
What is the relationship between granum and stroma?
Main Difference – Grana vs Thylakoid
- What are Grana – Definition, Characteristics, Function
- What is Thylakoid – Definition, Characteristics, Function
- What is the difference between Grana and Thylakoid
What is the difference between thylakoid and stroma?
What are the Similarities Between Grana and Thylakoid?
- Grana and thylakoids are located in the chloroplasts stroma of plant cells.
- Both are microscopic structures.
- Both are membranous structures.
- Both structures contain chlorophylls (plant pigments) for photosynthesis.
- Both structures involved in the light reaction of Photosynthesis
Is Stroma the same as mesenchyme?
Stromal cells, or mesenchymal stromal cells, are differentiating cells found in abundance within bone marrow but can also be seen all around the body. Stromal cells can become connective tissue cells of any organ, for example in the uterine mucosa ( endometrium ), prostate, bone marrow, lymph node and the ovary.
Does Granum or stroma contain pigments?
The stroma first begins to play a role in photosynthesis when the light energy captured by pigment molecules is converted into chemical energy through an electron transport chain. Photosystems I and II (PSI and PSII) on the thylakoid membrane contain pigments that can harness light energy and use it to release high energy electrons.
What is a stroma?
Definition of stroma 1a : a compact mass of fungal hyphae producing perithecia or pycnidia. b : the colorless proteinaceous matrix of a chloroplast in which the chlorophyll-containing lamellae are embedded. 2a : the supporting framework of an animal organ typically consisting of connective tissue.
What is grana and stroma of chloroplast?
Stroma. Grana are made of stacks of thylakoids. Stroma is the fluid present in the chloroplast. Light reactions occur here.
What is stroma thylakoids and grana?
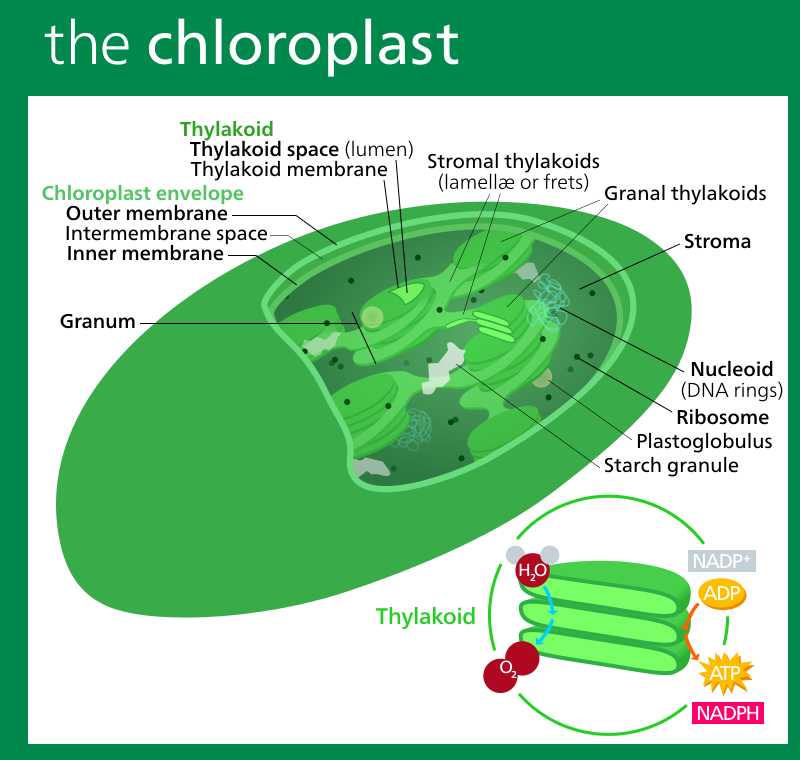
The internal structure of a chloroplast is highly organized. Within it there are closely packed thylakoid membranes. At intervals the thylakoids form tightly stacked regions called grana. A jellylike matrix called the stroma surrounds the thylakoids and grana.
What is grana in a cell?
Granum: (plural, grana) A stacked portion of the thylakoid membrane in the chloroplast. Grana function in the light reactions of photosynthesis. Lamella: A sheet like membrane found within a chloroplast of an autotrophic cell.
What is stroma and grana for Class 9?
Stroma is a matrix present in the chloroplast. It is bounded by a double membranous sheath. It contains a variety of photosynthetic enzymes, starch grains, DNA and ribosomes. Grana are stacks of membrane-bounded, flattened discoid sacs called as thylakoid. It contains chlorophyll molecules.
What is the role of stroma?
The main function of stroma cells is to help support organs and act as connective tissue for particular organs. The connective tissue here connects to the parenchyma cells of things such as blood vessels and nerves. The stroma cells will help to reduce stress over the organ.
Where are grana found?
the chloroplastGrana are found in the stroma of the chloroplast, which is connected by stroma thylakoids. The main difference between grana and thylakoid is that grana are the stacks of thylakoids whereas thylakoid is a membranebound compartment which is found in chloroplast.
What is the grana made of?
… tight stacks called grana (singular granum). Grana are connected by stromal lamellae, extensions that run from one granum, through the stroma, into a neighbouring granum. The thylakoid membrane envelops a central aqueous region known as the thylakoid lumen.
What is the function of thylakoid?
Thylakoids are the internal membranes of chloroplasts and cyanobacteria, and provide the platform for the light reactions of photosynthesis.
What is stroma thylakoid?
The internal (thylakoid) membrane vesicles are organized into stacks, which reside in a matrix known as the stroma. All the chlorophyll in the chloroplast is contained in the membranes of the thylakoid vesicles.
What is ADP and NADP?
ADP - Adenosine diphosphate. NADP - Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. NADPH - The reduced form of NADP. In the Light Dependent Processes i.e Light Reactions, the light strikes chlorophyll a in such a way as to excite electrons to a higher energy state.
What is the role of grana in chloroplast?
The grana in the chloroplast act together as a unit and are interconnected through small tunnels in the lower part of thylakoid stacks called stromal thylakoids. Grana help contribute to the chloroplast's large surface area. They help add more surface area to the thylakoids because they are organized and stacked.
Where are the grana located?
Grana are embedded in the stroma of the chloroplast. Each granum consists of 5-25 disc-shaped thylakoids stacked one on the other resembling a stack of coins. Thylakoids are also called granum lamellae, which encloses a space known as a locus.
What is the diameter of a granum?
Grana: Each granum consists of 5-25 disc-shaped thylakoids stacked one on the other resembling a stack of coins. Each has a diameter of 0.25 – 0.8 μ. Stroma: Fluid-filled matrix containing DNA, ribosomes, enzymes, oil droplets and starch grains.
What are the organelles of the chloroplast?
Chloroplasts are double-membrane organelles and discoid in shape. They are made up of chloroplast membrane, grana, stroma, plastid DNA, thylakoids, and sub-organelles. The key difference between grana and stroma is, grana refers to the stacks of thylakoids embedded in the stroma of a chloroplast while stroma refers to the colorless fluid ...
What enzymes are attached to granal membranes to synthesize ATP molecules?
The ATP synthase enzymes attach to granal membranes help to synthesize ATP molecules by chemiosmosis.
Which organelle houses the sub-organelles of chloroplasts and products of photosynthesis?
Stroma: Stroma houses the sub-organelles of chloroplast and products of photosynthesis and also provides space for the light-independent reaction of photosynthesis. Image Courtesy:
What is the meaning of stroma?
Stroma Definition – Meaning of Stroma. Stroma is the fluid filling up the inner space of the chloroplasts which encircle the grana and the thylakoids. In addition to providing support to the pigment thylakoids, the stroma are now known to contain chloroplast DNA, starch and ribosomes along with enzymes needed for Calvin cycle.
What is the structure of the stroma?
Structure of Stroma – Stroma in Chloroplast. Stroma is made of an outer membrane and a complex network of inner membranes that goes on to form the grana – disc like structures arranged in a stack. Membranous extensions connect various grana together. The inner membranes comprise the constituents involved to harvest light energy such as chlorophyll ...
Why is the stroma important?
For this, the stroma is needed as it contains the enzymes required for carbon fixation along with managing the chloroplast response to cellular stresses and signals between different organelles. Their role is important in both the light-independent and light-dependant reactions of photosynthesis.
Can stroma be autophagous?
The stroma in extreme stressful conditions can experience autophagy selectively without having to destroy the pigment molecules and inner membranous structures. Some stroma appear as finger-like projections and do not have thylakoids. They are linked with endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus conducive to crucial mechanisms.
Does stroma contain ribosomes?
Hence, stroma continues to contain ribosomes and DNA conducting synthesis of proteins. Such proteins are necessary for light-independent reactions of photosynthesis and reactions fixing inorganic materials in organic molecules.
What is the stroma?
Stroma commonly refers to the fluid filled inner space of chloroplasts surrounding thylakoids and grana. Initially, the stroma was thought to simply provide support for the pigmented thylakoids. However it is now known that the stroma contains starch, chloroplast DNA and ribosomes, as well as all the enzymes required for light-independent reactions ...
What is the function of stroma?
The stroma in endocrine glands support the formation of hormones in the follicles and lobules of the organ.
What is the function of the stroma in photosynthesis?
The stroma first begins to play a role in photosynthesis when the light energy captured by pigment molecules is converted into chemical energy through an electron transport chain. Thylakoid membrane. Photosystems I and II (PSI and PSII) on the thylakoid membrane contain pigments that can harness light energy ...
Why is the stroma important?
The stroma is essential for this because not only does it contain the enzymes necessary for carbon fixation, it also manages the chloroplast response to cellular stresses and signaling between various organelles.
What is stroma in animal tissue?
Stroma in Animal Tissue. In animals, stroma refers to those cells and tissues that support the key functional elements of an organ. For instance, in a heart, the muscle fibers and neurons perform the main function, while the cells of the coronary circulatory system and immune system form the stroma.
Why are chloroplasts semi-autonomous?
Chloroplasts are semi-autonomous because they contain their own genome, but also import a number of proteins and small molecules from the cytoplasm of the cell. Though they were initially free-living autotrophs, over evolutionary time, a number of their genes were transferred to the host nucleus.
Which organelle produces growth factors?
The stroma produces growth factors, contains cells involved in bone metabolism, has fat cells as well as macrophages. Macrophages are particularly important because they are involved in the turnover of red blood cells and provide the iron needed for the production of hemoglobin.
Terminology
Structure
Function
Evolution
Reactions
Formation
Applications
Mechanism
Chemistry
Other animals
- In animals, stroma refers to those cells and tissues that support the key functional elements of an organ. For instance, in a heart, the muscle fibers and neurons perform the main function, while the cells of the coronary circulatory system and immune system form the stroma. In addition, stroma also consists of non-cellular components such as colla...