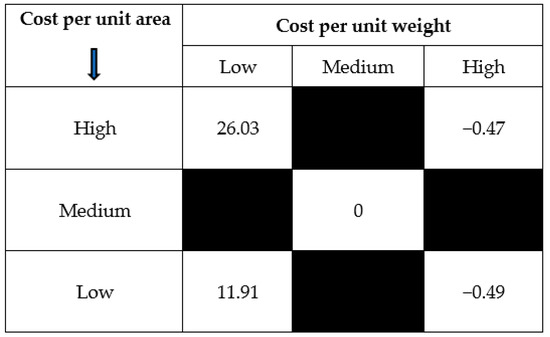
Stock-out Costs are the costs associated with the lost opportunity caused by the exhaustion of the inventory. The exhaustion of inventory could be a result of various factors. The most notable amongst them is defective shelf replenishment practices.
What is stock-out costs?
What is Stock-Out Costs? Stock-out Costs are the costs associated with the lost opportunity caused by the exhaustion of the inventory. The exhaustion of inventory could be a result of various factors.
How to avoid stock-outs in inventory management?
Effective Inventory management is the solution to avoid stock-outs. Regular audits of the inventory are carried out to check the frequency of stock-outs of different items. Advanced modelling tools and frameworks are used to determine the economic order quantity that will minimize the stock out and also the inventory carrying cost.
What are the costs associated with inventory management?
These expenses arise from keeping products shelved at a warehouse, distribution center or store and include storage, labor, transportation, handling, insurance, taxes, item replacement, shrinkage and depreciation. Opportunity cost —the investment possibilities a company must decline because its resources are tied up in inventory—is also a factor.
What happens when a customer has a stockout?
Customer cancels the order, and is no longer a customer - This is the worst-case scenario of a stockout. However, if a customer is unhappy with the communication or information supplied by the vendor then they may be willing to cut all ties and work with another vendor.
What is inventory stock out?
In ecommerce fulfillment a stockout occurs when customer orders for a product exceed the amount of inventory that is available on hand. This usually happens when demand for products is higher than expected, and the amount of inventory and safety stock is too low to fill all orders.
How is stock out calculated?
To calculate the stock out probability, simply divide the number of stock outs by the number of demand requests, then multiply by 100.
What stockout means?
a situation in which there are no goods of a particular kind available for sale: There were stockouts of the product at some locations over the summer. Can the retail industry really afford stockouts? More examples. Safety stock is stock needed to prevent a stockout.
Why do we have stock outs?
Stock-outs are caused by the following, the most significant being listed first: Under-estimating the demand for a product and, therefore, under ordering. Late delivery by a supplier. You ordered enough, but your supplier did not deliver when expected or only delivered part of your order.
How do you prevent stock out?
How to reduce stock levels and avoid stock outs.Master your lead times.Automate tasks with inventory management software.Calculate reorder points.Use accurate demand forecasting.Try vendor managed inventory.Implement a Just in Time (JIT) inventory system.Use consignment inventory.Make use of safety stock.More items...
What is meant by stock out costs?
A stockout is when inventory becomes unavailable, preventing an item from being purchased or shipped, resulting in a loss in sales. Stockout costs include the loss of income and customers due to a shortage of inventory from a stockout.
What is stock out cost example?
Examples of stock-out costs are: Lost contribution through the lost sale caused by the stockout. Loss of future sales as customers go elsewhere. Loss of customer goodwill.
What is a stock out in supply chain?
Stockouts are what happen when you run out of inventory of a particular item. An out-of-stock can happen anywhere in the supply chain, but it impacts retailers' shelves and profits the most when it occurs as the customer is about to purchase.
What is stockout in manufacturing?
The basic scenario for a stockout is when an item that is to be used for a customer's order or for a production order is not in stock when required. If an item is not available for manufacturing then it may be possible to change the production schedule, although there is a significant cost in this due to the changes in a machine, teardown costs, ...
What is the worst outcome of stockout?
Losing a customer to a stockout is the worst outcome, and comes with it the highest cost to the vendor. By a customer no longer placing any order with a vendor, every order is a cost that has to be considered. If a customer was a major purchaser of goods then the cost could be severe and put the vendor in financial difficulty.
What happens if you stock out?
Effects of a Stockout 1 Customer agrees to wait for the item - If the item is vital to the customer, then they may be prepared to wait. Despite the goodwill of the customer, there may be significant damage to the customer's satisfaction level. 2 Customer backorders the item - Not as ideal as when the customer agrees to wait for the order to be complete, but the order is still being fulfilled. Nevertheless, the customer's satisfaction level is still significantly reduced. 3 Customer cancels the order - If the customer is able to obtain the item from another vendor or does not need the item immediately, then the customer can cancel the order. It is still possible that the customer will order from you in the future, but their customer satisfaction level has been damaged. 4 Customer cancels the order, and is no longer a customer - This is the worst-case scenario of a stockout. However, if a customer is unhappy with the communication or information supplied by the vendor then they may be willing to cut all ties and work with another vendor.
What happens if you cancel an order due to stockout?
If a customer decides to cancel their order due to the stockout then they have probably found an alternate vendor for the item. Many companies will ensure that they have more than one source of supply for their key items; therefore, it may be easier to order from the alternate than to wait for the order to be completed.
What does "no inventory" mean?
This means that with no inventory of a certain item, production has to be stopped or a customer order will not be fulfilled. For a warehouse or inventory manager it is a scenario that they most dread and with it comes a significant cost to the company. An optimized supply chain will help you supply your customers with what they want, ...
Why is there an increase in shipping costs?
There are increased order processing costs as the customer service staff amends the order to create a new suitable delivery date. In addition, there may be additional shipping charges if the order was part of a larger delivery, then the backorder will require special transportation.
What is the best way to avoid stock outs?
Stock-outs could occur at any point of the supply chain. Effective Inventory management is the solution to avoid stock-outs. Regular audits of the inventory are carried out to check the frequency of stock-outs of different items.
Is stock outs costly?
Stock-outs could prove to be very costly for the companies. The subtle responses could be postponement of purchase. The more disastrous ones are the consumers may get frustrated and switch stores or even purchase substitute items (brands).
What is stockout in online stores?
A stockout is an event in which inventory is currently unavailable, preventing an item from being purchased or shipped. For online stores, a stockout can cause a lot of frustration for the customer especially if there is no indication on when the item will be back in stock and available for purchase.
How does stockout affect your business?
Stockouts can significantly impact a customer’s experience and they are something you will want to focus on avoiding at all costs. Stockouts create disappointment and frustration not only for you as a business owner but for the customer who is ready to buy and may need your product quickly.
Why do stockouts happen?
What causes stockouts. Stockouts happen for a variety of reasons. Factors such as underestimating customer demand, major supplier delays, and a lack of funds to purchase new inventory can all lead to products being out of stock. Many times, stockouts are inevitable and out of your control. For instance, production delays, delivery issues, unpaid ...
What is safety stock?
Safety stock is the excess product you keep on hand in case of an emergency or retail supply chain failure that causes a drop in inventory levels. To accurately calculate safety stock, you will need the following for each SKU:
Why is it important to keep products in stock?
But if products are constantly out of stock, it can cause a big dip in potential sales, drive customers away, and ultimately stunt business growth. In this article, we’ll go over what causes stockouts and how to prevent them from impacting long-term ...
What happens if you have a stockout?
If you have a stockout, not only will you see a major drop in conversions because there’ s nothing to buy, but the customer will most likely purchase from a competitor that has the item currently in stock. And they may continue to purchase from the competition again in the future.
Can you use historical inventory data to predict future sales trends?
By using historical inventory data to predict future sales trends, you can make better decisions on how much inventory you need in stock at a given time.
Ordering Cost
Cost of procurement and inbound logistics costs form a part of Ordering Cost. Ordering Cost is dependant and varies based on two factors - The cost of ordering excess and the Cost of ordering too less.
Carrying Cost
Inventory storage and maintenance involves various types of costs namely:
Inventory Storage Cost
Inventory storage costs typically include Cost of Building Rental and facility maintenance and related costs. Cost of Material Handling Equipments, IT Hardware and applications, including cost of purchase, depreciation or rental or lease as the case may be.
Cost of Capital
The inventory storage costs as well as cost of capital is dependant upon and varies with the decision of the management to manage inventory in house or through outsourced vendors and third party service providers.
What are the main categories of inventory related costs?
Ordering, holding, carrying, shortage and spoilage costs make up some of the main categories of inventory-related costs. These groupings broadly separate the many different inventory costs that exist, and below we will identify and describe some examples of the different types of cost in each category.
What are the types of costs?
Let's look at types of costs : 1. Ordering Costs. Ordering costs include payroll taxes, benefits and the wages of the procurement department, labor costs etc. These costs are typically included in an overhead cost pool and allocated to the number of units produced in each period. Transportation costs.
What happens if an organization does not maintain reorder levels?
As an example, an organization that does not maintain re-order levels and minimum order quantity levels for its stock items will always end up ordering stocks at the wrong time and with the incorrect quantity. This will thus result in higher inventory carrying costs.
What is stock ageing report?
Another essential element is stock ageing reports, which gives a good insight into which inventory has been lying with for the longest time.Regular analysis of this report can provide us with a good understanding of which inventory to keep in our warehouses and the quantum of these stocks.
How long does it take for product X to arrive in warehouse?
Product X takes 10 days to reach the warehouses after ordering. In order to fulfill orders, there must be the stock that lasts until at least 10 days in the inventory at all times. That means there must be at least 30 units of Product X, which will last 10 days, after which the stock gets replenished.
Does keeping stocks in stock hurt the cost?
Since these stocks' value is low, keeping them in stock will not hurt the costs much. But a good strategy would be to estimate their lead time, per day sales, and keep at least as much stock as is required till the lead time.
Is inventory holding cost a rental expense?
The inventory holding costs does show up as part of rental expense in the Profit & Loss statement. While the inventory carrying cost is seldom considered while calculating the gross profit, we usually take into account only the principle cost of the goods held in the warehouses.
What is inventory carrying cost?
Inventory carrying costs are a crucial metric that helps determine whether you’re running an efficient operation. High carrying costs could mean your organization has more inventory on hand than it needs based on demand, that you need to adjust the frequency with which you place orders with manufacturers or distributors or that you could do better at keeping stock moving.
How does obsolete inventory affect the market?
Organizations can minimize obsolete inventory by finding ways to offload stock while it still has some value, perhaps through deep discounting, donating it or by selling it to a liquidator. Otherwise, you’ll likely pay to dispose of it.
Why do companies need to measure their inventory carrying costs?
Companies need to regularly measure their inventory carrying costs to find out if holding costs represent a disproportionate amount of inventory value. This calculation will help businesses determine when they need to reevaluate their processes and practices.
What is inventory turnover ratio?
Inventory turnover ratio is a critical metric that shows how often certain products are sold and restocked over one year. This ratio informs purchasing decisions. A low turnover ratio for too many products leaves an organization with high inventory carrying costs and, eventually, obsolete inventory. That creates an overstuffed warehouse packed to the brim with stock that is neither moving quickly nor as valuable as it once was.
How does holding costs affect business?
Because holding costs may make up one quarter of all inventory spend, they can affect a business’ overall financial health. If an organization can’t quantify the cost of keeping stock on hand, such as by employing an inventory or stock control system, it may end up with cash flow problems.
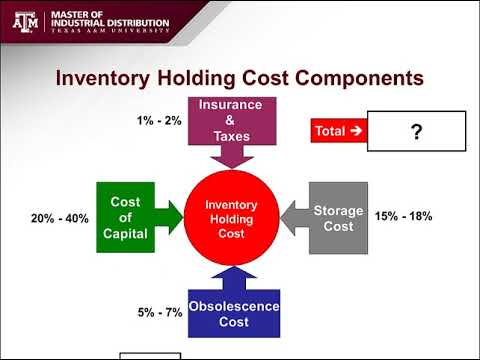
What are the four categories of inventory carrying costs?
Inventory carrying costs can be sorted into four categories: capital costs, storage costs, service costs and inventory risk costs . Capital expenditures are monies spent on products and any interest and fees incurred if the company took out a loan to pay for the goods.
What is dead inventory?
“Dead inventory” is another term for obsolete inventory. These are goods a company no longer believes it can sell and that are often written-off as a loss. Dead inventory may linger in a distribution center or the back room, quietly and continually raising inventory carrying costs without leaders even realizing it.