important to grasp that associations between stimuli and subsequent responses play a role?
When dealing with spontaneous recovery, it's important to grasp that associations between stimuli and subsequent responses play a role. When exposure to these associations decreases for extended periods, this leads to spontaneous recovery, not psychological extinction. There's a difference between learning a new response to a certain stimulus and merely seeing the emergence of past behaviors which previously had negative responses as subsequent associations.
What is spontaneous recovery?
In psychology, spontaneous recovery deals with the emergence of a behavior which was previously regarded as no more. Psychological conditioning also plays a role in this, seeing as behaviors which resurface during spontaneous recovered were supposed to be weeded out by either classical or operant conditioning.
How does trauma affect spontaneous recovery?
Traumatic memories can prompt spontaneous recoveries due to an essential override of prior classical conditioning. It's important to understand that the intensity of said past trauma can also impact the frequency or regularity of traumatic memories. Look at it this way: in a sense, classical conditioning programs individuals to associate certain actions with either positive or negative responses. With time and consistency, a pattern is eventually established. However, the emergence of trauma has the power to disrupt previously established patterns psychologically.
Why are spontaneous recoveries not positive?
Because of the inherent negativity associated with traumatic memories, spontaneous recoveries may not be positive. It's not uncommon for people who experience trauma to pull away from others, make lifestyle changes, and otherwise behave in ways which are out of character for them. In situations like these, it's generally advisable for survivors of trauma to seek psychological help, particularly therapy or counseling.
What are the two things that are liked to spontaneous recovery?
Thus far, there are two determined circumstances which are liked to spontaneous recovery: traumatic memories and retroactive inhibition. Understanding both of these causes and the impacts which they have on classical conditioning is very enlightening to spontaneous recovery.
How to understand spontaneous recovery?
To understand spontaneous recovery, one must first grasp conditioning and how much classical conditioning impacts the individual psyche and their subsequent responses to various elements.
How long does spontaneous recovery last?
This response can happen after only a few days, and in some instances, it may also occur after a period of months.
What is Spontaneous Recovery?
Spontaneous recovery is a term first associated with Ivan Pavlov and a learning process called classical conditioning. Pavlov conducted a series of experiments where the focus was learning and training conditioned responses. From his experiments he found that spontaneous recovery was the reappearance of a Conditioned Response (CR) that had been extinguished. In other words, it no longer occurred. Specifically, Pavlov found that spontaneous recovery can occur after a period of not being exposed to the Conditioned Stimulus (CS). This period is called spontaneous because the response seems to reappear unexpectedly.
Do conditioned responses return to full strength?
However, conditioned or trained responses generally do not return to full strength. Furthermore, with repeated cycles of recovery and extinction, conditioned/trained responses tend to be less intense with each recovery period. Recovery will take place even when there has not been any additional association between the two conditioned stimuli.
What is stimulus generalization?
Stimulus generalization occurs when an organism responds to a stimulus in the same way that it responds to a similar stimulus. This occurs during the classical conditioning process. For example, imagine that a dog has been conditioned to run to its owner when it hears a whistle.
What happens when stimulus generalization occurs?
If stimulus generalization occurs, the children will have trouble determining which response they are supposed to give. For example, the kids might all line up for lunch instead of sitting in their desks when the reading time bell sounds.
How does stimulus generalization affect people?
Stimulus generalization can have an impact on how people respond to different stimuli. For example, imagine in school that children are expected to line up for lunch when they hear the ding of a bell. However, another similar sounding bell also rings when the kids are expected to sit in their desks for reading time. If stimulus generalization occurs, the children will have trouble determining which response they are supposed to give. For example, the kids might all line up for lunch instead of sitting in their desks when the reading time bell sounds.
When is classical conditioning 2021?
What Is Classical Conditioning? November 16, 2021 In "Behavioral Psychology"
Is stimuli generalization good?
Stimulus generalization can have an impact on the learning process in both classical and operant conditioning . Sometimes this generalization can be a good thing. In school, kids may learn skills in one setting that can then be transferred over into similar situations. In other cases, it can lead to confusion and complication if there is a need ...
