A submandibular space infection is a bacterial infection of the floor of the mouth. Bacteria can spread from an infected lower tooth to the tissue under and around the tongue. People with poor dental hygiene and people who have had a tooth pulled or a jaw fracture are at higher risk.
What is the pathophysiology of submandibular space infections?
As well as occurring secondary to dental infections, submandibular space infections may be a consequence of submandibular gland sialadenitis, lymphadenitis, trauma, or surgery. Furthermore, the submandibular space may be involved secondary to an infection that has developed in other deep neck spaces.
What is the submandibular space?
Submandibular Space. The submandibular space extends from the hyoid bone to the mucosa of the floor of the mouth, and is bound anteriorly and laterally by the mandible and inferiorly by the superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia.
What is the treatment for submandibular space infection?
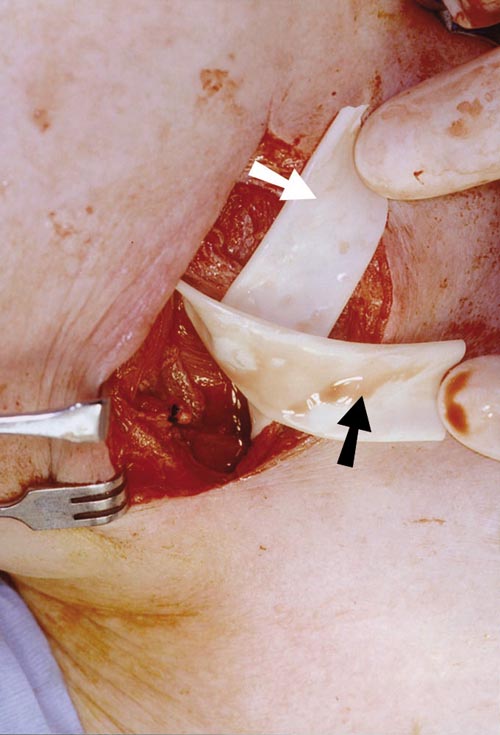
Treatment. Treatment for submandibular space infection must be done quickly to prevent blockage of the airway. Doctors take the person to the operating room and use a fiberoptic scope to help guide a plastic breathing tube through the nose into the windpipe (trachea) to keep the airway open. Then doctors surgically open the infected area...
What is a submaxillary space infection?
The submaxillary space may be further divided into a central submental space, between the anterior bellies of the digastric muscles, and lateral submaxillary spaces.7 As well as occurring secondary to dental infections, submandibular space infections may be a consequence of submandibular gland sialadenitis, lymphadenitis, trauma, or surgery.

What causes submandibular space infection?
A submandibular space infection is a bacterial infection of the floor of the mouth. Bacteria can spread from an infected lower tooth to the tissue under and around the tongue. People with poor dental hygiene and people who have had a tooth pulled or a jaw fracture are at higher risk.
How is submandibular space infection treated?
Treatment includes airway management, surgical drainage, and IV antibiotics. Submandibular space infection is a rapidly spreading, bilateral, indurated cellulitis occurring in the suprahyoid soft tissues, the floor of the mouth, and both sublingual and submaxillary spaces without abscess formation.
What is submandibular space?
The submandibular space is a suprahyoid deep compartment of the head and neck that encompasses the submandibular gland and surrounding structures.
How do you know you have a space infection?
Symptoms of Submandibular Space Infection People with a submandibular space infection have pain and tenderness under the tongue and/or under the jaw. The pain is worse with opening the mouth or swallowing. Fever and chills are common. Later, swelling worsens, which may cause drooling and noisy breathing.
How do you manage a space infection?
The treatment of fascial space infections includes aggressive intravenous high dose antibiotics (usually penicillin or cephalosporins and metronidazole), analgesic and fluid therapy in addition to establishment of surgical drainage and elimination of the source of infection.
What is space infection?
The infection begins in the floor of the mouth. It is characteristically an aggressive, rapidly spreading "woody" or brawny cellulitis involving the submandibular space. ● The infection is a rapidly spreading cellulitis without lymphatic involvement and generally without abscess formation.
Where is submandibular space?
The submandibular space extends from the hyoid bone to the mucosa of the floor of the mouth, and is bound anteriorly and laterally by the mandible and inferiorly by the superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia.
What are the borders of submandibular space?
Anatomic boundaries the skin, superficial fascia, platysma muscle and superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia inferiorly and laterally, the medial surface of the mandible anteriorly and laterally, the hyoid bone posteriorly, the anterior belly of the digastric muscle medially.
Where is the submandibular?
About the size of a walnut, the submandibular glands are located below the jaw. The saliva produced in these glands is secreted into the mouth from under the tongue. Like the parotid glands, the submandibular glands have two parts called the superficial lobe and the deep lobe.
Can tooth infection spread to neck?
Without treatment, a tooth infection can spread to the face and neck. Severe infections may even reach more distant parts of the body. In some cases, they may become systemic, affecting multiple tissues and systems throughout the body.
Why does my submental space hurt?
Submental space infection is characterized by a firm midline swelling beneath the chin and is due to infection from the mandibular incisors. Sublingual space infection is indicated by swelling of the mouth's floor with possible tongue elevation, pain, and dysphagia due to anterior mandibular tooth infection.
What antibiotics treat Ludwig's angina?
Penicillin, metronidazole, clindamycin, and ciprofloxacin are often the antibiotics of choice. Blind nasal intubation should be avoided as it could cause bleeding, laryngospasm, oedema of the airway, rupture of pus into the oral cavity, and aspiration.
Symptoms of Submandibular Space Infection
People with a submandibular space infection have pain and tenderness under the tongue and/or under the jaw. The pain is worse with opening the mouth or swallowing.
Diagnosis of Submandibular Space Infection
Doctors usually can diagnose submandibular space infection by examining the mouth.
Treatment of Submandibular Space Infection
Anosmia is the total loss of smell. Most people with anosmia can taste sweet, sour, salty, and bitter substances but cannot distinguish among specific flavors. This is because the sense of smell makes it possible to distinguish among flavors, not taste receptors as many people erroneously believe.
MSD and the MSD Manuals
Merck and Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA (known as MSD outside of the US and Canada) is a global healthcare leader working to help the world be well. From developing new therapies that treat and prevent disease to helping people in need, we are committed to improving health and well-being around the world.
What is submandibular space cellulitis?
It generally begins as a mixed flora infection around the mandibular molars. Aerobic and anaerobic pathogens are involved.
Where is the submandibular space?
The submandibular space extends from the hyoid bone to the mucosa of the floor of the mouth, and is bound anteriorly and laterally by the mandible and inferiorly by the superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia.
How to tell if submandibular space is infected?
Signs and symptoms of a submandibular space infection might include trismus (difficulty opening the mouth), inability to palpate (feel) the inferior border of the mandible and swelling of the face over the submandibular region . If the space contains pus, the usual treatment is by incision and drainage. The site of the incision is extra-oral, and ...
What is the submandibulare?
Latin. Spatium submandibulare. Anatomical terminology. The submandibular space is a fascial space of the head and neck (sometimes also termed fascial spaces or tissue spaces).
What are the anatomic boundaries of the submandibular space?
The anatomic boundaries of each submandibular space are: the mylohyoid muscle superiorly, the skin, superficial fascia, platysma muscle and superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia inferiorly and laterally, the medial surface of the mandible anteriorly and laterally, the hyoid bone posteriorly,
Where is the submental space?
medially and anteriorly to the submental space (located medial to the paired submandibular spaces, separated from them by the anterior bellies of the digastric muscles). posteriorly and superiorly to the sublingual space (located above the mylohyoid muscle) inferiorly to the lateral pharyngeal space.
What is the slanting attachment of mylohyoid?
This arrangement means that the apices of posterior teeth are more likely to be below the level of mylohyoid.
Can odontogenic infections spread to the mandibular space?
Infections may spread into the submandibular space, e.g. odontogenic infections, often related to the mandibular molar teeth. This is due to the fact that the attachment of mylohyoid (the mylohoid line) becomes more superior towards the posterior of the mandible, meaning that the roots of the posterior teeth are more likely to be below mylohyoid ...
Summary
The aims of this study were to review the clinical characteristics and management of submandibular space infections and to identify the predisposing factors of life-threatening complications.
Introduction
Despite a decrease in the incidence and mortality of deep neck infections (DNIs) as a result of the advent of antibiotics and improved dental care, these infections are not unusual and present a challenging problem because of the complex anatomy and potentially fatal complications that may occur. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Patients and methods
We retrieved and evaluated the records of all patients admitted to the University of Padua Otolaryngology Clinic at Treviso Regional Hospital with the diagnosis of submandibular space infection for the period 1998–2006.
Results
All descriptive data are reported in Table 1. A total of 81 patients with a submandibular space infection were identified for this evaluation. The 81 patients consisted of 42 males (51.9%) and 39 females (48.1%) ranging in age from 12 to 96 years (median 57 years).
Discussion
The management of DNIs remains particularly troublesome due to the complex anatomy of the neck, polymicrobial etiology, and life-threatening complications that may arise.
Can SMG mimic tumor?
Sometimes, low-grade, chronic infections can mimic tumor and present predominantly as an SMG/SMS mass.
Is parotid disease a SMG?
Viral infections are common in the parotid gland, but few SMG infections are attributed to that source. The most well known virus that may present as primarily SMG problems might be a manifestation of HIV infection, although those changes are usually seen in the context of obvious, usually bilateral, parotid disease ( Fig. 181.16 ).
What is the cause of submandibular glands to swell?
Sialolithiasis. Tiny stones can cause the submandibular glands to become swollen. Salivary stones ( sialolithiasis) are made of mineral deposits. Sialolithiasis most commonly affects people age 30 to 60, and they are more common in men than in women.
What is the submandibular gland?
Tests. The submandibular glands are a pair of glands situated on the floor of the mouth, below the lower jaw. They are one of the three pairs of glands that produce saliva. Submandibular glands can become swollen when small stones block the ducts that supply saliva to the mouth. Sometimes this can lead to an infection.
What is the name of the infection in the salivary gland?
An infection in the salivary glands is called sialadenitis. Infections in the salivary glands most often affect the parotid and the submandibular glands. Older people and those with chronic health conditions are most at risk of developing a salivary gland infection. Infections in the glands are caused by a bacteria, commonly Staphylococcus aureus.
What are the most common salivary gland tumors?
Most salivary gland tumors are benign (noncancerous). Benign tumors are most often removed via surgery. There are several different kinds of malignant tumors (cancerous tumors) of the salivary glands: 1 Mucoepidermoid carcinomas are the most common cancer of the salivary glands. They most often occur in the parotid glands but can also occur in the submandibular glands. 2 Adenoid cystic carcinoma often spreads along nerves, which makes it difficult to get rid of. The outlook is best for those with smaller tumors. 3 Adenocarcinomas are cancers that start in the gland cells. There are many types of adenocarcinomas, including acinic cell carcinoma, polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma (PLGA), adenocarcinoma, not otherwise specified (NOS), and rare adenocarcinomas. 4 Malignant mixed tumors are tumors of multiple tissue types. They include carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenomas, carcinosarcoma, and metastasizing mixed tumor. 5 Rare salivary gland cancers include squamous cell carcinoma, epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma, anaplastic small cell carcinoma, and undifferentiated carcinomas. 4
Which gland is located in the submandibular triangle?
The two other types of salivary glands are the parotid (the largest) and sublingual glands. The submandibular glands sit in the submandibular triangle, located underneath the mandible (lower jaw bone) and above the hyoid (tongue) bone. The mylohyoid muscle, a paired muscle that forms the floor of the mouth, separates a superficial ...
Which muscle separates the superficial and deep lobes of the mouth?
The mylohyoid muscle, a paired muscle that forms the floor of the mouth, separates a superficial and deep lobe in the gland. The submandibular duct, also called the Wharton's duct, is the excretory duct of the gland. It drains saliva from the glands at the base of the tongue .
Is salivary gland cancer benign?
Most salivary gland tumors are benign (noncancerous). Benign tumors are most often removed via surgery. There are several different kinds of malignant tumors (cancerous tumors) of the salivary glands: Mucoepidermoid carcinomas are the most common cancer of the salivary glands.
