
What is a stem and leaf diagram?
A stem-and-leaf diagram, also called a stem-and-leaf plot, is a diagram that quickly summarizes data while maintaining the individual data points. In such a diagram, the "stem" is a column of the unique elements of data after removing the last digit.
How do you do stem and leaf in statistics?
0:193:14Statistics - How to make a stem and leaf plot - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd all of these numbers and that will become our stem. And then with the other values in the numberMoreAnd all of these numbers and that will become our stem. And then with the other values in the number those will become the leaves. Alright so let's see how this works out by first creating the stems.
Why is a stem-and-leaf plot used in descriptive statistics?
Histograms and stem and leaf plots allow you to quickly assess the shape, centering and spread of a distribution. For categorical (nominal or ordinal) variables, see the page Bar Charts and Frequency Distributions.
What is a stem and leaf histogram?
A stem-and-leaf display or stem-and-leaf plot is a device for presenting quantitative data in a graphical format, similar to a histogram, to assist in visualizing the shape of a distribution. They evolved from Arthur Bowley's work in the early 1900s, and are useful tools in exploratory data analysis.
What is the difference between stem plot and histogram plot?
The primary difference between a histogram and a stem-and-leaf plot is that the stem-leaf plot shows individual data points whereas the histogram does not.
What is an advantage of using stem-and-leaf plot instead of a histogram?
The stem and leaf plot essentially provides the same information as a histogram, with the following added benefits: The plot can be constructed quickly using pencil and paper. The values of each individual data point can be recovered from the plot.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of stem-and-leaf plot?
The advantage of a stem leaf diagram is it gives a concise representation of data. The advantage of a frequency histogram is, that it is visually strong. Histograms are usually preferable to stem and leaf diagrams in large data sets. The disadvantage of a stem leaf diagram is not visual.
How are stem and leaf plots used in real life?
Admittedly stem and leaf diagrams are rarely used in 'real life'. In fact the only common examples we can find are timetables, such as the Japanese train timetable shown in the picture below (more examples here).
How do you read a stem and leaf display?
The 'stem' is shown on the left side of the table and shows the first digit or digits of data values. The 'leaf' is shown on the right side of the table and shows the last digit of the data value. For example, 443 and 447 can be shown together on a stem and leaf plot as 44 | 3,7.
How do you interpret a stem-and-leaf plot in SPSS?
1:439:42Creating and Interpreting a Stem-and-Leaf Plot in SPSSYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the way a stem-and-leaf plot works as it divides the values. Into two parts the stem. And theMoreSo the way a stem-and-leaf plot works as it divides the values. Into two parts the stem. And the leaf. And then in SPSS it also gives you the frequency.
How do you know if a stem-and-leaf plot is skewed?
Plots with an upward skew will have a mode that is smaller than either the mean or the median, and a mean that is greater than either the median or the mode. Downward-skewed plots will have a mean lesser than median or mode and a mode greater than either mean or median.
How do you find the sample size in a stem-and-leaf plot?
Sample size (n) The sample size is displayed at the top of the stem-and-leaf plot. In the previous example, the sample size is 50 (N = 50). Because a stem-and-leaf plot represents each data value, it is best when the sample size is less than approximately 50.
How do you find the stem unit and leaf unit?
The 'stem' is on the left displays the first digit or digits. The 'leaf' is on the right and displays the last digit. For example, 543 and 548 can be displayed together on a stem and leaf as 54 | 3,8.
How do you make a Stemplot with 3 digit numbers?
We call this the leaf. On the left side are the rest of the digits. This part is called the stem. When creating a three-digit stem-and-leaf plot, there will be one digit, or number, on the right (the leaf) and two on the left (the stem) for each number.
What does leaf unit 0.1 mean?
Our graph says the leaf unit = 1.0. That's simple because a leaf of 1 = 1, 2 = 2, and so on. If the unit had been 10, the leaves would've been 10, 20, 30, etc. Or, if it had been 0.1, leaves would represent 0.1, 0.2, and so on. This unit depends on how you or your software rounds the data.
How do you create a stem-and-leaf plot in Excel?
Use the following steps to create a stem-and-leaf plot in Excel.Step 1: Enter the data. ... Step 2: Identify the minimum and maximum values.Step 3: Manually enter the “stems” based on the minimum and maximum values.Step 4: Calculate the “leaves” for the first row. ... Step 5: Repeat the calculation for each row.
1. How do Stem and Leaf Plots Work?
A stem and leaf is a table used to display data. The 'stem' on the left side displays the first digit or digits. The 'leaf' is on the right side an...
2. What Does Stem and Leaf Plot Mean?
A Stem and Leaf plot is a way of organizing data values from least to greatest using place value. Typically, the last digit from each data value be...
3. What's a Double Stem and Leaf Plot?
Double Stem and Leaf plots are used to compare two distributions side-by-side. This type of Double Stem and Leaf plot contains three columns, each...
4. What are the uses of stem and leaf plots in real life?
Stem and leaf plots have several uses in real-life situations where one needs to present a set of data graphically. These plots are useful to displ...
5. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using stem and leaf plots?
As can be seen, stem and leaf plots find several uses in real life. These plots are used extensively as they have several advantages. These include...
When to use stem and leaf plot?
Stem-and-leaf plot graphs are usually used when there are large amounts of numbers to analyze. Some examples of common uses of these graphs are to track a series of scores on sports teams, a series of temperatures or rainfall over a period of time, or a series of classroom test scores. Check out this example of test scores:
Why do sports fans use stem and leaf graphs?
Sports fans often use these stem-and-leaf graphs to represent their teams' scores to compare success. Sometimes, when the record for wins is tied within a football league, the higher-ranked team will be determined by examining data sets that are more easily observable, including the median and mean of the two teams' scores.
How is data shown in a graph?
This data is arranged by place value where the digits in the largest place are referred to as the stem, while the digits in the smallest value or values are referred to as the leaf or leaves, which are displayed to the right of the stem on the diagram.
How to compare two sets of data?
To compare two sets of data, you can use a back-to-back stem-and-leaf plot. For instance, if you want to compare the scores of two sports teams, you can use the following stem-and-leaf plot: The tens column is now in the middle column, and the ones column is to the right and left of the stem column.
What does it mean when you count the number of leaves on a test?
When you count the total number of leaves, you know how many students took the test. Stem-and-leaf plots provide an at-a-glance tool for specific information in large sets of data. Otherwise, you would have a long list of marks to sift through and analyze.
Where is the tens column in the tens column?
The tens column is now in the middle column, and the ones column is to the right and left of the stem column. You can see that the Sharks had more games with a higher score than the Tigers because the Sharks only had two games with a score of 32, while the Tigers had four games—a 30, 33, 37 and a 39. You can also see that the Sharks and the Tigers tied for the highest score: a 59.
What is a stem and leaf plot?
Statistics - Stem and Leaf Plot. Stemplots are similar to histogram with the difference that in histogram, bars are used to compare data and in case of stemplots leaves represents actual numbers to be compared. Stemplots are also called stem and leaves plot as there is one step with largest place value digits on the left and at leaf (ves) ...
What are the left and right sides of a stemplot?
In a stemplot, left side entries are called stems; and the right side entries are called leaves. In figure above, the stems are tens (here 5 represents 50, 6 represents 60, and so on); and the leaves are actual values. Stems and leaves may be labelled as - millions, thousands, ones, tenths, etc.
Why are stem and leaf plots better than histograms?
Stem and leaf plots have one advantage over histograms because they display the original data, while histograms only summarize them.
What is the stem value of a leaf?
Because the leaf unit is 1, we know the stem values must start in the 10s place. Therefore, the stem values of 1, 2, 3, and 4 correspond to 10, 20, 30, and 40. Using this information, you can determine the value of every data point on this graph!
What is a stemplot?
Stem and leaf plots display the shape and spread of a continuous data distribution. These graphs are similar to histograms, but instead of using bars, they show digits. It’s a particularly valuable tool during exploratory data analysis. They can help you identify the central tendency, variability, skewness of your distribution, and outliers. Stem and leaf plots are also known as stemplots.
How many observations are there in a stem?
For example, the stem = 2 row with the leaf values of 4 and 5 has a count of 39. This number indicates there are 39 observations in this row and lower (towards the left tail). On the higher side of the median, the stem = 2 row with values of 8 and 9 has a count of 43. This count indicates there are 43 observations in that row and higher (towards the right tail).
How many rows are there in a body fat percentage graph?
For the body fat percentage data, the graph divides stem values into five rows. Each row contains only two leaf values (e.g., 0 and 1, 2 and 3, etc.) The leaf values stop at the minimum and maximum values of the dataset. Consequently, the extreme stem values can have fewer rows than the other stem values. In our graph, 1 and 4 are the extreme stem values, and they both have fewer rows than the middle values (2 and 3).
What is leaf unit?
The leaf unit or key allows us to interpret the value of each leaf. This stem and leaf plot uses a leaf unit, but others have a key, which provides similar information.
Why do you include a stem with no leaves on the plot?
If you have a stem with no leaves, include it on the plot anyway to preserve the horizontal axis scaling and highlight the lack of values. That can be important when looking for outliers.
What is the difference between a stem and leaf plot and a histogram?
The basic idea behind a stem-and-leaf plot is to divide each data point into a stem and a le af.
How many rows are there in a stem?
When you opt to use two rows for each stem, the first row is reserved for the leaves 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4, while the second row is reserved for the leaves 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. For example, note that the first 9 row contains the 0 to 4 leaves, while the second 9 row contains the 5 to 9 leaves.
What is a stem and leaf plot?
A Stem and Leaf Plot is a special table where each data value is split into a "stem" (the first digit or digits) and a "leaf" (usually the last digit). Like in this example:
Where is the stem in a score?
The "stem" values are listed down, and the "leaf" values go right (or left) from the stem values. The "stem" is used to group the scores and each "leaf" shows the individual scores within each group.
What are the advantages of a leaf diagram?
One advantage of this diagram is that the original data can be recovered (except the order the data is taken) from the diagram.
What is the first column in a frequency chart?
1. 14. 8. The first column, called depths, are used to display cumulative frequencies. Starting from the top, the depths indicate the number of observations that lie in a given row or before. For example, the 11 in the third row indicates that there are 11 observations in the first three rows.
What is a dot plot?
A dot plot displays the data as dots on a number line. It is useful to show the relative positions of the data.
How to display cumulative frequency?
The first column, called depths, are used to display cumulative frequencies. Starting from the top, the depths indicate the number of observations that lie in a given row or before. For example, the 11 in the third row indicates that there are 11 observations in the first three rows. The row that contains the middle observation is denoted by having a bracketed number of observations in that row; (7) for our example. We thus know that the middle value lies in the fourth row. The depths following that row indicate the number of observations that lie in a given row or after. For example, the 4 in the seventh row indicates that there are four observations in the last three rows.
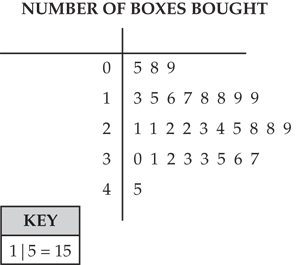
Using Stem-And-Leaf Plot Diagrams
Using Stem-And-Leaf Graphs For Multiple Sets of Data
- To compare two sets of data, you can use a back-to-back stem-and-leaf plot. For instance, if you want to compare the scores of two sports teams, you can use the following stem-and-leaf plot: The tens column is now in the middle column, and the ones column is to the right and left of the stem column. You can see that the Sharks had more games with a higher score than the Tigers …
Practice Using Stem-And-Leaf Plots
- Try your own stem-and-leaf plot with the following temperatures for June. Then, determine the medianfor the temperatures: 77 80 82 68 65 59 61 57 50 62 61 70 69 64 67 70 62 65 65 73 76 87 80 82 83 79 79 71 80 77 Once you've sorted the data by value and grouped them by the tens digit, put them into a graph called "Temperatures." Label the left column (the stem) as "Tens" an…
How to Solve to Practice Problem
- Now that you've had a chance to try this problem on your own, read on to see an example of the correct way to format this data set as a stem-and-leaf plot graph. You should always begin with the lowest number, or in this case temperature: 50. Since 50 was the lowest temperature of the month, enter a 5 in the tens column and a 0 in the ones column, then observe the data set for th…