
- Stockholders' equity is the value of a business's assets that remain after subtracting liabilities.
- This amount appears in the firm's balance sheet as well as the statement of stockholders' equity.
- For most companies, higher stockholders' equity indicates more stable finances and more flexibility in case of an economic or financial downturn.
How do you calculate stockholders equity?
Stockholders' equity is the remaining amount of assets available to shareholders after paying liabilities. Learn how to calculate stockholders’ equity.
How to calculate stockholder equity?
Stockholder's equity is calculated by subtracting a corporation's liabilities from its assets. Use the following equation to calculate stockholder's equity: Total assets - total liabilities = stockholder's equity. Stockholder's equity can also be calculated by taking the sum of share capital and retained earnings and deducting treasury stock.
What are the basic sources of stockholders equity?
What Are the Two Main Sources of Stockholders' Equity?
- Paid-in Capital. One of the two main sources of stockholders' equity is paid-in capital. ...
- Retained Earnings. Retained earnings are the other main source of stockholders' equity. ...
- Other Sources. In addition to paid-in capital and retained earnings, there are other sources of stockholders' equity.
- Warning: Stockholders' Equity Can Drop. ...
How is stockholders equity calculated?
- Shareholder’s equity = Total assets – Total liabilities
- = $3,000,000 – $2,200,000
- = $800,000
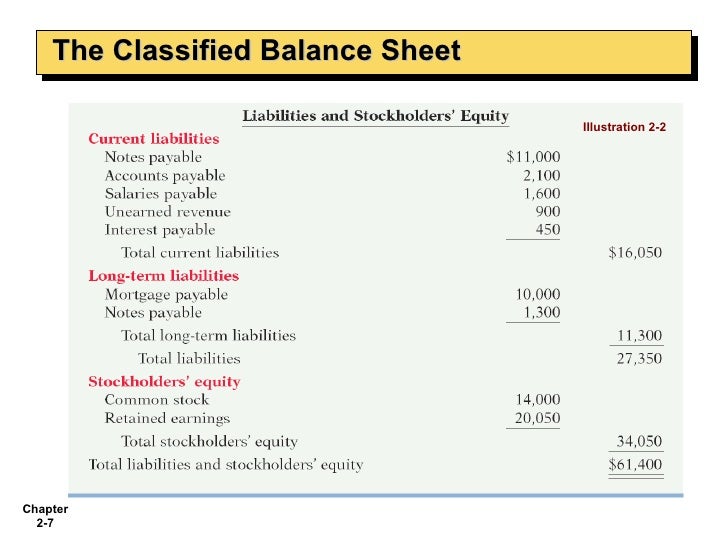
What is included in stockholders equity?
Four components that are included in the shareholders' equity calculation are outstanding shares, additional paid-in capital, retained earnings, and treasury stock. If shareholders' equity is positive, a company has enough assets to pay its liabilities; if it's negative, a company's liabilities surpass its assets.
What is considered stockholders equity on a balance sheet?
Key Takeaways. Shareholder equity is the owner's claim after subtracting total liabilities from total assets. You can calculate shareholder equity by adding together all assets and all liabilities from a company's balance sheet.
Is stockholders equity an asset on the balance sheet?
Stockholders' equity is the value of a company's assets that remain after subtracting liabilities and is located on the balance sheet and the statement of stockholders' equity.
Is stockholders equity the same as owner's equity?
It is calculated by deducting the total liabilities of a company from the value of the total assets. Shareholder's equity is one of the financial metrics that analysts use to measure the financial health of a company and determine a firm's valuation. Shareholder's Equity = Owner's Equity (they're the same thing).
Is stockholders equity a debt?
While preferred stock exhibits characteristics of both debt and equity products, there is little room for overlapping between the two. As a result, stockholder's equity is not debt. Additionally, most savvy investors look for a company with both debt and equity on the balance sheet.
Why is stockholder equity important?
For most companies, higher stockholders' equity indicates more stable finances and more flexibility in the case of an economic or financial downturn. Understanding stockholders' equity is one way investors can learn about the financial health of a firm.
Why do stockholders have higher equity?
Stockholders' equity increases when a firm generates or retains earnings. This helps balance debt and absorb surprise losses. For most firms, higher owners' equity means a larger cushion. This provides more flexibility to recover in the event that the firm experiences losses or must take on debt.
What is balance sheet?
A balance sheet provides a snapshot. It tells you about a company's assets, liabilities, and owners' equity at the end of a reporting period. Shareholders' equity on a balance sheet is adjusted for a number of items. For instance, the balance sheet has a section called "Other Comprehensive Income.".
Is the balance sheet at the bottom or top?
Some balance sheets will list assets at the top, then liabilities; finally, stockholders' equity is at the bottom. 1. In either case, total assets should equal the total liabilities plus owners' equity. A balance sheet provides a snapshot. It tells you about a company's assets, liabilities, and owners' equity at the end of a reporting period.
How to understand stockholders equity?
The easiest way to understand stockholders' equity is to see it as what's left over when you take the rest of the balance sheet into account. A company's assets are usually straightforward to understand, and the liabilities it owes to others are real obligations that help the company in its business pursuits.
Why is it important to look at a balance sheet?
Looking at a balance sheet might not sound like the most interesting thing to do, but it can greatly enhance your understanding of companies in which you invest. Learning what stockholders' equity is and what goes into it will help you gain insight into how companies become successful.
What is left on a balance sheet?
Mathematically, when you take the value of a company's assets and subtract out the value of its liabilities, what's left is stockholders' equity. On the balance sheet, what gets listed as stockholders' equity typically falls into two categories.
Does retained earnings show up in income statement?
If a company has unrealized gains and losses on its income statement, they will often show up not in Retained Earnings but rather in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income. However, those figures tend to cancel each other out, while Retained Earnings steadily rises in most successful companies.
Do investors ignore financial statements?
Many investors almost completely ignore the financial statements that companies report. Yet it's important to understand the ins and outs of companies in which you invest, and knowing the basics of the balance sheet is a great way to start. In particular, the concept of stockholders' equity carries clues to the true value of a company.
What is stockholders equity?
Stockholders' equity, also referred to as shareholders' or owners' equity, is the remaining amount of assets available to shareholders after all liabilities have been paid. It is calculated either as a firm's total assets less its total liabilities or alternatively as the sum of share capital and retained earnings less treasury shares.
What is equity in accounting?
Equity, also referred to as stockholders' or shareholders' equity, is the corporation's owners' residual claim on assets after debts have been paid.
What is the source of total stockholders' equity?
Investors contribute their share of (paid-in) capital as stockholders, which is the basic source of total stockholders' equity.
What is retained earnings?
Retained earnings (RE) are a company's net income from operations and other business activities retained by the company as additional equity capital. Retained earnings are thus a part of stockholders' equity. They represent returns on total stockholders' equity reinvested back into the company.
What does it mean when stockholders' equity is negative?
If this figure is negative, it may indicate an oncoming bankruptcy for that business, particularly if there exists a large debt liability as well.
What does it mean when a company has a positive equity?
Positive equity indicates the company has a positive worth . A company's share price is often considered to be a representation of a firm's equity position.
What is total assets?
All the information required to compute shareholders' equity is available on a company's balance sheet. Total assets include current and non-current assets. Current assets are assets that can be converted to cash within a year (e.g., cash, accounts receivable, inventory).
Classification
It is also known as the equity of owners or shareholders. The balance sheet and financial statements of a company, together with assets and liability, have all the information available. Stockholders’ shareholdings illuminate the qualities and the structure of a company’s economic stability.
Recognition
Typically, a company’s balance sheet contains two columns, one on the left, which lists the enterprise’s assets, and one on the right, which shows its liabilities and equity. Some balance sheets list the most important assets, next liabilities, and ultimately in the lower section, shares of the shareholders.
Debt vs Equity
In contrast to creditors, shareholders cannot request payments during tough periods, which permit an enterprise in financial downturns to commit its resources to meet its financial liabilities to creditors. Sometimes, but not usually, lower equities are a hint that a company needs to cut its debts.
Making the Investment Decision
The shareholders’ equity is not the only factor you should evaluate while making investing selections. In the financial statements of a corporation, a single item of data cannot tell you if this is a good risk or not. A balance sheet review of the equity of shareholders allows for more intelligent investments. But you must also consider:
Conclusion
Equity is the value of an asset of an undertaking that remains after the obligations are removed or its net value. This figure is included in the company’s balance sheet and also the equity statement.
What is stockholders equity?
Stockholders' equity (also known as shareholders' equity) is reported on a corporation's balance sheet and its amount is the difference between the amount of the corporation's assets and its liabilities.
What is Treasury stock?
Treasury stock. This is a reduction of stockholders' equity for the amount the corporation paid to purchase but not retire its own shares of capital stock. The changes which occurred in stockholders' equity during the accounting period are reported in the corporation's statement of stockholders' equity.
Is stockholders' equity a source of assets?
In other words, stockholders' equity is one source of the corporation's assets. (The other source are the corporation's creditors as evidenced by the liabilities.) Stockholders' equity and liabilities are also seen as the claims to the corporation's assets. However, the stockholders' claim comes after the liabilities have been paid.
What is stockholders equity?
Stockholders' equity (aka "shareholders' equity") is the accounting value ("book value") of stockholders' interest in a company. Keep in mind, the shareholders' interest is a residual one: Creditors have first claim on a company's assets. You get a sense of that priority of claims in the following expression of the basic accounting equation:
What are the components of stockholders' equity?
Assuming a company has any operating history whatsoever, the two basic components of stockholders' equity are: Paid-in capital. Retained earnings. Paid-in capital. As the name suggests, paid-in-capital (or 'contributed capital') is the money the company has raised from investors through the sale (s) of its stock.
What is Treasury stock?
Treasury stock#N#Treasury stock is created when a company repurchases its own common or preferred shares and holds them in treasury instead of retiring them. Treasury stock is issued, but not outstanding; it has no voting rights and does not receive dividends (for reporting purposes, retired shares are treated as authorized, but not issued). A company can hold treasury stock for multiple purposes: 1 To distribute to employees as part of a stock option plans. 2 To maintain control and ownership, for example to fend off a hostile takeover bid.
What is the major source of change in a company's equity?
Excluding these transactions, the major source of change in a company's equity is retained earnings, which are a component of comprehensive income. However, there are other sources and thus, ...
What is par value in stock?
The par value of issued stock is an arbitrary value assigned to shares in order to fulfill state law. The par value is typically set very low (a penny per share, for example) and is unrelated to the issue price of the shares or their market price.
What is retained earnings?
As the name suggests, retained earnings is the cumulative amount of net income the company has earned from the time it was created that it has not distributed to shareholders as dividends. Losses are included in the calculation, too: they subtract from retained earnings.
Is Treasury stock an asset?
Treasury stock is not an asset, it's a contra-stockholders' equity account, that is to say it is deducted from stockholders' equity. Treasury stock is most often carried on the balance sheet at cost. Here is Amazon.com 's stockholders' equity from its 2014 year-end balance sheet: Source: Amazon.com.
What is balance sheet?
In simple words, balance sheet gives the financial position of a company at the end of a given time period. It is one of the important financial statements for a company. It is referred by accountants and business owners at any point of time to get an understanding of the company’s financial position.
What are the accounts on an income statement?
Income statement accounts include revenue, gain, expense, and loss. Revenue and gain are supposed to increment a stockholders’ equity, whereas expense and loss are supposed to have reverse impact on a stockholders’ equity. If a company does an operation that results in an increase in its assets, then there is an increase in stockholders’ equity. This increase in stockholders’ equity takes place at the end of an accounting year only when the service revenue account is close to the stockholders’ equity.
What is shareholder equity?
Shareholders’ equity refers to the owners’ claim on the assets of a company after debts have been settled. It is also known as share capital. Share Capital Share capital (shareholders' capital, equity capital, contributed capital, or paid-in capital) is the amount invested by a company’s. , and it has two components.
How to calculate shareholder equity?
Shareholders’ equity is the shareholders’ claim on assets after all debts owed are paid up. It is calculated by taking the total assets minus total liabilities. Shareholders’ equity determines the returns generated by a business compared to the total amount invested in the company.
What is the difference between a positive and negative shareholder equity?
A negative shareholders’ equity means that shareholders will have nothing left when assets are liquidated and used to pay all debts owed. On the other hand, positive shareholder equity shows that the company’s assets have been grown to exceed the total liabilities, meaning that the company has enough assets to meet any liabilities that may arise.
What is dividend policy?
Dividend Policy A company’s dividend policy dictates the amount of dividends paid out by the company to its shareholders and the frequency with which the dividends are paid. by showing its decision to pay profits earned as dividends to shareholders or reinvest the profits back into the company. On the balance sheet, shareholders’ equity is broken ...
How to find total liabilities?
Total liabilities are obtained by adding current liabilities and long-term liabilities. All the values are available in a company’s balance sheet. What remains after deducting total liabilities from the total assets is the value that shareholders would get if the assets were liquidated and all debts were paid up.
What is the share capital method?
The share capital method is sometimes known as the investor’s equation. The above formula sums the retained earnings of the business and the share capital and subtracts the treasury shares. Retained earnings are the sum of the company’s cumulative earnings after paying dividends, and it appears in the shareholders’ equity section in the balance sheet.
How to find return on equity?
It is obtained by taking the net income of the business divided by the shareholders’ equity. Net income is the total revenue minus expenses and taxes that a company generates during a specific period.

Classification
Measurement
Recognition
Debt vs Equity
- It is also known as the equity of owners or shareholders. The balance sheet and financial statements of a company, together with assets and liability, have all the information available. Stockholders’ shareholdings illuminate the qualities and the structure of a company’s economic stability. Achieving a balance sheet understanding of equities is on...
Making The Investment Decision
- There are usually three main origins of equity: 1. In exchangefor the issuance of common equity shares or preference shares when the company raises capital, cash or any other assets paid to the company. 2. Excess pay-in:Investors’ capital contributed in return for stock, not the equity earned because of income or gifts (also known as paid-in capital). 3. Retained earnings:Accumu…
Conclusion
- Typically, a company’s balance sheet contains two columns, one on the left, which lists the enterprise’s assets, and one on the right, which shows its liabilities and equity. Some balance sheets list the most important assets, next liabilities, and ultimately in the lower section, shares of the shareholders. Entire assets should, in any event, equal the total liabilities plus equity of the s…