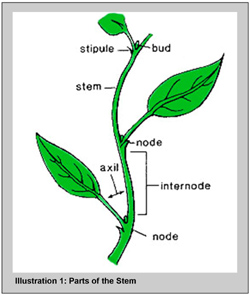
Ans: The stem is explained with the help of the diagram below:
- The stem is the ascending part of the plant that grows in upward directions (except in some plants) that bears leaves,...
- It has nodes and internodes, even if it is an underground stem. Node is the stiff region where leaves are born and...
- The stem apex is always apical in position and bears terminal buds.
Why is a stem so important for a plant?
- Ginger
- Teak wood
- Podina
- Thulasi
- Bamboo. Etc
What are the jobs of the stem of a plant?
- Agronomist: the “family doctor” of plants. ...
- Biochemist/Biotechnologist: both disciplines specialize in bio-engineering and genetics. ...
- Entomologist: the “bug expert” who studies how to protect crops from pests without harming beneficial insects like bees. ...
What are the functions of the stem of a plant?
They are of the following types:
- Thorns- These stem modifications appear as hard, woody and sharp outgrowths that protect the plant. ...
- Tendril – These types of stems are slender, twining strands that enable a plant to seek support while climbing on other surfaces.
- Phylloclade- This type of stem is a green, flattened or cylindrical one that resembles a leaf. ...
What role does a stem play in a plant?
The primary functions of the stem are to support the leaves; to conduct water and minerals to the leaves, where they can be converted into usable products by photosynthesis; and to transport these products from the leaves to other parts of the plant, including the roots. The stem conducts water and nutrient minerals from their site of absorption in the roots to the leaves by means of certain vascular tissues in the xylem.

What is the part of a stem?
The stem is divided into two parts; nodes and internodes. Nodes are where buds grow into leaves, stems, or flowers and internodes are the parts of the stem in between the nodes (see Figure 8). In most plants, stems are found above the ground, but for some plants, such as potatoes, stems are also found below the ground.
What is function of a stem?
The main functions of stems are to support and elevation of leaves, fruits, and flowers. Stem arranges leaves in a way that it gets direct sunlight to perform photosynthesis. Xylem and Phloem conduct water across the plant. Stems stores food, water, and nutrients. Cells of a stem, meristems, produce new living tissues.
What are the 2 types of stems?
Types of Plant Stems There are two main types of stems: woody and herbaceous.
What are the 4 parts of a stem?
What Are the Different Parts of a Stem. A typical plant stem consists of eight distinct parts, containing six elements and two organs. The six elements are: 1) nodes, 2) internodes, 3) terminal or apical bud, 4) lateral or axillary bud, 5) petiole and 6) pedicel. While the two organs are: 7) leaves and 8) flowers.
What are 5 main functions of a stem?
(i) It supports branches, leaves, flowers, and fruits. (ii) It transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and other parts of plants. (iii) It transports food from leaves to different parts of the plant. (iv) It holds the plant upright.
What are the 4 main functions of stem?
A stem connects the roots to the leaves, provides support, stores food, and holds the leaves, flowers, and buds.
What is a stem called?
The aerial stem of an adult tree is called a trunk. The dead, usually darker inner wood of a large diameter trunk is termed the heartwood and is the result of tylosis. The outer, living wood is termed the sapwood.
What are the examples of stem?
The edible stalks of plants when the stalk/stem is the main part of the vegetable. Examples are celery, asparagus, kohlrabi, rhubarb and turmeric.
What is the stem of a tree?
Trees: The stem is upright, very tall, very thick, hard. It is called the trunk. The trunk of a tree is its stem. The stem can be underground, for example that of garlic or onion.
What are types of stems?
There are three types of stem: Underground stem, Aerial stem and Sub- aerial stem.
What are the parts of the stem and their functions?
Describe Different Parts of Stem(i) Node – The place from where the lanes grow is the node. A node is a point on the stem from which leaves or buds arise.(ii) Internode – The space between the two nodes is the internode. ... (iii) Bud – A bud is an embryonic stem that has the potential for further plant growth. ... Function.
What is a plant stem kids?
Stem - The stem is the main structure that supports leaves and flowers. Stems have vascular tissues that move food and water around the plant to help it grow. Plants often store food in their stems.
What are the types of lines?
In geometry there are four types of lines: Horizontal Line Vertical lines Parallel lines Perpendicular lines
What is a ray?
A ray is a part of a line with one endpoint (i.e., starting point) and continues forever in the other direction.
What is perpendicular lines?
When two straight lines meet or intersect at an angle of 90 degrees, they are perpendicular to each other.
What is parallel lines?
Parallel lines are two straight lines that are always the same distance apart. They never meet or intersect at any point, even at infinity.
What is the stem of a plant?
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant, the other being the root. It supports leaves, flowers and fruits, transports water and dissolved substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem, stores nutrients, and produces new living tissue. The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes:
Where are the stems of plants located?
In most plants stems are located above the soil surface but some plants have underground stems . Stems have four main functions which are: Support for and the elevation of leaves, flowers and fruits. The stems keep the leaves in the light and provide a place for the plant to keep its flowers and fruits.
How long do plants live?
The normal lifespan of plant cells is one to three years. Stems have cells called meristems that annually generate new living tissue. Stems have two pipe-like tissues called xylem and phloem. The xylem tissue transports water by the action of transpiration pull, capillary action and root pressure.
What is a stem node?
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant, the other being the root. It supports leaves, flowers and fruits, ...
What is a corm stem?
Corm: a short enlarged underground, storage stem, e.g. taro, crocus, gladiolus. Decumbent stem in Cucurbita maxima. Decumbent: stems that lie flat on the ground and turn upwards at the ends. Fruticose: stems that grow shrublike with woody like habit.
What is a bulb?
Bulb: a short vertical underground stem with fleshy storage leaves attached, e.g. onion, daffodil, tulip. Bulbs often function in reproduction by splitting to form new bulbs or producing small new bulbs termed bulblets. Bulbs are a combination of stem and leaves so may better be considered as leaves because the leaves make up the greater part.
What is the division of a stem?
The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes: The nodes hold one or more leaves, as well as buds which can grow into branches (with leaves, conifer cones, or inflorescences (flowers)). Adventitious roots may also be produced from the nodes. The internodes distance one node from another.
What is the function of stems in plants?
Few green stems perform photosynthesis as well. The plant stem serves as a means of asexual reproduction in many plant species. Many plants, such as ginger, onion, and dahlia, grow from buds present on the stem’s surface.
What are the functions of the stem?
The stem performs many important functions that help plants to grow and survive. To provide mechanical support to the leaves and reproductive organs and transport of water and nutrients are the primary functions of the stem of the plant.
What is a non-green underground stem with distinct nodes and internodes and dry, scaly?
Rhizome: is a non-green underground stem with distinct nodes and internodes and dry, scaly leaves at the nodes. It grows horizontally or obliquely. Rhizomes store plant nutrition in the form of proteins and starches. Example: Ginger.
What is a stolon stem?
Stolon: It grows above ground for some time and then bends towards the ground until it touches the ground. Stolon arises from the lower part of the main axis. Example: Jasmine, colocasia, etc. Sucker: The sucker stem is very similar to the stolon, but it grows obliquely upwards and gives rise to a new plant.
What is the name of the stem of a plant covered by thin sheathing leaf bases of dead leaves called?
Corm: is a short, vertical, swollen underground stem of a plant-covered by thin sheathing leaf bases of dead leaves called scales. These dry leaf bases help protect the stem of the corm from harsh weather conditions and lack of moisture.
What part of a plant is the aerial part?
Except for a few plant stems, most of the stem is the aerial part of a plant, which bears buds, flowers, leaves, and fruits. It is also known as a “central axis” that connects the root system with the rest of the plant body. It is generally erect, strong, and usually grows away from the soil and towards sunlight.
What are the different types of stems?
Types of the Stem. Based on their adaptations, there are three types of stems: Underground stem, Aerial stem, Sub- aerial stem. 1. Underground Stem. The stem that grows inside the soil is known as the underground stem. They produce aerial shoots annually.
What is the stem of a plant?
The plant stem is a component of the shoot system, the portion of the plant body of the angiosperms having a phototropic response.
What is the function of the main stem?
1. It supports the leaves, flowers, and fruits and connects them with the roots. In trees and shrubs, the main stem or trunk provides a strong columnar structure from which branches are attached, raising the leaves upward to be exposed more fully to the sun.
What is a bud in plants?
A bud is an embryonic stem that has the potential for further plant growth. It may develop into a leaf, flower, or both. Such buds are called leaf buds, flower buds, and mixed buds, respectively. Many buds remain dormant within a certain duration or they may be embedded in the stem tissue as to become hardly visible. A single bud that is found at the apex of the stem is called terminal bud while lateral buds or axillary buds occur in the leaf axils, the upper angle between the stem and leaves. As a result of injury, adventitious buds may be formed also in the internode of the stems, in leaves, or roots. The “eyes” of the potato tuber are buds.
What is an offset stem?
Offshoot is a collective term for the short, thickened lateral shoot or branches with multiple nodes and having a rosette-like appearance, growing out of the main stem in certain plants. They are variously called offsets, suckers, slips, pips, etc. A stolon is a stem that grows horizontally along the ground (e.g. Bermuda grass, zoysia grass, mint). A runner is a stolon having long internodes which originate at the base of the crown of the plant (e.g. strawberry). A spur is a stem in woody plants with greatly shortened internodes and restricted growth. They appear laterally on branches. In apple and grape, the production of fruits is largely confined to the spurs. A crown is a compressed stem from which new shoots arise. They are generally found near the surface of the soil (e.g. strawberry, African violet).
What are the nodes of angiosperms?
All stems of the angiosperms, including those which are highly modified, are recognizable from other plant organs by their presence of nodes, internodes, buds, and leaves . A node is a point on the stem from which leaves or buds arise. The portion between two successive nodes is the internode.
What is the stem of a grass plant called?
In grass plants like rice, corn, and bamboo which belong to the botanical family Gramineae or Poaceae, the main stem is specially called a culm. Culms are either hollow or solid stems with pronounced nodes and internodes.
What are the scars on the leaves of a woody stem?
In woody stems, the following plant structures may be present in addition to the leaves and buds: leaf scars after the leaves fall, at the point of attachment of the leaves to the stem; bundle scars, the tiny raised dots in the leaf scars which are broken ends of vascular bundles connecting the stem to the petiole of leaves; bud scars which are small, narrow, circular marks around a twig left by the falling away of the bud scales; twig scars left by the falling away of twigs; and fruit scars where fruits are previously attached.
What is the stem of a plant?
Stem Definition. The stem is the ascending part of the axis that bears the leaves, branches, fruits and flowers. A stem develops from the plumule and epicotyl of the embryo of a germinating seed. It also bears buds which can be terminal or axillary.
What are the different types of stems?
Stems in various plants are modified to carry out various functions such as perennation, vegetative propagation, food storage or synthesis, etc. The stem is mainly classified into three types which are further divided into different groups based on modifications adopted by them. Three types of the stem are: 1 Aerial stem 2 Subaerial stem 3 Underground stem
What are the stem hairs on a flower called?
Flower buds are modified leaves that arise from meristem tissue. The stem bears multicellular stem hairs called trichomes on its external surface for protection and reduces transpiration rate.
What are the functions of stem modifications?
The various forms of modifications can be seen in these three types of the stem to perform many important functions like climbing for support, storage of food, protection, and vegetative propagation. Below are some examples of these modifications in each type:
What is an aerial stem?
A stem with a vertical or upright growth habit above the ground is called the aerial stem. The aerial stems have two forms, i.e. reduced stem and erect stem. Reduced Stems. This type of stem is reduced to a small disc. The nodes and internodes are not distinguished, e.g., carrot, radish, turnip, etc.
What happens to the dormant bud on a stem?
The dormant bud which is present on the stem becomes active and develops lateral branches of vegetative reproduction.
Why are leaves modified?
In xerophytic plants, leaves are modified into scales or spines to reduce transpiration. The stems here become thick, flattened, green, succulent, photosynthetic that helps the plant to grow in dry and xerophytic conditions. They have fleshy internodes and leaves are modified into small scaly leaves or spines.
What is the purpose of the stem in a plant?
One important part of a plant is the stem. The stem is the portion of the plant located above ground that helps to provide support to the flowers, leaves, and buds. Stems also help to transport nutrients and water throughout the plant. As such, stems help to connect the roots with the leaves and flowers (in an angiosperm, or flowering plant). Stems are classified as woody and herbaceous and can come in a variety of forms such as:
What is the internal structure of a plant?
The internal structure of the stem is comprised of the vascular system of the plant. The vascular system represents a system of tubes that help to transport nutrients, organic molecules, and water from the roots to the leaves. There are three main components of the vascular system in plants are xylem, phloem, and the vascular cambium.
What is the role of the vascular cambium in stem cell development?
The vascular cambium represents a layer of tissue that separates the phloem from the xylem. Moreover, cambium is responsible for producing new phloem and xylem cells, which help to increase the diameter of the stem.
What are the structures that connect a leaf to its associated node?
Petioles are the structures linking a leaf with its associated node. The internal structures of the stem, including the xylem and phloem extend through the petiole. Some petioles are edible, such as celery and rhubarb. Petioles can be short or long, or not even present at all. Leaves attached to a stem without the petiole are known as sessile.
What is a cross section of the xylem and phloem bundles in?
A cross-section of the xylem and phloem bundles in a monocot.
What is the function of phloem in plants?
The phloem represents the series of tubes carrying nutrients throughout the plant. The distribution of phloem within the stem depends on whether the plant is a monocot or a dicot.
What is the function of a plant node?
A plant node represents a structure responsible for attaching the petiole to the stem. Nodes are often associated with stem locations where leaves and buds grow. Because they are capable of generating a great deal of metabolic activity, nodes help to promote the growth of leaves, secondary stems, and flowers. Only stems are associated with nodes, as these structures are not found elsewhere on the plant. The place where the node attaches the petiole and associated leaf to the stem is known as a leaf axil. Nodes are important landmarks on the plant stem, as they help gardeners to locate the best spot for pruning plants. An experienced gardener or botanist will typically prune the plant a short distance away from a node.
What is the function of stems in plants?
Stem performs much vital work for the whole plant. They support the plant and held up towards the light. Stem acts like the plant’s transportation system. It receives water and minerals from the root and distributes it among all other parts including leaves for the food processor with the help of Xylem tissue.
Where is the root of a plant located?
The root is located below the ground. It helps to anchor the plant to the ground so it does not fall over. It absorbs water and nutrients from the soil and sends it to the stem.
What is the root system?
➤ THE ROOT SYSTEM – It is located below the ground, responsible for absorbing water and minerals from the soil as well as give firmness to the whole plant/tree. The root system includes organs such as the roots, tubers, and rhizomes
Why are leaves called plant food factories?
The leaf is known as a plant food factory because it prepares food for the entire plant through the process of photosynthesis. Under this process, the leaves make glucose, or food, using sunlight, water, chlorophyll and carbon dioxide.
What is the part of a flowering plant that protects the seeds?
A fruit is part of flowering plant which protect the seeds by covering it.
What is the reproductive organ of a plant?
Flowers are the reproductive organ of flowering plants. It makes seeds, which become new plants. Along with reproduction, flowers are also a rich source of food for other living organisms such as insects, birds, animals and humans.
Which part of the cell transports food in the form of glucose produced from photosynthesis?
And then stem transports food in the form of glucose produced from photosynthesis from leaves to other parts such as roots and stems with the help of Phloem tissue.

Overview
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant, the other being the root. It supports leaves, flowers and fruits, transports water and dissolved substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem, stores nutrients, and produces new living tissue.
The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes:
• The nodes hold one or more leaves, as well as buds which can grow into branches (with leaves, c…
Specialized terms
Stems are often specialized for storage, asexual reproduction, protection or photosynthesis, including the following:
• Acaulescent: used to describe stems in plants that appear to be stemless. Actually these stems are just extremely short, the leaves appearing to rise directly out of the ground, e.g. some Viola species.
Stem structure
Stem usually consist of three tissues, dermal tissue, ground tissue and vascular tissue. The dermal tissue covers the outer surface of the stem and usually functions to waterproof, protect and control gas exchange. The ground tissue usually consists mainly of parenchyma cells and fills in around the vascular tissue. It sometimes functions in photosynthesis. Vascular tissue provides long distance transport and structural support. Most or all ground tissue may be lost in woody st…
Relation to xenobiotics
Foreign chemicals such as air pollutants, herbicides and pesticides can damage stem structures.
Economic importance
There are thousands of species whose stems have economic uses. Stems provide a few major staple crops such as potato and taro. Sugarcane stems are a major source of sugar. Maple sugar is obtained from trunks of maple trees. Vegetables from stems are asparagus, bamboo shoots, cactus pads or nopalitos, kohlrabi, and water chestnut. The spice, cinnamon is bark from a tree trunk. Gum arabic is an important food additive obtained from the trunks of Acacia senegal trees. Chicle, the …
Further reading
• Speck, T.; Burgert, I. (2011). "Plant Stems: Functional Design and Mechanics". Annual Review of Materials Research. 41: 169–193. Bibcode:2011AnRMS..41..169S. doi:10.1146/annurev-matsci-062910-100425.
External links
• Media related to Plant stems at Wikimedia Commons