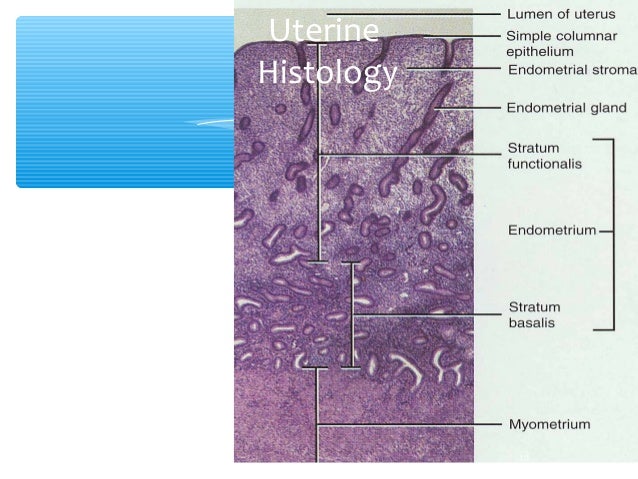
Stratum Functionalis - thick superficial inner layer that is sloughed off during menstruation and grows anew during each cycle. Supports implantation and growth of fertilized egg. Stratum Basalis - outer layer of endometrium, serve as source for cells during regrowth of the superficial stratum functionalis.
Where is the stratum functionalis located?
What are the two layers of the endometrium?
About this website
What is the function of stratum Functionalis?
The stratum functionalis is the layer that will host the fertilized egg.
What is stratum basalis and Functionalis?
The endometrium itself is divided into two layers, the stratum functionalis and stratum basalis. During the menstrual cycle, the stratum functionalis expands and vascularizes and is subsequently sloughed off during the process of menstruation, whereas the stratum basalis remains relatively constant.
What regenerates the stratum Functionalis?
The uterine wall is composed of three layers: Endometrium - specialized mucosa that undergoes marked changes during the menstrual cycle. Functional Layer (or stratum functionalis) - upper two thirds that regenerates from cells in the basal layer under the influence of estrogen.
What are the three layers of the uterine?
The uterus has three tissue layers which include the following:Endometrium: the inner lining and consists of the functional (superficial) and basal endometrium. ... Myometrium: the muscle layer and is composed of smooth muscle cells.Serosa/Perimetrium: the thin outer layer composed of epithelial cells.
Where is the stratum Functionalis functional layer of the uterus?
The uterine wall is composed of three layers: Endometrium - specialized mucosa that undergoes marked changes during the menstrual cycle. Functional Layer (or stratum functionalis) - upper two thirds of the mucosa that contains the glands.
What are the 3 layers of the myometrium?
The layers are three in number: external, middle, and internal. The external and middle layers constitute the muscular coat proper, while the inner layer is a greatly hypertrophied muscularis mucosæ. During pregnancy the muscular tissue becomes more prominently developed, the fibers being greatly enlarged.
What happens to the stratum Functionalis of the endometrium during menstruation?
The endometrium itself is divided into two layers, the stratum functionalis and stratum basalis. During the menstrual cycle, the stratum functionalis expands and vascularizes and is subsequently sloughed off during the process of menstruation, whereas the stratum basalis remains relatively constant.
Which type of arteries supply the stratum Functionalis?
R: Straight arterioles supply blood to the stratum functionalis. A: Stratum basalis lines the uterine cavity and sloughs off during menstruation. R: Straight arterioles supply blood to the stratum functionalis.
During which phase of the uterine cycle will stratum Functionalis develop with?
The proliferative phaseproliferative (preovulatory) phase. The proliferative phase is regulated by estrogens. During this phase, the stratum functionalis is rebuilt. Epithelial cells in the basal portion of the glands reconstitute the glands and migrate to cover the denuded endometrial surface.
What two strata are in the endometrium?
The endometrium is functionally subdivided into two layers.The stratum functionalis is a thick superficial layer that is sloughed off during menstruation and grows anew during each cycle. ... The stratum basalis consists of permanent stromal tissue and deep ends of the uterine glands.
What are the four basic types of uterus?
In mammals, the four main forms of the uterus are: duplex, bipartite, bicornuate and simplex. There are two wholly separate uteri, with one fallopian tube each.
What is the inner layer of the uterus called?
endometriumThe uterus has a muscular outer layer called the myometrium and an inner lining called the endometrium.
What is a stratum Basalis?
The stratum basalis is the bottommost layer of the epidermis, adjacent to the dermis, and it is the location of most mitotic activity in the epidermis under basal conditions, which can be seen with Ki-67 or tritiated thymidine staining.
What are the 3 layers of the uterus and what is their purpose?
Perimetrium: The outermost, protective layer. Myometrium: The highly muscular middle layer. This is what expands during pregnancy and contracts to push your baby out. Endometrium: The inner layer or lining of your uterus (uterine lining).
What is the function of the stratum basalis?
Hint: The stratum basalis layer is the deepest tissue of the endometrium and is adjacent to the myometrium. It's the constant layer of endometrium that doesn't undergo conformational changes during the uterine cycle and its purpose is to exchange tissue loss during menstruation.
What is stratum basale?
Stratum basale, also known as stratum germinativum, is the deepest layer, separated from the dermis by the basement membrane (basal lamina) and attached to the basement membrane by hemidesmosomes.
The Hormones of the Placenta - Lander College for Men
36 Shay to two layers. These layers include the cytotrophoblast and the syncytiotrophoblast (Carlson, 2004). The cytotrophobast, which is the inner layer, consists of mononucleated cells that migrate
Differences between Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis - VEDANTU
Learn Differences between Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis topic in Biology in details explained by subject experts on vedantu.com. Register free for online tutoring session to clear your doubts.
Where is the stratum functionalis located?
The stratum functionalis is adjacent to the uterine cavity, develops from the stratum basalis, and is shed at menstruation.
What are the two layers of the endometrium?
Explanation: The endometrium is composed of two layers: the basal layer or stratum basalis and the functional layer or stratum functionalis . The stratum basalis is adjacent to the myometrium, is not shed at menstruation, and gives rise to the stratum functionalis.
Oviduct
After release from the ovary, the ovum enters the oviduct. The oviduct consists of several segments: the infundibulum, which lies closest to the ovary, followed by the ampulla, the isthmus, and the pars interstitialis.
Oviduct Epithelium
The oviduct epithelium consists of two distinct cell types. The ciliated cells dominate and serve to move the ovum away from the ovary and toward the uterus. The non-ciliated secretory cells, also known as peg cells, release a secretion that lubricates the tube and provides nourishment and protection to the traveling ovum.
Uterus
The uterus is divided into several layers that have distinct structural and functional characteristics. The simplest classification of these layers is their division into a mucosal layer, or endometrium, a muscularis layer, or myometrium, and a serosal layer, or perimetrium.
Uterine Cycle
The endometrium undergoes dramatic structural and functional changes during the menstrual cycle. These changes are divided into two phases: proliferative and secretory.
Proliferative Phase
The proliferative phase is characterized by robust growth of the epithelial cells in the stratum functionalis and the formation of coiled and densely packed glands. This changes in this phase are driven by estrogen.
Secretory Phase
The secretory phase of the uterine cycle begins at ovulation. In this phase, the glands become even more complexly coiled and the endometrial lining reaches its maximal thickness, whereas the stratum basalis and myometrium remain relatively unchanged. Note the saw-toothed appearance of the glands.
Menstrual Phase
If fertilization does not occur, the placental tissue does not produce hCG and the corpus luteum degenerates. The uterine lining does not receive the progesterone, causing the spiral arteries constrict and the endometrial tissue to become ischemic. This causes cell death and the sloughing of the stratum functionalis.
What happens if the endometrium doesn't shed?
If pregnancy doesn’t occur, the endometrium sheds in a process known as menstruation . If conception takes place, the embryo implants into the endometrium. Conditions that involve the endometrium and may impact fertility include: Adenomyosis. Asherman’s syndrome ( uterine adhesions) Endometrial cancer.
How does the endometrium work?
The serosa is the outer skin of the uterus. It secretes a watery fluid to prevent friction between the uterus and nearby organs. The myometrium is the middle uterine layer.
What is the inner lining of the uterus called?
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. Each month, the endometrium thickens and renews itself, preparing for pregnancy. If pregnancy doesn’t occur, the endometrium sheds in a process known as menstruation .
How to treat adenomyosis?
The primary treatments for adenomyosis have been endoscopic endometrial ablation (which involves the destruction of the endometrium) or hysterectomy (which is the removal of the uterus). Neither of these treatments is appropriate if you still want to have children. For women who want to preserve their fertility, options include: 1 Selective embolization (which is targeted only at the adenomyosis region and not the entire endometrium) 2 Hormonal treatments with GnRH agonists (like Lupron) 3 A combination of hormonal and surgical treatment
What is the myometrium made of?
The myometrium is made up of thick, smooth muscle tissue. During pregnancy, the myometrium expands to accommodate the growing baby. During labor, contractions of the myometrium assist in birth. The endometrium makes up the inner lining of the uterus. It is a mucosal lining and changes in thickness throughout the menstrual cycle.
What is the deepest layer of the endometrium?
The endometrium itself is made up of three layers: Stratum basalis: Also known as the basal layer, this is the deepest endometrial layer that sits against the myometrium. It does not change much throughout the cycle. Think of it as the base from which the changing layers of the endometrium grow.
How to preserve fertility?
There are ways to preserve fertility when the diagnosis is early. For example, hormonal treatment (instead of surgical treatment) of endometrial cancer may better preserve fertility. With conservative surgical treatment, women post-endometrial cancer treatment can have problems with a thin endometrium.
What are spiral arteries?
As they enter the endometrium they run a straight course and supply the stratum basalis and as they enter the superficval layer of the stratume functionalis they become coiled and are called the spiral arteries. The straight arteries do not undergo cyclic changes, and hey supply stable unchanging blood supply to the stratum basalis which does not shed at the menses. The spiral arteries in the startum functionalis on the other hand are subject to significant change with hormonal fluxews. Just before menstruation the spiral arteries coil, and initially vasodialte and then there is an intense vasoconstriction causing ischemia and subsequent ischemia and destruction of the stratum functionalis which sheds as a result.
What is the color of the spiral arteries in the stroma?
A closer view of the endometrium as seen in the premenstrual phase exemplified by the characteristic spiral (helical) arteries running in the stroma (pink) between the simple tubular test tube shaped glands (purple) The spiral arteries supply the functional layer (stratum functionalis deep orange) and the straight arteries supply the basal layer (stratum basalis- light orange). Beneath the basal layer is the myometrium- Subendometrial smooth muscle or junctional zone (dark pink).
What is the relationship between the spiral arteries and the stratum functionalis?
The spiral arteries undergo vasoconstriction at the time of the menses, resulting in ischemia of the stratum functionalis and subsequent shedding of this layer leaving stratum basalis intact.
What is the iliac system?
The Iliac System. The diagram of the blood supply to the uterus in its most basic form and shows the large inflow arteries into the pelvis. The main artery is the aorta which branches into the common iliac arteries which in turn branch into the external and internal iliac arteries. The internal iliac branches into an anterior division ...
Which layer of the endometrium is shed during menstruation?
The superficial layer of the endometrium (functionalis) is shed during menstruation. A basal layer, the basalis is permanent and it regenerates after each menstruation. At the onset of menstruation the spiral arteries coil, and initially vasodialte and then follows an intense vasoconstriction at the time of shedding.
Where does blood come from in the uterus?
The blood supply to the uterus is from the uterine arteries which take their origin from the iliac system. The uterine artery collateralizes with the ovarian artery and there are also rich anastomoses between the left and right sides both anterior to and posterior to the uterus. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved ...
Which artery runs along the lateral wall of the uterus?
The uterine artery runs along the lateral wall of the uterus, and then penetrates the myometrium and divides in general into an anterior and posterior branches. As they course toward th center they are called the arcuate arteries whose direction in general is circumferential around the the uterus.
What is phase 2?
Phase 2 = Proliferative Phase triggered by rising levels of estrogen in the uterus, the endometrium of the uterus grows . The increase in estrogen levels is the cause of the thickening of the endometrium.
What causes the endometrium to proliferate?
The increasing levels of estrogen cause the endometrium of the uterus to proliferate and develop the functional layer of the endometrium.
Where are spiral arterioles located?
The spiral arterioles located in the stratum functionalis layer of the endometrium.
Which layer of the endometrium is the source of cells during regrowth?
Stratum Basalis - outer layer of endometrium, serve as source for cells during regrowth of the superficial stratum functionalis.
Which theory of menstruation is more cost effective than maintaining the uterus in fertile form throughout the entire cycle?
Strassman's Menstruation Theory : Energy Conservation - menstruation (lining is shed and then rebuilt for the 2nd half of the cycle) is actually more cost effective than maintaining the uterus in fertile form throughout the entire cycle.
What is the outer layer of the uterus?
Outer Layer = Perimetrium, thin protective layer made of epithelial cells that envelop the uterus
Is endometriosis a fibroids?
Endometriosis symptoms are similar to fibroids in that endometriosis also
Where is the stratum functionalis located?
The stratum functionalis is adjacent to the uterine cavity, develops from the stratum basalis, and is shed at menstruation.
What are the two layers of the endometrium?
Explanation: The endometrium is composed of two layers: the basal layer or stratum basalis and the functional layer or stratum functionalis . The stratum basalis is adjacent to the myometrium, is not shed at menstruation, and gives rise to the stratum functionalis.
