What are advantages and disadvantages of Systematic sampling?
Advantages of systematic sampling ensure even coverage of an area and simplicity. Disadvantages include bias and risk of patterns or under-representation. Systematic sampling is useful for many types of research, including any research types that require looking at individuals, such as human, plant or animal research.
Why do you use systematic sampling?
The three main types of quantitative sampling are:
- Random sampling: Random sampling is when all individuals in a population have an equal chance of being selected.
- Stratified sampling: Stratified sampling is when the researcher defines the types of individuals in the population based on specific criteria for the study. ...
- Systematic sampling: Systemic sampling is choosing a sample on an orderly basis. ...
When to use systematic sampling instead of random sampling?
You can use systematic sampling with a list of the entire population, as in simple random sampling. However, unlike with simple random sampling, you can also use this method when you’re unable to access a list of your population in advance.
What is the formula of Systematic sampling?
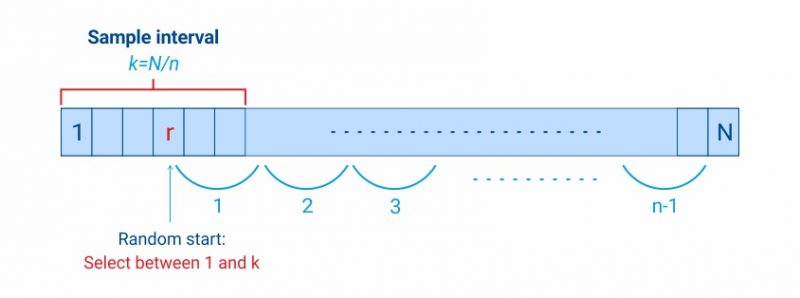
Systematic sampling is a type of probability sampling method in which sample members from a larger population are selected according to a random starting point but with a fixed, periodic interval. This interval, called the sampling interval, is calculated by dividing the population size by the desired sample size.

What is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which researchers select members of the population at a regular interval (or k) determined in advance.
Why is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is popular with researchers because of its simplicity. Researchers generally assume the results are representative of most normal populations, unless a random characteristic disproportionately exists with every "nth" data sample (which is unlikely).
What is an example of a systematic sample?
Systematic sampling example For instance, if a local NGO is seeking to form a systematic sample of 500 volunteers from a population of 5000, they can select every 10th person in the population to build a sample systematically.
What is systematic sampling Wikipedia?
In survey methodology, systematic sampling is a statistical method involving the selection of elements from an ordered sampling frame. The most common form of systematic sampling is an equiprobability method.
Where is systematic sampling used?
Use systematic sampling when there's low risk of data manipulation. Systematic sampling is the preferred method over simple random sampling when a study maintains a low risk of data manipulation.
What is the difference between random sampling and systematic sampling?
Simple random sampling requires that each element of the population be separately identified and selected, while systematic sampling relies on a sampling interval rule to select all individuals.
How do you do systematic sampling?
There are three key steps in systematic sampling: Define and list your population, ensuring that it is not ordered in a cyclical or periodic order. Decide on your sample size and calculate your interval, k, by dividing your population by your target sample size. Choose every kth member of the population as your sample.
Which is the best example of selecting a systematic random sample?
Which is the best example of selecting a systematic random sample? Members of a population are listed in order of birthday, and every 5th person is selected until a sample of 100 people is formed.
Is systematic sampling non probability?
Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample. Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.
Is systematic sampling random?
Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population.
Is systematic sampling biased?
With systematic sampling, each participant is a fixed distance from the next. This means that samples are clearly separated and helps minimize the chance for bias. Also, by using a fixed interval, researchers have no influence over which individuals are chosen for sampling.
What is sampling and its types?
In statistics, sampling is a method when researchers determine a representative segment of a larger population that is then used to conduct a study. Sampling generally comes in two forms — probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
Why is systematic sampling not always possible?
1. This process requires a close approximation of a population. The systematic sampling method must assume that the size of the population in specific demographics is available and measurable. If that isn't possible, then this method requires a reasonable approximation of the demographic in question.
Why is systematic random sampling sometimes used in place of simple random sampling?
b) A large part of the population may be physically inaccessible. Why is systematic random sampling sometimes used in place of simple random sampling? It is an easier and faster process.
What is systematic in statistics?
Systematic sampling and cluster sampling are both statistical measures used by researchers, analysts, and marketers to study samples of a population. Systematic sampling involves selecting fixed intervals from the larger population to create the sample.
When should I take a systematic sample of size n?
When taking a systematic random sample of size n, every group of size n from the population has the same chance of being selected.
What is probability sampling?
Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample. Probability sampling met...
What is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method where researchers select members of the population at a regular interval – for example, by...
How do I perform systematic sampling?
There are three key steps in systematic sampling : Define and list your population , ensuring that it is not ordered in a cyclical or periodic or...
What is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is defined as a probability sampling method where the researcher chooses elements from a target population by selecting a random starting point and selects sample members after a fixed ‘sampling interval. ’
Why is systematic sampling important?
Here are the advantages of systematic sampling. It’s extremely simple and convenient for the researchers to create, conduct, analyze samples. As there’s no need to number each member of a sample, it is better for representing a population in a faster and simpler manner.
How to calculate sampling interval?
Researchers calculate the sampling interval by dividing the entire population size by the desired sample size. Systematic sampling is an extended implementation of probability sampling in which each member of the group is selected at regular periods to form a sample.
What is the sample interval for 5000?
For example, the sample interval should be 10, which is the result of the division of 5000 (N= size of the population) and 500 (n=size of the sample).
What are the samples of K=3?
If we consider k=3, the samples will be – ad, be, ca, db and ec.
Is convenience sampling biased?
In the other methods of probability samplingmethods such as cluster samplingand stratified sampling or non-probability methods such as convenience sampling, there are chances of the clusters created to be highly biased which is avoided in systematic sampling as the members are at a fixed distance from one another.
What is systematic sampling?
according to a predetermined pattern is known as systematic sampling. In its simplest form, called linear systematic
What were the developments in systematic sampling related to?
developments in systematic sampling were highly related to problems of forestry. This made Buckland (1951),
How many variance estimators are used in systematic sampling?
Seven variance estimators to be used under systematic sampling are evaluated in a simulation study with 270 artificial spatial populations with different levels and structure of autocorrelation. In settings without an auxiliary variable a proposed new spatial resampling estimator RHO is recommended. In setting with an auxiliary variable, an estimator based on post-stratification (PST), and one with a correction for spatial autocorrelation (DOR), generated estimates with less bias than the SRS estimator in the majority of studied settings. Only in populations with either a near zero autocorrelation at the interval of sampling, or a very strong correlation between the target and the auxiliary variable did the otherwise conservative SRS estimator perform as well as the alternatives.
What is the label for groups in a sample?
groups is selected in the sample. The sample obtained will hence comprise the units with labels R+ ( j−1)k
What are the drawbacks of systematic design?
First, if the population size is not an integral multiple of the desired sample size, the actual sample size will be random. Second, a single systematic sample cannot provide an unbiased estimator for the sampling variance.
Why is systematic sampling so popular?
Systematic sampling is one of the most prevalent sampling techniques. The popularity of the systematic design is mainly due to its practicality. Compared with simple random sampling, it is easier to draw a systematic sample specially when the selection of sample units is done in the field. In addition, systematic sampling can provide more precise ...
Who first proposed systematic sampling?
The theory of systematic sampling was first studied by Madow and Madow (1944). However, along time before
What is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is a method that imitates many of the randomization benefits of simple random sampling, but is slightly easier to conduct. You can use systematic sampling with a list of the entire population, as in simple random sampling. However, unlike with simple random sampling, you can also use this method when you’re unable ...
What happens if you use systematic sampling?
For example, if you are sampling from a list of individuals ordered by age, systematic sampling will result in a population drawn from the entire age spectrum. If you instead used simple random sampling, it is possible (although unlikely) that you would end up with only younger or older individuals.
What is probability sampling?
Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample. Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.
What is a simple random sampling?
As in simple random sampling, you should try to make sure every individual you have chosen for your sample actually participates in your study. If those who decide to participate do so for reasons connected with the variables that you are collecting, this could bias your study. Example: Data collection.
What is the purpose of population order?
If the population order is random or random-like (e.g., alphabetical), then this method will give you a representative sample that can be used to draw conclusions about the population.
What order should a population list be in?
Ensure that your list contains the entire population and is not in a periodic or cyclic order. Ideally, it should be in a random or random-like (such as alphabetical) order , which will allow you to imitate the randomization benefits of simple random sampling.
Why do you sample every 20th individual?
If you sample every 20th individual, because each department is ordered by age, your population will consist of the oldest person in each one. This will most likely not provide a representative sample of the entire hospital population.